Nanoscopy Reveals Heparan Sulfate Clusters as Docking Sites for SARS-CoV-2 Attachment and Entry
et al., bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.09.08.674976, Sep 2025
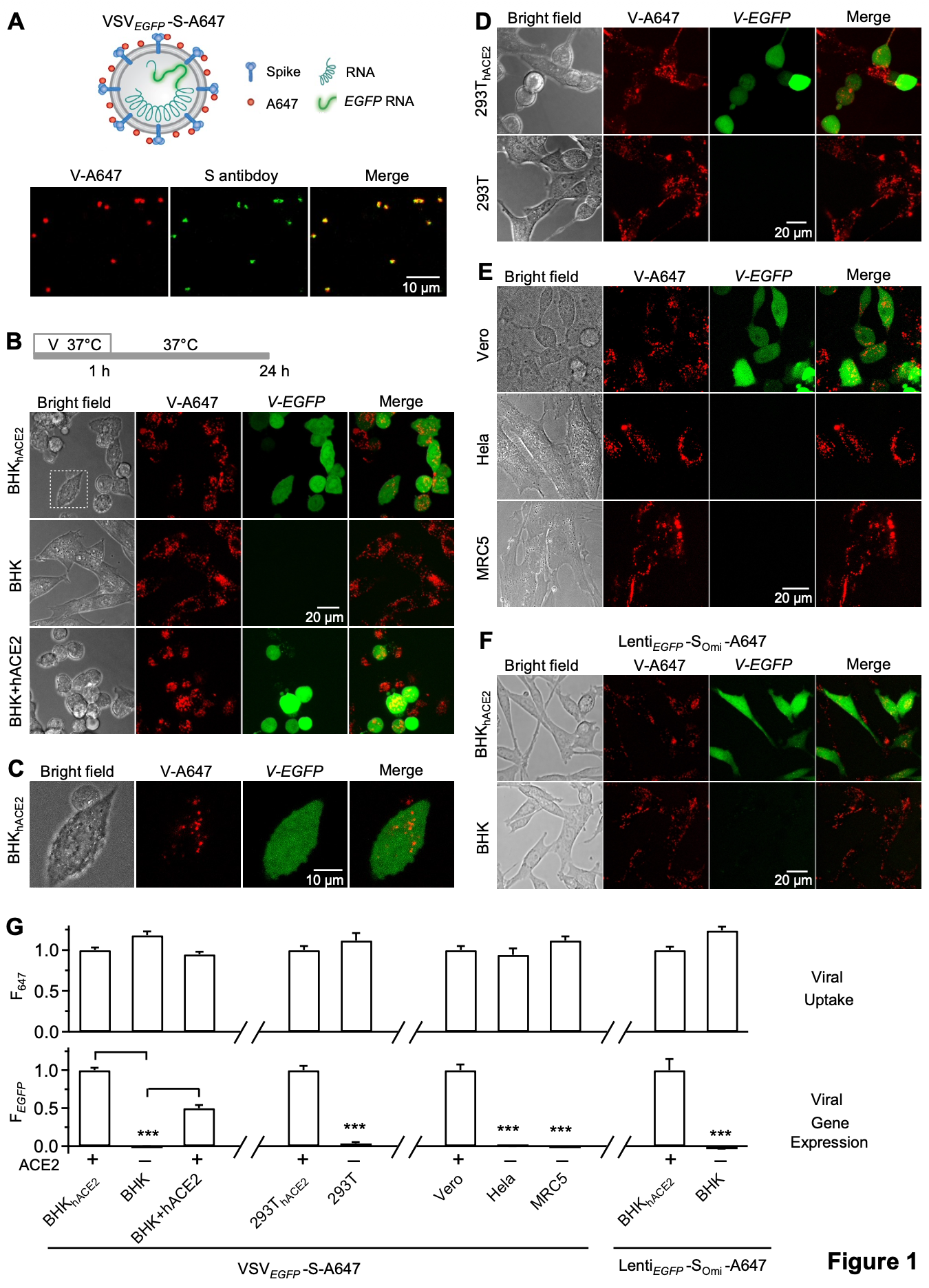
In vitro study showing that heparan sulfate clusters, not ACE2, serve as the primary attachment receptor for SARS-CoV-2 cell entry, with pixantrone inhibiting viral binding and infection in primary human airway cells. Authors used advanced microscopy techniques including STED, MINFLUX, and electron microscopy to demonstrate that SARS-CoV-2 (including JN.1 variant) binds to clusters of 6-137 heparan sulfate molecules extending 60-410 nm above the plasma membrane surface for initial attachment and endocytosis. ACE2 functions downstream after endocytosis to enable viral genome expression rather than mediating initial cell surface attachment.
Han et al., 11 Sep 2025, preprint, 14 authors.
Contact: jyewdell@nih.gov, wul@ninds.nih.gov.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Nanoscopy Reveals Heparan Sulfate Clusters as Docking Sites for SARS-CoV-2 Attachment and Entry
doi:10.1101/2025.09.08.674976
Virus entry is thought to involve binding a unique receptor for cell attachment and cytosolic entry. For SARS-CoV-2 underlying the COVID-19 pandemic, angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is widely assumed as the receptor. Using advanced light microscopy to resolve individual virions and receptors, we found instead that heparan sulfate (HS), not ACE2, mediates SARS-CoV-2 cell-surface attachment and subsequent endocytosis. ACE2 functions only downstream of HS to enable viral genome expression. Instead of binding single HS molecules that electrostatically interact with viral surface proteins weakly, SARS-CoV-2 binds clusters of ~6-137 HS molecules projecting 60-410 nm above the plasma membrane. These tall, HS-rich clusters, present at about one per 6 μm², act as docking sites for viral attachment. Blocking HS binding with the clinically used HSbinding agent pixantrone strongly inhibited the clinically relevant SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 subvariant from attaching to and infecting human airway cells. This work establishes a revised entry paradigm in which HS clusters mediate SARS-CoV-2 attachment and endocytosis, with ACE2 acting downstream, thereby identifying HS interactions as a key anti-COVID-19 strategy. This paradigm and its therapeutic implications may apply broadly beyond COVID-19 because, analogous to SARS-CoV-2, HS binds many other viruses but is only considered an attachment regulator.
Images: Immunolabeled N-protein images from ALI cells being incubated with viruses with a protocol for viral genome expression in three conditions, including 1) control (Ctrl), 2) 105 and is also made available for use under a CC0 license.
References
Antonny, Burd, De Camilli, Chen, Daumke et al., Membrane fission by dynamin: what we know and what we need to know, EMBO J
Asaad, Bethel, Coulson, Dawson, Ford et al., Dipeptidyl nitrile inhibitors of Cathepsin L, Bioorg Med Chem Lett
Bayati, Kumar, Francis, Mcpherson, SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, J Biol Chem
Bermejo-Jambrina, Eder, Kaptein, Van Hamme, Helgers et al., Infection and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 depend on heparan sulfate proteoglycans, EMBO J
Cagno, Tseligka, Jones, Tapparel, Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias?, Viruses
Case, Rothlauf, Chen, Kafai, Fox et al., Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Vaccine Vector Protects against SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Pathogenesis in Mice, Cell Host Microbe
Chanaday, Cousin, Milosevic, Watanabe, Morgan, The Synaptic Vesicle Cycle Revisited: New Insights into the Modes and Mechanisms, J Neurosci
Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2, Cell
Cureton, Massol, Saffarian, Kirchhausen, Whelan, Vesicular stomatitis virus enters cells through vesicles incompletely coated with clathrin that depend upon actin for internalization, PLoS Pathog
Cureton, Massol, Whelan, Kirchhausen, The length of vesicular stomatitis virus particles dictates a need for actin assembly during clathrin-dependent endocytosis, PLoS Pathog
Dieterle, Haslwanter, Bortz, Wirchnianski, Lasso et al., A Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus for Studies of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Cell Entry and Its Inhibition, Cell Host Microbe
Esko, Stewart, Taylor, Animal cell mutants defective in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Esko, Weinke, Taylor, Ekborg, Rodén et al., Inhibition of chondroitin and heparan sulfate biosynthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in galactosyltransferase I, J Biol Chem
Guo, Han, Wei, Arpino, Shin et al., Real-time visualization of exo-and endocytosis membrane dynamics with confocal and super-resolution microscopy, STAR Protoc
Gwosch, Pape, Balzarotti, Hoess, Ellenberg et al., MINFLUX nanoscopy delivers 3D multicolor nanometer resolution in cells, Nat Methods
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Huang, Bosch, Li, Li, Lee et al., SARS coronavirus, but not human coronavirus NL63, utilizes cathepsin L to infect ACE2-expressing cells, J Biol Chem
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Koehler, Delguste, Sieben, Gillet, Alsteens, Initial Step of Virus Entry: Virion Binding to Cell-Surface Glycans, Annu Rev Virol
Kowarz, Loscher, Marschalek, Optimized Sleeping Beauty transposons rapidly generate stable transgenic cell lines, Biotechnol J
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature
Lang, Yang, Deng, Liu, Yang et al., Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans, PLoS One
Lebsir, Zoulim, Grigorov, Heparanase-1: From Cancer Biology to a Future Antiviral Target, Viruses
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature
Liu, Chopra, Li, Bouwman, Tompkins et al., Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans as Attachment Factor for SARSCoV-2, Acs Central Sci
Lopez-Munoz, Santos, Yewdell, Cell surface nucleocapsid protein expression: A betacoronavirus immunomodulatory strategy, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
López-Muñoz, Kosik, Holly, Yewdell, Cell surface SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein modulates innate and adaptive immunity, Sci Adv
Macia, Ehrlich, Massol, Boucrot, Brunner et al., Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin, Dev. Cell
Mercer, Schelhaas, Helenius, Virus entry by endocytosis, Annu Rev Biochem
Milewska, Zarebski, Nowak, Stozek, Potempa et al., Human coronavirus NL63 utilizes heparan sulfate proteoglycans for attachment to target cells, J Virol
Mulhall, Gharpure, Lee, Dubin, Aaron et al., Direct observation of the conformational states of PIEZO1, Nature
O'hearn, Wang, Cheng, Lear-Rooney, Koning et al., Role of EXT1 and Glycosaminoglycans in the Early Stage of Filovirus Entry, J Virol
Pape, Stephan, Balzarotti, Buchner, Lange et al., Multicolor 3D MINFLUX nanoscopy of mitochondrial MICOS proteins, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Paz, Melchior, Shayo, Frangos, Heparan sulfates mediate the interaction between platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) and the Galphaq/11 subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins, J Biol Chem
Schmidt, Weihs, Wurm, Jansen, Rehman et al., MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope, Nat Commun
Shaner, Lambert, Chammas, Ni, Cranfill et al., A bright monomeric green fluorescent protein derived from Branchiostoma lanceolatum, Nat. Methods
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature
Shin, Ge, Arpino, Villarreal, Hamid et al., Visualization of Membrane Pore in Live Cells Reveals a Dynamic-Pore Theory Governing Fusion and Endocytosis, Cell
Shin, Wei, Arpino, Ge, Guo et al., Preformed Omega-profile closure and kiss-and-run mediate endocytosis and diverse endocytic modes in neuroendocrine chromaffin cells, Neuron
Simmons, Gosalia, Rennekamp, Reeves, Diamond et al., Inhibitors of cathepsin L prevent severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus entry, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Suzuki, Yamasoba, Kimura, Wang, Kishimoto et al., Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Nature
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein, Cell
Wang, Zhang, Wu, Niu, Song et al., Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2, Cell
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM Structure of the 2019-nCoV Spike in the Prefusion Conformation
Wu, Chan, Membrane transformations of fusion and budding, Nat Commun
Wu, Hamid, Shin, Chiang, Exocytosis and endocytosis: modes, functions, and coupling mechanisms, Annu. Rev. Physiol
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science
Ye, Chiem, Park, Oladunni, Platt et al., Rescue of SARS-CoV-2 from a Single Bacterial Artificial Chromosome, mBio
Zhang, Chen, Swaroop, Xu, Wang et al., Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro, Cell Discov
Zhang, Liang, Wang, Ye, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 hijacks 105 and is also made available for use under a CC0 license. macropinocytosis to facilitate its entry and promote viral spike-mediated cell-to-cell fusion, J Biol Chem
Zhao, Hamid, Shin, Wen, Krystofiak et al., Hemi-fused structure mediates and controls fusion and fission in live cells, Nature
Zhao, Yang, Yang, Zhang, Huang et al., Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development, Signal Transduct Target Ther
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2025.09.08.674976",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2025.09.08.674976",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Virus entry is thought to involve binding a unique receptor for cell attachment and cytosolic entry. For SARS-CoV-2 underlying the COVID-19 pandemic, angiotensin- converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is widely assumed as the receptor. Using advanced light microscopy to resolve individual virions and receptors, we found instead that heparan sulfate (HS), not ACE2, mediates SARS-CoV-2 cell-surface attachment and subsequent endocytosis. ACE2 functions only downstream of HS to enable viral genome expression. Instead of binding single HS molecules that electrostatically interact with viral surface proteins weakly, SARS-CoV-2 binds clusters of ∼6–137 HS molecules projecting 60–410 nm above the plasma membrane. These tall, HS-rich clusters, present at about one per 6 μm², act as docking sites for viral attachment. Blocking HS binding with the clinically used HS- binding agent pixantrone strongly inhibited the clinically relevant SARS-CoV-2 Omicron JN.1 subvariant from attaching to and infecting human airway cells. This work establishes a revised entry paradigm in which HS clusters mediate SARS-CoV-2 attachment and endocytosis, with ACE2 acting downstream, thereby identifying HS interactions as a key anti-COVID-19 strategy. This paradigm and its therapeutic implications may apply broadly beyond COVID-19 because, analogous to SARS-CoV-2, HS binds many other viruses but is only considered an attachment regulator.</jats:p>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Statement of Significance</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Viral entry, a crucial antiviral target, is typically thought to involve binding its unique receptor for the cell surface attachment and subsequent entry. We examined this concept with advanced microscopies to resolve individual receptors and SARS-CoV-2 virions responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. We discovered two receptors for viral entry: heparan sulfate, a polysaccharide that may bind many viruses, mediates viral attachment and subsequent endocytosis, whereas angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the generally assumed SARS-CoV-2 receptor, acts only downstream to facilitate viral infection. This new model suggests perturbation of HS binding as a more effective anti-COVID-19 strategy than previously recognized. It may apply broadly beyond COVID-19 because, analogous to SARS-CoV-2, HS binds many other viruses but is only considered an attachment regulator.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
9
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8451-8592",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Han",
"given": "Sue",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Tiansheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohseni",
"given": "Ammar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kosik",
"given": "Ivan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6726-5087",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Chung Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Muñoz",
"given": "Alberto Domingo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matthias",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suddaby",
"given": "Reid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0879-5728",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Zhixiong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3826-1081",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Albert J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wurm",
"given": "Christian A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3826-1906",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yewdell",
"given": "Jonathan W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Ling-Gang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-11T13:55:15Z",
"timestamp": 1757598915000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-13T09:30:21Z",
"timestamp": 1757755821000
},
"group-title": "Microbiology",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-16T18:50:29Z",
"timestamp": 1758048629173,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "bioRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
11
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1757548800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2025.09.08.674976",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
11
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-122019-070025",
"article-title": "Initial Step of Virus Entry: Virion Binding to Cell-Surface Glycans",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Virol",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15010237",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.2",
"unstructured": "N. Lebsir , F. Zoulim , B. Grigorov , Heparanase-1: From Cancer Biology to a Future Antiviral Target. Viruses 15, (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11070596",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.3",
"unstructured": "V. Cagno , E. D. Tseligka , S. T. Jones , C. Tapparel , Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans and Viral Attachment: True Receptors or Adaptation Bias? Viruses 11, (2019)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.6",
"unstructured": "J. Shang , G. Ye , K. Shi , Y. Wan , C. Luo , H. Aihara , Q. Geng , A. Auerbach , F. Li , Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-00222-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.10",
"unstructured": "Q. Zhang , C. Z. Chen , M. Swaroop , M. Xu , L. Wang , J. Lee , A. Q. Wang , M. Pradhan , N. Hagen , L. Chen , M. Shen , Z. Luo , X. Xu , Y. Xu , W. Huang , W. Zheng , Y. Ye , Heparan sulfate assists SARS-CoV-2 in cell entry and can be targeted by approved drugs in vitro. Cell Discov 6, 80 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0023710",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02078-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21652-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.15",
"unstructured": "R. Schmidt , T. Weihs , C. A. Wurm , I. Jansen , J. Rehman , S. J. Sahl , S. W. Hell , MINFLUX nanometer-scale 3D imaging and microsecond-range tracking on a common fluorescence microscope. Nat Commun 12, 1478 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-019-0688-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.06.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.17",
"unstructured": "M. E. Dieterle , D. Haslwanter , R. H. Bortz , 3rd, A. S. Wirchnianski, G. Lasso, O. Vergnolle, S. A. Abbasi, J. M. Fels, E. Laudermilch, C. Florez, A. Mengotto, D. Kimmel, R. J. Malonis, G. Georgiev, J. Quiroz, J. Barnhill, L. A. Pirofski, J. P. Daily, J. M. Dye, J. R. Lai, A. S. Herbert, K. Chandran, R. K. Jangra, A Replication-Competent Vesicular Stomatitis Virus for Studies of SARS-CoV-2 Spike-Mediated Cell Entry and Its Inhibition. Cell Host Microbe 28, 486-496 e486 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.07.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuron.2021.07.019",
"article-title": "Preformed Omega-profile closure and kiss-and-run mediate endocytosis and diverse endocytic modes in neuroendocrine chromaffin cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3119",
"journal-title": "Neuron",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.23",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-44539-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.24",
"unstructured": "L. G. Wu , C. Y. Chan , Membrane transformations of fusion and budding. Nat Commun 15, 21 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-biochem-060208-104626",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102511",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.27",
"unstructured": "Y. Y. Zhang , R. Liang , S. J. Wang , Z. W. Ye , T. Y. Wang , M. Chen , J. Liu , L. Na , Y. L. Yang , Y. B. Yang , S. Yuan , X. Yin , X. H. Cai , Y. D. Tang , SARS-CoV-2 hijacks macropinocytosis to facilitate its entry and promote viral spike-mediated cell-to-cell fusion. J Biol Chem 298, 102511 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-physiol-021113-170305",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1158-19.2019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.201694613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.05.071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M508381200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0505577102",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00558-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.34",
"unstructured": "M. M. Zhao , W. L. Yang , F. Y. Yang , L. Zhang , W. J. Huang , W. Hou , C. F. Fan , R. H. Jin , Y. M. Feng , Y. C. Wang , J. K. Yang , Cathepsin L plays a key role in SARS-CoV-2 infection in humans and humanized mice and is a promising target for new drug development. Signal Transduct Target Ther 6, 134 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2304087120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.36",
"unstructured": "R. Suzuki , D. Yamasoba , I. Kimura , L. Wang , M. Kishimoto , J. Ito , Y. Morioka , N. Nao , H. Nasser , K. Uriu , Y. Kosugi , M. Tsuda , Y. Orba , M. Sasaki , R. Shimizu , R. Kawabata , K. Yoshimatsu , H. Asakura , M. Nagashima , K. Sadamasu , K. Yoshimura , C. Genotype to Phenotype Japan, H. Sawa, T. Ikeda, T. Irie, K. Matsuno, S. Tanaka, T. Fukuhara, K. Sato, Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. Nature 603, 700-705 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0021-9258(18)45335-5",
"article-title": "Inhibition of chondroitin and heparan sulfate biosynthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants defective in galactosyltransferase I",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12189",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.37",
"volume": "262",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.82.10.3197",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abp9770",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.39",
"unstructured": "A. D. López-Muñoz , I. Kosik , J. Holly , J. W. Yewdell , Cell surface SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein modulates innate and adaptive immunity. Sci Adv 8, eabp9770 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.11.944462",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.41",
"unstructured": "D. Wrapp , N. Wang , K. S. Corbett , J. A. Goldsmith , C. L. Hsieh , O. Abiona , B. S. Graham , J. S. McLellan , Cryo-EM Structure of the 2019-nCoV Spike in the Prefusion Conformation. bioRxiv, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.1c00010",
"article-title": "Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans as Attachment Factor for SARSCoV- 2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1009",
"journal-title": "Acs Central Sci",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.42",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100306",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.43",
"unstructured": "A. Bayati , R. Kumar , V. Francis , P. S. McPherson , SARS-CoV-2 infects cells after viral entry via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J Biol Chem 296, 100306 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03689-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biot.201400821",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02168-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.46",
"unstructured": "C. Ye , K. Chiem , J. G. Park , F. Oladunni , R. N. Platt , 2nd, T. Anderson, F. Almazan, J. C. de la Torre, L. Martinez-Sobrido, Rescue of SARS-CoV-2 from a Single Bacterial Artificial Chromosome. mBio 11, (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.2413",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101404",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.48",
"unstructured": "X. Guo , S. Han , L. Wei , G. Arpino , W. Shin , X. Wang , L. G. Wu , Real-time visualization of exo- and endocytosis membrane dynamics with confocal and super-resolution microscopy. STAR Protoc 3, 101404 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2006.04.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature18598",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M113.542514",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06427-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2009364117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091302301172000_2025.09.08.674976v1.53"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://biorxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2025.09.08.674976"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Nanoscopy Reveals Heparan Sulfate Clusters as Docking Sites for SARS-CoV-2 Attachment and Entry",
"type": "posted-content"
}