Getting in on the action: New tools to see SARS-CoV-2 infect a cell
et al., Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010, Mar 2023
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 423 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
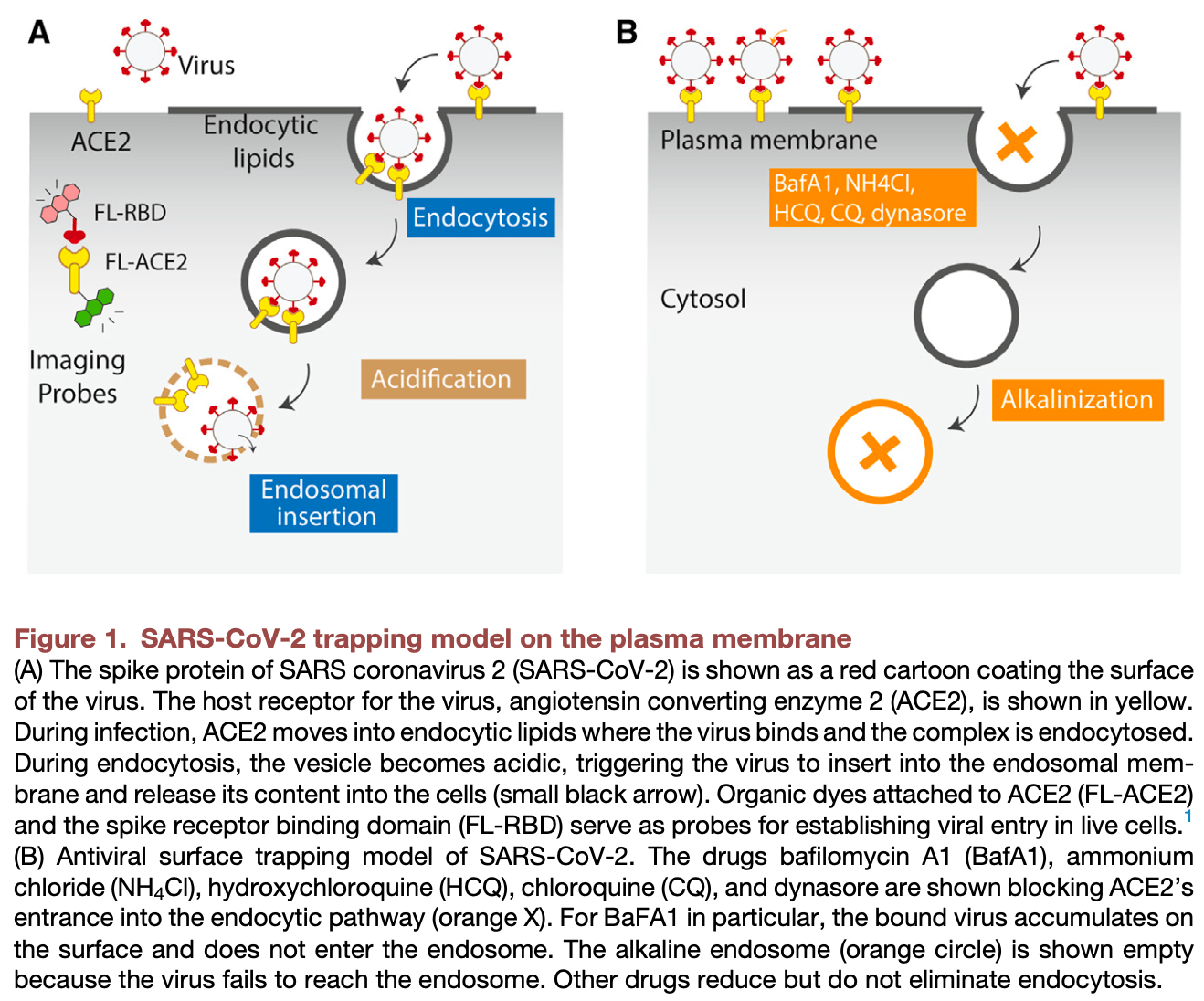
Discussion of1, an in vitro study showing that the antiviral compounds bafilomycin a1 (BafA1), ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), chloroquine (CQ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), and dynasore trap SARS-CoV-2 on the cell surface, preventing viral entry through the endocytic pathway. Using live cell imaging with organic dye probes attached to the host receptor ACE2 and viral spike protein, authors track the viral entry pathway from the cell surface to the late endosome. Treatment with 100 nM BafA1 trapped the virus on the cell surface, with almost no virus detected in late endosomes. Other compounds including HCQ also significantly reduced the endosomal to surface virus ratio, suggesting they block endocytic viral entry.
Antiviral compounds like BafA1, NH4Cl, CQ, and HCQ were thought to trap SARS-CoV-2 in late endosomes through alkalinization mechanisms that block a critical proteolytic step needed for viral entry. However, these results suggest that alkalinization of the endosome may not be the only or primary mechanism. It is possible that both of these mechanims play a role:
- Blocking ACE2 endocytosis: the imaging data shows that compounds like HCQ can trap the virus on the cell surface by preventing the internalization of the ACE2 receptor. This suggests that inhibiting viral entry at an early stage is an important mechanism of action for these drugs.
- Endosomal alkalinization: prior studies have shown that compounds like BafA1, NH4Cl, CQ, and HCQ can raise the pH of endosomes, which is thought to inhibit the proteolytic processing needed for SARS-CoV-2 to fuse with the endosomal membrane and release its contents into the cell. The imaging data suggests this may not be the primary mechanism, however it could still play a role in inhibiting any virus particles that manage to enter endosomes, or in different cells/environments where the previous mechanism is less effective.
Note that authors did not perform dose response analysis and the single dose tested for HCQ/CQ is relatively high. Only a small percentage of patients in Ruiz et al. had ELF concentrations exceeding this dose for 400mg HCQ daily. The new mechanism of action here may require higher concentrations.
Hansen et al., 31 Mar 2023, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Getting in on the action: New tools to see SARS-CoV-2 infect a cell
Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010
In this issue of Cell Chemical Biology, Miao et al. develop probes for live cell tracking of SARS-CoV-2. The probes reveal the endocytic pathway for viral entry. Unexpectedly, the antiviral compound BafA1 traps the virus on the cell surface, highlighting the power of super-resolution imaging in live cells.
References
Bayati, Kumar, Francis, Mcpherson, SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306
Bonazzi, Hennezel, Beckwith, Xu, Fazal et al., Discovery and characterization of a selective IKZF2 glue degrader for cancer immunotherapy, Cell Chemical Biology, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.005
Fischer, Bohm, Lydeard, Yang, Stadler et al., Structure of the DDB1-CRBN E3 ubiq-uitin ligase in complex with thalidomide, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature13527
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kr€ Uger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Kim, Barnitz, Kreslavsky, Brown, Moffett et al., Stable inhibitory activity of regulatory T cells requires the transcription factor Helios, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aad0616
Kreutzberger, Sanyal, Saminathan, Bloyet, Stumpf et al., SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.2209514119
Kronke, Udeshi, Narla, Grauman, Hurst et al., Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1244851
Lu, Middleton, Sun, Naniong, Ott et al., The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1244917
Matyskiela, Lu, Ito, Pagarigan, Lu et al., A novel cereblon modulator recruits GSPT1 to the CRL4(CRBN) ubiquitin ligase, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature18611
Meng, Abdullahi, Ferreira, Goonawardane, Saito et al., Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x
Miao, Yan, Chen, Zhou, Zhou et al., SIM imaging Resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells, Cell Chem Biol
Nakagawa, Sido, Reyes, Kiers, Cantor et al., Instability of Helios-deficient Tregs is associated with conversion to a T-effector phenotype and enhanced antitumor immunity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.1604765113
Rusinova, He, Andersen, Mechanisms underlying drug-mediated regulation of membrane protein function, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, doi:10.1073/pnas.2113229118
Sievers, Petzold, Bunker, Renneville, S1abicki et al., Defining the human C2H2 zinc finger degrome targeted by thalidomide analogs through CRBN, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aat0572
Stanton, Chory, Crabtree, Chemically induced proximity in biology and medicine, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aao5902
Wang, Verano, Nowak, Yuan, Donovan et al., Acute pharmacological degradation of Helios destabilizes regulatory T cells, Nat. Chem. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41589-021-00802-w
Wang, Yuan, Pavel, Hansen, The role of high cholesterol in aged related COVID19 lethality, Preprint at bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.09.086249
Yoshimori, Yamamoto, Moriyama, Futai, Tashiro, Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(19)47429-2
Yuan, Hansen, Cholesterol regulation of membrane proteins revealed by two-color super-resolution imaging, Membranes, doi:10.3390/membranes13020250
Yuan, Pavel, Wang, Kwachukwu, Mediouni et al., Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture, Commun. Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010",
"ISSN": [
"2451-9456"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010",
"alternative-id": [
"S2451945623000594"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Getting in on the action: New tools to see SARS-CoV-2 infect a cell"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Cell Chemical Biology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hansen",
"given": "Scott B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Zixuan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cell Chemical Biology",
"container-title-short": "Cell Chemical Biology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cell.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-16T14:54:08Z",
"timestamp": 1678978448000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-17T06:14:15Z",
"timestamp": 1710656055000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-17T06:40:34Z",
"timestamp": 1710657634320
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 381,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1710547200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451945623000594?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451945623000594?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "233-234",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.001",
"article-title": "SIM imaging Resolves endocytosis of SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD in living cells",
"author": "Miao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Cell Chem Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib1",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib2",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2209514119",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells",
"author": "Kreutzberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib3",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04474-x",
"article-title": "Altered TMPRSS2 usage by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron impacts infectivity and fusogenicity",
"author": "Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib4",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-022-03841-8",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine blocks SARS-CoV-2 entry into the endocytic pathway in mammalian cell culture",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "958",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib5",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of high cholesterol in aged related COVID19 lethality",
"author": "Wang",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(19)47429-2",
"article-title": "Bafilomycin A1, a specific inhibitor of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase, inhibits acidification and protein degradation in lysosomes of cultured cells",
"author": "Yoshimori",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17707",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib7",
"volume": "266",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis",
"author": "Bayati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100306",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib8",
"volume": "296",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/membranes13020250",
"article-title": "Cholesterol regulation of membrane proteins revealed by two-color super-resolution imaging",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "Membranes",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib9",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2113229118",
"article-title": "Mechanisms underlying drug-mediated regulation of membrane protein function",
"author": "Rusinova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.02.010_bib10",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2451945623000594"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmacology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Biochemistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Getting in on the action: New tools to see SARS-CoV-2 infect a cell",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "30"
}
