Transcriptomic insights into the immune dynamics of wild-type mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant
et al., Laboratory Animal Research, doi:10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4, Jan 2026
Mouse study showing transcriptomic immune responses in wild-type C57BL/6J mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant (B.1.351).
Jahantigh et al., 28 Jan 2026, USA, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: mkumar8@gsu.edu.
Transcriptomic insights into the immune dynamics of wild-type mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant
Laboratory Animal Research, doi:10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4
Background Mice are useful small animal models to study the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. As the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strains did not utilize murine Ace2 as a receptor, wild-type mice were not susceptible to the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Infection of human ACE2-expressing transgenic mice with SARS-CoV-2 induces fatal encephalitis, which is not commonly observed in humans. We and others have previously demonstrated the ability of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant to productively infect wild-type mice. Herein, we employed RNA-seq to investigate the transcriptomic landscapes in the lungs after the infection of wild-type mice with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant.
Methods We intranasally infected 6-week-old wild-type C57BL/6J mice with the SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.351 strain) and collected lungs at 3-and 6-days post-infection for RNA-sequencing. We used the Limma-Voom package to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and the fgsea package for pathway enrichment analysis. We used Cytoscape to identify hub genes and gene networks. Lastly, we employed RT-qPCR and multiplex assay to validate the RNA-seq data.
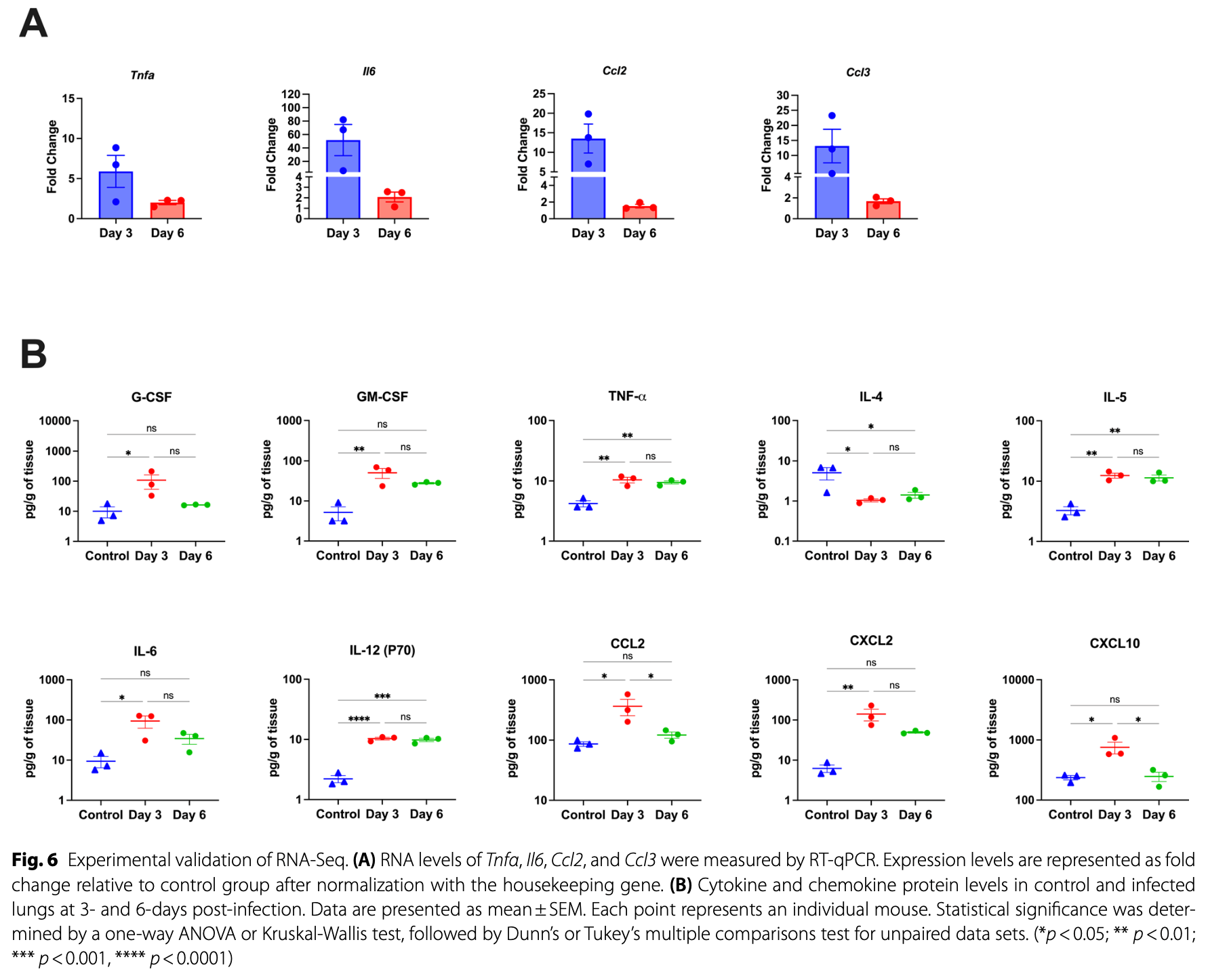
Results Using a cutoff of an adjusted p-value below 0.05 and an absolute log2 fold change value greater than 0.75, we identified 285 DEGs on day 3 and 46 DEGs on day 6. The canonical pathways analysis showed that several key pathways such as apoptosis and cytokine response were upregulated in the infected lungs. Protein-protein interaction analyses identified innovative target genes such as Kif11, Ccna2, and Aurkb. We also identified the top 10 hub genes that included Prc1, Ube2c, Ccnb2, Ncapg, Aurkb, Cep55, Mki67, Dlgap5, Ccna2, and Kif11. RT-qPCR analysis for Tnfa, Il6, Ccl2, and Ccl3 further validated the RNA-seq analysis. Consistent with gene expression results, we detected significantly increased protein levels of various inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, CCL2, CXCL2, and CXCL10 in the infected lungs. Conclusions This is the first transcriptomic analysis of the lungs of wild-type mice infected with a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2. Our findings provide a further understanding of the pathogenic events that occur in this mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Abbreviations
ACE2 Angiotensin-converting enzyme
Declarations Institutional review board The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Georgia State University (Protocol: A24003). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Alenzi, Survivin, A key apoptosis inhibitor in COVID-19 infection and its implication for treatment protocol, Saudi J Biol Sci
Assou, Ahmed, Morichon, Nasri, Foisset et al., The transcriptome landscape of the in vitro human airway epithelium response to SARS-CoV-2, Int J Mol Sci
Attiq, Yao, Afzal, Khan, The triumvirate of NF-κB, inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19, Int Immunopharmacol
Barton, Macgowan, Kutuzov, Dushek, Barton et al., Effects of common mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD and its ligand, the human ACE2 receptor on binding affinity and kinetics, eLife
Carossino, Kenney, Connell, Montanaro, Tseng et al., Fatal neurodissemination and SARS-CoV-2 tropism in K18-hACE2 mice is only partially dependent on hACE2 expression, Viruses
Chen, Xia, Sui, Shi, Huang et al., Identification of hub genes associated with COVID-19 and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by integrated bioinformatics analysis, PLoS ONE
Chiesa, Piccardo, Ghetti, Harris, Neurological illlness in Transgenic mice expressing a prion protein with an insertional mutation, Neuron
Chin, Chen, Wu, Ho, Ko et al., CytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome, BMC Syst Biol
Deng, Siddique, Transgenic mouse models and human neurodegenerative disorders, Arch Neurol
Elsharkawy, Jahantigh, Guglani, Stone, Arora et al., Virusspecific host responses and gene signatures following infection with major SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: role of ZBP1 in viral clearance and lung inflammation, Front Immunol
Escalera, Gonzalez-Reiche, Aslam, Mena, Laporte et al., Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern link to increased Spike cleavage and virus transmission, Cell Host Microbe
Giardine, Riemer, Hardison, Burhans, Elnitski et al., Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis, Genome Res
Glebov, Understanding SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis for COVID-19 drug repurposing, FEBS J
Grossegesse, Bourquain, Neumann, Schaade, Schulze et al., Deep time course proteomics of SARS-CoV-and SARS-CoV-2-infected human lung epithelial cells (Calu-3) reveals strong induction of interferonstimulated gene expression by SARS-CoV-2 in contrast to SARS-CoV, J Proteome Res
Hariharan, Hakeem, Radhakrishnan, Reddy, Rela, The role and therapeutic potential of NF-kappa-B pathway in severe COVID-19 patients, Inflammopharmacology
Islam, Habib, Badruddza, Rahman, Islam et al., The association of cytokines IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-10 with the disease severity of COVID-19: A study from Bangladesh, Cureus
Jin, Li, Yu, Zeng, Liu et al., Analysis and identification of potential type II helper T cell (Th2)-Related key genes and therapeutic agents for COVID-19, Comput Biol Med
Karolchik, Barber, Casper, Clawson, Cline et al., The UCSC genome browser database: 2014 update, Nucleic Acids Res
Kohl, Wiese, Warscheid, Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Data mining in proteomics: from standards to applications, Methods Mol Biol
Lazarevic, Pravica, Miljanovic, Cupic, Immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants: what have we learnt so far?, Viruses
Liu, Long, Liang, Lv, Huang et al., Bioinformatics analysis based on high-throughput sequencing data to identify hub genes related to different clinical types of COVID-19, Funct Integr Genomics
Lui, Guaraldi, Drug treatment of COVID-19 infection, Curr Opin Pulm Med
Mahajan, Alnatsha, Li, Oehrle, Weiss et al., Plasma metabolome profiling identifies metabolic subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, Cells
Mahase, Covid-19: how many variants are there, and what do we know about them?, BMJ
Natekar, Pathak, Stone, Kumari, Sharma et al., Differential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in human ACE2-expressing mice, Viruses
Ni, Yang, Yang, Bao, Li et al., Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19, Crit Care
Pan, Chen, He, Yuan, Deng et al., Infection of wild-type mice by SARS-CoV-2 B. 1.351 variant indicates a possible novel cross-species transmission route, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Pertea, Pertea, Antonescu, Chang, Mendell et al., StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads, Nat Biotechnol
Ramesh, Govindarajulu, Parise, Neel, Shankar et al., Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants: a review of its mutations, its implications and vaccine efficacy, Vaccines
Ren, Zhu, Wang, Shi, Yu et al., Comparative analysis reveals the species-specific genetic determinants of ACE2 required for SARS-CoV-2 entry, PLoS Pathog
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Haider, Abbasi et al., The emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Ther Adv Infect Dis
Scovino, Dahab, Vieira, Freire-De-Lima, Freire-De-Lima et al., SARS-CoV-2's variants of concern: A brief characterization, Front Immunol
Seyedalinaghi, Mirzapour, Dadras, Pashaei, Karimi et al., Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 different variants and related morbidity and mortality: a systematic review, Eur J Med Res
Shannon, Markiel, Ozier, Baliga, Wang et al., Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks, Genome Res
Shultz, Brehm, Garcia-Martinez, Greiner, Humanized mice for immune system investigation: progress, promise and challenges, Nat Rev Immunol
Stone, Elsharkawy, Burleson, Hauser, Domi et al., Multiantigen viral-vectored vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 and variants in a lethal hACE2 Transgenic mouse model, Vaccines
Stone, Rothan, Natekar, Kumari, Sharma et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern infect the respiratory tract and induce inflammatory response in wild-type laboratory mice, Viruses
Tian, Yu, Zhang, Zhang, Gong, Correction to: Exploration of the potential common pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19 and silicosis by using bioinformatics and system biology, Funct Integr Genomics
Tian, Yu, Zhang, Zhang, Gong, Exploration of the potential common pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19 and silicosis by using bioinformatics and system biology, Funct Integr Genomics
Tulimilli, Dallavalasa, Basavaraju, Rao, Chikkahonnaiah et al., Variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and vaccine effectiveness, Vaccines
Vandel, Gheeraert, Staels, Eeckhoute, Lefebvre et al., GIANT: galaxy-based tool for interactive analysis of transcriptomic data, Sci Rep
Wu, Hu, Xu, Chen, Guo et al., ClusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data, Innov (Camb)
Xia, Yang, Wang, Huang, Qiu et al., Case fatality rates of COVID-19 during epidemic periods of variants of concern: A meta-analysis by continents, Int J Infec Dis
Yi, Sun, Lin, Gu, Ding et al., Comprehensive mapping of binding hot spots of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific neutralizing antibodies for tracking immune escape variants, Genome Med
Zhou, Dejnirattisai, Supasa, Liu, Mentzer et al., Evidence of escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant B. 1.351 from natural and vaccine-induced Sera, Cell
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4",
"ISSN": [
"2233-7660"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Mice are useful small animal models to study the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. As the ancestral SARS-CoV-2 strains did not utilize murine Ace2 as a receptor, wild-type mice were not susceptible to the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Infection of human ACE2-expressing transgenic mice with SARS-CoV-2 induces fatal encephalitis, which is not commonly observed in humans. We and others have previously demonstrated the ability of the SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant to productively infect wild-type mice. Herein, we employed RNA-seq to investigate the transcriptomic landscapes in the lungs after the infection of wild-type mice with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We intranasally infected 6-week-old wild-type C57BL/6J mice with the SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.351 strain) and collected lungs at 3- and 6-days post-infection for RNA-sequencing. We used the Limma-Voom package to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and the fgsea package for pathway enrichment analysis. We used Cytoscape to identify hub genes and gene networks. Lastly, we employed RT-qPCR and multiplex assay to validate the RNA-seq data.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n Using a cutoff of an adjusted p-value below 0.05 and an absolute log2 fold change value greater than 0.75, we identified 285 DEGs on day 3 and 46 DEGs on day 6. The canonical pathways analysis showed that several key pathways such as apoptosis and cytokine response were upregulated in the infected lungs. Protein-protein interaction analyses identified innovative target genes such as\n <jats:italic>Kif11</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ccna2</jats:italic>\n , and\n <jats:italic>Aurkb</jats:italic>\n . We also identified the top 10 hub genes that included\n <jats:italic>Prc1</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ube2c</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ccnb2</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ncapg</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Aurkb</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Cep55</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Mki67</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Dlgap5</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ccna2</jats:italic>\n , and\n <jats:italic>Kif11.</jats:italic>\n RT-qPCR analysis for\n <jats:italic>Tnfa</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Il6</jats:italic>\n ,\n <jats:italic>Ccl2</jats:italic>\n , and\n <jats:italic>Ccl3</jats:italic>\n further validated the RNA-seq analysis. Consistent with gene expression results, we detected significantly increased protein levels of various inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, CCL2, CXCL2, and CXCL10 in the infected lungs.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This is the first transcriptomic analysis of the lungs of wild-type mice infected with a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2. Our findings provide a further understanding of the pathogenic events that occur in this mouse model of SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"264"
],
"article-number": "3",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "8 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "15 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "28 January 2026"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Institutional review board",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The animal study was approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Georgia State University (Protocol: A24003). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jahantigh",
"given": "Hamid Reza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elsharkawy",
"given": "Amany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "Komal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dim",
"given": "Chinonye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0970-4875",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Mukesh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Laboratory Animal Research",
"container-title-short": "Lab Anim Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-28T10:00:41Z",
"timestamp": 1769594441000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-28T11:04:22Z",
"timestamp": 1769598262000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100008545",
"award": [
"Georgia State University"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"Georgia State University"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100008545",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Georgia State University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-28T22:45:36Z",
"timestamp": 1769640336300,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1769558400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1769558400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCP.0000000000000953",
"author": "G Lui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "174",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Pulm Med",
"key": "264_CR1",
"unstructured": "Lui G, Guaraldi G. Drug treatment of COVID-19 infection. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2023;29(3):174–83.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n1971",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "264_CR2",
"unstructured": "Mahase E. Covid-19: how many variants are there, and what do we know about them? BMJ. 2021;374:n1971."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40001-021-00524-8",
"author": "S SeyedAlinaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "51",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med Res",
"key": "264_CR3",
"unstructured": "SeyedAlinaghi S, Mirzapour P, Dadras O, Pashaei Z, Karimi A, MohsseniPour M, et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 different variants and related morbidity and mortality: a systematic review. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):51.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2022.01.006",
"author": "A Escalera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "373",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "264_CR4",
"unstructured": "Escalera A, Gonzalez-Reiche AS, Aslam S, Mena I, Laporte M, Pearl RL, et al. Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern link to increased Spike cleavage and virus transmission. Cell Host Microbe. 2022;30(3):373–87. e7.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13071192",
"author": "I Lazarevic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1192",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "264_CR5",
"unstructured": "Lazarevic I, Pravica V, Miljanovic D, Cupic M. Immune evasion of SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants: what have we learnt so far? Viruses. 2021;13(7):1192.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines9101195",
"author": "S Ramesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1195",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "264_CR6",
"unstructured": "Ramesh S, Govindarajulu M, Parise RS, Neel L, Shankar T, Patel S, et al. Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants: a review of its mutations, its implications and vaccine efficacy. Vaccines. 2021;9(10):1195.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "A Sanyaolu",
"first-page": "204993612110243",
"journal-title": "Ther Adv Infect Dis",
"key": "264_CR7",
"unstructured": "Sanyaolu A, Okorie C, Marinkovic A, Haider N, Abbasi AF, Jaferi U, et al. The emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Ther Adv Infect Dis. 2021;8:20499361211024372.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.834098",
"author": "AM Scovino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "834098",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "264_CR8",
"unstructured": "Scovino AM, Dahab EC, Vieira GF, Freire-de-Lima L, Freire-de-Lima CG, Morrot A. SARS-CoV-2’s variants of concern: A brief characterization. Front Immunol. 2022;13:834098.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2024.01.017",
"author": "Q Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106950",
"journal-title": "Int J Infec Dis",
"key": "264_CR9",
"unstructured": "Xia Q, Yang Y, Wang F, Huang Z, Qiu W, Mao A. Case fatality rates of COVID-19 during epidemic periods of variants of concern: A meta-analysis by continents. Int J Infec Dis. 2024;141:106950.",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.70658",
"author": "MI Barton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e70658",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "264_CR10",
"unstructured": "Barton MI, MacGowan SA, Kutuzov MA, Dushek O, Barton GJ, van der Merwe PA. Effects of common mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike RBD and its ligand, the human ACE2 receptor on binding affinity and kinetics. eLife. 2021;10:e70658.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13073-021-00985-w",
"author": "C Yi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Genome Med",
"key": "264_CR11",
"unstructured": "Yi C, Sun X, Lin Y, Gu C, Ding L, Lu X, et al. Comprehensive mapping of binding hot spots of SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific neutralizing antibodies for tracking immune escape variants. Genome Med. 2021;13(1):164.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101751",
"author": "SV Tulimilli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1751",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "264_CR12",
"unstructured": "Tulimilli SV, Dallavalasa S, Basavaraju CG, Kumar Rao V, Chikkahonnaiah P, Madhunapantula. Variants of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and vaccine effectiveness. Vaccines (Basel). 2022;10(10):1751.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.037",
"author": "D Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2348",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "264_CR13",
"unstructured": "Zhou D, Dejnirattisai W, Supasa P, Liu C, Mentzer AJ, Ginn HM, et al. Evidence of escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant B. 1.351 from natural and vaccine-induced Sera. Cell. 2021;184(9):2348–61. e6.",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3311",
"author": "LD Shultz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "786",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "264_CR14",
"unstructured": "Shultz LD, Brehm MA, Garcia-Martinez JV, Greiner DL. Humanized mice for immune system investigation: progress, promise and challenges. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12(11):786–98.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80653-4",
"author": "R Chiesa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1339",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Neuron",
"key": "264_CR15",
"unstructured": "Chiesa R, Piccardo P, Ghetti B, Harris DA. Neurological illlness in Transgenic mice expressing a prion protein with an insertional mutation. Neuron. 1998;21(6):1339–51.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archneur.57.12.1695",
"author": "H-X Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1695",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Arch Neurol",
"key": "264_CR16",
"unstructured": "Deng H-X, Siddique T. Transgenic mouse models and human neurodegenerative disorders. Arch Neurol. 2000;57(12):1695–702.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00848-1",
"author": "T Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "420",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "264_CR17",
"unstructured": "Pan T, Chen R, He X, Yuan Y, Deng X, Li R, et al. Infection of wild-type mice by SARS-CoV-2 B. 1.351 variant indicates a possible novel cross-species transmission route. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):420.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14010027",
"author": "S Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "264_CR18",
"unstructured": "Stone S, Rothan HA, Natekar JP, Kumari P, Sharma S, Pathak H, et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern infect the respiratory tract and induce inflammatory response in wild-type laboratory mice. Viruses. 2021;14(1):27.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14061139",
"author": "JP Natekar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1139",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "264_CR19",
"unstructured": "Natekar JP, Pathak H, Stone S, Kumari P, Sharma S, Auroni TT, et al. Differential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in human ACE2-expressing mice. Viruses. 2022;14(6):1139.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkt1168",
"author": "D Karolchik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "D764",
"issue": "D1",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "264_CR20",
"unstructured": "Karolchik D, Barber GP, Casper J, Clawson H, Cline MS, Diekhans M, et al. The UCSC genome browser database: 2014 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42(D1):D764–70.",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt.3122",
"author": "M Pertea",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "264_CR21",
"unstructured": "Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang T-C, Mendell JT, Salzberg SL. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat Biotechnol. 2015;33(3):290–5.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-76769-w",
"author": "J Vandel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19835",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "264_CR22",
"unstructured": "Vandel J, Gheeraert C, Staels B, Eeckhoute J, Lefebvre P, Dubois-Chevalier J. GIANT: galaxy-based tool for interactive analysis of transcriptomic data. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19835.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.4086505",
"author": "B Giardine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1451",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Genome Res",
"key": "264_CR23",
"unstructured": "Giardine B, Riemer C, Hardison RC, Burhans R, Elnitski L, Shah P, et al. Galaxy: a platform for interactive large-scale genome analysis. Genome Res. 2005;15(10):1451–5.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"author": "T Wu",
"first-page": "100141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Innov (Camb)",
"key": "264_CR24",
"unstructured": "Wu T, Hu E, Xu S, Chen M, Guo P, Dai Z, et al. ClusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innov (Camb). 2021;2(3):100141.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10071821",
"author": "UM Mahajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1821",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "264_CR25",
"unstructured": "Mahajan UM, Alnatsha A, Li Q, Oehrle B, Weiss F-U, Sendler M, et al. Plasma metabolome profiling identifies metabolic subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cells. 2021;10(7):1821.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.1239303",
"author": "P Shannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2498",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Genome Res",
"key": "264_CR26",
"unstructured": "Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498–504.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-60761-987-1_18",
"author": "M Kohl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "291",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "264_CR27",
"unstructured": "Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B. Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Data mining in proteomics: from standards to applications. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;696:291–303.",
"volume": "696",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11",
"author": "C-H Chin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S11",
"issue": "Suppl 4",
"journal-title": "BMC Syst Biol",
"key": "264_CR28",
"unstructured": "Chin C-H, Chen S-H, Wu H-H, Ho C-W, Ko M-T, Lin C-Y. CytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8(Suppl 4):S11.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines13040411",
"author": "S Stone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "411",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "264_CR29",
"unstructured": "Stone S, Elsharkawy A, Burleson J, Hauser M, Domi A, Kumari P, et al. Multi-antigen viral-vectored vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 and variants in a lethal hACE2 Transgenic mouse model. Vaccines (Basel). 2025;13(4):411.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009392",
"author": "W Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1009392",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "264_CR30",
"unstructured": "Ren W, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Shi H, Yu Y, Hu G, et al. Comparative analysis reveals the species-specific genetic determinants of ACE2 required for SARS-CoV-2 entry. PLoS Pathog. 2021;17(3):e1009392.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14030535",
"author": "M Carossino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "535",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "264_CR31",
"unstructured": "Carossino M, Kenney D, O’Connell AK, Montanaro P, Tseng AE, Gertje HP, et al. Fatal neurodissemination and SARS-CoV-2 tropism in K18-hACE2 mice is only partially dependent on hACE2 expression. Viruses. 2022;14(3):535.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0",
"author": "W Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "422",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "264_CR32",
"unstructured": "Ni W, Yang X, Yang D, Bao J, Li R, Xiao Y, et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):422.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2025.1557535",
"author": "A Elsharkawy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1557535",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "264_CR33",
"unstructured": "Elsharkawy A, Jahantigh HR, Guglani A, Stone S, Arora K, Kumar M. Virus-specific host responses and gene signatures following infection with major SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern: role of ZBP1 in viral clearance and lung inflammation. Front Immunol. 2025;16:1557535.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15369",
"author": "OO Glebov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3664",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "264_CR34",
"unstructured": "Glebov OO. Understanding SARS-CoV-2 endocytosis for COVID-19 drug repurposing. FEBS J. 2020;287(17):3664–71.",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "F Islam",
"first-page": "e57610",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "264_CR35",
"unstructured": "Islam F, Habib S, Badruddza K, Rahman M, Islam MR, Sultana S, et al. The association of cytokines IL-2, IL-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-10 with the disease severity of COVID-19: A study from Bangladesh. Cureus. 2024;16(4):e57610.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9",
"author": "A Hariharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "264_CR36",
"unstructured": "Hariharan A, Hakeem AR, Radhakrishnan S, Reddy MS, Rela M. The role and therapeutic potential of NF-kappa-B pathway in severe COVID-19 patients. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29:91–100.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108255",
"author": "A Attiq",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108255",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "264_CR37",
"unstructured": "Attiq A, Yao LJ, Afzal S, Khan MA. The triumvirate of NF-κB, inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101:108255.",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sjbs.2024.104021",
"author": "FQB Alenzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104021",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Saudi J Biol Sci",
"key": "264_CR38",
"unstructured": "Alenzi FQB, Survivin. A key apoptosis inhibitor in COVID-19 infection and its implication for treatment protocol. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024;31(7):104021.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.106134",
"author": "Q Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106134",
"journal-title": "Comput Biol Med",
"key": "264_CR39",
"unstructured": "Jin Q, Li W, Yu W, Zeng M, Liu J, Xu P. Analysis and identification of potential type II helper T cell (Th2)-Related key genes and therapeutic agents for COVID-19. Comput Biol Med. 2022;150:106134.",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10142-023-01092-2",
"author": "Y Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "199",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Funct Integr Genomics",
"key": "264_CR40",
"unstructured": "Tian Y, Yu B, Zhang Y, Zhang S, lv B, Gong S, et al. Exploration of the potential common pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19 and silicosis by using bioinformatics and system biology. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(3):199.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10142-023-00998-1",
"author": "S Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Funct Integr Genomics",
"key": "264_CR41",
"unstructured": "Liu S, Long J, Liang T, Lv M, Huang X, Liang X, et al. Bioinformatics analysis based on high-throughput sequencing data to identify hub genes related to different clinical types of COVID-19. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(1):71.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10142-023-01165-2",
"author": "Y Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "240",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Funct Integr Genomics",
"key": "264_CR42",
"unstructured": "Tian Y, Yu B, Zhang Y, Zhang S, lv B, Gong S, et al. Correction to: Exploration of the potential common pathogenic mechanisms in COVID–19 and silicosis by using bioinformatics and system biology. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023;23(3):240.",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0262737",
"author": "Q Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0262737",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "264_CR43",
"unstructured": "Chen Q, Xia S, Sui H, Shi X, Huang B, Wang T. Identification of hub genes associated with COVID-19 and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by integrated bioinformatics analysis. PLoS ONE. 2022;17(1):e0262737.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jproteome.1c00783",
"author": "M Grossegesse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Proteome Res",
"key": "264_CR44",
"unstructured": "Grossegesse M, Bourquain D, Neumann M, Schaade L, Schulze J, Mache C, et al. Deep time course proteomics of SARS-CoV-and SARS-CoV-2-infected human lung epithelial cells (Calu-3) reveals strong induction of interferon-stimulated gene expression by SARS-CoV-2 in contrast to SARS-CoV. J Proteome Res. 2022;21(2):459–69.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241512017",
"author": "S Assou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12017",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "264_CR45",
"unstructured": "Assou S, Ahmed E, Morichon L, Nasri A, Foisset F, Bourdais C, et al. The transcriptome landscape of the in vitro human airway epithelium response to SARS-CoV-2. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(15):12017.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1186/s42826-025-00264-4"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Transcriptomic insights into the immune dynamics of wild-type mice challenged with SARS-CoV-2 Beta variant",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "42"
}