Beneficial effects of the combination of BCc1 and Hep-S nanochelating-based medicines on IL-6 in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 adult patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
et al., Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2, IRCT20170731035423N2, Nov 2023
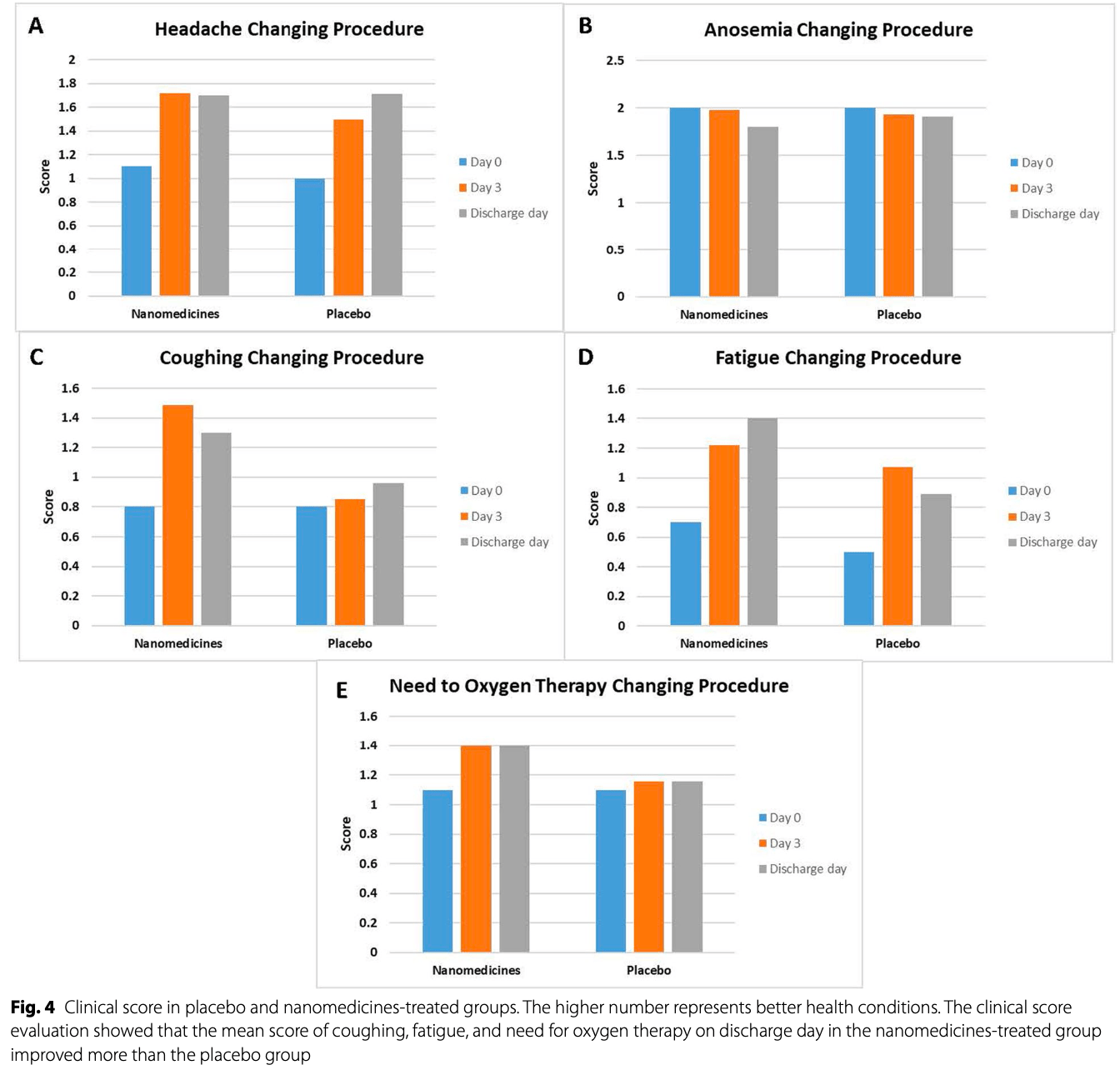
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 122 moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran, evaluating the addition of BCc1 iron chelator and Hep-S selenium nanomedicines to standard treatment. The nanomedicine group showed a significant 77% reduction in IL-6 levels by day 28 compared to an 18% increase in the placebo group, along with improvements in TNF-alpha and clinical scores for cough, fatigue, and oxygen need, without statistical significance.
|
risk of death, 35.5% lower, RR 0.65, p = 0.68, treatment 2 of 62 (3.2%), control 3 of 60 (5.0%), NNT 56.
|
|
relative improvement in oxygen score, 81.5% better, RR 0.19, treatment 58, control 57.
|
|
relative improvement in fever score, 22.0% better, RR 0.78, treatment 58, control 57.
|
|
relative improvement in cough score, 66.7% better, RR 0.33, treatment 58, control 57.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hafizi et al., 11 Nov 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 17 authors, study period 2 October, 2020 - 20 March, 2021, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with BCc1) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial IRCT20170731035423N2.
Contact: crc@sbmu.ac.ir, hamidjamaati@hotmail.com, mnazaran@nanochelatingtechnology.com.
Beneficial effects of the combination of BCc1 and Hep-S nanochelating-based medicines on IL-6 in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 adult patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2
Background In the severe forms of COVID-19 and many other infectious diseases, the patients develop a cytokine storm syndrome (CSS) where pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α play a key role in the development of this serious process. Selenium and iron are two important trace minerals, and their metabolism is tightly connected to immune system function. Numerous studies highlight the role of selenium and iron metabolism changes in the procedure of COVID-19 inflammation. The immunomodulator effect of nanomedicines that are synthesized based on nanochelating technology has been proved in previous studies. In the present study, the effects of the combination of BCc1(with iron-chelating property) and Hep-S (containing selenium) nanomedicines on mentioned cytokines levels in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 patients were evaluated. Methods Laboratory-confirmed moderate COVID-19 patients were enrolled to participate in a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study in two separate groups: combination of BCc1 and Hep-S (N = 62) (treatment) or placebo (N = 60) (placebo). The blood samples were taken before medications on day zero, at discharge, and 28 days after consumption to measure hematological and biochemical parameters and cytokine levels. The clinical symptoms of all the patients were recorded according to an assessment questionnaire before the start of the treatment and on days 3 and discharge day.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1186/ s13063-023-07624-2.
Additional file 1: Table S A) Descriptive Statistics of cell blood count by Group (nanomedicines vs. Placebo). B) Tests of Within-Subjects Effects. The blood samples were taken and analyzed on day zero, at discharge, and at the end of the treatment (on day 28). The results indicated that all the measured parameters were at normal range on day 28, and there was no significant difference between the treatment and placebo groups.
Authors' contributions MH and SF performed most of the experiments and data acquisition and also wrote the manuscript. SK carried out the synthesis of the BCc1 and Hep-S nanomedicine. AF, SL, SM, MM, JH, MB, HZ, AN, MP, PK, and SY collected the data and selected the patients. MHN contributed to the conception and design of the BCc1 and Hep-S nanomedicine. MEA and HJ designed the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests Mohammad Hassan Nazaran is the owner of Nanochelating Technology. The authors declare that they have no competing interests. • fast, convenient online submission • thorough peer review by experienced researchers in your field
• rapid publication on acceptance • support for research data, including large and complex data types • gold Open Access which fosters..
References
Abbina, Design of safe nanotherapeutics for the excretion of excess systemic toxic iron, ACS Cent Sci
Alimohamadi, Determine the most common clinical symptoms in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Prev Med Hyg
Atal, IL-6 inhibitors in the treatment of serious COVID-19: a promising therapy?, Pharmaceut Med
Avery, Hoffmann, Selenium, selenoproteins, and immunity, Nutrients
Aygun, Kaya, Alhajj, Identifying side effects of commonly used drugs in the treatment of Covid 19, Sci Rep
Azizi, Pentoxifylline effects on hospitalized patients with COVID19: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, Int Immunopharmacol
Bascones-Martinez, Immunomodulatory drugs: oral and systemic adverse effects, Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal
Berlutti, Antiviral properties of lactoferrin-a natural immunity molecule, Molecules
Birlutiu, Birlutiu, Chicea, Off-label tocilizumab and adjuvant iron chelator effectiveness in a group of severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients: a single center experience, Medicine
Cecchini, Cecchini, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression, Med Hypotheses
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin Immunopathol
Chung, Thone, Kwon, COVID-19 vaccines: the status and perspectives in delivery points of view, Adv Drug Deliv Rev
Dalamaga, Karampela, Mantzoros, Commentary: could iron chelators prove to be useful as an adjunct to COVID-19 treatment regimens?, Metabolism
Drakesmith, Prentice, Viral infection and iron metabolism, Nat Rev Microbiol
Edeas, Saleh, Peyssonnaux, Iron: Innocent bystander or vicious culprit in COVID-19 pathogenesis?, Int J Infect Dis
Fakharzadeh, BCc1 nanomedicine therapeutic effects in streptozotocin and high-fat diet induced diabetic kidney disease, Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes
Fakharzadeh, DIBc nano metal-organic framework improves biochemical and pathological parameters of experimental chronic kidney disease, J Trace Elem Med Biol
Fakharzadeh, DIBc, a nanochelating-based nano metal-organic framework, shows anti-diabetic effects in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Int J Nanomed
Fakharzadeh, The new nano-complex, Hep-c, improves the immunogenicity of the hepatitis B vaccine, Vaccine
Fakharzadeh, The therapeutic effects of MSc1 nanocomplex, synthesized by nanochelating technology, on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitic C57/BL6 mice, Int J Nanomed
Fiteni, Endpoints in cancer clinical trials, J Visc Surg
Guaraldi, Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol
Hafizi, A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation of BCc1 nanomedicine effect on survival and quality of life in metastatic and non-metastatic gastric cancer patients, J Nanobiotechnol
Hafizi, Moaiery, Khayamzadeh, Noorian, An investigation on the effect of BCc1 nanomedicine on gastric cancer patients using EORTC QLQ-STO30 questionnaire, Quest ionna ire
Hernandez-Cedeño, CIGB-258, a peptide derived from human heat-shock protein 60, decreases hyperinflammation in COVID-19 patients, Cell Stress Chaperones
Hoffmann, Berry, The influence of selenium on immune responses, Mol Nutr Food Res
Jaspers, Selenium deficiency alters epithelial cell morphology and responses to influenza, Free Radic Biol Med
Kalanaky, BCc1, the novel antineoplastic nanocomplex, showed potent anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo, Drug Des Devel Ther
Karimi-Sales, Neuroprotective effect of new nanochelating-based nano complex, ALZc3, against Abeta (1-42)-induced toxicity in rat: a comparison with memantine, Pharm Res
Kell, Pretorius, Serum ferritin is an important inflammatory disease marker, as it is mainly a leakage product from damaged cells, Metallomics
Kernan, Carcillo, Hyperferritinemia and inflammation, Int Immunol
Khatiwada, Subedi, A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Curr Nutr Rep
Kontoghiorghe, Kontoghiorghes, New developments and controversies in iron metabolism and iron chelation therapy, World J Methodol
Kuba, A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat Med
Lagunas-Rangel, Chavez-Valencia, High IL-6/IFN-gamma ratio could be associated with severe disease in COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol
Larvie, COVID-19 severity is associated with selenium intake among young adults with low selenium and zinc intake in North Carolina, Curr Dev Nutr
Liu, Selenium (Se) plays a key role in the biological effects of some viruses: Implications for COVID-19, Environ Res
Liu, Tocilizumab: the key to stop coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)?, Front Med
Lv, Association between iron status and the risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19, Clin Nutr
Mahmoodpoor, The effect of intravenous selenium on oxidative stress in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Immunol Invest
Manzanares, High-dose selenium reduces ventilator-associated pneumonia and illness severity in critically ill patients with systemic inflammation, Intensive Care Med
Mcdermid, Mortality in HIV infection is independently predicted by host iron status and SLC11A1 and HP genotypes, with new evidence of a gene-nutrient interaction, Am J Clin Nutr
Mehta, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mh, Chelate compounds
Mortaz, The immune response and immunopathology of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Nasonov, Samsonov, The role of Interleukin 6 inhibitors in therapy of severe COVID-19, Biomed Pharmacother
Ni, Potential metal-related strategies for prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Rare Met
Organization, Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13
Qiu, The therapeutic effect and safety of the drugs for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Raj, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC, Nature
Sathish, Challenges and approaches for the development of safer immunomodulatory biologics, Nat Rev Drug Discov
Saxena, Drug-based lead discovery: the novel ablative antiretroviral profile of deferiprone in HIV-1-infected cells and in HIV-infected treatment-naive subjects of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized exploratory trial, PLoS ONE
Sciascia, Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19, Clin Exp Rheumatol
Siddiqi, Mehra, COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transpl
Strohbehn, COVIDOSE: low-dose tocilizumab in the treatment of Covid-19, medRxiv
Tanaka, Narazaki, Kishimoto, IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol
Taneri, Anemia and iron metabolism in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur J Epidemiol
Tsai, Impact of tocilizumab administration on mortality in severe COVID-19, Sci Rep
Tseng, Selenium is inversely associated with interleukin-6 in the elderly, J Nutr Health Aging
Valle, An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat Med
Vatansever, Becer, Relationship between IL-6 and COVID-19: to be considered during treatment, Future Virol
Wang, Possible immunity, inflammation, and oxidative stress mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease in COVID-19 patients, Clin Neurol Neurosurg
Williams, Meyer, Desferrioxamine as immunomodulatory agent during microorganism infection, Curr Pharm Des
Xu, Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Zhang, COVID-19-induced neurological symptoms: focus on the role of metal ions, Inflammopharmacology
Zhang, Selenium and selenoproteins in viral infection with potential relevance to COVID-19, Redox Biol
Zhao, Cytokine storm and immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19: Role of chloroquine and anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies, Int J Antimicrob Agents
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2",
"ISSN": [
"1745-6215"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In the severe forms of COVID-19 and many other infectious diseases, the patients develop a cytokine storm syndrome (CSS) where pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α play a key role in the development of this serious process. Selenium and iron are two important trace minerals, and their metabolism is tightly connected to immune system function. Numerous studies highlight the role of selenium and iron metabolism changes in the procedure of COVID-19 inflammation. The immunomodulator effect of nanomedicines that are synthesized based on nanochelating technology has been proved in previous studies. In the present study, the effects of the combination of BCc1(with iron-chelating property) and Hep-S (containing selenium) nanomedicines on mentioned cytokines levels in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 patients were evaluated.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Laboratory-confirmed moderate COVID-19 patients were enrolled to participate in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in two separate groups: combination of BCc1 and Hep-S (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic> = 62) (treatment) or placebo (<jats:italic>N</jats:italic> = 60) (placebo). The blood samples were taken before medications on day zero, at discharge, and 28 days after consumption to measure hematological and biochemical parameters and cytokine levels. The clinical symptoms of all the patients were recorded according to an assessment questionnaire before the start of the treatment and on days 3 and discharge day.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The results revealed that consumption of the nanomedicines led to a significant decrease in the mean level of IL-6 cytokine, and at the end of the study, there was a 77% downward trend in IL-6 in the nanomedicine group, while an 18% increase in the placebo group (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> < 0.05). In addition, the patients in the nanomedicines group had lower TNF-α levels; accordingly, there was a 21% decrease in TNF-α level in the treatment group, while a 31% increase in this cytokine level in the placebo was observed (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> > 0.05). On the other hand, in nanomedicines treated groups, clinical scores of coughing, fatigue, and need for oxygen therapy improved.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In conclusion, the combination of BCc1 and Hep-S inhibits IL-6 as a highly important and well-known cytokine in COVID-19 pathophysiology and presents a promising view for immunomodulation that can manage CSS.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://en.irct.ir/trial/48049\">RCT20170731035423N2</jats:ext-link>. Registered on June 12, 2020.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"7624"
],
"article-number": "720",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "8 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "5 September 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "11 November 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "This trial is registered with Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials; Reg. No. IRCT20170731035423N2. It has also received the ethic approval of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran; Reg. No. IR.SBMU.CRC.REC.1399.001. Consent to participate is not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Mohammad Hassan Nazaran is the owner of Nanochelating Technology. The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hafizi",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalanaky",
"given": "Somayeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fakharzadeh",
"given": "Saideh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karimi",
"given": "Pegah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fakharian",
"given": "Atefeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lookzadeh",
"given": "Somayeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mortaz",
"given": "Esmaeil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirenayat",
"given": "Maryam Sadat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heshmatnia",
"given": "Jalal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karam",
"given": "Mehrdad Bakhshayesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zamani",
"given": "Homa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nadji",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toutkaboni",
"given": "Mihan Pourabdollah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oraee-Yazdani",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbari",
"given": "Mohammad Esmaeil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamaati",
"given": "Hamidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9413-2295",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nazaran",
"given": "Mohammad Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Trials",
"container-title-short": "Trials",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-11T08:02:00Z",
"timestamp": 1699689720000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-11T20:02:45Z",
"timestamp": 1699732965000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-11T20:41:15Z",
"timestamp": 1699735275155
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1699660800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1699660800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Organization, W.H",
"key": "7624_CR1",
"unstructured": "Organization, W.H. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020. World Health Organization; 2020.",
"volume-title": "Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"author": "K Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "875",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "7624_CR2",
"unstructured": "Kuba K, et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat Med. 2005;11(8):875–9.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature12005",
"author": "VS Raj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "251",
"issue": "7440",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "7624_CR3",
"unstructured": "Raj VS, et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature. 2013;495(7440):251–4.",
"volume": "495",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"author": "R Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "529",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathol",
"key": "7624_CR4",
"unstructured": "Channappanavar R, Perlman S. Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol. 2017;39(5):529–39.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"author": "P Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "7624_CR5",
"unstructured": "Mehta P, et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020;395(10229):1033–4.",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Atal",
"first-page": "223",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceut Med",
"key": "7624_CR6",
"unstructured": "Atal S, Fatima Z. IL-6 inhibitors in the treatment of serious COVID-19: a promising therapy? Pharmaceut Med. 2020;34(4):223–31.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0168",
"author": "HS Vatansever",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "817",
"journal-title": "Future Virol",
"key": "7624_CR7",
"unstructured": "Vatansever HS, Becer E. Relationship between IL-6 and COVID-19: to be considered during treatment. Future Virol. 2020;15:817.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a016295",
"author": "T Tanaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol",
"key": "7624_CR8",
"unstructured": "Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014;6(10): a016295.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.addr.2020.12.011",
"author": "JY Chung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv Drug Deliv Rev",
"key": "7624_CR9",
"unstructured": "Chung JY, Thone MN, Kwon YJ. COVID-19 vaccines: the status and perspectives in delivery points of view. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;170:1–25.",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000025532",
"author": "R Qiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore)",
"key": "7624_CR10",
"unstructured": "Qiu R, et al. The therapeutic effect and safety of the drugs for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(16): e25532.",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-78697-1",
"author": "I Aygun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21508",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "7624_CR11",
"unstructured": "Aygun I, Kaya M, Alhajj R. Identifying side effects of commonly used drugs in the treatment of Covid 19. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21508.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1930",
"author": "H Drakesmith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "541",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "7624_CR12",
"unstructured": "Drakesmith H, Prentice A. Viral infection and iron metabolism. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2008;6(7):541–52.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.27709",
"author": "JM McDermid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "225",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "7624_CR13",
"unstructured": "McDermid JM, et al. Mortality in HIV infection is independently predicted by host iron status and SLC11A1 and HP genotypes, with new evidence of a gene-nutrient interaction. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;90(1):225–33.",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00678-5",
"author": "PE Taneri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "763",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol",
"key": "7624_CR14",
"unstructured": "Taneri PE, et al. Anemia and iron metabolism in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2020;35(8):763–73.",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.11.033",
"author": "Y Lv",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3462",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "7624_CR15",
"unstructured": "Lv Y, et al. Association between iron status and the risk of adverse outcomes in COVID-19. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(5):3462–9.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091203",
"author": "JC Avery",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1023",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "7624_CR16",
"unstructured": "Avery JC, Hoffmann PR. Selenium, selenoproteins, and immunity. Nutrients. 2018;10(9):1023.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.200700330",
"author": "PR Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1273",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Mol Nutr Food Res",
"key": "7624_CR17",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann PR, Berry MJ. The influence of selenium on immune responses. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2008;52(11):1273–80.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4",
"author": "S Khatiwada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Nutr Rep",
"key": "7624_CR18",
"unstructured": "Khatiwada S, Subedi A. A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Curr Nutr Rep. 2021;10(2):125–36.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-020-2773-6",
"author": "R Karimi-Sales",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "48",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Pharm Res",
"key": "7624_CR19",
"unstructured": "Karimi-Sales R, et al. Neuroprotective effect of new nanochelating-based nano complex, ALZc3, against Abeta (1–42)-induced toxicity in rat: a comparison with memantine. Pharm Res. 2020;37(3):48.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126547",
"author": "S Fakharzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Trace Elem Med Biol",
"key": "7624_CR20",
"unstructured": "Fakharzadeh S, et al. DIBc nano metal-organic framework improves biochemical and pathological parameters of experimental chronic kidney disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020;61: 126547.",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12951-019-0484-0",
"author": "M Hafizi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "52",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Nanobiotechnol",
"key": "7624_CR21",
"unstructured": "Hafizi M, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled investigation of BCc1 nanomedicine effect on survival and quality of life in metastatic and non-metastatic gastric cancer patients. J Nanobiotechnol. 2019;17(1):52.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DMSO.S240757",
"author": "S Fakharzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1179",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes",
"key": "7624_CR22",
"unstructured": "Fakharzadeh S, et al. BCc1 nanomedicine therapeutic effects in streptozotocin and high-fat diet induced diabetic kidney disease. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020;13:1179–88.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Fakharzadeh",
"first-page": "3841",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomed",
"key": "7624_CR23",
"unstructured": "Fakharzadeh S, et al. The therapeutic effects of MSc1 nanocomplex, synthesized by nanochelating technology, on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitic C57/BL6 mice. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9:3841–53.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.03.030",
"author": "S Fakharzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2591",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "7624_CR24",
"unstructured": "Fakharzadeh S, et al. The new nano-complex, Hep-c, improves the immunogenicity of the hepatitis B vaccine. Vaccine. 2013;31(22):2591–7.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "7624_CR25",
"unstructured": "MH, N., Chelate compounds. United States patent US 8288587 B2. Oct 16, 2012. https://patents.google.com/patent/US8288587B2/en."
},
{
"author": "S Kalanaky",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Drug Des Devel Ther",
"key": "7624_CR26",
"unstructured": "Kalanaky S, et al. BCc1, the novel antineoplastic nanocomplex, showed potent anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016;10:59–70.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108227",
"author": "H Azizi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "7624_CR27",
"unstructured": "Azizi H, et al. Pentoxifylline effects on hospitalized patients with COVID19: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;101: 108227.",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12192-021-01197-2",
"author": "M Hernandez-Cedeño",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "Cell Stress Chaperones",
"key": "7624_CR28",
"unstructured": "Hernandez-Cedeño M, et al. CIGB-258, a peptide derived from human heat-shock protein 60, decreases hyperinflammation in COVID-19 patients. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2021;26:515–25.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.02037",
"author": "E Mortaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2037",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "7624_CR29",
"unstructured": "Mortaz E, et al. The immune response and immunopathology of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2037.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2013.10.001",
"author": "F Fiteni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Visc Surg",
"key": "7624_CR30",
"unstructured": "Fiteni F, et al. Endpoints in cancer clinical trials. J Visc Surg. 2014;151(1):17–22.",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"author": "HK Siddiqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "405",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transpl",
"key": "7624_CR31",
"unstructured": "Siddiqi HK, Mehra MR. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transpl. 2020;39(5):405–7.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30173-9",
"author": "G Guaraldi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e474",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "7624_CR32",
"unstructured": "Guaraldi G, et al. Tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(8):e474–84.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2005615117",
"author": "X Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10970",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "7624_CR33",
"unstructured": "Xu X, et al. Effective treatment of severe COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(20):10970–5.",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Sciascia",
"first-page": "529",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Rheumatol",
"key": "7624_CR34",
"unstructured": "Sciascia S, et al. Pilot prospective open, single-arm multicentre study on off-label use of tocilizumab in patients with severe COVID-19. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2020;38(3):529–32.",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clineuro.2020.106414",
"author": "H Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Neurol Neurosurg",
"key": "7624_CR35",
"unstructured": "Wang H, et al. Possible immunity, inflammation, and oxidative stress mechanisms of Alzheimer’s disease in COVID-19 patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2021;201: 106414.",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110102",
"author": "R Cecchini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "7624_CR36",
"unstructured": "Cecchini R, Cecchini AL. SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression. Med Hypotheses. 2020;143: 110102.",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101715",
"author": "J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "7624_CR37",
"unstructured": "Zhang J, et al. Selenium and selenoproteins in viral infection with potential relevance to COVID-19. Redox Biol. 2020;37: 101715.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2021.110984",
"author": "Q Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Environ Res",
"key": "7624_CR38",
"unstructured": "Liu Q, et al. Selenium (Se) plays a key role in the biological effects of some viruses: Implications for COVID-19. Environ Res. 2021;196: 110984.",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C3MT00347G",
"author": "DB Kell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "748",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Metallomics",
"key": "7624_CR39",
"unstructured": "Kell DB, Pretorius E. Serum ferritin is an important inflammatory disease marker, as it is mainly a leakage product from damaged cells. Metallomics. 2014;6(4):748–73.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.110",
"author": "M Edeas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "7624_CR40",
"unstructured": "Edeas M, Saleh J, Peyssonnaux C. Iron: Innocent bystander or vicious culprit in COVID-19 pathogenesis? Int J Infect Dis. 2020;97:303–5.",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxx031",
"author": "KF Kernan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "401",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Int Immunol",
"key": "7624_CR41",
"unstructured": "Kernan KF, Carcillo JA. Hyperferritinemia and inflammation. Int Immunol. 2017;29(9):401–9.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154260",
"author": "M Dalamaga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "7624_CR42",
"unstructured": "Dalamaga M, Karampela I, Mantzoros CS. Commentary: could iron chelators prove to be useful as an adjunct to COVID-19 treatment regimens? Metabolism. 2020;108: 154260.",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000025832",
"author": "V Birlutiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore)",
"key": "7624_CR43",
"unstructured": "Birlutiu V, Birlutiu RM, Chicea L. Off-label tocilizumab and adjuvant iron chelator effectiveness in a group of severe COVID-19 pneumonia patients: a single center experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100(18): e25832.",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules16086992",
"author": "F Berlutti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6992",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "7624_CR44",
"unstructured": "Berlutti F, et al. Antiviral properties of lactoferrin–a natural immunity molecule. Molecules. 2011;16(8):6992–7018.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0154842",
"author": "D Saxena",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "7624_CR45",
"unstructured": "Saxena D, et al. Drug-based lead discovery: the novel ablative antiretroviral profile of deferiprone in HIV-1-infected cells and in HIV-infected treatment-naive subjects of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized exploratory trial. PLoS ONE. 2016;11(5): e0154842.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5662/wjm.v6.i1.1",
"author": "CN Kontoghiorghe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "World J Methodol",
"key": "7624_CR46",
"unstructured": "Kontoghiorghe CN, Kontoghiorghes GJ. New developments and controversies in iron metabolism and iron chelation therapy. World J Methodol. 2016;6(1):1–19.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acscentsci.9b00284",
"author": "S Abbina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "917",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "ACS Cent Sci",
"key": "7624_CR47",
"unstructured": "Abbina S, et al. Design of safe nanotherapeutics for the excretion of excess systemic toxic iron. ACS Cent Sci. 2019;5(5):917–26.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "7624_CR48",
"unstructured": "Maryam Hafizi , S.K., Hassan Moaiery , Maryam Khayamzadeh , Sajad Noorian, An investigation on the effect of BCc1 nanomedicine on gastric cancer patients using EORTC QLQ-STO30 questionnaire. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/337481750_An_Investigation_on_the_Effect_of_BCc1_Nanomedicine_on_Gastric_Cancer_Patients_Using_EORTC_QLQSTO30_Questionnaire."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"author": "DM Del Valle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1636",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "7624_CR49",
"unstructured": "Del Valle DM, et al. An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival. Nat Med. 2020;26(10):1636–43.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110698",
"author": "E Nasonov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "7624_CR50",
"unstructured": "Nasonov E, Samsonov M. The role of Interleukin 6 inhibitors in therapy of severe COVID-19. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110698.",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.571597",
"author": "D Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "7624_CR51",
"unstructured": "Liu D, et al. Tocilizumab: the key to stop coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)? Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:571597.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105982",
"author": "M Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "7624_CR52",
"unstructured": "Zhao M. Cytokine storm and immunomodulatory therapy in COVID-19: Role of chloroquine and anti-IL-6 monoclonal antibodies. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;55(6):105982.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4317/medoral.19087",
"author": "A Bascones-Martinez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e24",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal",
"key": "7624_CR53",
"unstructured": "Bascones-Martinez A, et al. Immunomodulatory drugs: oral and systemic adverse effects. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2014;19(1):e24–31.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd3974",
"author": "JG Sathish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "306",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discov",
"key": "7624_CR54",
"unstructured": "Sathish JG, et al. Challenges and approaches for the development of safer immunomodulatory biologics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(4):306–24.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "7624_CR55",
"unstructured": "Strohbehn GW, et al. COVIDOSE: low-dose tocilizumab in the treatment of Covid-19. medRxiv, 2020. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7386518/."
},
{
"key": "7624_CR56",
"unstructured": "Roche provides an update on the phase III COVACTA trial of Actemra/RoActemra in hospitalised patients with severe COVID-19 associated pneumonia. 2020; Available from: https://www.roche.com/investors/updates/inv-update-2020-07-29."
},
{
"key": "7624_CR57",
"unstructured": "A Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia (COVACTA). Identifier NCT04320615. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Tocilizumab in Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia. 2020. Jul 31 [cited Last accessed on 2020 Aug 04; Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04320615."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-76187-y",
"author": "A Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19131",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "7624_CR58",
"unstructured": "Tsai A, et al. Impact of tocilizumab administration on mortality in severe COVID-19. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):19131.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25900",
"author": "FA Lagunas-Rangel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1789",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "7624_CR59",
"unstructured": "Lagunas-Rangel FA, Chavez-Valencia V. High IL-6/IFN-gamma ratio could be associated with severe disease in COVID-19 patients. J Med Virol. 2020;92(10):1789–90.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Y Alimohamadi",
"first-page": "E304",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Prev Med Hyg",
"key": "7624_CR60",
"unstructured": "Alimohamadi Y, et al. Determine the most common clinical symptoms in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prev Med Hyg. 2020;61(3):E304.",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cdnut.2023.100044",
"author": "DY Larvie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Dev Nutr",
"key": "7624_CR61",
"unstructured": "Larvie DY, et al. COVID-19 severity is associated with selenium intake among young adults with low selenium and zinc intake in North Carolina. Curr Dev Nutr. 2023;7(3): 100044.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12598-021-01894-y",
"author": "Y-Q Ni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Rare Met",
"key": "7624_CR62",
"unstructured": "Ni Y-Q, et al. Potential metal-related strategies for prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Rare Met. 2022;41(4):1129–41.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-023-01176-2",
"author": "YY Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "7624_CR63",
"unstructured": "Zhang YY, et al. COVID-19-induced neurological symptoms: focus on the role of metal ions. Inflammopharmacology. 2023;31:1–21.",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138161209787846801",
"author": "A Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharm Des",
"key": "7624_CR64",
"unstructured": "Williams A, Meyer D. Desferrioxamine as immunomodulatory agent during microorganism infection. Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(11):1261–8.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08820139.2018.1496098",
"author": "A Mahmoodpoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "147",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Immunol Invest",
"key": "7624_CR65",
"unstructured": "Mahmoodpoor A, et al. The effect of intravenous selenium on oxidative stress in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Immunol Invest. 2019;48(2):147–59.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-012-0376-6",
"author": "CK Tseng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "280",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Health Aging",
"key": "7624_CR66",
"unstructured": "Tseng CK, et al. Selenium is inversely associated with interleukin-6 in the elderly. J Nutr Health Aging. 2013;17(3):280–4.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.017",
"author": "I Jaspers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1826",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Free Radic Biol Med",
"key": "7624_CR67",
"unstructured": "Jaspers I, et al. Selenium deficiency alters epithelial cell morphology and responses to influenza. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;42(12):1826–37.",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-011-2212-6",
"author": "W Manzanares",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1120",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "7624_CR68",
"unstructured": "Manzanares W, et al. High-dose selenium reduces ventilator-associated pneumonia and illness severity in critically ill patients with systemic inflammation. Intensive Care Med. 2011;37(7):1120–7.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJN.S196050",
"author": "S Fakharzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2145",
"journal-title": "Int J Nanomed",
"key": "7624_CR69",
"unstructured": "Fakharzadeh S, et al. DIBc, a nanochelating-based nano metal-organic framework, shows anti-diabetic effects in high-fat diet and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:2145–56.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 69,
"references-count": 69,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-023-07624-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Beneficial effects of the combination of BCc1 and Hep-S nanochelating-based medicines on IL-6 in hospitalized moderate COVID-19 adult patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "24"
}