The Proportion and Associated Factors for Mortality among COVID-19 Infection with Diabetes in Iraq
et al., The Review of Diabetic Studies, doi:10.1900/RDS.2024.20.12, Jun 2024
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
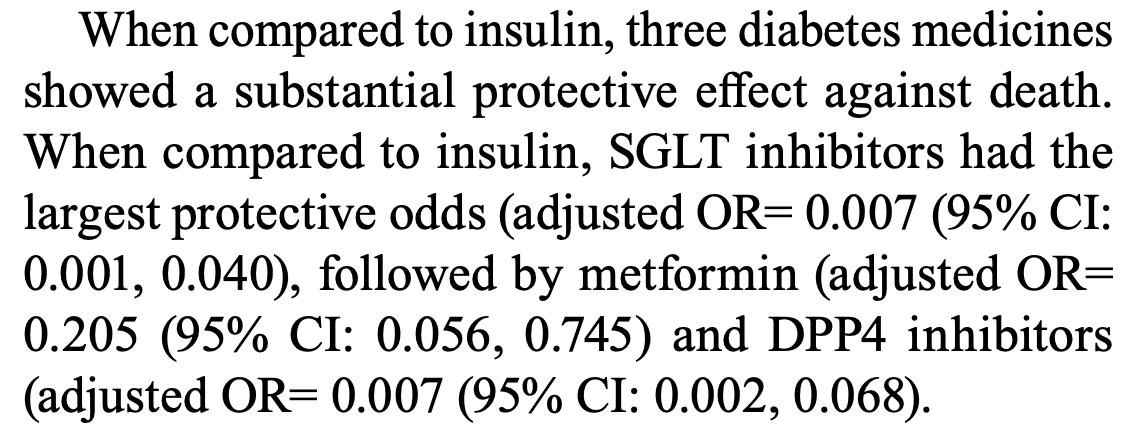
Retrospective 545 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes showing high mortality (33%). Metformin, SGLT inhibitors, and DPP4 inhibitors were associated with lower mortality compared with insulin.
|
risk of death, 63.8% lower, RR 0.36, p = 0.048, treatment 30 of 158 (19.0%), control 60 of 110 (54.5%), NNT 2.8, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hussein et al., 30 Jun 2024, retrospective, Iraq, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
The Proportion and Associated Factors for Mortality among COVID-19 Infection with Diabetes in Iraq
doi:10.1900/RDS.2024.20.12
Objective: The study aims to determine the proportion, clinical characteristics, and associated factors for the mortality among hospitalised COVID-19 patients with diabetes in Ramadi, Iraq. Methods: This retrospective cohort study included all adult diabetic patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 who were hospitalised between January 2020 and December 2020 in Ramadi Province, Iraq. Data on demographics, medical history, and laboratory investigations were obtained from medical records. The poor outcomes were mortality during hospitalisation. Multivariate logistic regression was used to analyse for the associated factors for mortality. Results: A total of 545 health records of diabetic patients were reviewed. There were 340 males (62.4%) and 205 females (37.6%). The mean age was 64.54±10.86 years. The proportion of mortality was 32.84%. The protective factors for mortality were rural residency, duration of hospitalisation, and diabetic medication (SGLT inhibitors, DPP4 inhibitors and metformin). Cardiac disease, liver disease, temperature, CRP and D-dimer level were found to be predictive factors for mortality. Conclusion: The study revealed that the proportion of mortality among diabetic patients with COVID-19 infection was high in Iraq. The findings highlighted the predictive and protective factors among this vulnerable group for poor outcomes.
Rev Diabet Stud (2024) 20: [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] Copyright © by Lab & Life Press of statistics at the Ramadi Teaching Hospital, Anbar Province, Iraq, for their cooperation during data collection.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest
References
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Pichelin, Al-Salameh et al., Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia
Chen, Yang, Cheng, Chen, Peng et al., Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 in Association With Glucose-Lowering Medication, Diabetes Care
Ciotti, Ciccozzi, Terrinoni, Jiang, Wang et al., The COVID-19 pandemic, Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci
Cuadros, Branscum, Mukandavire, Miller, Mackinnon, Dynamics of the COVID-19 epidemic in urban and rural areas in the United States, Ann Epidemiol
Fadini, Morieri, Longato, Avogaro, Prevalence and impact of diabetes among people infected with SARS-CoV-2, J Endocrinol Invest
Huang, Lim, Pranata, Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia -A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Izzi-Engbeaya, Distaso, Amin, Yang, Idowu et al., Adverse outcomes in COVID-19 and diabetes: a retrospective cohort study from three London teaching hospitals, BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care
Miller, Bhattacharyya, Miller, Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of hospital mortality in patients with Covid-19: Systematic review with metaanalysis, Medicine
Mirsoleymani, Taherifard, Taherifard, Taghrir, Marzaleh et al., Predictors of mortality among covid-19 patients with or without comorbid diabetes mellitus, Acta Medica Iranica
Mishra, Pathak, Mohakuda, Tilak, Sen, Relation of D-dimer levels of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Ong, Tan, Cañete, Lim, Robles, Association Between Metformin Use and Mortality among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Hospitalized for COVID-19 Infection, J ASEAN Fed Endocr Soc
Patoulias, Doumas, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and COVID-19-Related Deaths among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, Endocrinol Metab
Porcheddu, Serra, Kelvin, Rubino, Similarity in Case Fatality Rates (CFR) of COVID-19/SARS-COV-2 in Italy and China, J Infect Dev Ctries
Ramirez, Lee, COVID-19 Emergence and Social and Health Determinants in Colorado: A Rapid Spatial Analysis, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Saha, Al-Rifai, Saha, Diabetes prevalence and mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, J Diabetes Metab Disord
Yang, Zhong, Tian, Xie, Fu et al., The effect of diabetes on mortality of COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Zhang, Schwartz, Spatial Disparities in Coronavirus Incidence and Mortality in the United States: An Ecological Analysis as of May 2020, J Rural Health
