Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial
et al., The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4, RECOVERY, NCT04381936, Oct 2020
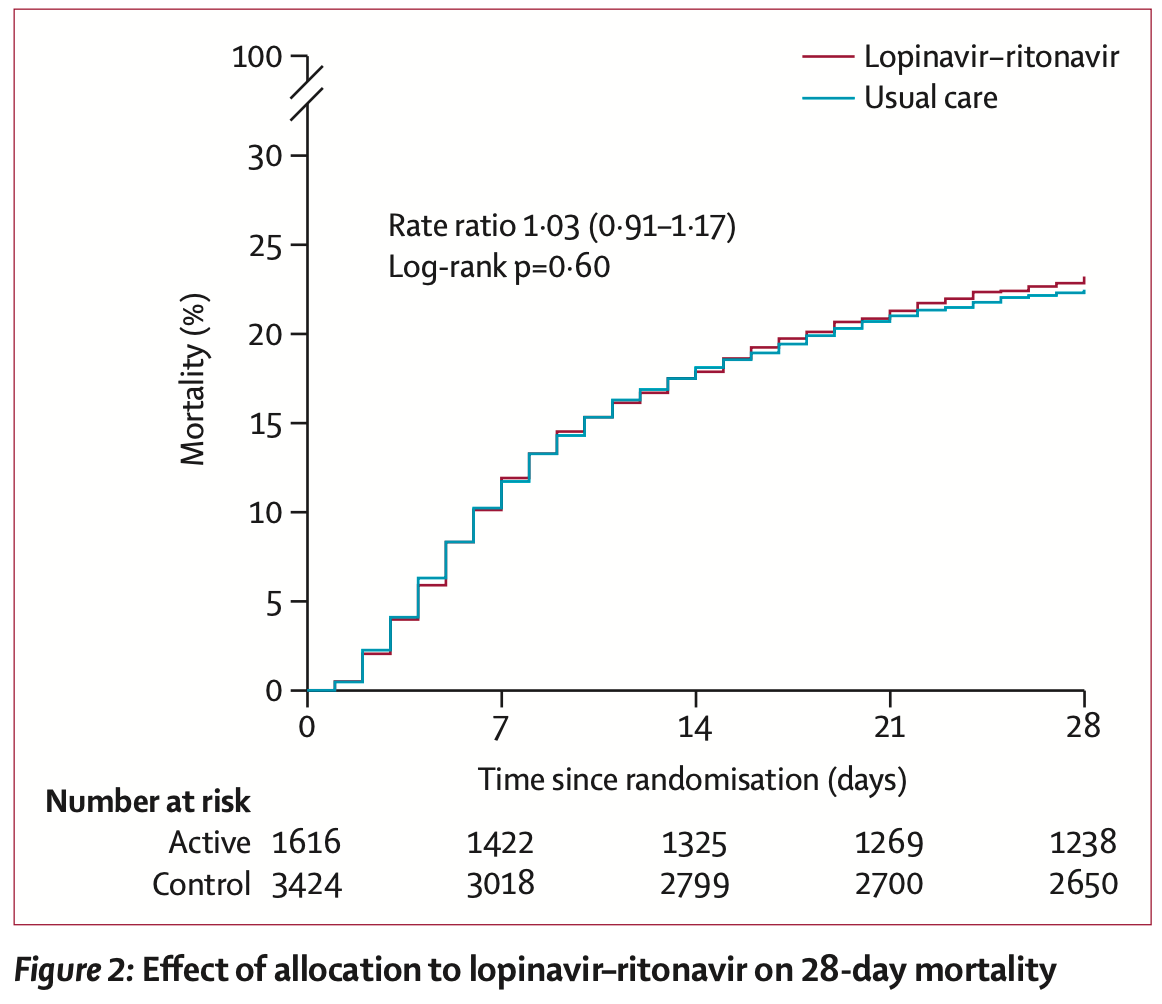
RCT 1,616 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant differences with lopinavir-ritonavir treatment compared to usual care. 6-month results are from Horby et al.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the United Kingdom, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments2.
The United Kingdom focused on expensive high-profit treatments, approving only one low-cost early treatment, which required a prescription and had limited adoption. The high-cost prescription treatment strategy reduces the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminates complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
risk of death, 7.0% higher, RR 1.07, p = 0.24, treatment 451 of 1,616 (27.9%), control 932 of 3,424 (27.2%), day 180.
|
|
risk of death, 3.0% higher, RR 1.03, p = 0.60, treatment 374 of 1,616 (23.1%), control 767 of 3,424 (22.4%), day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 15.0% higher, RR 1.15, p = 0.15, treatment 152 of 1,556 (9.8%), control 279 of 3,280 (8.5%), day 28.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 2.0% higher, RR 1.02, p = 0.53, treatment 1,616, control 3,424, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Horby et al., 31 Oct 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, United Kingdom, peer-reviewed, mean age 66.2, 26 authors, study period 19 March, 2020 - 29 June, 2020, trial NCT04381936 (history) (RECOVERY).
Contact: recoverytrial@ndph.ox.ac.uk.
Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial
The Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32013-4
Background Lopinavir-ritonavir has been proposed as a treatment for COVID-19 on the basis of in vitro activity, preclinical studies, and observational studies. Here, we report the results of a randomised trial to assess whether lopinavir-ritonavir improves outcomes in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19.
Methods In this randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, a range of possible treatments was compared with usual care in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19. The trial is underway at 176 hospitals in the UK. Eligible and consenting patients were randomly allocated to either usual standard of care alone or usual standard of care plus lopinavir-ritonavir (400 mg and 100 mg, respectively) by mouth for 10 days or until discharge (or one of the other RECOVERY treatment groups: hydroxychloroquine, dexamethasone, or azithromycin) using web-based simple (unstratified) randomisation with allocation concealment. Randomisation to usual care was twice that of any of the active treatment groups (eg, 2:1 in favour of usual care if the patient was eligible for only one active group, 2:1:1 if the patient was eligible for two active groups). The primary outcome was 28-day all-cause mortality. Analyses were done on an intention-to-treat basis in all randomly assigned participants. The trial is registered with ISRCTN, 50189673, and ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04381936. Findings Between March 19, 2020, and June 29, 2020, 1616 patients were randomly allocated to receive lopinavirritonavir and 3424 patients to receive usual care. Overall, 374 (23%) patients allocated to lopinavir-ritonavir and 767 (22%) patients allocated to usual care died within 28 days (rate ratio 1•03, 95% CI 0•91-1•17; p=0•60). Results were consistent across all prespecified subgroups of patients. We observed no significant difference in time until discharge alive from hospital (median 11 days [IQR 5 to >28] in both groups) or the proportion of patients discharged from hospital alive within 28 days (rate ratio 0•98, 95% CI 0•91-1•05; p=0•53). Among patients not on invasive mechanical ventilation at baseline, there was no significant difference in the proportion who met the composite endpoint of invasive mechanical ventilation or death (risk ratio 1•09, 95% CI 0•99-1•20; p=0•092). Interpretation In patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19, lopinavir-ritonavir was not associated with reductions in 28-day mortality, duration of hospital stay, or risk of progressing to invasive mechanical ventilation or death. These findings do not support the use of lopinavir-ritonavir for treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19.
References
Arshad, Pertinez, Box, Prioritization of anti-SARS-Cov-2 drug repurposing opportunities based on plasma and target site concentrations derived from their established human pharmacokinetics, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.1909
Baldelli, Corbellino, Clementi, Cattaneo, Gervasoni, Lopinavir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients: maybe yes, but at what dose?, J Antimicrob Chemother
Best, Capparelli, Diep, Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ritonavir crushed versus whole tablets in children, J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cattaneo, Cattaneo, Gervasoni, Does lopinavir really inhibit SARS-CoV-2?, Pharmacol Res
Chan, Yao, Yeung, Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-β1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset, J Infect Dis
Chen, Chan, Jiang, In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds, J Clin Virol
Choy, Wong, Kaewpreedee, Remdesivir, lopinavir, emetine, and homoharringtonine inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro, Antiviral Res
Chu, Cheng, Hung, Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings, Thorax
Dagens, Sigfrid, Cai, Scope, quality, and inclusivity of clinical guidelines produced early in the covid-19 pandemic: rapid review, BMJ
De Wilde, Jochmans, Posthuma, Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ
Gregoire, Turnier, Gaborit, Lopinavir pharmacokinetics in COVID-19 patients, J Antimicrob Chemother
Havlichek, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19-preliminary report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Horby, Mafham, Linsell, Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: preliminary results from a multi-centre, randomized, controlled trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.15.20151852(preprint).21EMC.Kaletra200mg/50mgfilm-coatedtablets
Lecronier, Beurton, Burrel, Comparison of hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir, and standard of care in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: an opportunistic retrospective analysis, Crit Care
Liu, Wang, Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically approved medicines, J Genet Genomics
Lê, Jaquet, Patrier, Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ ritonavir oral solution to treat COVID-19 in mechanically ventilated ICU patients, J Antimicrob Chemother
Marzolini, Stader, Stoeckle, Effect of systemic inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2 on lopinavir and hydroxychloroquine plasma concentrations, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Nukoolkarn, Lee, Malaisree, Aruksakulwong, Hannongbua, Molecular dynamic simulations analysis of ritonavir and lopinavir as SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibitors, J Theor Biol
Osborne, Davies, Lane, Lopinavir-ritonavir in the treatment of COVID-19: a dynamic systematic benefit-risk assessment, Drug Saf
Park, Yu, Kim, Antiviral efficacies of FDA-approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets, MBio
Schoergenhofer, Jilma, Stimpfl, Karolyi, Zoufaly, Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir and ritonavir in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M20-1550
Sheahan, Sims, Leist, Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV, Nat Commun
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis, Lancet Infect Dis
Who, Solidarity" clinical trial for COVID-19 treatments
Yan, Liu, Zhu, Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding and impact of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment in hospitalised non-critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur Respir J
Ye, Luo, Xia, Clinical efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)32013-4",
"ISSN": [
"0140-6736"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4",
"alternative-id": [
"S0140673620320134"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32078-X"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Horby",
"given": "Peter W",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mafham",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "Jennifer L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Linsell",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Staplin",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Emberson",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palfreeman",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Raw",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elmahi",
"given": "Einas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prudon",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carley",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chadwick",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wise",
"given": "Matthew P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baillie",
"given": "J Kenneth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chappell",
"given": "Lucy C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faust",
"given": "Saul N",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaki",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jefferey",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Wei Shen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Montgomery",
"given": "Alan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juszczak",
"given": "Edmund",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haynes",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Landray",
"given": "Martin J",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"thelancet.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-05T22:31:41Z",
"timestamp": 1601937101000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-23T10:43:18Z",
"timestamp": 1603449798000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-14T00:35:43Z",
"timestamp": 1726274143535
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 507,
"issue": "10259",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10259",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601337600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673620320134?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0140673620320134?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1345-1352",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"article-title": "Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis",
"author": "Verity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "669",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib1",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Docherty",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib2",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Scope, quality, and inclusivity of clinical guidelines produced early in the covid-19 pandemic: rapid review",
"author": "Dagens",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib3",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtbi.2008.07.030",
"article-title": "Molecular dynamic simulations analysis of ritonavir and lopinavir as SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibitors",
"author": "Nukoolkarn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "J Theor Biol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib4",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgg.2020.02.001",
"article-title": "Potential inhibitors against 2019-nCoV coronavirus M protease from clinically approved medicines",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J Genet Genomics",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib5",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.003",
"article-title": "In vitro susceptibility of 10 clinical isolates of SARS coronavirus to selected antiviral compounds",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib6",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.03011-14",
"article-title": "Screening of an FDA-approved compound library identifies four small-molecule inhibitors of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication in cell culture",
"author": "de Wilde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4875",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib7",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-13940-6",
"article-title": "Comparative therapeutic efficacy of remdesivir and combination lopinavir, ritonavir, and interferon beta against MERS-CoV",
"author": "Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104786",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, lopinavir, emetine, and homoharringtonine inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in vitro",
"author": "Choy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib9",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiv392",
"article-title": "Treatment with lopinavir/ritonavir or interferon-β1b improves outcome of MERS-CoV infection in a nonhuman primate model of common marmoset",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1904",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib10",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01114-20",
"article-title": "Antiviral efficacies of FDA-approved drugs against SARS-CoV-2 infection in ferrets",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01114",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib11",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thorax.2003.012658",
"article-title": "Role of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of SARS: initial virological and clinical findings",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib12",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00799-2020",
"article-title": "Factors associated with prolonged viral shedding and impact of lopinavir/ritonavir treatment in hospitalised non-critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib13",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical efficacy of lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Ye",
"first-page": "3390",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib14",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03117-9",
"article-title": "Comparison of hydroxychloroquine, lopinavir/ritonavir, and standard of care in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: an opportunistic retrospective analysis",
"author": "Lecronier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib15",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40264-020-00966-9",
"article-title": "Lopinavir–ritonavir in the treatment of COVID-19: a dynamic systematic benefit–risk assessment",
"author": "Osborne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "809",
"journal-title": "Drug Saf",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib16",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib17",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2008043",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in Covid-19",
"author": "Havlichek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e68",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib18",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19—preliminary report",
"author": "Horby",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: preliminary results from a multi-centre, randomized, controlled trial",
"author": "Horby",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104898",
"article-title": "Does lopinavir really inhibit SARS-CoV-2?",
"author": "Cattaneo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib22",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1909",
"article-title": "Prioritization of anti-SARS-Cov-2 drug repurposing opportunities based on plasma and target site concentrations derived from their established human pharmacokinetics",
"author": "Arshad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-1550",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir and ritonavir in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Schoergenhofer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa195",
"article-title": "Lopinavir pharmacokinetics in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Gregoire",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2702",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib25",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa190",
"article-title": "Lopinavir/ritonavir in COVID-19 patients: maybe yes, but at what dose?",
"author": "Baldelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2704",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib26",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01177-20",
"article-title": "Effect of systemic inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2 on lopinavir and hydroxychloroquine plasma concentrations",
"author": "Marzolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01177",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib27",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAI.0b013e318232b057",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ritonavir crushed versus whole tablets in children",
"author": "Best",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib28",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkaa261",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetics of lopinavir/ritonavir oral solution to treat COVID-19 in mechanically ventilated ICU patients",
"author": "Lê",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2657",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4_bib29",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140673620320134"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Lopinavir–ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "396"
}