COVID-19 and heme oxygenase: novel insight into the disease and potential therapies
, P., Cell Stress and Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9, Jun 2020
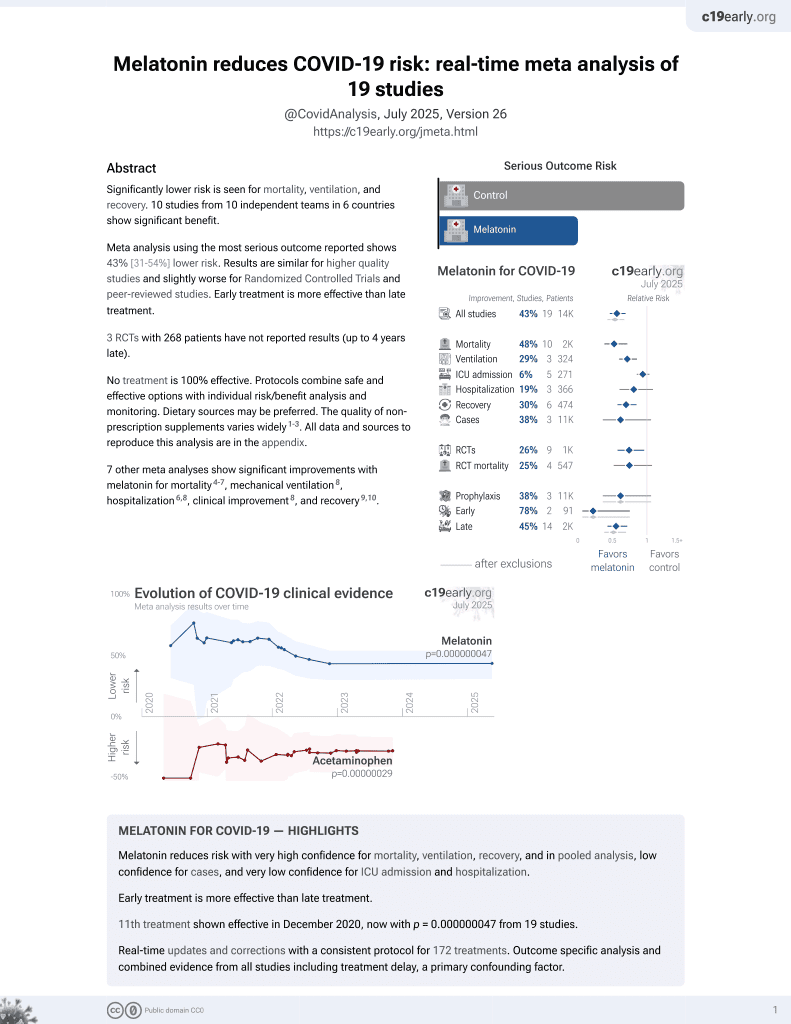
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Proposal that COVID-19 risk is related to low intracellular heme oxygenase (HO-1), and that therapies that raise HO-1 may be beneficial, which includes fluvoxamine, certain anesthetics (sevoflurane or isoflurane), hemin, estrogen, statins, curcumin, resveratrol, and melatonin. Authors note that cigarette smoke is associated with increased HO-1 in lung fibroblasts and vascular endothelial cells, which may help explain the lower risk for smokers seen in several studies.
Hooper et al., 4 Jun 2020, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
COVID-19 and heme oxygenase: novel insight into the disease and potential therapies
Cell Stress and Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9
The COVID-19 pandemic needs therapies that are presently available and safe. We propose that subjects with metabolic syndrome, old age, and male gender have the greatest morbidity and mortality and have low stress proteins, in particular, low intracellular heme oxygenase (HO-1), making them particularly vulnerable to the disease. Additionally, COVID-19's heme reduction may contribute to even lower HO-1. Low-grade inflammation associated with these risk factors contributes to triggering a cytokine storm that spreads to multi-organ failure and near death. The high mortality of those treated with ventilator assistance may partially be explained by ventilator-induced inflammation. The cytoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties of HO-1 can limit the infection's damage. A paradox of COVID-19 hospital admissions data suggests that fewer cigarettesmokers are admitted compared with non-smokers in the general population. This unexpected observation may result from smoke induction of HO-1. Therapies with anti-viral properties that raise HO-1 include certain anesthetics (sevoflurane or isoflurane), hemin, estrogen, statins, curcumin, resveratrol, and melatonin. Controlled trials of these HO-1 inducers should be done in order to prevent or treat COVID-19 disease.
References
Abouhashem, Singh, Azzazy, Sen, Is low alveolar type II cell SOD3 in the lungs of elderly linked to the observed severity of COVID-19?, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2020.8111
Aggarwal, Gupta, Sung, Curcumin: an orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers, doi:10.1111/bph.12131
Anderson, Reiter, Melatonin: roles in influenza, Covid-19, and other viral infections, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2109
Baglole, Sime, Phipps, Cigarette smoke-induced expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human lung fibroblasts is regulated by intracellular glutathione, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.90215.2008
Belperio, Keane, Lynch, Strieter, Ali et al., The role of cytokines during the pathogenesis of ventilatorassociated and ventilator-induced, Lung Injury, doi:10.1055/s-2006-948289
Bloomer, Zhang, Brown, Kregel, Differential regulation of hepatic heme oxygenase-1 protein with aging and heat stress, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/gln056
Brioni, Varughese, Ahmed, Bein, A clinical review of inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane: from early research to emerging topics, J Anesth, doi:10.1007/s00540-017-2375-6
Chen, Wang, Xie, Chen, Zhu et al., Heme oxygenase-1 reduces sepsis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and acute, Lung Injury, doi:10.1155/2018/9413876
De Maio, Hightower, COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT): what is the link?, Cell Stress Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-020-01121-0
El Kalamouni, Frumence, Bos, Turpin, Nativel et al., Subversion of the heme oxygenase-1 antiviral activity by zika virus, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11010002
El-Hawary, Ss, Ali, Younis, Hepatoprotective potential of standardized Ficus species in intrahepatic cholestasis rat model: involvement of nuclear factor-κB, and Farnesoid X receptor signaling pathways, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.026
Espinoza, León, Céspedes, Gómez, Canedo-Marroquín et al., Heme oxygenase-1 modulates human respiratory syncytial virus replication and lung pathogenesis during infection, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1601414
Fedson, Jacobson, Rordam, Opal, Treating the host response to ebola virus disease with generic statins and angiotensin receptor blockers, mBIO, doi:10.1128/mBio.00716-15
Fujioka, Kalish, Zhao, Lu, Wong et al., Induction of heme oxygenase-1 attenuates the severity of sepsis in a non-surgical preterm mouse model, Shock, doi:10.1097/SHK.0000000000000689
Geier, Da ; Godman, Chheda, Hightower, Perdrizet et al., Hyperbaric oxygen induces a cytoprotective and angiogenic response in human microvascular endothelial cells, Cell Stress Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-009-0159-0
Hooper, Balogh, Rivas, Kavanagh, Vigh, The importance of the cellular stress response in the pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes, Cell Stress and Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-014-0493-8
Hooper, Hightower, Hooper, Loss of stress response as a consequence of viral infection: implications for disease and therapy, Cell Stress Chaperones, doi:10.1007/s12192-012-0352-4
Hooper, Hooper, Loss of defense against stress: diabetes and heat shock proteins, Diabetes Technol Ther, doi:10.1089/dia.2005.7.204
Hornuss, Firsching, Dolch, Martignoni, Peraud et al., Long-term isoflurane therapy for refractory bronchospasm associated with herpes simplex pneumonia in a heart transplant patient, Case Rep Med, doi:10.1155/2010/746263
Hsieh, Chen, Schmitz, King, Chen et al., Candidate genes associated with susceptibility for SARScoronavirus, doi:10.1007/s11538-009-9440-8
Hsu, Yeh, Chen, Kuo, Lin et al., Role of Akt/HO-1 pathway in estrogen-mediated attenuation of trauma-hemorrhage-induced lung injury, J Surg Res, doi:10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.926
Huang, Falgout, Takeda, Yamada, Dhawan, Nrf2-dependent induction of innate host defense via heme oxygenase-1 inhibits Zika virus replication, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2016.12.019
Kapetanovic, Muzzio, Huang, Thompson, Mccormick, Pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, and metabolic profile of resveratrol and its dimethylether analog, pterostilbene, in rats, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s00280-010-1525-4
Knowlton, Korzick, Estrogen and the female heart, Mol Cell Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.mce.2014.01.002
Laffont, Rouquié, Azar, Seillet, Plumas et al., None, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1303400
Lee, Chang, Zhu, Simvastatin induces heme oxygenase-1 a novel mechanism of vessel protection, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000140694.67251.9C
Lindenfeld, Ghali, Krause-Steinrauf, Khan, Adams et al., Hormone replacement therapy is associated with improved survival in women with advanced heart failure, J Am Coll Cardiol, doi:10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00938-0
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Moghadamtousi, Kadir, Hassandarvish, Tajik, Abubakar et al., A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/186864
Nacoti, Colombo, Fochi, Bonacina, Fazzi et al., series of infants with severe bronchiolitis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, doi:10.1002/ccr3.1490
Patriarca, Furfaro, Cosso, Maineri, Balbis et al., Heme oxygenase 1 expression in rat liver during ageing and ethanol intoxication, Biogerontology, doi:10.1007/s10522-006-9079-x
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Schmidt, Cobalt protoporphyrin as a potential therapeutic agent? 79106, doi:10.1096/fj.07-0904ltr
Shi, Lei, Tang, Wang, Xia, Melatonin attenuates acute kidney ischemia / reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by activation of the SIRT1 / Nrf2 / HO-1 signaling pathway
Suba, Prevention and therapy of COVID-19 via exogenous estrogen treatment for both male and female patients; an opinion paper
Takeda, Sasai, Adachi, Ohnishi, Fujisawa et al., Potential role of heme metabolism in the inducible expression of heme oxygenase-1, Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.03.018
Wenzhong, Li, COVID-19: attacks the 1-beta chain of hemoglobin and captures the porphyrin to inhibit human heme metabolism, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.11938173.v8
Yang, Li, Wu, Liu, Ni et al., Anti-oxidant effect of heme oxygenase-1 on cigarette smokeinduced vascular injury, Mol Med Rep, doi:10.3892/mmr.2015.3722
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9",
"ISSN": [
"1355-8145",
"1466-1268"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9",
"alternative-id": [
"1126"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "14 May 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "22 May 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "25 May 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "4 June 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Change Date",
"name": "change_date",
"order": 5,
"value": "29 June 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Change Type",
"name": "change_type",
"order": 6,
"value": "Correction"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Change Details",
"name": "change_details",
"order": 7,
"value": "In the original publication, one of the last paragraphs should have read as follows:"
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9458-1202",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hooper",
"given": "Philip L.",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Cell Stress and Chaperones"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-04T17:03:16Z",
"timestamp": 1591290196000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-04T00:11:08Z",
"timestamp": 1622765468000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-30T19:27:41Z",
"timestamp": 1638300461625
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 24,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1355-8145"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1466-1268"
}
],
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1591228800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1591228800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12192-020-01126-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "707-710",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
4
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2020.8111",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR1",
"unstructured": "Abouhashem AS, Singh K, Azzazy HM, Sen CK (2020) Is low alveolar type II cell SOD3 in the lungs of elderly linked to the observed severity of COVID-19? Antioxid Redox Signal:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2020.8111"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.12131",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR2",
"unstructured": "Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC, Sung B (2013) Curcumin: an orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12131"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2109",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR3",
"unstructured": "Anderson G, Reiter RJ (2020) Melatonin: roles in influenza, Covid-19, and other viral infections. Rev Med Virol:e2109. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmv.2109"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.90215.2008",
"author": "CJ Baglole",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2006",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "1126_CR4",
"unstructured": "Baglole CJ, Sime PJ, Phipps RP (2008) Cigarette smoke-induced expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human lung fibroblasts is regulated by intracellular glutathione. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295(4):2006–2007. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.90215.2008",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2006-948289",
"author": "JA Belperio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "350",
"issue": "212",
"journal-title": "Lung Injury",
"key": "1126_CR5",
"unstructured": "Belperio JA, Keane MP, Lynch JP, Strieter RM, Ali THE, Lung A (2006) The role of cytokines during the pathogenesis of ventilator-associated and ventilator-induced. Lung Injury 1(212):350–364. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-948289",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/gln056",
"author": "SA Bloomer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "419",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci",
"key": "1126_CR6",
"unstructured": "Bloomer SA, Zhang HJ, Brown KE, Kregel KC (2009) Differential regulation of hepatic heme oxygenase-1 protein with aging and heat stress. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(4):419–425. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gln056",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00540-017-2375-6",
"author": "JD Brioni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "764",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Anesth",
"key": "1126_CR7",
"unstructured": "Brioni JD, Varughese S, Ahmed R, Bein B (2017) A clinical review of inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane: from early research to emerging topics. J Anesth 31(5):764–778). Springer Tokyo. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-017-2375-6",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/9413876",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR8",
"unstructured": "Chen X, Wang Y, Xie X, Chen H, Zhu Q, Ge Z, Wei H, Deng J, Xia Z, Lian Q (2018) Heme oxygenase-1 reduces sepsis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and acute. Lung Injury. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/9413876"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-020-01121-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR9",
"unstructured": "De Maio A, Hightower LE (2020) COVID-19, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), and hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT): what is the link? Cell Stress Chaperones:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-020-01121-0"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11010002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR10",
"unstructured": "El Kalamouni C, Frumence E, Bos S, Turpin J, Nativel B, Harrabi W, Wilkinson DA, Meilhac O, Gadea G, Desprès P, Krejbich-Trotot P, Viranaïcken W (2019) Subversion of the heme oxygenase-1 antiviral activity by zika virus. Viruses 11(1). https://doi.org/10.3390/v11010002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.026",
"author": "SS El-hawary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "262",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol",
"key": "1126_CR11",
"unstructured": "El-hawary SS, Ali ZY, Younis IY (2019) Hepatoprotective potential of standardized Ficus species in intrahepatic cholestasis rat model: involvement of nuclear factor-κB, and Farnesoid X receptor signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 231:262–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.11.026",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1601414",
"author": "JA Espinoza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "212",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "1126_CR12",
"unstructured": "Espinoza JA, León MA, Céspedes PF, Gómez RS, Canedo-Marroquín G, Riquelme SA, Salazar-Echegarai FJ, Blancou P, Simon T, Anegon I, Lay MK, González PA, Riedel CA, Bueno SM, Kalergis AM (2017) Heme oxygenase-1 modulates human respiratory syncytial virus replication and lung pathogenesis during infection. J Immunol 199(1):212–223. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1601414",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00716-15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR13",
"unstructured": "Fedson DS, Jacobson JR, Rordam M, Opal M (2015) Treating the host response to ebola virus disease with generic statins and angiotensin receptor blockers. mBIO 6(3):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00716-15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/SHK.0000000000000689",
"author": "K Fujioka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "242",
"journal-title": "Shock.",
"key": "1126_CR14",
"unstructured": "Fujioka K, Kalish F, Zhao H, Lu S, Wong S, Wong RJ, Stevenson DK (2017) Induction of heme oxygenase-1 attenuates the severity of sepsis in a non-surgical preterm mouse model. Shock. 47:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000689",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "1126_CR15",
"unstructured": "Geier MR, Geier DA (2020) Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID- 19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect , the company ’ s public news and information . January"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-009-0159-0",
"author": "CA Godman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "431",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperones",
"key": "1126_CR16",
"unstructured": "Godman CA, Chheda KP, Hightower LE, Perdrizet G, Shin DG, Giardina C (2010) Hyperbaric oxygen induces a cytoprotective and angiogenic response in human microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Stress Chaperones 15(4):431–442. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-009-0159-0",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-111-3-263_2",
"author": "PL Hooper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "1126_CR17",
"unstructured": "Hooper PL (1989) Toxic shock syndrome and estrogen therapy. Ann Intern Med 111(3):263–264. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-111-3-263_2",
"volume": "111",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/dia.2005.7.204",
"author": "PL Hooper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "204",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Technol Ther",
"key": "1126_CR18",
"unstructured": "Hooper PL, Hooper JJ (2005) Loss of defense against stress: diabetes and heat shock proteins. Diabetes Technol Ther 7:204–208. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2005.7.204",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-012-0352-4",
"author": "PL Hooper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperones",
"key": "1126_CR19",
"unstructured": "Hooper PL, Hightower LE, Hooper PL (2012) Loss of stress response as a consequence of viral infection: implications for disease and therapy. Cell Stress Chaperones 17:647–655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-012-0352-4",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-014-0493-8",
"author": "PL Hooper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "447",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperones",
"key": "1126_CR20",
"unstructured": "Hooper PL, Balogh G, Rivas E, Kavanagh K, Vigh L (2014) The importance of the cellular stress response in the pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes. Cell Stress Chaperones 19(4):447–464. Cell Stress and Chaperones. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-014-0493-8",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2010/746263",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR21",
"unstructured": "Hornuss C, Firsching M, Dolch M, Martignoni A, Peraud A, Briegel J (2010) Long-term isoflurane therapy for refractory bronchospasm associated with herpes simplex pneumonia in a heart transplant patient. Case Rep Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/746263"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11538-009-9440-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR22",
"unstructured": "Hsieh Y, Chen CWS, Schmitz SH, King C, Chen W, Wu Y, Ho M (2010). Candidate genes associated with susceptibility for SARS-coronavirus. 122–132. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-009-9440-8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2016.12.019",
"author": "H Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "1126_CR23",
"unstructured": "Huang H, Falgout B, Takeda K, Yamada KM, Dhawan S (2017) Nrf2-dependent induction of innate host defense via heme oxygenase-1 inhibits Zika virus replication. Virology 503:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2016.12.019",
"volume": "503",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00280-010-1525-4",
"author": "IM Kapetanovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Cancer Chemother Pharmacol",
"key": "1126_CR24",
"unstructured": "Kapetanovic IM, Muzzio M, Huang Z, Thompson TN, McCormick DL (2011) Pharmacokinetics, oral bioavailability, and metabolic profile of resveratrol and its dimethylether analog, pterostilbene, in rats. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 68:593–601. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-010-1525-4",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mce.2014.01.002",
"author": "AA Knowlton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell Endocrinol",
"key": "1126_CR25",
"unstructured": "Knowlton AA, Korzick DH (2014) Estrogen and the female heart. Mol Cell Endocrinol 389:31–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2014.01.002",
"volume": "389",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1303400",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR26",
"unstructured": "Laffont S, Rouquié N, Azar P, Seillet C, Plumas J, Aspord C, Guéry J (2020) from women. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1303400"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000140694.67251.9C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR27",
"unstructured": "Lee T, Chang C, Zhu Y (2004) Simvastatin induces heme oxygenase-1 a novel mechanism of vessel protection. Circulation 110:1296–1302. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000140694.67251.9C"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00938-0",
"author": "JA Lindenfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1238",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Cardiol",
"key": "1126_CR28",
"unstructured": "Lindenfeld JA, Ghali JK, Krause-Steinrauf HJ, Khan S, Adams K, Goldman S, Peberdy MA, Yancy C, Thaneemit-Chen S, Larsen RL, Young J, Lowes B, Rosenberg YD (2003) Hormone replacement therapy is associated with improved survival in women with advanced heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 42(7):1238–1245. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0735-1097(03)00938-0",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1126_CR29",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, Mcauley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ, Across HLH, Collaboration, S (2020) COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 395(10229):1033–1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/186864",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR30",
"unstructured": "Moghadamtousi S, Abdul Kadir H, Hassandarvish P, Tajik H, Abubakar S, Zandi K (2014) A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/186864"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ccr3.1490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR31",
"unstructured": "Nacoti M, Colombo J, Fochi O, Bonacina D, Fazzi F, Bellani G, Bonanomi E (2018) Sevoflurane improves respiratory mechanics and gas exchange in a case series of infants with severe bronchiolitis-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. https://doi.org/10.1002/ccr3.1490"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10522-006-9079-x",
"author": "S Patriarca",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "365",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biogerontology",
"key": "1126_CR32",
"unstructured": "Patriarca S, Furfaro AL, Cosso L, Pesce Maineri E, Balbis E, Domenicotti C, Nitti M, Cottalasso D, Marinari UM, Pronzato MA, Traverso N (2007) Heme oxygenase 1 expression in rat liver during ageing and ethanol intoxication. Biogerontology 8(3):365–372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-006-9079-x",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR33",
"unstructured": "Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M et al (2020) Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area. JAMA. Network. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6775"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.07-0904ltr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR34",
"unstructured": "Schmidt R (2004) Cobalt protoporphyrin as a potential therapeutic agent? 79106. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.07-0904ltr"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20181614",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1126_CR35",
"unstructured": "Shi S, Lei S, Tang C, Wang K, Xia Z (2019) Melatonin attenuates acute kidney ischemia / reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by activation of the SIRT1 / Nrf2 / HO-1 signaling pathway. 0(January):1–13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18433/jpps31069",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1126_CR36",
"unstructured": "Suba Z (2020) Prevention and therapy of COVID-19 via exogenous estrogen treatment for both male and female patients; an opinion paper. 75–85"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.03.018",
"author": "TA Takeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj",
"key": "1126_CR37",
"unstructured": "Takeda TA, Sasai M, Adachi Y, Ohnishi K, Fujisawa JI, Izawa S, Taketani S (2017) Potential role of heme metabolism in the inducible expression of heme oxygenase-1. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1861(7):1813–1824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.03.018",
"volume": "1861",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.926",
"author": "J Te Hsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "319",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Surg Res",
"key": "1126_CR38",
"unstructured": "Te Hsu J, Yeh HC, Chen TH, Kuo CJ, Lin CJ, Chiang KC, Yeh TS, Hwang TL, Chaudry II (2013) Role of Akt/HO-1 pathway in estrogen-mediated attenuation of trauma-hemorrhage-induced lung injury. J Surg Res 182(2):319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.10.926",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.26434/chemrxiv.11938173.v8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1126_CR39",
"unstructured": "Wenzhong L, Li H (2020) COVID-19: attacks the 1-beta chain of hemoglobin and captures the porphyrin to inhibit human heme metabolism. 1. https://doi.org/10.26434/chemrxiv.11938173.v8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2015.3722",
"author": "G Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2481",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "1126_CR40",
"unstructured": "Yang G, Li Y, Wu W, Liu B, Ni L, Wang Z, Miao S, Wang L, Liu C (2015) Anti-oxidant effect of heme oxygenase-1 on cigarette smoke-induced vascular injury. Mol Med Rep 12(2):2481–2486. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3722",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Cell Stress and Chaperones"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"COVID-19 and heme oxygenase: novel insight into the disease and potential therapies"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "25"
}
hooper