Alteration of the Gut–Lung Axis After Severe COVID-19 Infection and Modulation Through Probiotics: A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Study
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16223840, NCT04813718, Nov 2024
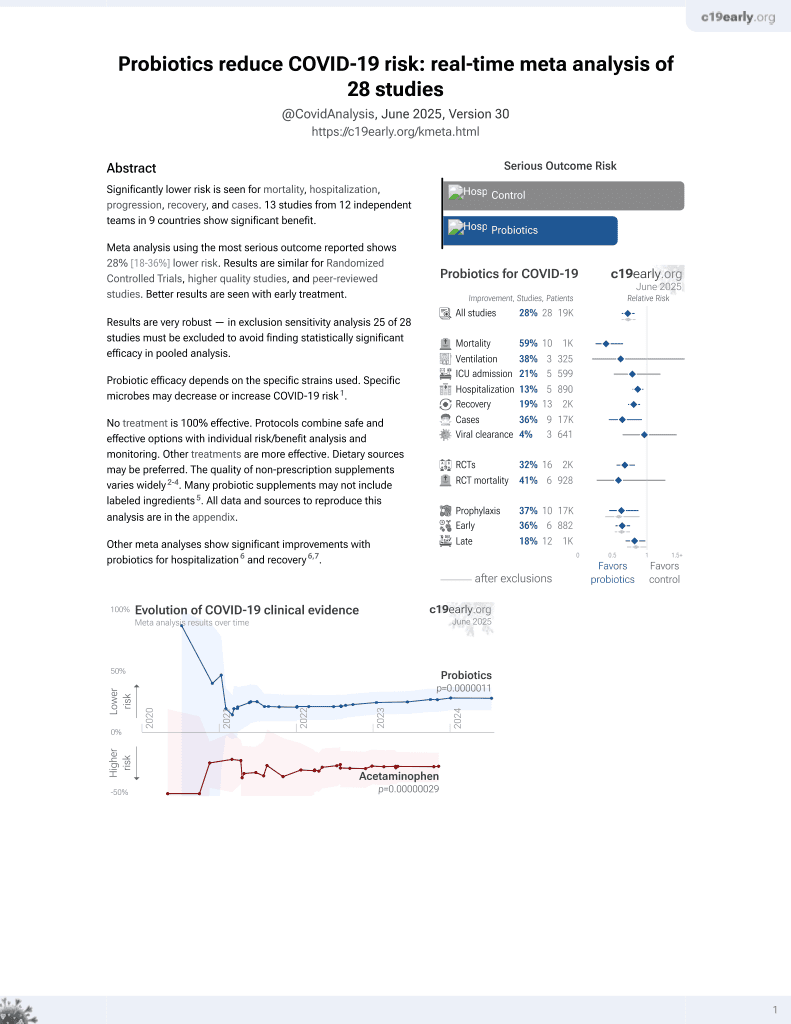
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
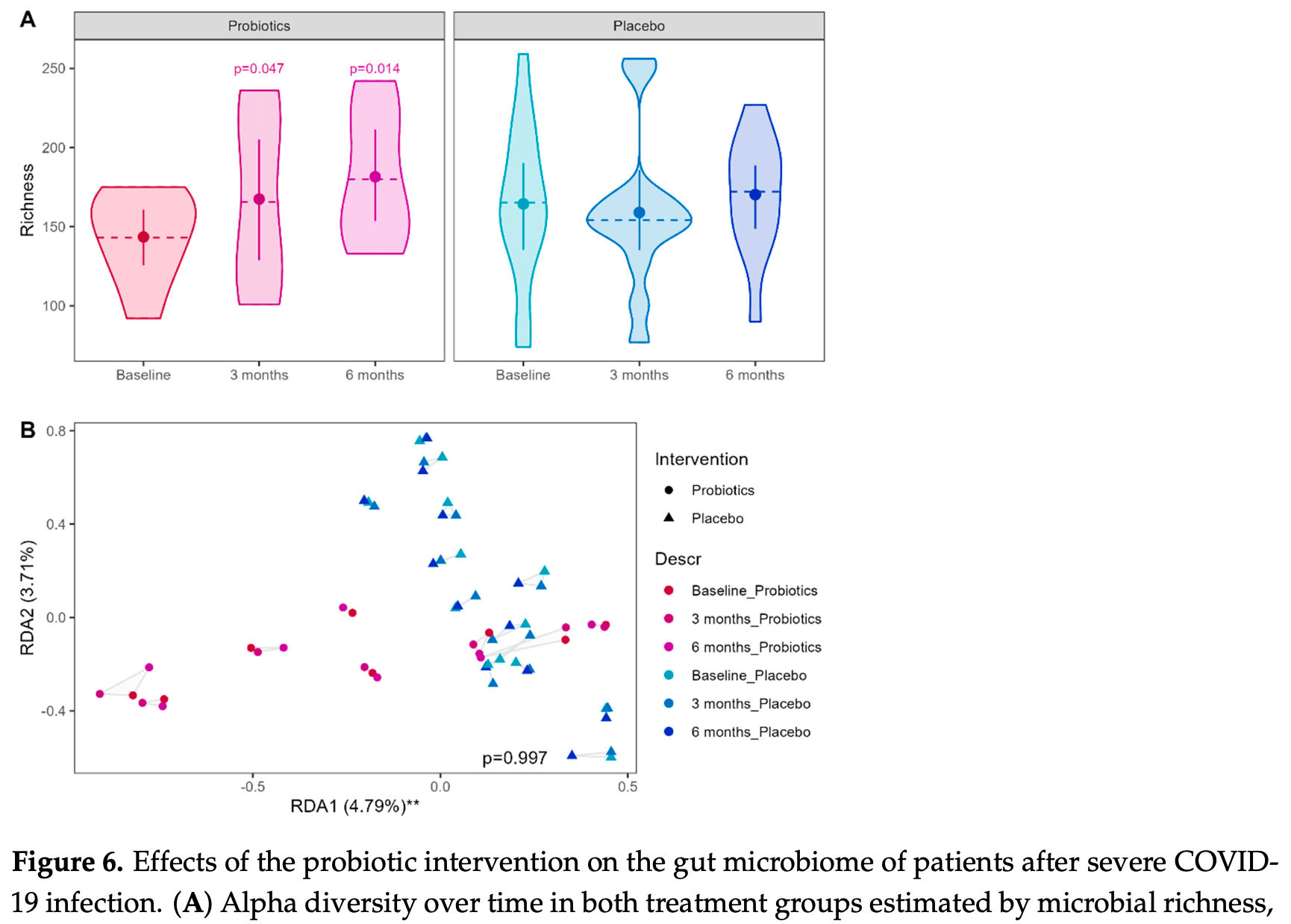
Randomized controlled trial of 21 patients after severe COVID-19 infection showing improved microbial richness, stool metabolites, innate immune function, and quality of life with a multispecies probiotic compared to placebo over 6 months. The study also found persistent differences in the gut microbiome, metabolome, and immune parameters in patients after severe compared to mild COVID-19 infection at baseline, 7-10 months after infection.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
Horvath et al., 8 Nov 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Austria, peer-reviewed, 15 authors, study period 2 June, 2021 - 17 July, 2022, trial NCT04813718 (history).
Contact: vanessa.stadlbauer@medunigraz.at (corresponding author), angela.horvath@cbmed.at, barbara.prietl@cbmed.at, verena.pfeifer@cbmed.at, dr.irina.balazs@gmail.com, nicole.feldbacher@cbmed.at, kristina.zukauskaite@medunigraz.at, hansjoerg.habisch@medunigraz.at, tobias.madl@medunigraz.at, gabor.kovacs@uniklinikum.kages.at, vasile.foris@medunigraz.at, nikolaus.john@medunigraz.at, daniela.kleinschek@lvr.lbg.ac.at, henning.gronbaek@aarhus.rm.dk, holgmoel@rm.dk.
Alteration of the Gut–Lung Axis After Severe COVID-19 Infection and Modulation Through Probiotics: A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Study
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16223840
Background: The gut-lung axis could be a potential therapeutic target for improving post-acute COVID-19 symptoms, and probiotics have been proposed as possible modulators. Aim: We conducted a pilot study to understand alterations in the gut-lung axis and to explore the effects of a probiotic in post-acute COVID-19 disease. Methods: We included patients after severe COVID-19 disease (sCOV, n = 21) in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to test the effect of a probiotic (Pro-Vi 5, Institute Allergosan, Graz, Austria) in a six-month intervention and used patients after mild disease (mCOV, n = 10) as controls, to compare the intestinal microbiome, metabolome, and patient-reported outcomes and biomarkers along the gut-lung axis at baseline and throughout probiotic intervention. Results: Compared to mCOV patients, sCOV patients showed lower microbial richness, which was significantly improved by probiotic intervention. A reorganization of Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae taxa was observed in sCOV patients but remained unaffected by the intervention. Serum metabolome showed a dysregulation of lipoproteins in accordance with higher BMI and comorbidities in sCOV patients. HDL and LDL fractions/components were temporarily decreased in the probiotic group. Stool metabolome was altered at baseline in sCOV patients and an increase in L-DOPA after 3 months and butyrate after 6 months of intervention could be observed. Probiotics partially improved reduced quality of life and modulated altered immune responses in sCOV patients. Increased intestinal permeability at baseline remained unaffected. Conclusion: The study provides evidence of long-term alterations of the gut-lung axis after severe COVID-19 infection and suggests that probiotics can modulate the biomarkers of the gut-lung axis.
Author Contributions: Conceptualization, A.H. and V.S.; formal analysis, A.H. and I.B.; methodology, A.H.; visualization, A.H.; writing-original draft preparation, A.H. and V.S.; writing-review and editing, A.H., K.Ž. and V.S.; data curation, H.H., B.P., V.P., I.B., G.K., V.F., N.J., D.K., N.F., H.G., H.J.M. and T.M.; project administration, N.F. and K.Ž.; funding acquisition, V.S.; investigation, V.S.; supervision, V.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board
References
Aabenhus, Thorsen, Siersma, Brodersen, The development and validation of a multidimensional sum-scaling questionnaire to measure patient-reported outcomes in acute respiratory tract infections in primary care: The acute respiratory tract infection questionnaire, Value Health, doi:10.1016/j.jval.2013.06.011
Afrin, Weinstock, Molderings, COVID-19 hyperinflammation and post-COVID-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016
Aktas, Aslim, Gut-lung axis and dysbiosis in COVID-19, Turk. J. Biol, doi:10.3906/biy-2005-102
Alharbi, Singh, Hassan Almalki, Rawat, Afzal et al., Gut Microbiota Disruption in COVID-19 or Post-COVID Illness Association with severity biomarkers: A Possible Role of Pre/Pro-biotics in manipulating microflora, Chem. Biol. Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109898
Alkodaymi, Omrani, Fawzy, Shaar, Almamlouk et al., Prevalence of post-acute COVID-19 syndrome symptoms at different follow-up periods: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Microbiol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.01.014
Allali, Bakri, Amzazi, Ghazal, Gut-Lung Axis in COVID-19, Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1155/2021/6655380
Ancona, Alagna, Alteri, Palomba, Tonizzo et al., Gut and airway microbiota dysbiosis and their role in COVID-19 and long-COVID, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1080043
Aponte, Murru, Shoukat, Therapeutic, Prophylactic, and Functional Use of Probiotics: A Current Perspective, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.562048
Baindara, Chakraborty, Holliday, Mandal, Schrum, Oral probiotics in coronavirus disease 2019: Connecting the gut-lung axis to viral pathogenesis, inflammation, secondary infection and clinical trials, New Microbes New Infect, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100837
Balazs, Horvath, Leber, Feldbacher, Sattler et al., Serum bile acids in liver cirrhosis promote neutrophil dysfunction, Clin. Transl. Med, doi:10.1002/ctm2.735
Barroso, De Jesus, De Castro, Batista, Ferreira et al., Intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii (pExu:hsp65) Prevents the Inflammation and the Disorganization of the Intestinal Mucosa in a Mouse Model of Mucositis, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms9010107
Bernini, Simao, De Souza, Alfieri, Segura et al., Effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on inflammatory markers and oxidative stress in subjects with and without the metabolic syndrome, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114518001861
Blesl, Jungst, Lammert, Fauler, Rainer et al., Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Critically Ill Patients Alters the Gut-Liver Axis: A Case Control Study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092728
Caporaso, Lauber, Walters, Berg-Lyons, Huntley et al., Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms, ISME J, doi:10.1038/ismej.2012.8
Carfi, Bernabei, Landi, Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12603
Ceban, Ling, Lui, Lee, Gill et al., Fatigue and cognitive impairment in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Brain Behav. Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2021.12.020
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation, J. Chronic Dis, doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
Chen, Gu, Chen, Lu, Shi et al., Six-month follow-up of gut microbiota richness in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324090
Chen, Li, Chang, Dong, Yang et al., Lactobacillus bulgaricus or Lactobacillus rhamnosus Suppresses NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway and Protects against AFB(1)-Induced Hepatitis: A Novel Potential Preventive Strategy for Aflatoxicosis?, Toxins, doi:10.3390/toxins11010017
Chen, Vitetta, Modulation of Gut Microbiota for the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10132903
Chowdhury, Alam, Rabbi, Rahman, Reza, Does higher body mass index increase COVID-19 severity? A systematic review and meta-analysis, Obes. Med, doi:10.1016/j.obmed.2021.100340
Datta, Talwar, Lee, A Proposed Framework and Timeline of the Spectrum of Disease Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Illness Beyond Acute Infection and Public Health Implications, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22717
De Oliveira, Oliveira, Pinzan, De Salis, Cardoso, Microbiota Modulation of the Gut-Lung Axis in COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.635471
Dieterle, Ross, Schlotterbeck, Senn, Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/ac051632c
Din, Mazhar, Waseem, Ahmad, Bibi et al., SARS-CoV-2 microbiome dysbiosis linked disorders and possible probiotics role, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110947
Duan, Tang, Wang, Qian, Fu et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates intestinal inflammation induced by Fusobacterium nucleatum infection by restoring the autophagic flux, Int. J. Mol. Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4780
Eapen, Lu, Gaikwad, Bhattarai, Chia et al., Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: A precursor to post-COVID-19 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vascular obliteration?, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.03167-2020
Erny, Hrabe De Angelis, Jaitin, Wieghofer, Staszewski et al., Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS, Nat. Neurosci, doi:10.1038/nn.4030
Eypasch, Williams, Wood-Dauphinee, Ure, Schmulling et al., Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index: Development, validation and application of a new instrument, Br. J. Surg, doi:10.1002/bjs.1800820229
Fang, Fang, Chiang Chiau, Yeung, Chan et al., Inhibitory effects of Lactobacillus casei subsp. rhamnosus on Salmonella lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and epithelial barrier dysfunction in a co-culture model using Caco-2/peripheral blood mononuclear cells, J. Med. Microbiol, doi:10.1099/jmm.0.009662-0
Finlay, Amato, Azad, Blaser, Bosch et al., The hygiene hypothesis, the COVID pandemic, and consequences for the human microbiome, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2010217118
Fuertes-Martin, Correig, Vallve, Amigo, Title: Human Serum/Plasma Glycoprotein Analysis by (1)H-NMR, an Emerging Method of Inflammatory Assessment, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9020354
Gamallat, Meyiah, Kuugbee, Hago, Chiwala et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus induced epithelial cell apoptosis, ameliorates inflammation and prevents colon cancer development in an animal model, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.001
Gao, Major, Rendon, Lugo, Jackson et al., Histamine H2 Receptor-Mediated Suppression of Intestinal Inflammation by Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.01358-15
Ghini, Meoni, Pelagatti, Celli, Veneziani et al., Profiling metabolites and lipoproteins in COMETA, an Italian cohort of COVID-19 patients, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1010443
Giron, Dweep, Yin, Wang, Damra et al., Plasma Markers of Disrupted Gut Permeability in Severe COVID-19 Patients, Front. Immunol
Gustine, Jones, Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Am. J. Pathol, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009
Halpin, Mcivor, Whyatt, Adams, Harvey et al., Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26368
Hanna, Codd, Gea-Mallorqui, Scourfield, Richter et al., T cell phenotypes in COVID-19-A living review, Oxf. Open Immunol, doi:10.1093/oxfimm/iqaa007
Hanus, Parada-Venegas, Landskron, Wielandt, Hurtado et al., Immune System, Microbiota, and Microbial Metabolites: The Unresolved Triad in Colorectal Cancer Microenvironment, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.612826
Hocini, Wiedemann, Blengio, Lefebvre, Cervantes-Gonzalez et al., Neutrophil Activation and Immune Thrombosis Profiles Persist in Convalescent COVID-19, J. Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1007/s10875-023-01459-x
Jimenez, Holmes, Heude, Tolson, Harvey et al., Quantitative Lipoprotein Subclass and Low Molecular Weight Metabolite Analysis in Human Serum and Plasma by (1)H NMR Spectroscopy in a Multilaboratory Trial, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02412
Kano, Kita, Makino, Ikegami, Itoh, Oral administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 suppresses inflammation by decreasing interleukin-6 responses in a murine model of atopic dermatitis, J. Dairy Sci, doi:10.3168/jds.2012-6514
Karmakar, Chu, Sundaram, Astier, Garside et al., Immune complexinduced apoptosis and concurrent immune complex clearance are anti-inflammatory neutrophil functions, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03528-8
Kaushik, Kumari, Singh, Suri, The role of gut microbiota in etiopathogenesis of long COVID syndrome, Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1515/hmbci-2022-0079
Khan, Bai, Zha, Ullah, Ullah et al., Mechanism of the Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance and Enteric Pathogen Infection, Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.716299
Kitazawa, Villena, Modulation of Respiratory TLR3-Anti-Viral Response by Probiotic Microorganisms: Lessons Learned from Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00201
Kumpitsch, Fischmeister, Mahnert, Lackner, Wilding et al., Reduced B12 uptake and increased gastrointestinal formate are associated with archaeome-mediated breath methane emission in humans, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-021-01130-w
Laforge, Elbim, Frere, Hemadi, Massaad et al., Tissue damage from neutrophilinduced oxidative stress in COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1
Ley, Backhed, Turnbaugh, Lozupone, Knight et al., Obesity alters gut microbial ecology, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0504978102
Li, Fang, Liu, Hu, Lu et al., Lactobacillus reuteri attenuated allergic inflammation induced by HDM in the mouse and modulated gut microbes, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0231865
Li, Hsu, Chang, Shih, Combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Shows a Stronger Anti-Inflammatory Effect than Individual Strains in HT-29 Cells, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11050969
Li, Liu, Tian, Zou, Gao et al., Soluble CD206 levels correlate with disease deterioration and predict prognosis of anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis related interstitial lung disease, Clin. Respir. J, doi:10.1111/crj.13616
Liu, Chen, Li, Gu, Liu et al., Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Prevents Liver Fibrosis Through Inhibiting Hepatic Bile Acid Synthesis and Enhancing Bile Acid Excretion in Mice, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.30975
Liu, Fatheree, Mangalat, Rhoads, Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri strains differentially reduce intestinal inflammation, Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00124.2010
Lodge, Nitschke, Kimhofer, Wist, Bong et al., Diffusion and Relaxation Edited Proton NMR Spectroscopy of Plasma Reveals a High-Fidelity Supramolecular Biomarker Signature of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04952
Lopez-Hernandez, Oropeza-Valdez, Garcia Lopez, Borrego, Murgu et al., Untargeted analysis in post-COVID-19 patients reveals dysregulated lipid pathways two years after recovery, Front. Mol. Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2023.1100486
Loria, Rance, Palmer, A Relaxation-Compensated Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill Sequence for Characterizing Chemical Exchange by NMR Spectroscopy, J. Am. Chem. Soc, doi:10.1021/ja983961a
Louis, Hold, Flint, The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro3344
Ludwig, Viant, Two-dimensional J-resolved NMR spectroscopy: Review of a key methodology in the metabolomics toolbox, Phytochem. Anal, doi:10.1002/pca.1186
Ma, Piao, Mahfuz, Long, Wang, The interaction among gut microbes, the intestinal barrier and short chain fatty acids, Anim. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.012
Manna, Baindara, Mandal, Molecular pathogenesis of secondary bacterial infection associated to viral infections including SARS-CoV-2, J. Infect. Public. Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.003
Masso-Silva, Moshensky, Lam, Odish, Patel et al., Increased Peripheral Blood Neutrophil Activation Phenotypes and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Case Series and Review of the Literature, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab437
Masuda, Lodge, Whiley, Gray, Lawler et al., Exploration of Human Serum Lipoprotein Supramolecular Phospholipids Using Statistical Heterospectroscopy in n-Dimensions (SHY-n): Identification of Potential Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers Related to SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05389
Mohtashami, Mohamadi, Azimi-Nezhad, Saeidi, Nia et al., Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Lactobacillus plantarum improve diabetic wound healing through modulating inflammatory factors, Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem, doi:10.1002/bab.2064
Moller, Hald, Moestrup, Characterization of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for soluble CD163, Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig, doi:10.1080/003655102760145852
Munblit, Nicholson, Akrami, Apfelbacher, Chen et al., A core outcome set for post-COVID-19 condition in adults for use in clinical practice and research: An international Delphi consensus study, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00169-2
Munblit, O'hara, Akrami, Perego, Olliaro et al., Aiming for a consensus, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00135-7
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Madhavan, Mcgroder et al., Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Ng, Tipih, Makoah, Vermeulen, Goedhals et al., Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.03647-20
Nitschke, Lodge, Kimhofer, Masuda, Bong et al., J-Edited DIffusional Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Measurement of Glycoprotein and Supramolecular Phospholipid Biomarkers of Inflammation in Human Serum, Anal. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04576
O'sullivan, Houston, Ladlow, Barker-Davies, Chamley et al., Factors influencing medium-and long-term occupational impact following COVID-19, Occup. Med, doi:10.1093/occmed/kqad041
O'toole, Shiels, The role of the microbiota in sedentary lifestyle disorders and ageing: Lessons from the animal kingdom, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13021
Pang, Zhou, Chong, Xia, Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of COVID-19 Global Metabolomics Datasets, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11010044
Philippe, Favre, Foata, Adolfsson, Perruisseau-Carrier et al., Bifidobacterium lactis attenuates onset of inflammation in a murine model of colitis, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459
Pi, Zhang, Zeng, Editorial: Gut-lung interaction axis, Front. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1159629
Prietl, Odler, Kirsch, Artinger, Eigner et al., Chronic Inflammation Might Protect Hemodialysis Patients From Severe COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.821818
Rocha, Lakhdari, Blottiere, Blugeon, Sokol et al., Anti-inflammatory properties of dairy lactobacilli, Inflamm. Bowel Dis, doi:10.1002/ibd.21834
Rodgaard-Hansen, Rafique, Christensen, Maniecki, Sandahl et al., A soluble form of the macrophage-related mannose receptor (MR/CD206) is present in human serum and elevated in critical illness, Clin. Chem. Lab. Med, doi:10.1515/cclm-2013-0451
Rossini, Tolosa-Enguis, Frances-Cuesta, Sanz, Gut microbiome and anti-viral immunity in COVID-19, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2143476
Sawadogo, Dighero-Kemp, Ouedraogo, Hensley, Sakande, How NETosis could drive "Post-COVID-19 syndrome" among survivors, Immunol. Lett, doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.005
Schmidt, Raes, Bork, The Human Gut Microbiome: From Association to Modulation, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.044
Sekar, Krishnasamy, Arockiya, Intermodulation of gut-lung axis microbiome and the implications of biotics to combat COVID-19, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1994875
Shimizu, Hashiguchi, Shiga, Tamura, Mochizuki, Meta-Analysis: Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Lipid Profiles in Normal to Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Individuals, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0139795
Sichetti, De Marco, Pagiotti, Traina, Pietrella, Anti-inflammatory effect of multistrain probiotic formulation (L. rhamnosus, B. lactis, and B. longum), Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.005
Silveira, Veronez, Lopes-Junior, Anatriello, Brunaldi et al., Lactobacillus bulgaricus inhibits colitis-associated cancer via a negative regulation of intestinal inflammation in azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate model, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v26.i43.6782
Su, Lau, Liu, Chan, Ng, Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and gut dysbiosis linger beyond 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 clearance, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328319
Su, Yuan, Chen, Ng, Wang et al., Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.014
Tale, Ghosh, Meitei, Kolli, Garbhapu et al., Post-COVID-19 pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis, QJM, doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcaa255
Thomas, Saulnier, Spinler, Hemarajata, Gao et al., FolC2-mediated folate metabolism contributes to suppression of inflammation by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri, Microbiologyopen, doi:10.1002/mbo3.371
Tian, Babor, Lane, Schulten, Patil et al., Unique phenotypes and clonal expansions of human CD4 effector memory T cells re-expressing CD45RA, Nat. Commun
Turner, Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri2653
Valles-Colomer, Falony, Darzi, Tigchelaar, Wang et al., The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-018-0337-x
Veenith, Martin, Le Breuilly, Whitehouse, Gao-Smith et al., High generation of reactive oxygen species from neutrophils in patients with severe COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-13825-7
Veiga, Gallini, Beal, Michaud, Delaney et al., Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis fermented milk product reduces inflammation by altering a niche for colitogenic microbes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1011737107
Venegas, De La Fuente, Landskron, Gonzalez, Quera et al., Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, Front. Immunol
Villena, Chiba, Tomosada, Salva, Marranzino et al., Orally administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus modulates the respiratory immune response triggered by the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern poly(I:C), BMC Immunol, doi:10.1186/1471-2172-13-53
Wahab, Almaghaslah, Mahmood, Ahmad, Alsayegh et al., Pharmacological Efficacy of Probiotics in Respiratory Viral Infections: A Comprehensive Review, J. Pers. Med, doi:10.3390/jpm12081292
Wang, Zhou, Huang, Kuai, Shao, The potential therapeutic role of Lactobacillus reuteri for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, Am. J. Transl. Res
Ware, Jr, Sherbourne, The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection, Med. Care, doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
Wen, Jiang, Gao, Zhou, Xiao et al., Clinical characteristics and predictive value of lower CD4(+)T cell level in patients with moderate and severe COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective study, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-020-05741-w
Wibowo, Yang, Borry, Hubner, Huang et al., Reconstruction of ancient microbial genomes from the human gut, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03532-0
Widyarman, Drestia, Bachtiar, Bachtiar, The Anti-inflammatory Effects of Glycerol-supplemented Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri on Infected Epithelial cells In vitro, Contemp. Clin. Dent, doi:10.4103/ccd.ccd_53_18
Wu, Chen, Ding, Wu, Hou et al., The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24482-1
Xu, Zhang, Guo, Xiao, Fu et al., Integrated analysis of gut microbiome and host immune responses in COVID-19, Front. Med, doi:10.1007/s11684-022-0921-6
Yan, Liu, Zhao, Wang, Wang et al., Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis V9 attenuates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, AMB Express, doi:10.1186/s13568-020-01038-y
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Zhang, Liu et al., Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020
Yin, Peluso, Thomas, Shin, Neidleman et al., Long COVID manifests with T cell dysregulation, inflammation, and an uncoordinated adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1038/s41590-023-01724-6
Zhang, Zhang, Xia, Sun, Microbiome and intestinal pathophysiology in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, Genes. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.034
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16223840",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu16223840",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: The gut–lung axis could be a potential therapeutic target for improving post-acute COVID-19 symptoms, and probiotics have been proposed as possible modulators. Aim: We conducted a pilot study to understand alterations in the gut–lung axis and to explore the effects of a probiotic in post-acute COVID-19 disease. Methods: We included patients after severe COVID-19 disease (sCOV, n = 21) in a randomized, placebo-controlled trial to test the effect of a probiotic (Pro-Vi 5, Institute Allergosan, Graz, Austria) in a six-month intervention and used patients after mild disease (mCOV, n = 10) as controls, to compare the intestinal microbiome, metabolome, and patient-reported outcomes and biomarkers along the gut–lung axis at baseline and throughout probiotic intervention. Results: Compared to mCOV patients, sCOV patients showed lower microbial richness, which was significantly improved by probiotic intervention. A reorganization of Ruminococcaceae and Lachnospiraceae taxa was observed in sCOV patients but remained unaffected by the intervention. Serum metabolome showed a dysregulation of lipoproteins in accordance with higher BMI and comorbidities in sCOV patients. HDL and LDL fractions/components were temporarily decreased in the probiotic group. Stool metabolome was altered at baseline in sCOV patients and an increase in L-DOPA after 3 months and butyrate after 6 months of intervention could be observed. Probiotics partially improved reduced quality of life and modulated altered immune responses in sCOV patients. Increased intestinal permeability at baseline remained unaffected. Conclusion: The study provides evidence of long-term alterations of the gut–lung axis after severe COVID-19 infection and suggests that probiotics can modulate the biomarkers of the gut–lung axis.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu16223840"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Horvath",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5537-506X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Otto Loewi Research Center, Medicinal Chemistry, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "BioTechMed-Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Habisch",
"given": "Hansjörg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Prietl",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division of Endocrinology and Diabetes, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Pfeifer",
"given": "Verena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2026-3521",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Balazs",
"given": "Irina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Kovacs",
"given": "Gabor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8863-0298",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Foris",
"given": "Vasile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "John",
"given": "Nikolaus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ludwig Boltzmann Institute for Lung Vascular Research, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Kleinschek",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Feldbacher",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Hepatology and Gastroenterology, Aarhus University Hospital, 8200 Aarhus, Denmark"
},
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, 8000 Aarhus, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Grønbæk",
"given": "Henning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Medicine, Aarhus University, 8000 Aarhus, Denmark"
},
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Biochemistry, Aarhus University Hospital, 8200 Aarhus, Denmark"
}
],
"family": "Møller",
"given": "Holger Jon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Institute of Biosciences, Life Sciences Center, Vilnius University, 01513 Vilnius, Lithuania"
}
],
"family": "Žukauskaitė",
"given": "Kristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9725-5231",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Otto Loewi Research Center, Medicinal Chemistry, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "BioTechMed-Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Madl",
"given": "Tobias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5508-8271",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biomarker Research in Medicine (CBmed), Division of Translational Precision Medicine, Division of Precision Medicine Technologies, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Division for Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Medical University of Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
},
{
"name": "BioTechMed-Graz, 8010 Graz, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Stadlbauer",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T16:59:17Z",
"timestamp": 1731085157000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T17:00:52Z",
"timestamp": 1731085252000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-09T05:18:41Z",
"timestamp": 1731129521949,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "22",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "22",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1731024000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/22/3840/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3840",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"article-title": "Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19",
"author": "Carfi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Nalbandian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00135-7",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Aiming for a consensus",
"author": "Munblit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "632",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22717",
"article-title": "A Proposed Framework and Timeline of the Spectrum of Disease Due to SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Illness Beyond Acute Infection and Public Health Implications",
"author": "Datta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2251",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26368",
"article-title": "Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: A cross-sectional evaluation",
"author": "Halpin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1013",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.016",
"article-title": "COVID-19 hyperinflammation and post-COVID-19 illness may be rooted in mast cell activation syndrome",
"author": "Afrin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.005",
"article-title": "How NETosis could drive “Post-COVID-19 syndrome” among survivors",
"author": "Sawadogo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Lett.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/qjmed/hcaa255",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis",
"author": "Tale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "837",
"journal-title": "QJM",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03167-2020",
"article-title": "Endothelial to mesenchymal transition: A precursor to post-COVID-19 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis and vascular obliteration?",
"author": "Eapen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2003167",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/biy-2005-102",
"article-title": "Gut-lung axis and dysbiosis in COVID-19",
"author": "Aktas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Turk. J. Biol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/6655380",
"article-title": "Gut-Lung Axis in COVID-19",
"author": "Allali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6655380",
"journal-title": "Interdiscip. Perspect. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110947",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Din, A.U., Mazhar, M., Waseem, M., Ahmad, W., Bibi, A., Hassan, A., Ali, N., Gang, W., Qian, G., and Ullah, R. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 microbiome dysbiosis linked disorders and possible probiotics role. Biomed. Pharmacother., 133."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hmbci-2022-0079",
"article-title": "The role of gut microbiota in etiopathogenesis of long COVID syndrome",
"author": "Kaushik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100837",
"article-title": "Oral probiotics in coronavirus disease 2019: Connecting the gut-lung axis to viral pathogenesis, inflammation, secondary infection and clinical trials",
"author": "Baindara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100837",
"journal-title": "New Microbes New Infect.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109898",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Alharbi, K.S., Singh, Y., Hassan Almalki, W., Rawat, S., Afzal, O., Alfawaz Altamimi, A.S., Kazmi, I., Al-Abbasi, F.A., Alzarea, S.I., and Singh, S.K. (2022). Gut Microbiota Disruption in COVID-19 or Post-COVID Illness Association with severity biomarkers: A Possible Role of Pre/Pro-biotics in manipulating microflora. Chem. Biol. Interact., 358."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1080043",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Ancona, G., Alagna, L., Alteri, C., Palomba, E., Tonizzo, A., Pastena, A., Muscatello, A., Gori, A., and Bandera, A. (2023). Gut and airway microbiota dysbiosis and their role in COVID-19 and long-COVID. Front. Immunol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002",
"article-title": "The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection",
"author": "Ware",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "473",
"journal-title": "Med. Care",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "30",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/bjs.1800820229",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal Quality of Life Index: Development, validation and application of a new instrument",
"author": "Eypasch",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Surg.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "82",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2013.06.011",
"article-title": "The development and validation of a multidimensional sum-scaling questionnaire to measure patient-reported outcomes in acute respiratory tract infections in primary care: The acute respiratory tract infection questionnaire",
"author": "Aabenhus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "987",
"journal-title": "Value Health",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00169-2",
"article-title": "A core outcome set for post-COVID-19 condition in adults for use in clinical practice and research: An international Delphi consensus study",
"author": "Munblit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ismej.2012.8",
"article-title": "Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms",
"author": "Caporaso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1621",
"journal-title": "ISME J.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ja983961a",
"article-title": "A Relaxation-Compensated Carr−Purcell−Meiboom−Gill Sequence for Characterizing Chemical Exchange by NMR Spectroscopy",
"author": "Loria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2331",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Chem. Soc.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "121",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pca.1186",
"article-title": "Two-dimensional J-resolved NMR spectroscopy: Review of a key methodology in the metabolomics toolbox",
"author": "Ludwig",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "22",
"journal-title": "Phytochem. Anal.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04576",
"article-title": "J-Edited DIffusional Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Measurement of Glycoprotein and Supramolecular Phospholipid Biomarkers of Inflammation in Human Serum",
"author": "Nitschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1333",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02412",
"article-title": "Quantitative Lipoprotein Subclass and Low Molecular Weight Metabolite Analysis in Human Serum and Plasma by (1)H NMR Spectroscopy in a Multilaboratory Trial",
"author": "Jimenez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11962",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9020354",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Fuertes-Martin, R., Correig, X., Vallve, J.C., and Amigo, N. (2020). Title: Human Serum/Plasma Glycoprotein Analysis by (1)H-NMR, an Emerging Method of Inflammatory Assessment. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-021-01130-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Kumpitsch, C., Fischmeister, F.P.S., Mahnert, A., Lackner, S., Wilding, M., Sturm, C., Springer, A., Madl, T., Holasek, S., and Hogenauer, C. (2021). Reduced B12 uptake and increased gastrointestinal formate are associated with archaeome-mediated breath methane emission in humans. Microbiome, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ac051632c",
"article-title": "Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in 1H NMR metabonomics",
"author": "Dieterle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4281",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/003655102760145852",
"article-title": "Characterization of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for soluble CD163",
"author": "Moller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2013-0451",
"article-title": "A soluble form of the macrophage-related mannose receptor (MR/CD206) is present in human serum and elevated in critical illness",
"author": "Rafique",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chem. Lab. Med.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-021-03528-8",
"article-title": "Immune complex-induced apoptosis and concurrent immune complex clearance are anti-inflammatory neutrophil functions",
"author": "Karmakar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.735",
"article-title": "Serum bile acids in liver cirrhosis promote neutrophil dysfunction",
"author": "Balazs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e735",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J. Chronic Dis.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.01.014",
"article-title": "Prevalence of post-acute COVID-19 syndrome symptoms at different follow-up periods: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Alkodaymi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard (2023, April 22). World Health Organisation. Available online: https://covid19.who.int."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2023.1159629",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Pi, J., Zhang, G., and Zeng, G. (2023). Editorial: Gut-lung interaction axis. Front. Microbiol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2021.1994875",
"article-title": "Intermodulation of gut-lung axis microbiome and the implications of biotics to combat COVID-19",
"author": "Sekar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14262",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.635471",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "de Oliveira, G.L.V., Oliveira, C.N.S., Pinzan, C.F., de Salis, L.V.V., and Cardoso, C.R.B. (2021). Microbiota Modulation of the Gut-Lung Axis in COVID-19. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Yeoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "698",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324090",
"article-title": "Six-month follow-up of gut microbiota richness in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11684-022-0921-6",
"article-title": "Integrated analysis of gut microbiome and host immune responses in COVID-19",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2022.2143476",
"article-title": "Gut microbiome and anti-viral immunity in COVID-19",
"author": "Rossini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4587",
"journal-title": "Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gendis.2023.03.034",
"article-title": "Microbiome and intestinal pathophysiology in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100978",
"journal-title": "Genes. Dis.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-328319",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and gut dysbiosis linger beyond 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 clearance",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1230",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092728",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_45",
"unstructured": "Blesl, A., Jungst, C., Lammert, F., Fauler, G., Rainer, F., Leber, B., Feldbacher, N., Stromberger, S., Wildburger, R., and Spindelbock, W. (2020). Secondary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Critically Ill Patients Alters the Gut-Liver Axis: A Case Control Study. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2021.100340",
"article-title": "Does higher body mass index increase COVID-19 severity? A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chowdhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100340",
"journal-title": "Obes. Med.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.03647-20",
"article-title": "Comorbidities in SARS-CoV-2 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Ng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e03647-20",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0504978102",
"article-title": "Obesity alters gut microbial ecology",
"author": "Ley",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11070",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2010217118",
"article-title": "The hygiene hypothesis, the COVID pandemic, and consequences for the human microbiome",
"author": "Finlay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2010217118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.779064",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_50",
"unstructured": "Giron, L.B., Dweep, H., Yin, X., Wang, H., Damra, M., Goldman, A.R., Gorman, N., Palmer, C.S., Tang, H.Y., and Shaikh, M.W. (2021). Plasma Markers of Disrupted Gut Permeability in Severe COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10875-023-01459-x",
"article-title": "Neutrophil Activation and Immune Thrombosis Profiles Persist in Convalescent COVID-19",
"author": "Hocini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "882",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab437",
"article-title": "Increased Peripheral Blood Neutrophil Activation Phenotypes and Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Patients: A Case Series and Review of the Literature",
"author": "Moshensky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.009",
"article-title": "Immunopathology of Hyperinflammation in COVID-19",
"author": "Gustine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/crj.13616",
"article-title": "Soluble CD206 levels correlate with disease deterioration and predict prognosis of anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis related interstitial lung disease",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Clin. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/oxfimm/iqaa007",
"article-title": "T cell phenotypes in COVID-19—A living review",
"author": "Hanna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "iqaa007",
"journal-title": "Oxf. Open Immunol.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.821818",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Prietl, B., Odler, B., Kirsch, A.H., Artinger, K., Eigner, M., Schmaldienst, S., Pfeifer, V., Stanzer, S., Eberl, A., and Raml, R. (2022). Chronic Inflammation Might Protect Hemodialysis Patients From Severe COVID-19. Front. Immunol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-023-01724-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Yin, K., Peluso, M.J., Thomas, R., Shin, M.G., Neidleman, J., Luo, X., Hoh, R., Anglin, K., Huang, B., and Argueta, U. (2024). Long COVID manifests with T cell dysregulation, inflammation, and an uncoordinated adaptive immune response to SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-020-05741-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Wen, X.S., Jiang, D., Gao, L., Zhou, J.Z., Xiao, J., Cheng, X.C., He, B., Chen, Y., Lei, P., and Tan, X.W. (2021). Clinical characteristics and predictive value of lower CD4(+)T cell level in patients with moderate and severe COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective study. BMC Infect. Dis., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.014",
"article-title": "Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "881",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24482-1",
"article-title": "The trans-omics landscape of COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4543",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo11010044",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_61",
"unstructured": "Pang, Z., Zhou, G., Chong, J., and Xia, J. (2021). Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of COVID-19 Global Metabolomics Datasets. Metabolites, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010443",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_62",
"unstructured": "Ghini, V., Meoni, G., Pelagatti, L., Celli, T., Veneziani, F., Petrucci, F., Vannucchi, V., Bertini, L., Luchinat, C., and Landini, G. (2022). Profiling metabolites and lipoproteins in COMETA, an Italian cohort of COVID-19 patients. PLoS Pathog., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2023.1100486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Lopez-Hernandez, Y., Oropeza-Valdez, J.J., Garcia Lopez, D.A., Borrego, J.C., Murgu, M., Valdez, J., Lopez, J.A., and Monarrez-Espino, J. (2023). Untargeted analysis in post-COVID-19 patients reveals dysregulated lipid pathways two years after recovery. Front. Mol. Biosci., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.1c05389",
"article-title": "Exploration of Human Serum Lipoprotein Supramolecular Phospholipids Using Statistical Heterospectroscopy in n-Dimensions (SHY-n): Identification of Potential Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers Related to SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Masuda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4426",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04952",
"article-title": "Diffusion and Relaxation Edited Proton NMR Spectroscopy of Plasma Reveals a High-Fidelity Supramolecular Biomarker Signature of SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Lodge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3976",
"journal-title": "Anal. Chem.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.003",
"article-title": "Molecular pathogenesis of secondary bacterial infection associated to viral infections including SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Manna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public. Health",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aninu.2021.09.012",
"article-title": "The interaction among gut microbes, the intestinal barrier and short chain fatty acids",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "Anim. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2653",
"article-title": "Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease",
"author": "Turner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.716299",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_69",
"unstructured": "Khan, I., Bai, Y., Zha, L., Ullah, N., Ullah, H., Shah, S.R.H., Sun, H., and Zhang, C. (2021). Mechanism of the Gut Microbiota Colonization Resistance and Enteric Pathogen Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.044",
"article-title": "The Human Gut Microbiome: From Association to Modulation",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1198",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm12081292",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_71",
"unstructured": "Wahab, S., Almaghaslah, D., Mahmood, S.E., Ahmad, M.F., Alsayegh, A.A., Abu Haddash, Y.M., Rahman, M.A., Ahamd, I., Ahmad, W., and Khalid, M. (2022). Pharmacological Efficacy of Probiotics in Respiratory Viral Infections: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pers. Med., 12."
},
{
"article-title": "Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Lactobacillus plantarum improve diabetic wound healing through modulating inflammatory factors",
"author": "Mohtashami",
"first-page": "1421",
"journal-title": "Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v26.i43.6782",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus bulgaricus inhibits colitis-associated cancer via a negative regulation of intestinal inflammation in azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate model",
"author": "Silveira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6782",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/toxins11010017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_74",
"unstructured": "Chen, Y., Li, R., Chang, Q., Dong, Z., Yang, H., and Xu, C. (2019). Lactobacillus bulgaricus or Lactobacillus rhamnosus Suppresses NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway and Protects against AFB(1)-Induced Hepatitis: A Novel Potential Preventive Strategy for Aflatoxicosis?. Toxins, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3168/jds.2012-6514",
"article-title": "Oral administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subspecies bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 suppresses inflammation by decreasing interleukin-6 responses in a murine model of atopic dermatitis",
"author": "Kano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3525",
"journal-title": "J. Dairy Sci.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ibd.21834",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory properties of dairy lactobacilli",
"author": "Lakhdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Bowel Dis.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms9010107",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "Barroso, F.A.L., de Jesus, L.C.L., de Castro, C.P., Batista, V.L., Ferreira, E., Fernandes, R.S., de Barros, A.L.B., Leclerq, S.Y., Azevedo, V., and Mancha-Agresti, P. (2021). Intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii (pExu:hsp65) Prevents the Inflammation and the Disorganization of the Intestinal Mucosa in a Mouse Model of Mucositis. Microorganisms, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4780",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus rhamnosus attenuates intestinal inflammation induced by Fusobacterium nucleatum infection by restoring the autophagic flux",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2016.07.001",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus rhamnosus induced epithelial cell apoptosis, ameliorates inflammation and prevents colon cancer development in an animal model",
"author": "Gamallat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "536",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.009662-0",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of Lactobacillus casei subsp. rhamnosus on Salmonella lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and epithelial barrier dysfunction in a co-culture model using Caco-2/peripheral blood mononuclear cells",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "573",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.005",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effect of multistrain probiotic formulation (L. rhamnosus, B. lactis, and B. longum)",
"author": "Sichetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2014.00201",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_82",
"unstructured": "Kitazawa, H., and Villena, J. (2014). Modulation of Respiratory TLR3-Anti-Viral Response by Probiotic Microorganisms: Lessons Learned from Lactobacillus rhamnosus CRL1505. Front. Immunol., 5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2172-13-53",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_83",
"unstructured": "Villena, J., Chiba, E., Tomosada, Y., Salva, S., Marranzino, G., Kitazawa, H., and Alvarez, S. (2012). Orally administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus modulates the respiratory immune response triggered by the viral pathogen-associated molecular pattern poly(I:C). BMC Immunol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.30975",
"article-title": "Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Prevents Liver Fibrosis Through Inhibiting Hepatic Bile Acid Synthesis and Enhancing Bile Acid Excretion in Mice",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2050",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The potential therapeutic role of Lactobacillus reuteri for treatment of inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Transl. Res.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0231865",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_86",
"unstructured": "Li, L., Fang, Z., Liu, X., Hu, W., Lu, W., Lee, Y.K., Zhao, J., Zhang, H., and Chen, W. (2020). Lactobacillus reuteri attenuated allergic inflammation induced by HDM in the mouse and modulated gut microbes. PLoS ONE, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mbo3.371",
"article-title": "FolC2-mediated folate metabolism contributes to suppression of inflammation by probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri",
"author": "Thomas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "802",
"journal-title": "Microbiologyopen",
"key": "ref_87",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01358-15",
"article-title": "Histamine H2 Receptor-Mediated Suppression of Intestinal Inflammation by Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01358-15",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpgi.00124.2010",
"article-title": "Human-derived probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri strains differentially reduce intestinal inflammation",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "G1087",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "299",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ccd.ccd_53_18",
"article-title": "The Anti-inflammatory Effects of Glycerol-supplemented Probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri on Infected Epithelial cells In vitro",
"author": "Widyarman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "298",
"journal-title": "Contemp. Clin. Dent.",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13568-020-01038-y",
"article-title": "Probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis V9 attenuates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "AMB Express",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v17.i4.459",
"article-title": "Bifidobacterium lactis attenuates onset of inflammation in a murine model of colitis",
"author": "Philippe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1011737107",
"article-title": "Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis fermented milk product reduces inflammation by altering a niche for colitogenic microbes",
"author": "Veiga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18132",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_93",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114518001861",
"article-title": "Effect of Bifidobacterium lactis HN019 on inflammatory markers and oxidative stress in subjects with and without the metabolic syndrome",
"author": "Bernini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "645",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11050969",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_95",
"unstructured": "Li, S.C., Hsu, W.F., Chang, J.S., and Shih, C.K. (2019). Combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Shows a Stronger Anti-Inflammatory Effect than Individual Strains in HT-29 Cells. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2021.12.020",
"article-title": "Fatigue and cognitive impairment in Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Ceban",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "ref_96",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors influencing medium- and long-term occupational impact following COVID-19",
"author": "Houston",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Occup. Med.",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03532-0",
"article-title": "Reconstruction of ancient microbial genomes from the human gut",
"author": "Wibowo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "234",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "594",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13021",
"article-title": "The role of the microbiota in sedentary lifestyle disorders and ageing: Lessons from the animal kingdom",
"author": "Shiels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0139795",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_100",
"unstructured": "Shimizu, M., Hashiguchi, M., Shiga, T., Tamura, H.O., and Mochizuki, M. (2015). Meta-Analysis: Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Lipid Profiles in Normal to Mildly Hypercholesterolemic Individuals. PLoS ONE, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.562048",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_101",
"unstructured": "Aponte, M., Murru, N., and Shoukat, M. (2020). Therapeutic, Prophylactic, and Functional Use of Probiotics: A Current Perspective. Front. Microbiol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-018-0337-x",
"article-title": "The neuroactive potential of the human gut microbiota in quality of life and depression",
"author": "Falony",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "623",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_102",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.01486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_103",
"unstructured": "Parada Venegas, D., De la Fuente, M.K., Landskron, G., Gonzalez, M.J., Quera, R., Dijkstra, G., Harmsen, H.J.M., Faber, K.N., and Hermoso, M.A. (2019). Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs)-Mediated Gut Epithelial and Immune Regulation and Its Relevance for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Immunol., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.612826",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_104",
"unstructured": "Hanus, M., Parada-Venegas, D., Landskron, G., Wielandt, A.M., Hurtado, C., Alvarez, K., Hermoso, M.A., Lopez-Kostner, F., and De la Fuente, M. (2021). Immune System, Microbiota, and Microbial Metabolites: The Unresolved Triad in Colorectal Cancer Microenvironment. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro3344",
"article-title": "The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer",
"author": "Louis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "661",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_105",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nn.4030",
"article-title": "Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS",
"author": "Erny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "965",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_106",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10132903",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_107",
"unstructured": "Chen, J., and Vitetta, L. (2021). Modulation of Gut Microbiota for the Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-13825-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_108",
"unstructured": "Veenith, T., Martin, H., Le Breuilly, M., Whitehouse, T., Gao-Smith, F., Duggal, N., Lord, J.M., Mian, R., Sarphie, D., and Moss, P. (2022). High generation of reactive oxygen species from neutrophils in patients with severe COVID-19. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0407-1",
"article-title": "Tissue damage from neutrophil-induced oxidative stress in COVID-19",
"author": "Laforge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_109",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-017-01728-5",
"article-title": "Unique phenotypes and clonal expansions of human CD4 effector memory T cells re-expressing CD45RA",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_110",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 110,
"references-count": 110,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/22/3840"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Alteration of the Gut–Lung Axis After Severe COVID-19 Infection and Modulation Through Probiotics: A Randomized, Controlled Pilot Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}