HLA Polymorphisms and COVID‐19 Susceptibility and Severity: Insights From an Iranian Patients Cohort
et al., Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1111/jcmm.70570, May 2025
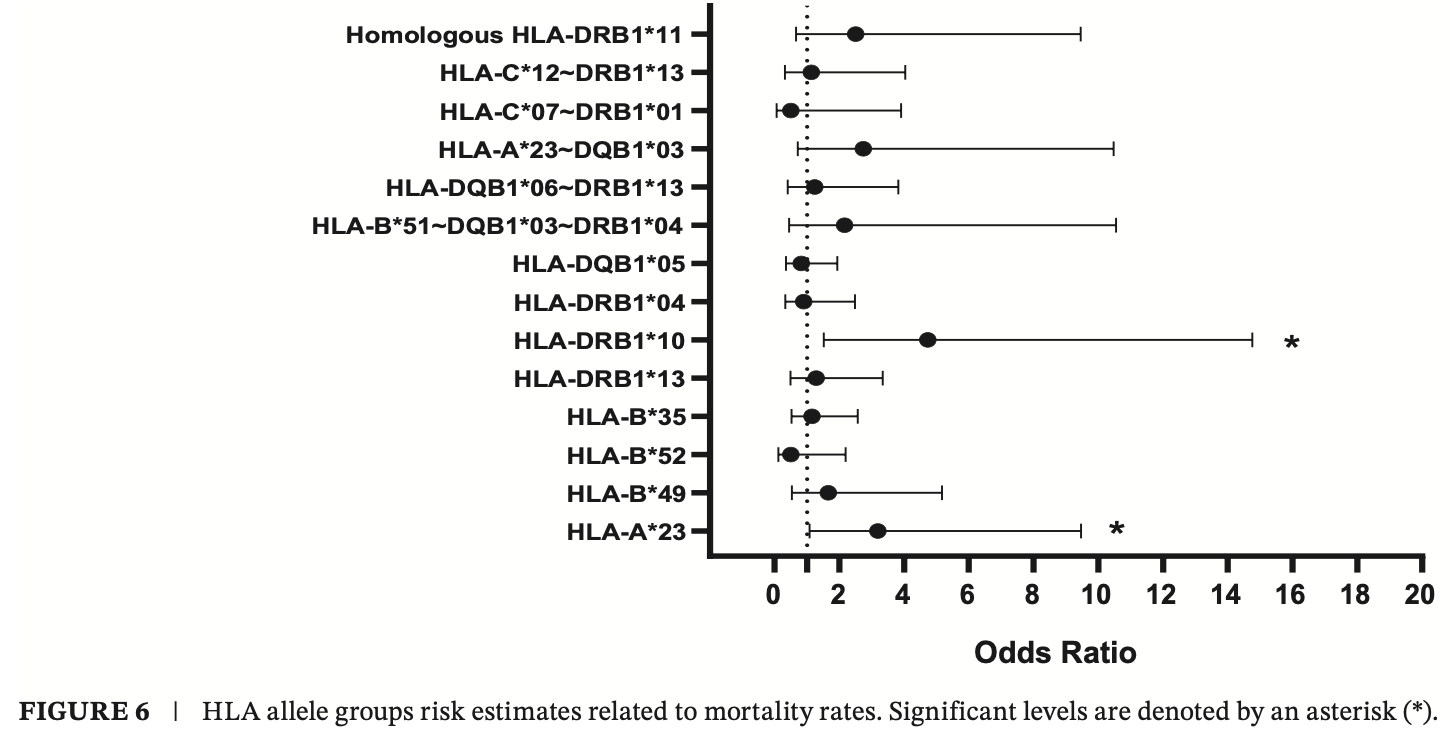
Cross-sectional study of 290 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing that certain HLA alleles (HLA-B*49, HLA-B*52, HLA-C*12, HLA-DRB1*04, and HLA-DQB1*05) were associated with increased susceptibility to COVID-19, while others (HLA-A*23, HLA-DRB1*10, and HLA-DRB1*13) were linked to greater disease severity.
Hakimi et al., 14 May 2025, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: lteimoori@pasteur.ac.ir.
HLA Polymorphisms and COVID‐19 Susceptibility and Severity: Insights From an Iranian Patients Cohort
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1111/jcmm.70570
The HLA system is a crucial immune response component against infectious agents, including SARS-CoV-2. Certain polymorphisms may impart varying levels of protection or vulnerability to COVID-19. This research aims to understand the possible relationship between HLA polymorphisms and the susceptibility to COVID-19 and its severity. We recruited 290 hospitalised Iranian COVID-19 patients (130 severe and 160 moderate). Using PCR-SSP methods, we conducted a detailed analysis of polymorphisms in HLA class I (HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C) and II (HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1) molecules at low resolution. The study found that certain HLA alleles, including HLA-B*49, HLA-B*52, HLA-C*12, HLA-DRB1*04, and HLA-DQB1*05, were associated with disease susceptibility. Additionally, HLA-A*23, DRB1*10, and DRB1*13 were indicators of disease severity. The study also noted that individuals carrying the HLA-A*23 allele showed a significant decrease in lymphocyte levels and an elevated likelihood of developing thrombosis. We hypothesise that a maladaptive immune response may occur based on these findings. This might be due to the strong affinity of the HLA-A*23 allele group for presenting a wide range of SARS-CoV-2 peptides. Such a presentation possibly leads to a cytokine storm, followed by lymphocyte apoptosis and an increase in platelet count.
Author Contributions Pooria Hakimi: conceptualization (supporting), data curation (lead), formal analysis (lead), methodology (supporting), validation (supporting), writing -original draft (supporting). Kasra Arbabi Zaboli: data curation (lead), formal analysis (lead), methodology (lead), software (lead), validation (lead), writing -original draft (lead). Mohammadreza Golbabapour-Samakoush: formal analysis (supporting), investigation (supporting). Susan Azizimohammadi: investigation (supporting), resources (supporting). Fatemeh Soleimani: software (supporting), validation (supporting). Mohammad Hosein Salmani: data curation (supporting), formal analysis (supporting). Ladan Teimoori-Toolabi: conceptualization (lead), funding acquisition (lead), project administration (lead), resources (lead), supervision (lead), writing -review and editing (lead).
Ethics Statement The study protocol and amendments were approved by the Ethics Committee of the National Institute of Medical Research Development (NIMAD) (IR.NIMAD.REC.1399.088). All patients have signed the informed consent.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting Information Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section.
References
Abedini, Rahmanian, Heidari, Feizi, Sherkat et al., Diversity of HLA Class I and Class II Alleles in Iran Populations: Systematic Review and Meta-Analaysis, Transplant Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.trim.2021.101472
Bal, Dogan, Cabalak, Dirican, Lymphocyte-To-C-Reactive Protein Ratio May Serve as an Effective Biomarker to Determine COVID-19 Disease Severity, Turkish Journal of Biochemistry, doi:10.1515/tjb-2020-0410
Barquera, Collen, Di, Binding Affinities of 438 HLA Proteins to Complete Proteomes of Seven Pandemic Viruses and Distributions of Strongest and Weakest HLA Peptide Binders in Populations Worldwide, HLA
Basir, Majzoobi, Ebrahimi, Susceptibility and Severity of COVID-19 Are Both Associated With Lower Overall Viral-Peptide Binding Repertoire of HLA Class I Molecules, Especially in Younger People, Frontiers in Immunology
Blackwell, Jamieson, Burgner, HLA and Infectious Diseases, Clinical Microbiology Reviews
Bubnova, Pavlova, Terentieva, HLA Genotypes in Patients With Infection Caused by Different Strains of SARS-CoV-2, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph192114024
Cesta, Zippoli, Marsiglia, Neutrophil Activation and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs) in COVID-19 ARDS and Immunothrombosis, European Journal of Immunology, doi:10.1002/eji.202250010
Correale, Mutti, Pentimalli, HLA-B* 44 and C* 01 Prevalence Correlates With Covid19 Spreading Across Italy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms21155205
Croft, Smith, Pickering, Most Viral Peptides Displayed by Class I MHC on Infected Cells Are Immunogenic, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.1815239116
Crux, Elahi, Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) and Immune Regulation: How Do Classical and Non-Classical HLA Alleles Modulate Immune Response to Human Immunodeficiency Virus and Hepatitis C Virus Infections?, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00832
Cui, Chen, Li, Liu, Wang, Prevalence of Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With Severe Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia, Haemostasis, doi:10.1111/jth.14830
De Meira Leite, Gonzalez-Galarza, Da Silva, Middleton, Santos, Predictive Immunogenetic Markers in COVID-19, Human Immunology
Debnath, Banerjee, Berk, Genetic Gateways to COVID-19 Infection: Implications for Risk, Severity, and Outcomes, FASEB Journal, doi:10.1096/fj.202001115R
Dendrou, Petersen, Rossjohn, Fugger, HLA Variation and Disease, Nature Reviews. Immunology, doi:10.1038/nri.2017.143
Dobrijević, Gligorijević, Šunderić, The Association of Human Leucocyte Antigen (HLA) Alleles With COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Reviews in Medical Virology
Ebrahimi, Ghasemi-Basir, Majzoobi, Rasouli-Saravani, Hajilooi et al., HLA-DRB1* 04 May Predict the Severity of Disease in a Group of Iranian COVID-19 Patients, Human Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2021.07.004
Ertosun, Özkan, Darbaş, The Relationship Between COVID-19 and HLA in Kidney Transplant Recipients, an Evaluation of Predictive and Prognostic Factors, Clinical Transplantation
Giamarellos-Bourboulis, Netea, Rovina, Complex Immune Dysregulation in COVID-19 Patients With Severe Respiratory Failure, Cell Host & Microbe
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Gutiérrez-Bautista, Rodriguez-Nicolas, Rosales-Castillo, Study of HLA-A,-B,-C,-DRB1 And-DQB1 Polymorphisms in COVID-19 Patients, Journal of Microbiology, Immunology
Hajebi, Ajam, Karbalai, Association Between Human Leukocyte Antigen and COVID-19 Severity, Acta Medica Iranica
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical Features of Patients Infected With 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet (London, England), doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Ishii, Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Class I Susceptible Alleles Against COVID-19 Increase Both Infection and Severity Rate, Cureus
Khor, Omae, Nishida, HLA-B* 52: 01: 02: 02, Age and Sex Are Associated With Severity of Japanese COVID-19 With Respiratory Failure, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.658570
La Porta, Zapperi, Estimating the Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Peptides to HLA Class I in Human Subpopulations Using Artificial Neural Networks, Cell Systems
Langton, Bourke, Lie, The Influence of HLA Genotype on the Severity of COVID-19 Infection, HLA, doi:10.1111/tan.14284
Liao, Liang, Chen, Hsu, Yang et al., IL-19 Induces Production of IL-6 and TNF-α and Results in Cell Apoptosis Through TNF-α, Journal of Immunology
Lin, Tseng, Trejaut, Association of HLA Class I With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection, BMC Medical Genetics, doi:10.1186/1471-2350-4-9
Littera, Campagna, Deidda, Human Leukocyte Antigen Complex and Other Immunogenetic and Clinical Factors Influence Susceptibility or Protection to SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severity of the Disease Course. The Sardinian Experience, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.605688
Litvinov, Evtugina, Peshkova, Altered Platelet and Coagulation Function in Moderate-To-Severe COVID-19, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-95397-6
Mangalmurti, Hunter, Cytokine Storms: Understanding COVID-19, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017
Mcgonagle, The Company's Public News, Information
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression, Lancet (London, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Mian, Gan Ran, None, Za Zhi, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2021.08.009
Naemi, Al-Adwani, Al-Khatabi, Al-Nazawi, Association Between the HLA Genotype and the Severity of COVID-19 Infection Among South Asians, Journal of Medical Virology
Ng, Lau, Li, Association of Human-Leukocyte-Antigen Class I (B* 0703) and Class II (DRB1* 0301) Genotypes With Susceptibility and Resistance to the Development of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Journal of Infectious Diseases
Nikonovas, Spessa, Doerr, Clay, Mezbahuddin, Near-Complete Loss of Fire-Resistant Primary Tropical Forest Cover in Sumatra and Kalimantan, Environment, doi:10.1038/s43247-020-00069-4
Olwenyi, Dyavar, Acharya, Immuno-Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Journal of Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1007/s00109-020-01961-4
Ouedraogo, Traoré, Ouattara, Association of HLA-DRB1* 11 and HLA-DRB1* 12 Gene Polymorphism With COVID-19 in Burkina Faso, BMC Medical Genomics
Pappas, Marin, Hollenbach, Mack, Bridging ImmunoGenomic Data Analysis Workflow Gaps (BIGDAWG): An Integrated Case-Control Analysis Pipeline, Human Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2015.12.006
Poulton, Wright, Hughes, A Role for Human Leucocyte Antigens in the Susceptibility to SARS-Cov-2 Infection Observed in Transplant Patients, International Journal of Immunogenetics, doi:10.1111/iji.12505
Pretti, Galvani, Vieira, Bonomo, Bonamino et al., Class I HLA Allele Predicted Restricted Antigenic Coverages for Spike and Nucleocapsid Proteins Are Associated With Deaths Related to COVID-19, Frontiers in Immunology
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clinical Infectious Diseases: An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Ranucci, Ballotta, Di Dedda, The Procoagulant Pattern of Patients With COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis: JTH, doi:10.1111/jth.14854
Rod, Oviedo-Trespalacios, Cortes-Ramirez, A Brief-Review of the Risk Factors for Covid-19 Severity, Revista de Saúde Pública
Romero-López, Carnalla-Cortés, Pacheco-Olvera, A Bioinformatic Prediction of Antigen Presentation From SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Revealed a Theoretical Correlation of HLA-DRB1* 01 With COVID-19 Fatality in Mexican Population: An Ecological Approach, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26561
Saadati, Chegni, Ghaffari, Hassan, The Potential Association of Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)-A And-B With COVID-19 Mortality: A Neglected Risk Factor, Iranian Journal of Public Health
Shiina, Hosomichi, Inoko, Kulski, The HLA Genomic Loci Map: Expression, Interaction, Diversity and Disease, Journal of Human Genetics, doi:10.1038/jhg.2008.5
Suslova, Vavilov, Belyaeva, Distribution of HLA-A,-B,-C,-DRB1,-DQB1,-DPB1 Allele Frequencies in Patients With COVID-19 Bilateral Pneumonia in Russians, Living in the Chelyabinsk Region (Russia), Human Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2022.04.009
Tavasolian, Rashidi, Hatam, HLA, Immune Response, and Susceptibility to COVID-19, Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.601886
Teimoori-Toolabi, Vahedi, Mollahajian, Three Common CARD15 Mutations Are Not Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Crohn's Disease in Iranians, Hepato-Gastroenterology
Wang, Zhang, Zhang, He, Zhu, Distribution of HLA Allele Frequencies in 82 Chinese Individuals With Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19), HLA
Warren, Birol, Retrospective In Silico HLA Predictions From COVID-19 Patients Reveal Alleles Associated With Disease Prognosis, medRxiv: The Preprint Server for Health Science
Weiner, Suwalski, Holtgrewe, Increased Risk of Severe Clinical Course of COVID-19 in Carriers of HLA-C*04: 01, EClinicalMedicine
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Xiao, Wu, Liang, C-Reactive Protein to Lymphocyte Ratio Is a Significant Predictive Factor for Poor Short-Term Clinical Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 BA. 2.2 Patients, Frontiers in Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1168375
Xu, Zhao, Teng, Systematic Comparison of Two Animal-To-Human Transmitted Human Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12020244
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.70570",
"ISSN": [
"1582-1838",
"1582-4934"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70570",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:p>The HLA system is a crucial immune response component against infectious agents, including SARS‐CoV‐2. Certain polymorphisms may impart varying levels of protection or vulnerability to COVID‐19. This research aims to understand the possible relationship between HLA polymorphisms and the susceptibility to COVID‐19 and its severity. We recruited 290 hospitalised Iranian COVID‐19 patients (130 severe and 160 moderate). Using PCR‐SSP methods, we conducted a detailed analysis of polymorphisms in HLA class I (HLA‐A, HLA‐B, and HLA‐C) and II (HLA‐DRB1 and HLA‐DQB1) molecules at low resolution. The study found that certain HLA alleles, including HLA‐B*49, HLA‐B*52, HLA‐C*12, HLA‐DRB1*04, and HLA‐DQB1*05, were associated with disease susceptibility. Additionally, HLA‐A*23, DRB1*10, and DRB1*13 were indicators of disease severity. The study also noted that individuals carrying the HLA‐A*23 allele showed a significant decrease in lymphocyte levels and an elevated likelihood of developing thrombosis. We hypothesise that a maladaptive immune response may occur based on these findings. This might be due to the strong affinity of the HLA‐A*23 allele group for presenting a wide range of SARS‐CoV‐2 peptides. Such a presentation possibly leads to a cytokine storm, followed by lymphocyte apoptosis and an increase in platelet count.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/jcmm.70570"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-11-26"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-04-17"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-05-14"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Department, Biotechnology Research Center Pasteur Institute of Iran Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Hakimi",
"given": "Pooria",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Department, Biotechnology Research Center Pasteur Institute of Iran Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Zaboli",
"given": "Kasra Arbabi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Department, Biotechnology Research Center Pasteur Institute of Iran Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Golbabapour‐Samakoush",
"given": "Mohammadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hajar Hospital Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Azizimohammadi",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Department, Biotechnology Research Center Pasteur Institute of Iran Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Soleimani",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hajar Hospital Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Salmani",
"given": "Mohammad Hosein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6588-9774",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Molecular Medicine Department, Biotechnology Research Center Pasteur Institute of Iran Tehran Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Teimoori‐Toolabi",
"given": "Ladan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Cellular Molecular Medi",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-14T14:23:48Z",
"timestamp": 1747232628000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T04:26:22Z",
"timestamp": 1747283182000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012155",
"award": [
"IR.NIMAD.REC.1399.088"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100012155",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute for Medical Research Development"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T04:40:10Z",
"timestamp": 1747284010357,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 13,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1747180800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/jcmm.70570",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11606/s1518-8787.2020054002481",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1",
"unstructured": "Mcgonagle DJTC‐rcihoEC “The Company's Public News Information. Since January 2020 Elsevier has Created a COVID‐19 Resource Centre With Free Information in English and Mandarin on the Novel Coronavirus COVID‐19 ”2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109‐020‐01961‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2017.143",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jhg.2008.5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00048-08",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Class I Susceptible Alleles Against COVID‐19 Increase Both Infection and Severity Rate",
"author": "Ishii T.",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001115R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471‐2350‐4‐9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21155205",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14830",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12020244",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The Potential Association of Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA)‐A And‐B With COVID‐19 Mortality: A Neglected Risk Factor",
"author": "Saadati M.",
"first-page": "2433",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Iranian Journal of Public Health",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Association Between Human Leukocyte Antigen and COVID‐19 Severity",
"author": "Hajebi R.",
"first-page": "400",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Acta Medica Iranica",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.humimm.2021.07.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/421523",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.00832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43247‐020‐00069‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1815239116",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.601886",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2021.08.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph192114024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.658570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.humimm.2021.01.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.891816",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.605688",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.27.20220863",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"unstructured": "R. L.WarrenandI. J. M.Birol “Retrospective In Silico HLA Predictions From COVID‐19 Patients Reveal Alleles Associated With Disease Prognosis ”medRxiv: The Preprint Server for Health Science. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101099",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.humimm.2022.04.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/iji.12505",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tan.14284",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tan.13941",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.565730",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ctr.14525",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12920-023-01684-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cels.2020.08.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tan.13956",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26561",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.169.8.4288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2023.1168375",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/tjb‐2020‐0410",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598‐021‐95397‐6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(20)30183‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14854",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140‐6736(20)30628‐0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.202250010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_54_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trim.2021.101472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_55_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Three Common CARD15 Mutations Are Not Responsible for the Pathogenesis of Crohn's Disease in Iranians",
"author": "Teimoori‐Toolabi L.",
"first-page": "275",
"issue": "98",
"journal-title": "Hepato‐Gastroenterology",
"key": "e_1_2_10_56_1",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.humimm.2015.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_57_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jcmm.70570"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "<scp>HLA</scp> Polymorphisms and <scp>COVID</scp>‐19 Susceptibility and Severity: Insights From an Iranian Patients Cohort",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "29"
}