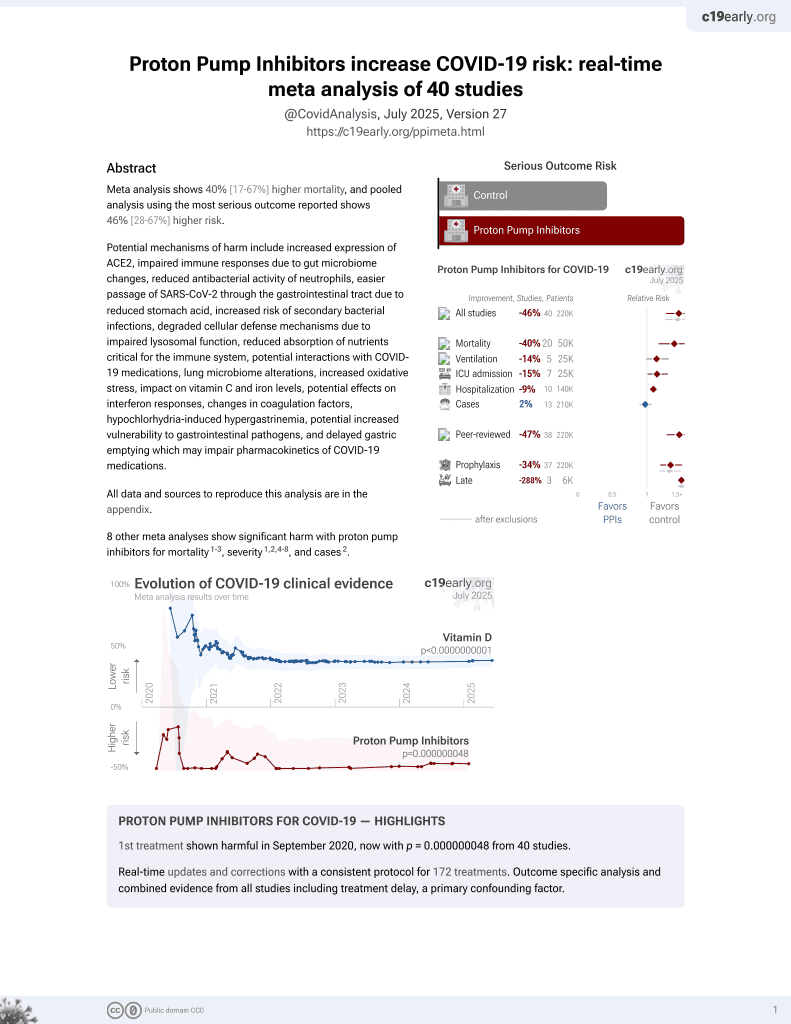
Acid pH Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Risk of Death by COVID-19
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.637885, Aug 2021
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
In vitro study showing lower pH increased ACE2 expression and viral load on SARS-CoV-2 infection, and retrospective study showing proton pump inhibitor use, which is correlated with low gastric pH-related diseases, was associated with higher mortality.
Study covers proton pump inhibitors and alkalinization.
|
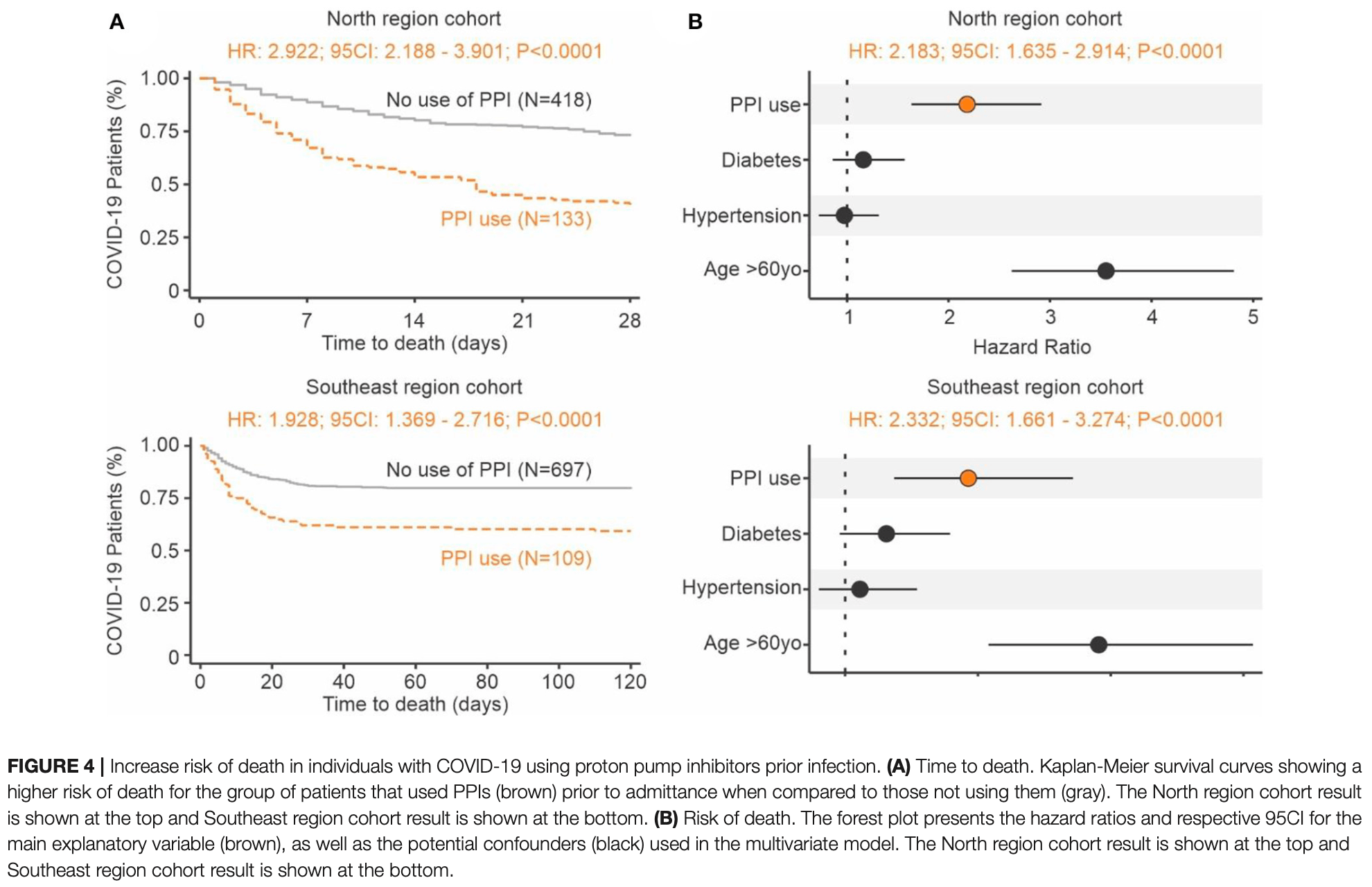
risk of death, 124.4% higher, HR 2.24, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, both regions combined.
|
|
risk of death, 118.3% higher, HR 2.18, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of death, 133.2% higher, HR 2.33, p < 0.001, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jimenez et al., 20 Aug 2021, retrospective, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 21 authors, southeast region.
Contact: hnakaya@usp.br.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.637885",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2021.637885",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) can infect a broad range of human tissues by using the host receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2). Individuals with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19 display higher levels of <jats:italic>ACE2</jats:italic> in the lungs compared to those without comorbidities, and conditions such as cell stress, elevated glucose levels and hypoxia may also increase the expression of <jats:italic>ACE2</jats:italic>. Here, we showed that patients with Barrett's esophagus (BE) have a higher expression of <jats:italic>ACE2</jats:italic> in BE tissues compared to normal squamous esophagus, and that the lower pH associated with BE may drive this increase in expression. Human primary monocytes cultured in reduced pH displayed increased <jats:italic>ACE2</jats:italic> expression and higher viral load upon SARS-CoV-2 infection. We also showed in two independent cohorts of 1,357 COVID-19 patients that previous use of proton pump inhibitors is associated with 2- to 3-fold higher risk of death compared to those not using the drugs. Our work suggests that pH has a great influence on SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 severity.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2021.637885"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jimenez",
"given": "Leandro",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campos Codo",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sampaio",
"given": "Vanderson de Souza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Antonio E. R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Lucas Kaoru Kobo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davanzo",
"given": "Gustavo Gastão",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brito Monteiro",
"given": "Lauar de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Victor Virgilio-da-Silva",
"given": "João",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borba",
"given": "Mayla Gabriela Silva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fabiano de Souza",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zini",
"given": "Nathalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andrade Gandolfi",
"given": "Flora de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Muraro",
"given": "Stéfanie Primon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luiz Proença-Modena",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Val",
"given": "Fernando Almeida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cardoso Melo",
"given": "Gisely",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monteiro",
"given": "Wuelton Marcelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nogueira",
"given": "Maurício Lacerda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacerda",
"given": "Marcus Vinícius Guimarães",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moraes-Vieira",
"given": "Pedro M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nakaya",
"given": "Helder I.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-20T05:06:06Z",
"timestamp": 1629435966000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-20T05:06:12Z",
"timestamp": 1629435972000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001807",
"award": [
"2018/14933-2",
"2020/04836-0"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-17T14:52:41Z",
"timestamp": 1673967161527
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629417600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2021.637885/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.003",
"article-title": "Prevalence and mortality of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tariq",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1632",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15166",
"article-title": "Diarrhea and altered inflammatory cytokine pattern in severe coronavirus disease 2019: impact on disease course and in-hospital mortality",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "421",
"journal-title": "J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.03.065",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection and virus load in fecal samples from a Hong Kong Cohort: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.5471",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Bourgonje",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "J Pathol",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-020-0754-0",
"article-title": "Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "185",
"journal-title": "Front Med.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321013",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "997",
"journal-title": "Gut.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa332",
"article-title": "ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Pinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "556",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20130291",
"article-title": "Epigenetic regulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) by SIRT1 under conditions of cell energy stress",
"author": "Clarke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci (Lond).",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3606770",
"article-title": "Elevated glucose levels favor SARS-CoV-2 infection and monocyte response through a HIF-1α/glycolysis-dependent axis",
"author": "Codo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "437",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1314704",
"article-title": "Barrett's esophagus",
"author": "Spechler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "836",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btm254",
"article-title": "GEOquery: a bridge between the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) and BioConductor",
"author": "Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1846",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv007",
"article-title": "limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies",
"author": "Ritchie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e47",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "B13",
"unstructured": "PradaC\n LimaD\n NakayaHI\n São PauloBioconductorMetaVolcanoR: Gene Expression Meta-analysis Visualization Tool2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-14-128",
"article-title": "Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "128",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinformatics.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-13-226",
"article-title": "Network enrichment analysis: extension of gene-set enrichment analysis to gene networks",
"author": "Alexeyenko",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinformatics.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-06796-9",
"article-title": "Single cell RNA-seq reveals profound transcriptional similarity between Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal submucosal glands",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4261",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.031",
"article-title": "Comprehensive integration of single-cell data",
"author": "Stuart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1888",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4236",
"article-title": "SC3: consensus clustering of single-cell RNA-seq data",
"author": "Kiselev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "483",
"journal-title": "Nat Methods.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-03608-y",
"article-title": "BEARscc determines robustness of single-cell clusters using simulated technical replicates",
"author": "Severson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1187",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5607/en20009",
"article-title": "Development of a laboratory-safe and low-cost detection protocol for SARS-CoV-2 of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Won",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Exp Neurobiol.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"article-title": "Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Poverty.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cll.2014.08.008",
"article-title": "The impact of proton pump inhibitors on the human gastrointestinal microbiome",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "771",
"journal-title": "Clin Lab Med.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.10.003",
"article-title": "Identification of target genes of the transcription factor HNF1beta and HNF1alpha in a human embryonic kidney cell line",
"author": "Senkel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "179",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "1731",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/js.2016-1071",
"article-title": "Forkhead box transcription factors of the FOXA class are required for basal transcription of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "370",
"journal-title": "J Endocr Soc.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1091",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: retrospective study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1091",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.90415.2008",
"article-title": "Role of HIF-1alpha in the regulation ACE and ACE2 expression in hypoxic human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L631",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "297",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073",
"article-title": "Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: a pooled analysis",
"author": "Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1722",
"journal-title": "Am J Emerg Med.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-021-06872-z",
"article-title": "Does famotidine reduce the risk of progression to severe disease, death, and intubation for COVID-19 patients? A systemic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "B29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.074",
"article-title": "Will proton pump inhibitors lead to a higher risk of COVID-19 infection and progression to severe disease? A Meta-analysis",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jpn J Infect Dis",
"key": "B30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1707",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2021.637885/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Acid pH Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Risk of Death by COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "8"
}