Androgen sensitivity in COVID‐19 and antiandrogens: Prospective data are still needed
et al., Dermatologic Therapy, doi:10.1111/dth.14166, Sep 2020
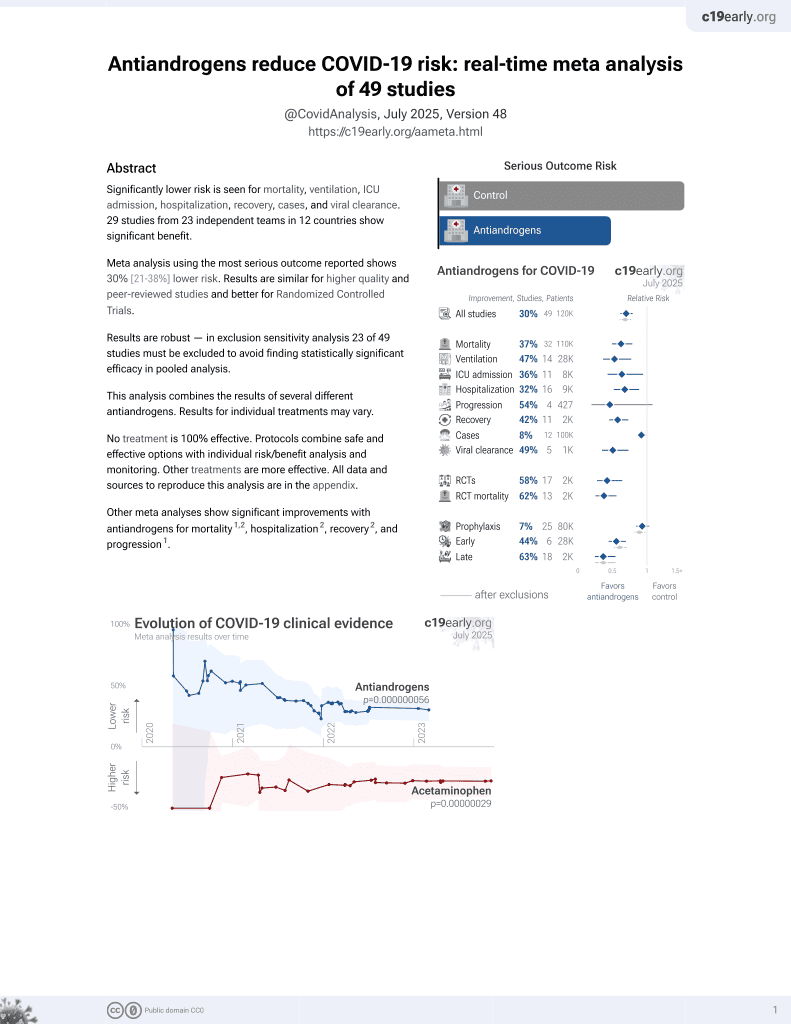
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
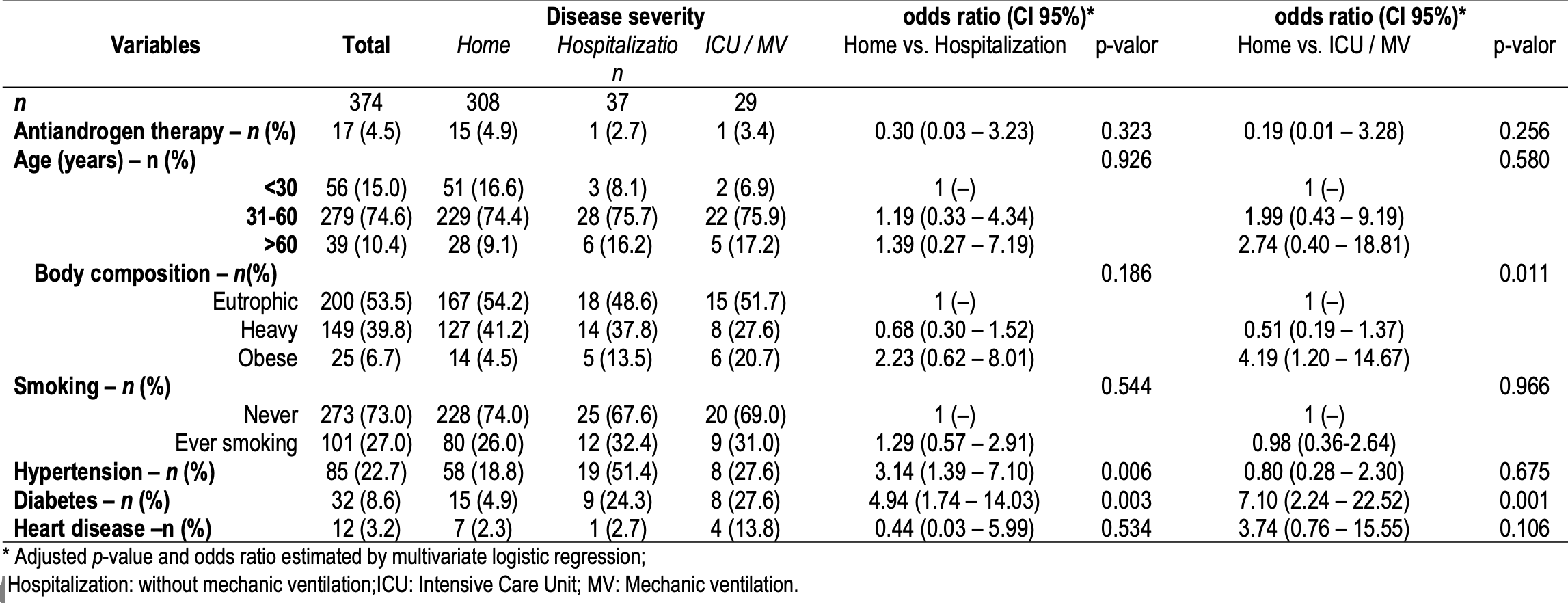
Retrospective survey of 41,529 participants, including 571 on antiandrogen therapy, showing no significant association between antiandrogen use and COVID-19 incidence, hospitalization, or ICU admission/mechanical ventilation.
|
risk of ICU admission, 79.7% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.26, treatment 1 of 17 (5.9%), control 28 of 357 (7.8%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 65.7% lower, RR 0.34, p = 0.32, treatment 2 of 17 (11.8%), control 64 of 357 (17.9%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of case, 1.4% higher, RR 1.01, p = 0.90, treatment 17 of 571 (3.0%), control 357 of 12,161 (2.9%), unadjusted, total count not provided, estimated from percentage.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ianhez et al., 3 Sep 2020, retrospective, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: ianhez@hotmail.com.
Abstract: Title: Androgen sensitivity in COVID-19 and antiandrogens: prospective data are
still needed.
Author´s list:
Mayra Ianhez1, Paulo Müller Ramos2, Andy Goren3, Hélio Amante Miot2
Author´s Affiliations:
1
Department of Tropical Medicine and Dermatology, Federal University of Goiás,
Goiânia - GO, Brazil
Address: 1a Avenida, s/n, St Leste Universitário, CEP: 74605-020, Goiânia-GO, Brazil
2
Department of Dermatology and Radiotherapy, São Paulo State University –
UNESP, Botucatu - SP, Brazil
Address:
Av.
Prof.
Mário
Bairro:
UNESP
18618687, Botucatu, SP - Brasil
3
Rubens
Guimarães
Campus
Montenegro,
s/n
de
Botucatu
Applied Biology, Irvine - California, USA
Address: 17780 Fitch, Irvine, CA 92614, Estados Unidos
Acknowledgements: none
Keywords: alopecia; antiandrogen; SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19; therapy-systemic
Running head: Antiandrogens in COVID-19
Funding: None
Correspondence:
Mayra Ianhez, MD, PhD
Department of Tropical Medicine and Dermatology
Federal University of Goiás
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
1ª avenida, s/ no, Setor Leste Universitário, Goiânia-GO
CEP: 74605-020
Email: (*ianhez@hotmail.com)
Phone/FAX: +55 62 985315443
Men are disproportionately affected by COVID-19 and have an increased
risk of ICU admittance as well as mortality. In contrast, prepubescents appear to
be largely protected from COVID-19 severe symptoms1. The androgen receptor
regulates the transcription of the transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2),
and angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) which are required for the COVID19 infectivity; thus, raising the hypothesis of androgen sensitivity as a risk
factor2,3. The recent association of androgenetic alopecia (AGA) with COVID-19
severity strengthens the androgen theory2. Testosterone levels are low not only
in prepubescents but also in elderly men4 and recent observations point out that
disease severity may be best correlated with specific gene loci, rather than ACE2
or TMPRSS2 receptors5. Furthermore, serum androgens do not always correlate
with tissue androgens or androgen mediated disease. For example, AGA and
prostate cancer can be exacerbated by elevated tissue androgen in genetically
predisposed patients6.
In order to elucidate the effect of androgens on COVID-19 outcomes,
some epidemiological studies were conducted. Since TMPRSS2 are expressed
in the lungs, the use of antiandrogens or androgen-depleting therapies (ADT),
This article is protected by copyright. All rights reserved.
currently used for prostate cancer, represent an appealing target for prevention
or treatment of COVID-19 4. An Italian study compared infectivity and outcomes
of COVID-19 in prostate cancer patients treated with or without ADT (androgen
deprivation therapies). The study concluded that ADT was associated with
reduced risk of infection and with reduced COVID-19 disease burden7; however,
to-date, no large epidemiological study attempted to evaluate the potential
protective role of diverse antiandrogens in COVID-19 infection.
To gather large scale data, we performed a population survey through
snowball sampling. Participants were invited to complete an electronic
questionnaire comprising baseline demographic, COVID-19 status (never,
suspected or confirmed), disease severity (home, hospitalization without
mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit/mechanical ventilation – ICU/MV), use
of antiandrogen therapy (ADT for prostate cancer, finasteride, dutasteride,
flutamide, bicalutamide,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.14166",
"ISSN": [
"1396-0296",
"1529-8019"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dth.14166",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/dth.14166"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-07-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-08-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-09-03"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3604-3128",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Tropical Medicine and Dermatology Federal University of Goiás Goiânia Goiás Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ianhez",
"given": "Mayra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1561-414X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Dermatology and Radiotherapy São Paulo State University—UNESP Botucatu São Paulo Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramos",
"given": "Paulo Müller",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8190-2289",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Applied Biology Irvine CA USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Goren",
"given": "Andy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2596-9294",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Dermatology and Radiotherapy São Paulo State University—UNESP Botucatu São Paulo Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Miot",
"given": "Hélio Amante",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Dermatologic Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Dermatologic Therapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-09T16:41:25Z",
"timestamp": 1596991285000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-23T17:59:02Z",
"timestamp": 1671818342000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-10T14:21:34Z",
"timestamp": 1704896494062
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1599091200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1599091200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.wiley.com/onlinelibrary/tdm/v1/articles/10.1111%2Fdth.14166",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/dth.14166",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/dth.14166",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/dth.14166",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "98",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Hindawi Limited",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Gender differences in patients with COVID‐19: focus on severity and mortality",
"author": "Jian‐Min J",
"issue": "152",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "e_1_2_3_2_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21688",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_3_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Androgen regulates SARS‐CoV‐2 receptor levels and is associated with severe COVID‐19 symptoms in men",
"author": "Ghazizadeh Z",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_3_4_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154252",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2020283",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00403-012-1265-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00649-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1005374",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_3_10_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 9,
"references-count": 9,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/dth.14166"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Dermatology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Androgen sensitivity in\n <scp>COVID</scp>\n ‐19 and antiandrogens: Prospective data are still needed",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "33"
}