Does behavior mediate the effect of weather on SARS-CoV-2 transmission? Evidence from cell-phone data
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0305323, Jun 2024
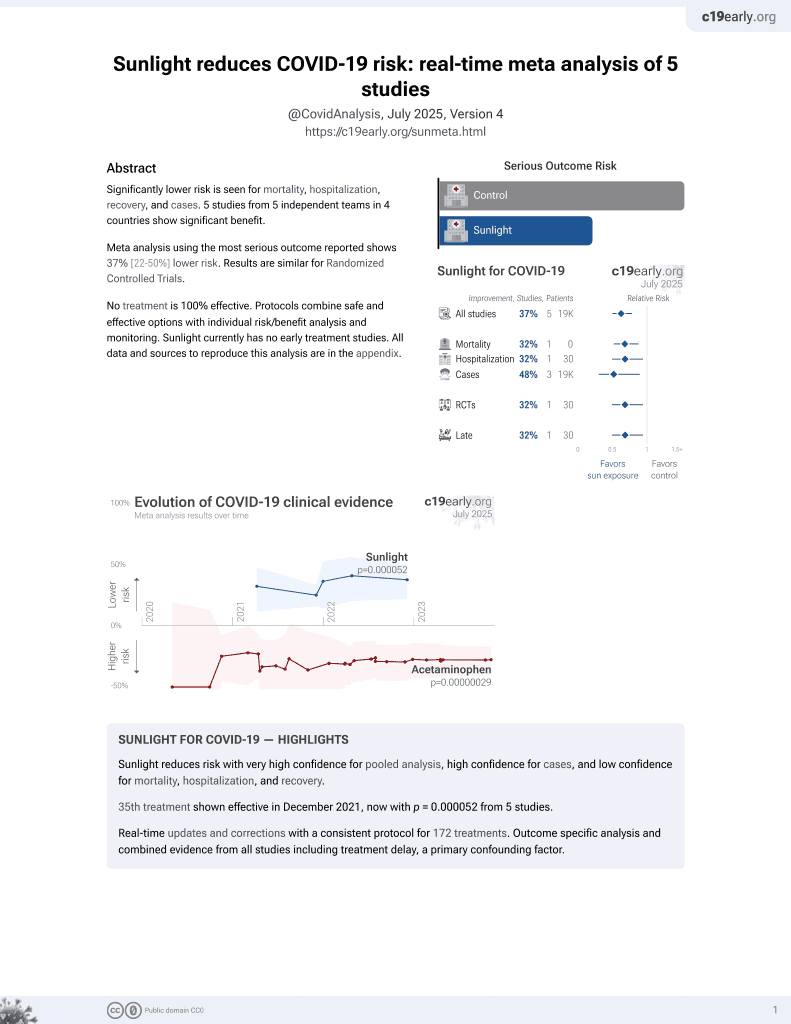
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
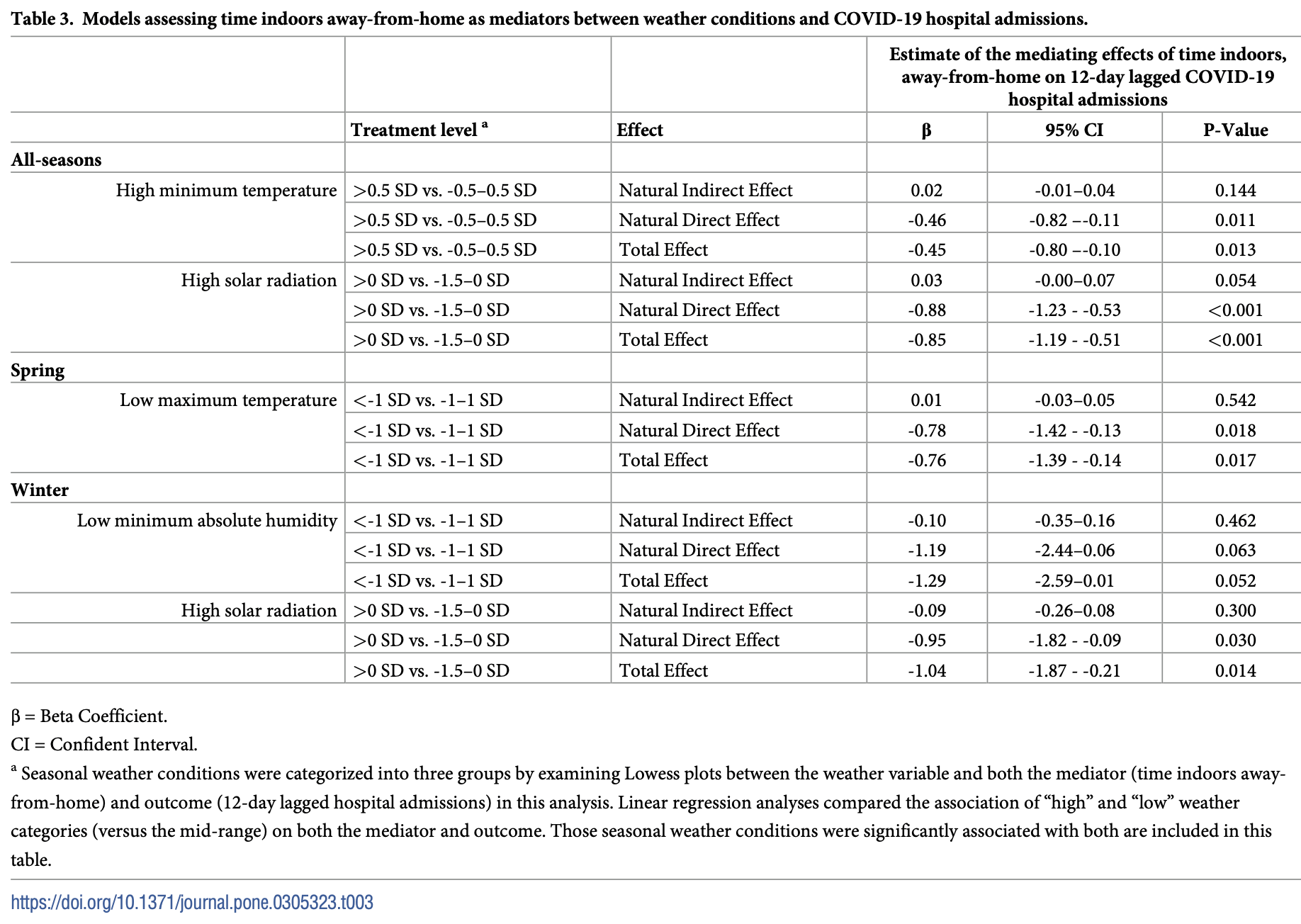
Mediation analysis of meteorological, cell-phone mobility, and building footprint data from five Colorado counties, showing that weather directly impacted COVID-19 hospitalizations, while the indirect effect via changes in time spent indoors away from home was minimal. Above average minimum temperature and solar radiation across all seasons, below average maximum temperature in the spring, and above average solar radiation in the winter were directly associated with decreased COVID-19 hospitalizations.
Grover et al., 21 Jun 2024, USA, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 4 March, 2020 - 31 January, 2021.
Contact: elizabeth.carlton@cuanschutz.edu.
Does behavior mediate the effect of weather on SARS-CoV-2 transmission? evidence from cell-phone data
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0305323
There is growing evidence that weather alters SARS-CoV-2 transmission, but it remains unclear what drives the phenomenon. One prevailing hypothesis is that people spend more time indoors in cooler weather, leading to increased spread of SARS-CoV-2 related to time spent in confined spaces and close contact with others. However, the evidence in support of that hypothesis is limited and, at times, conflicting. We use a mediation framework, and combine daily weather, COVID-19 hospital surveillance, cellphone-based mobility data and building footprints to estimate the relationship between daily indoor and outdoor weather conditions, mobility, and COVID-19 hospitalizations. We quantify the direct health impacts of weather on COVID-19 hospitalizations and the indirect effects of weather via time spent indoors away-from-home on COVID-19 hospitalizations within five Colorado counties between March 4 th 2020 and January 31 st 2021. We also evaluated the evidence for seasonal effect modification by comparing the results of all-season (using season as a covariate) to season-stratified models. Four weather conditions were associated with both time spent indoors away-from-home and 12-day lagged COVID-19 hospital admissions in one or more season: high minimum temperature (all-season), low maximum temperature (spring), low minimum absolute humidity (winter), and high solar radiation (all-season & winter). In our mediation analyses, we found evidence that changes in 12-day lagged hospital admissions were primarily via the direct effects of weather conditions, rather than via indirect effects by which weather changes time spent indoors away-from-home. Our findings do not support the hypothesis that weather impacted SARS-CoV-2 transmission via changes in mobility patterns during the first year of the pandemic. Rather, weather appears to have impacted SARS-CoV-2 transmission primarily via mechanisms other than human movement. We recommend further analysis of this phenomenon to determine whether these findings generalize to current SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics, as well as other seasonal respiratory pathogens.
Supporting information
S1 Table. Detailed regression results between control variables and categorical weather variables on time indoors away-from-home, and 12-day lagged hospitalizations. (DOCX)
S2 Table. Sensitivity analysis results of the linear regression results using categorical weather conditions on time at home and COVID hospitalizations. (DOCX)
S3 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing mediation results of categorical weather conditions and time at home as the mediator. (DOCX)
S4 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing linear regression results for continuous weather conditions on time indoors and away-from-home and COVID hospitalizations. (DOCX)
S5 Table. Sensitivity analysis results for the mediation models using continuous weather variables and time indoors away-from-home as the mediator. (DOCX)
S6 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing linear regression results of continuous weather conditions on time at home, and on hospitalizations. (DOCX)
S7 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing mediation results assessing time at home as a mediator between continuous weather conditions and COVID hospital admissions. (DOCX)
S8 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing mediation results without hospitalization growth, using categorical weather conditions and time indoors away from home as the mediator. (DOCX)
S9 Table. Sensitivity analysis detailing mediation results without hospitalization growth, using categorical weather conditions and time at home as the mediator...
References
Abatzoglou, Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling, International Journal of Climatology, doi:10.1002/joc.3413
Adekunle, Tella, Oyesiku, Oseni, Spatio-temporal analysis of meteorological factors in abating the spread of COVID-19 in Africa, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04749
Alkhowailed, Shariq, Alqossayir, Alzahrani, Rasheed et al., Impact of meteorological parameters on COVID-19 pandemic: A comprehensive study from Saudi Arabia, Inform Med Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2020.100418
Anice, Steel, Mubareka, Palese, High Temperature (30˚C) Blocks Aerosol but Not Contact Transmission of Influenza Virus, Journal of virology, doi:10.1128/jvi.00325-08
Buchwald, Bayham, Adams, Bortz, Colborn et al., Estimating the Impact of Statewide Policies to Reduce Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Real Time, Colorado, USA, Emerging Infectious Disease journal, doi:10.3201/eid2709.204167
Bulfone, Malekinejad, Rutherford, Razani, Outdoor Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review, The Journal of infectious diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa742
Byun, Heo, Kim, Kim, Lee, Is coronavirus disease (COVID-19) seasonal? A critical analysis of empirical and epidemiological studies at global and local scales, Environmental research, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.110972
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiology and infection, doi:10.1017/S0950268806007175
Carleton, Cornetet, Huybers, Meng, Proctor, Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.2012370118
Cleveland, Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots, Journal of the American Statistical Association, doi:10.1080/01621459.1979.10481038
Crawford, Jones, Cartter, Dean, Warren et al., Impact of close interpersonal contact on COVID-19 incidence: Evidence from 1 year of mobile device data, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abi5499
Damette, Mathonnat, Goutte, Meteorological factors against COVID-19 and the role of human mobility, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252405
Donaldson, Seemungal, Jeffries, Wedzicha, Effect of temperature on lung function and symptoms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, The European respiratory journal, doi:10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.13d25.x
Eames, Tilston, Brooks-Pollock, Edmunds, Measured dynamic social contact patterns explain the spread of H1N1v influenza, PLoS Comput Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002425
Even-Tzur, Zaretsky, Grinberg, Davidovich, Kloog et al., Climate chamber for environmentally controlled laboratory airflow experiments, Technology and health care: official journal of the European Society for Engineering and Medicine, doi:10.3233/THC-2010-0577
Foxman, Storer, Fitzgerald, Wasik, Hou et al., Temperature-dependent innate defense against the common cold virus limits viral replication at warm temperature in mouse airway cells, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.1411030112
Guo, Bo, Lin, Li, Zeng et al., Meteorological factors and COVID-19 incidence in 190 countries: An observational study, The Science of the total environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143783
Gupta, Banerjee, Das, Significance of geographical factors to the COVID-19 outbreak in India, Model Earth Syst Environ, doi:10.1007/s40808-020-00838-2
Jackson, Hart, Mcculloch, Adler, Brandstetter et al., Effects of weather-related social distancing on city-scale transmission of respiratory viruses: a retrospective cohort study, BMC infectious diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06028-4
Jamshidi, Baniasad, Niyogi, Global to USA County Scale Analysis of Weather, Urban Density, Mobility, Homestay, and Mask Use on COVID-19, International journal of environmental research and public health, doi:10.3390/ijerph17217847
Kang, Ellgen, Kulstad, Possible effects of air temperature on COVID-19 disease severity and transmission rates, Journal of medical virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27042
Klepeis, Nelson, Ott, Robinson, Tsang et al., The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): a resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants, Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology, doi:10.1038/sj.jea.7500165
Klingberg, Olero ¨d, Konar, Petzold, Hammarsten, Seasonal variations in serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in a Swedish cohort, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-015-0548-3
Kudo, Song, Yockey, Rakib, Wong et al., Low ambient humidity impairs barrier function and innate resistance against influenza infection, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.1902840116
Kulkarni, Khandait, Narlawar, Rathod, Mamtani, Independent association of meteorological characteristics with initial spread of Covid-19 in India. The Science of the total environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142801
Leech, Nelson, Burnett, Aaron, Raizenne, It's about time: a comparison of Canadian and American time-activity patterns, Journal of exposure analysis and environmental epidemiology, doi:10.1038/sj.jea.7500244
Li, Li, Yang, Kolosov, Perelman et al., Cold temperature induces mucin hypersecretion from normal human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro through a transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8)-mediated mechanism, The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2011.04.032
Lin, Hamilton, Gatalo, Haghpanah, Igusa et al., Investigating the effects of absolute humidity and movement on COVID-19 seasonality in the United States, Scientific reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-19898-8
Lowen, Mubareka, Steel, Palese, Influenza Virus Transmission Is Dependent on Relative Humidity and Temperature, PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151
Mackinnon, Krull, Lockwood, Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect, Prevention science: the official journal of the Society for Prevention Research, doi:10.1023/a:1026595011371
Magurano, Baggieri, Marchi, Rezza, Nicoletti, SARS-CoV-2 infection: the environmental endurance of the virus can be influenced by the increase of temperature, Clinical microbiology and infection: the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.034
Mcclymont, Hu, Weather Variability and COVID-19 Transmission: A Review of Recent Research, International journal of environmental research and public health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18020396
Menebo, Temperature and precipitation associate with Covid-19 new daily cases: A correlation study between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Oslo, Norway, The Science of the total environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139659
Moriyama, Hugentobler, Iwasaki, Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections, Annual review of virology, doi:10.1146/annurev-virology-012420-022445
Mossong, Hens, Jit, Beutels, Auranen et al., Social contacts and mixing patterns relevant to the spread of infectious diseases, PLoS medicine, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0050074
Paireau, Charpignon, Larrieu, Calba, Hoze et al., Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France, BMC infectious diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1
Pani, Lin, Ravindrababu, Association of COVID-19 pandemic with meteorological parameters over Singapore. The Science of the total environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140112
Polozov, Bezrukov, Gawrisch, Zimmerberg, Progressive ordering with decreasing temperature of the phospholipids of influenza virus, Nat Chem Biol, doi:10.1038/nchembio.77
Purpleair, PurpleAir Sensors Functional Overview
Qian, Miao, Liu, Zheng, Luo et al., Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Indoor Air, doi:10.1111/ina.12766
Ratnesar-Shumate, Williams, Green, Krause, Holland et al., Simulated Sunlight Rapidly Inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on Surfaces, The Journal of infectious diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa274
Romero Starke, Mauer, Karskens, Pretzsch, Reissig et al., The Effect of Ambient Environmental Conditions on COVID-19 Mortality: A Systematic Review, International journal of environmental research and public health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18126665
Rosario, Mutz, Bernardes, Ca, Relationship between COVID-19 and weather: Case study in a tropical country, International journal of hygiene and environmental health, doi:10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113587
Sagripanti, Lytle, Estimated Inactivation of Coronaviruses by Solar Radiation With Special Reference to COVID-19, Photochem Photobiol, doi:10.1111/php.13293
Schober, Boer, Schwarte, Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation, Anesthesia & Analgesia, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864
Shao, Xie, Zhu, Mediation by human mobility of the association between temperature and COVID-19 transmission rate, Environmental research, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2020.110608
Smith, Flaxman, Gallinat, Kinosian, Stemkovski et al., Temperature and population density influence SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the absence of nonpharmaceutical interventions, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, doi:10.1073/pnas.2019284118
Sobral, Duarte, Da, Sobral, Marinho et al., Association between climate variables and global transmission oF SARS-CoV-2. The Science of the total environment, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138997
Sposato, Serafini, Simoncini, Croci, Guidoni et al., COVID-19 severity appears to be reduced in spring/summer, Epidemiologia e prevenzione, doi:10.19191/ep23.1.A503.016
Statacorp, Stata: Causal Inference and Treatment-Effects Estimation Reference Manual
Tellier, Aerosol transmission of influenza A virus: a review of new studies, J R Soc Interface, doi:10.1098/rsif.2009.0302.focus
Vanderweele, Explanation in causal inference: methods for mediation and interaction
Weaver, Head, Gould, Carlton, Remais, Environmental Factors Influencing COVID-19 Incidence and Severity, Annual review of public health, doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-052120-101420
Wiemken, Khan, Puzniak, Yang, Simmering et al., Seasonal trends in COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and mortality in the United States and Europe, Scientific reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31057-1
Willem, Van Kerckhove, Chao, Hens, Beutels, A Nice Day for an Infection? Weather Conditions and Social Contact Patterns Relevant to Influenza Transmission, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0048695
Wu, Huang, Tu, Bi, Chen et al., Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Zhuhai, China, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa557
Wu, Kang, Guo, Liu, Liu et al., Incubation Period of COVID-19 Caused by Unique SARS-CoV-2 Strains: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.28008
Yang, Elankumaran, Marr, Relationship between humidity and influenza A viability in droplets and implications for influenza's seasonality, PloS one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046789
Zeng, Santhya, Soong, Malhotra, Pushparajah et al., Serial Intervals and Incubation Periods of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants, Singapore, Emerging Infectious Disease journal, doi:10.3201/eid2904.220854
Zhao, Zhu, Xie, Zheng, Luo et al., The moderating effect of solar radiation on the association between human mobility and COVID-19 infection in Europe, Environmental science and pollution research international, doi:10.1007/s11356-021-15738-w
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0305323",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305323",
"abstract": "<jats:p>There is growing evidence that weather alters SARS-CoV-2 transmission, but it remains unclear what drives the phenomenon. One prevailing hypothesis is that people spend more time indoors in cooler weather, leading to increased spread of SARS-CoV-2 related to time spent in confined spaces and close contact with others. However, the evidence in support of that hypothesis is limited and, at times, conflicting. We use a mediation framework, and combine daily weather, COVID-19 hospital surveillance, cellphone-based mobility data and building footprints to estimate the relationship between daily indoor and outdoor weather conditions, mobility, and COVID-19 hospitalizations. We quantify the direct health impacts of weather on COVID-19 hospitalizations and the indirect effects of weather via time spent indoors away-from-home on COVID-19 hospitalizations within five Colorado counties between March 4<jats:sup>th</jats:sup> 2020 and January 31<jats:sup>st</jats:sup> 2021. We also evaluated the evidence for seasonal effect modification by comparing the results of all-season (using season as a covariate) to season-stratified models. Four weather conditions were associated with both time spent indoors away-from-home and 12-day lagged COVID-19 hospital admissions in one or more season: high minimum temperature (all-season), low maximum temperature (spring), low minimum absolute humidity (winter), and high solar radiation (all-season & winter). In our mediation analyses, we found evidence that changes in 12-day lagged hospital admissions were primarily via the direct effects of weather conditions, rather than via indirect effects by which weather changes time spent indoors away-from-home. Our findings do not support the hypothesis that weather impacted SARS-CoV-2 transmission via changes in mobility patterns during the first year of the pandemic. Rather, weather appears to have impacted SARS-CoV-2 transmission primarily via mechanisms other than human movement. We recommend further analysis of this phenomenon to determine whether these findings generalize to current SARS-CoV-2 transmission dynamics, as well as other seasonal respiratory pathogens.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8845-1591",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Grover",
"given": "Elise N.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Buchwald",
"given": "Andrea G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6618-1316",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "Debashis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8664-9606",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Carlton",
"given": "Elizabeth J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-21T17:28:03Z",
"timestamp": 1718990883000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-21T17:29:23Z",
"timestamp": 1718990963000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Rajeev",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"MIDASSUP2020-3"
],
"name": "MIDAS Coordination Center"
},
{
"award": [
"NU38OT000297"
],
"name": "The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Council of State and Territorial Epidemiologists"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000057",
"award": [
"3U24GM132013-02S2"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institute of General Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-22T00:27:54Z",
"timestamp": 1719016074244
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1718928000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305323",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0305323",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Seasonality of Respiratory Viral Infections",
"author": "M Moriyama",
"journal-title": "Annual review of virology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27042",
"article-title": "Possible effects of air temperature on COVID-19 disease severity and transmission rates",
"author": "D Kang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5358",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Journal of medical virology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref002",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08106-1",
"article-title": "Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions, weather, vaccination, and variants on COVID-19 transmission across departments in France",
"author": "J Paireau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "190",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC infectious diseases",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref003",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 severity appears to be reduced in spring/summer",
"author": "B Sposato",
"first-page": "34",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Epidemiologia e prevenzione",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref004",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-023-31057-1",
"article-title": "Seasonal trends in COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations, and mortality in the United States and Europe",
"author": "TL Wiemken",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3886",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific reports",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref005",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-publhealth-052120-101420",
"article-title": "Environmental Factors Influencing COVID-19 Incidence and Severity",
"author": "AK Weaver",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Annual review of public health",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref006",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18020396",
"article-title": "Weather Variability and COVID-19 Transmission: A Review of Recent Research",
"author": "H McClymont",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "International journal of environmental research and public health",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref007",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18126665",
"article-title": "The Effect of Ambient Environmental Conditions on COVID-19 Mortality: A Systematic Review",
"author": "K Romero Starke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "International journal of environmental research and public health",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref008",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.jea.7500165",
"article-title": "The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): a resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants",
"author": "NE Klepeis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref009",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "It’s about time: a comparison of Canadian and American time-activity patterns",
"author": "JA Leech",
"first-page": "427",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of exposure analysis and environmental epidemiology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref010",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002425",
"article-title": "Measured dynamic social contact patterns explain the spread of H1N1v influenza",
"author": "KT Eames",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1002425",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Comput Biol",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref011",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.0050074",
"article-title": "Social contacts and mixing patterns relevant to the spread of infectious diseases",
"author": "J Mossong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e74",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS medicine",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref012",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0048695",
"article-title": "A Nice Day for an Infection? Weather Conditions and Social Contact Patterns Relevant to Influenza Transmission",
"author": "L Willem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e48695",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref013",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06028-4",
"article-title": "Effects of weather-related social distancing on city-scale transmission of respiratory viruses: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "ML Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "335",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC infectious diseases",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref014",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph17217847",
"article-title": "Global to USA County Scale Analysis of Weather, Urban Density, Mobility, Homestay, and Mask Use on COVID-19",
"author": "S Jamshidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "International journal of environmental research and public health",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref015",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Temperature and population density influence SARS-CoV-2 transmission in the absence of nonpharmaceutical interventions",
"author": "TP Smith",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref016",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142801",
"article-title": "Independent association of meteorological characteristics with initial spread of Covid-19 in India",
"author": "H Kulkarni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "142801",
"journal-title": "The Science of the total environment",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref017",
"volume": "764",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.110608",
"article-title": "Mediation by human mobility of the association between temperature and COVID-19 transmission rate",
"author": "W Shao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110608",
"journal-title": "Environmental research",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref018",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0252405",
"article-title": "Meteorological factors against COVID-19 and the role of human mobility",
"author": "O Damette",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0252405",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref019",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1026595011371",
"article-title": "Equivalence of the mediation, confounding and suppression effect",
"author": "DP MacKinnon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Prevention science: the official journal of the Society for Prevention Research",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref020",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1411030112",
"article-title": "Temperature-dependent innate defense against the common cold virus limits viral replication at warm temperature in mouse airway cells",
"author": "EF Foxman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "827",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref021",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.13d25.x",
"article-title": "Effect of temperature on lung function and symptoms in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "GC Donaldson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "844",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "The European respiratory journal",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref022",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2011.04.032",
"article-title": "Cold temperature induces mucin hypersecretion from normal human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro through a transient receptor potential melastatin 8 (TRPM8)-mediated mechanism",
"author": "M Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "The Journal of allergy and clinical immunology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref023",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/THC-2010-0577",
"article-title": "Climate chamber for environmentally controlled laboratory airflow experiments",
"author": "N Even-Tzur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Technology and health care: official journal of the European Society for Engineering and Medicine",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref024",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1902840116",
"article-title": "Low ambient humidity impairs barrier function and innate resistance against influenza infection",
"author": "E Kudo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10905",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref025",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"article-title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"author": "JJ Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology and infection",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref026",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12020-015-0548-3",
"article-title": "Seasonal variations in serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels in a Swedish cohort",
"author": "E Klingberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "800",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref027",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Aerosol transmission of influenza A virus: a review of new studies",
"author": "R. Tellier",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J R Soc Interface",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref028",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00325-08",
"article-title": "High Temperature (30°C) Blocks Aerosol but Not Contact Transmission of Influenza Virus",
"author": "C Lowen Anice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5650",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Journal of virology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref029",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.0030151",
"article-title": "Influenza Virus Transmission Is Dependent on Relative Humidity and Temperature",
"author": "AC Lowen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e151",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLOS Pathogens",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref030",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0046789",
"article-title": "Relationship between humidity and influenza A viability in droplets and implications for influenza’s seasonality",
"author": "W Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e46789",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref031",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nchembio.77",
"article-title": "Progressive ordering with decreasing temperature of the phospholipids of influenza virus",
"author": "IV Polozov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "248",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Chem Biol",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref032",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.034",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection: the environmental endurance of the virus can be influenced by the increase of temperature",
"author": "F Magurano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clinical microbiology and infection: the official publication of the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref033",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa274",
"article-title": "Simulated Sunlight Rapidly Inactivates SARS-CoV-2 on Surfaces",
"author": "S Ratnesar-Shumate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "The Journal of infectious diseases",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref034",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/php.13293",
"article-title": "Estimated Inactivation of Coronaviruses by Solar Radiation With Special Reference to COVID-19",
"author": "JL Sagripanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "731",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Photochem Photobiol",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref035",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "pone.0305323.ref036",
"unstructured": "PurpleAir. PurpleAir Sensors Functional Overview 2021 [updated July 19, 2023; cited 2024 February 1, 2024]. Available from: https://community.purpleair.com/t/purpleair-sensors-functional-overview/150."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/joc.3413",
"article-title": "Development of gridded surface meteorological data for ecological applications and modelling",
"author": "JT Abatzoglou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Climatology",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref037",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2021.110972",
"article-title": "Is coronavirus disease (COVID-19) seasonal? A critical analysis of empirical and epidemiological studies at global and local scales",
"author": "WS Byun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110972",
"journal-title": "Environmental research",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref038",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100418",
"article-title": "Impact of meteorological parameters on COVID-19 pandemic: A comprehensive study from Saudi Arabia",
"author": "M Alkhowailed",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100418",
"journal-title": "Inform Med Unlocked",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref039",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04749",
"article-title": "Spatio-temporal analysis of meteorological factors in abating the spread of COVID-19 in Africa",
"author": "IA Adekunle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e04749",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref040",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140112",
"article-title": "Association of COVID-19 pandemic with meteorological parameters over Singapore",
"author": "SK Pani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "140112",
"journal-title": "The Science of the total environment",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref041",
"volume": "740",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143783",
"article-title": "Meteorological factors and COVID-19 incidence in 190 countries: An observational study",
"author": "C Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143783",
"journal-title": "The Science of the total environment",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref042",
"volume": "757",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113587",
"article-title": "Relationship between COVID-19 and weather: Case study in a tropical country",
"author": "DKA Rosario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113587",
"journal-title": "International journal of hygiene and environmental health",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref043",
"volume": "229",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139659",
"article-title": "Temperature and precipitation associate with Covid-19 new daily cases: A correlation study between weather and Covid-19 pandemic in Oslo, Norway",
"author": "MM Menebo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139659",
"journal-title": "The Science of the total environment",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref044",
"volume": "737",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Significance of geographical factors to the COVID-19 outbreak in India",
"author": "A Gupta",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Model Earth Syst Environ",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref045",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138997",
"article-title": "Association between climate variables and global transmission oF SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "MFF Sobral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138997",
"journal-title": "The Science of the total environment",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref046",
"volume": "729",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abi5499",
"article-title": "Impact of close interpersonal contact on COVID-19 incidence: Evidence from 1 year of mobile device data",
"author": "FW Crawford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Science Advances",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref047",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ina.12766",
"article-title": "Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "H Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Indoor Air",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref048",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa742",
"article-title": "Outdoor Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Respiratory Viruses: A Systematic Review",
"author": "TC Bulfone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "550",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "The Journal of infectious diseases",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref049",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa557",
"article-title": "Household Transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Zhuhai, China, 2020",
"author": "J Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2099",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref050",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2904.220854",
"article-title": "Serial Intervals and Incubation Periods of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta Variants, Singapore",
"author": "K Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Emerging Infectious Disease journal",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref051",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Incubation Period of COVID-19 Caused by Unique SARS-CoV-2 Strains: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis",
"author": "Y Wu",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref052",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Estimating the Impact of Statewide Policies to Reduce Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Real Time, Colorado, USA",
"author": "A Buchwald",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Emerging Infectious Disease journal",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref053",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000002864",
"article-title": "Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation",
"author": "P Schober",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Anesthesia & Analgesia",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref054",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01621459.1979.10481038",
"article-title": "Robust Locally Weighted Regression and Smoothing Scatterplots",
"author": "WS Cleveland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "829",
"issue": "368",
"journal-title": "Journal of the American Statistical Association",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref055",
"volume": "74",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"key": "pone.0305323.ref056",
"unstructured": "StataCorp. Stata: Causal Inference and Treatment-Effects Estimation Reference Manual, Release 182023. Available from: Available from: https://www.stata.com/manuals/causal.pdf."
},
{
"author": "Oxford University Press",
"journal-title": "Explanation in causal inference: methods for mediation and interaction",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref057",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates",
"author": "T Carleton",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref058",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-19898-8",
"article-title": "Investigating the effects of absolute humidity and movement on COVID-19 seasonality in the United States",
"author": "G Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16729",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Scientific reports",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref059",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-021-15738-w",
"article-title": "The moderating effect of solar radiation on the association between human mobility and COVID-19 infection in Europe",
"author": "W Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "828",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Environmental science and pollution research international",
"key": "pone.0305323.ref060",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "pone.0305323.ref061",
"unstructured": "Microsoft Maps. US Building Footprints 2022 [cited 2024 February 6]. V2.0:[Available from: https://github.com/microsoft/USBuildingFootprints."
}
],
"reference-count": 61,
"references-count": 61,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0305323"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Does behavior mediate the effect of weather on SARS-CoV-2 transmission? evidence from cell-phone data",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "19"
}