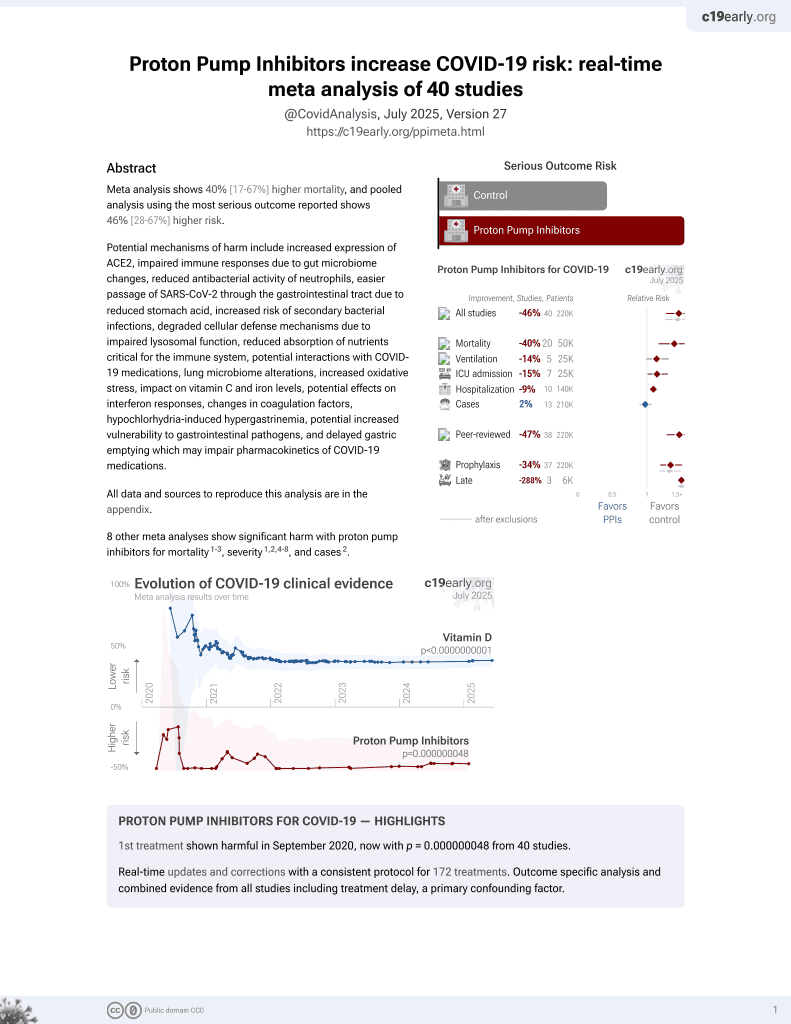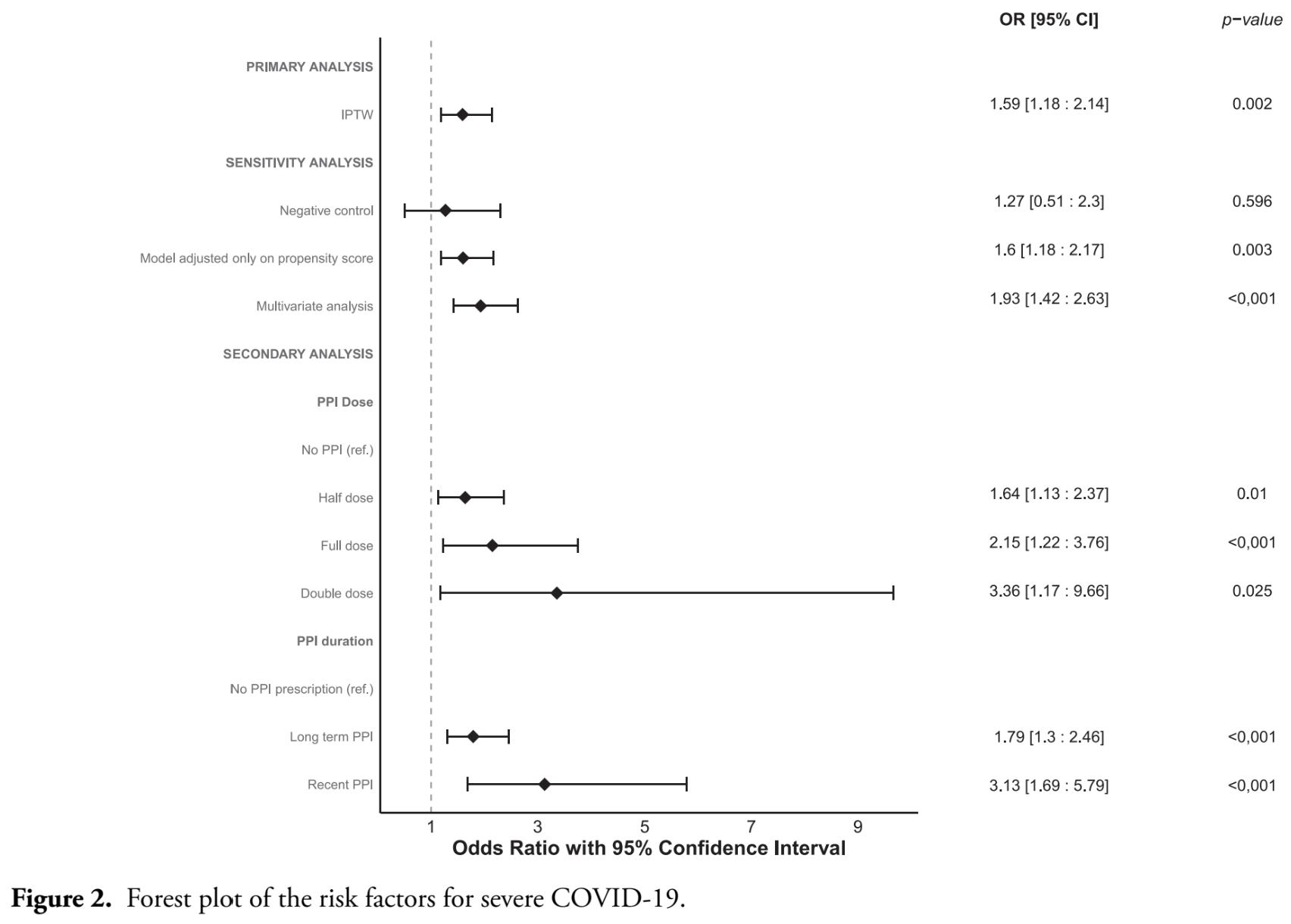
Proton pump inhibitors and risk of severe COVID-19 in older people
et al., Age and Ageing, doi:10.1093/ageing/afae082, Apr 2024
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 834 elderly patients in France showing higher risk of severe COVID-19 with PPI use, and increasing risk with increasing dosage.
|
risk of severe case, 59.0% higher, OR 1.59, p = 0.002, treatment 424, control 410, propensity score weighting, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gramont et al., 15 Apr 2024, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, study period March 2020 - February 2021.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ageing/afae082",
"ISSN": [
"0002-0729",
"1468-2834"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afae082",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Introduction</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 is a viral respiratory infection that can cause systemic disorders and lead to death, particularly in older people. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) increase the risk of enteric and lung infections. Considering the broad use of PPIs in older people, the potential role of PPIs in COVID-19 could be of dramatic significance. The objective of our study was to evaluate the link between PPIs and severe COVID-19 in older people.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Method</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We performed a retrospective cohort study, including all patients aged ≥65, hospitalised for a diagnosis of COVID-19. Epidemiological, clinical and biological data were extracted and we performed an Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighing method based on a propensity score.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>From March 2020 to February 2021, a total of 834 patients were included, with a median age of 83 and 52.8% were male. A total of 410 patients had a PPIs prescription, 358 (87.3%) were long-term PPIs-users and 52 (12.7%) were recent PPIs-users. Among PPIs-users, 163 (39.8%) patients developed severe COVID-19 versus 113 (26.7%) in PPIs-non users (odds ratio (OR) = 1.59 [1.18–2.14]; P &lt; 0.05). Moreover, the double dose PPI-users had a higher risk of developing severe COVID-19 (OR = 3.36 [1.17–9.66]; P &lt; 0.05) than the full dose PPI-users (OR = 2.15 [1.22–3.76]; P &lt; 0.05) and the half dose PPI-users (OR = 1.64 [1.13–2.37]; P &lt; 0.05).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Our study reports evidence that the use of PPIs was associated with an increased risk of severe COVID-19 in older people.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2678-0028",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Team GIMAP , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Université de Lyon, Université Jean Monnet, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, INSERM, U1111, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), UMR530 , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gramont",
"given": "Baptiste",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Practice, Université Jean Monnet , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Fayolle",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Public Health and Medical Information, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Beltramin",
"given": "Diva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Practice, Université Jean Monnet , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Bidat",
"given": "Nisrine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of General Practice, Université Jean Monnet , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Boudet",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Public Health and Medical Information, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Chaux",
"given": "Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Grange",
"given": "Lucile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Team GIMAP , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Université de Lyon, Université Jean Monnet, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, INSERM, U1111, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), UMR530 , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Barrau",
"given": "Mathilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Team GIMAP , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Université de Lyon, Université Jean Monnet, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, INSERM, U1111, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), UMR530 , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Department, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Gagneux-Brunon",
"given": "Amandine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Cathébras",
"given": "Pascal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Team GIMAP , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Université de Lyon, Université Jean Monnet, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, INSERM, U1111, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), UMR530 , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Killian",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Team GIMAP , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Université de Lyon, Université Jean Monnet, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, INSERM, U1111, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), UMR530 , CIRI—Centre International de Recherche en Infectiologie, , F42023 Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Infectious Disease Department, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Botelho-Nevers",
"given": "Elisabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Gerontology, Saint-Etienne University Hospital , Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Chaire Santé des Ainés, Université Jean Monnet , Saint-Etienne , France"
},
{
"name": "Gérontopôle Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes , Saint-Etienne , France"
}
],
"family": "Célarier",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Age and Ageing",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T17:32:46Z",
"timestamp": 1712079166000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-15T10:49:58Z",
"timestamp": 1713178198000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-15T11:17:04Z",
"timestamp": 1713179824781
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1711929600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article-pdf/53/4/afae082/57232541/afae082.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article-pdf/53/4/afae082/57232541/afae082.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
15
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: prevalence and outcomes",
"author": "Song",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore)",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref2",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.001",
"article-title": "AGA Institute rapid review of the gastrointestinal and liver manifestations of COVID-19, meta-analysis of international data, and recommendations for the consultative management of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Sultan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref3",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2608.200681",
"article-title": "Infectious SARS-CoV-2 in feces of patient with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1920",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref4",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13232",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal bleeding in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched cohort study",
"author": "Trindade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "887",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref5",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal bleeding in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review with meta-analysis",
"author": "Marasco",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref6",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gtc.2022.10.004",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal bleeding in COVID-19-infected patients",
"author": "Cappell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterol Clin North Am",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref7",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13766",
"article-title": "Trends in prescription drug use among adults in the United States from 1999-2012",
"author": "Kantor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1818",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref8",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imj.12757",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors utilisation in older people in New Zealand from 2005 to 2013",
"author": "Nishtala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "624",
"journal-title": "Intern Med J",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref9",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitor use",
"author": "Yibirin",
"first-page": "e12759",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15103",
"article-title": "Association of proton-pump inhibitor use with adverse health outcomes: a systematic umbrella review of meta-analyses of cohort studies and randomised controlled trials",
"author": "Veettil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1551",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref11",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7193",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of chronic kidney disease",
"author": "Lazarus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref12",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015735",
"article-title": "Risk of death among users of proton pump inhibitors: a longitudinal observational cohort study of United States veterans",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref13",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.7927",
"article-title": "Adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Schoenfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref14",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0128004",
"article-title": "Risk of community-acquired pneumonia with outpatient proton-pump inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lambert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/ice.2016.202",
"article-title": "A novel risk factor associated with colonization by carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae: use of proton pump inhibitors in addition to antimicrobial treatment",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1418",
"journal-title": "Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref16",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2018.05.023",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use as a risk factor for Enterobacteriaceal infection: a case-control study",
"author": "Cunningham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "60",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Infect",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref17",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciw743",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use is associated with extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae rectal carriage at hospital admission: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Huizinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "361",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref18",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2019.05.056",
"article-title": "Safety of proton pump inhibitors based on a large, multi-year, randomized trial of patients receiving rivaroxaban or aspirin",
"author": "Moayyedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "682",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref19",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.16205",
"article-title": "Association between acute gastroenteritis and continuous use of proton pump inhibitors during winter periods of highest circulation of enteric viruses",
"author": "Vilcu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref20",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-020-00963-x",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors are risk factors for viral infections: even for COVID-19?",
"author": "Charpiat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "897",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref21",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1707",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref22",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13121",
"article-title": "Treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and ARDS in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor?",
"author": "Luxenburger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref23",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref24",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/tropicalmed7030037",
"article-title": "The use of proton pump inhibitors and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Fatima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Trop Med Infect Dis",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref25",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref26",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000002138",
"article-title": "Assessment of proton-pump inhibitor use, race, socioeconomic status, and mortality in individuals with COVID-19",
"author": "Aby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref27",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref28",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/sag-2103-80",
"article-title": "Long-term proton pump inhibitor use is a risk factor for mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19",
"author": "Yozgat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1675",
"journal-title": "Turk J Med Sci",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref29",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.12.05005",
"article-title": "Use of proton pump inhibitors are associated with higher mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "05005",
"journal-title": "J Glob Health",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref30",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-11680-0",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor therapy usage and associated hospitalization rates and critical care outcomes of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Shupp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7596",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref31",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198005",
"article-title": "Co-infection with respiratory pathogens among COVID-2019 cases",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref32",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "What is the role of proton pump inhibitors consumption on the clinical presentation and severity of COVID-19 infection?",
"author": "Shokri",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharm Fr",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref33",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323668",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor or famotidine use and severe COVID-19 disease: a propensity score-matched territory-wide study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2012",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref34",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-021-01907-8",
"article-title": "Relation of severe COVID-19 to polypharmacy and prescribing of psychotropic drugs: the REACT-SCOT case-control study",
"author": "McKeigue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "BMC Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref35",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.011",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis",
"author": "Israelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1845",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref36",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000933",
"article-title": "Are proton pump inhibitors contributing to SARS-COV-2 infection?",
"author": "Tarlow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1920",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref37",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.028",
"article-title": "Effect of acid suppressants on the risk of COVID-19: a propensity score-matched study using UK Biobank",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "455",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref38",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "People exposed to proton pump inhibitors shortly preceding COVID-19 diagnosis are not at an increased risk of subsequent hospitalizations and mortality: a nation-wide matched cohort study",
"author": "Kodvanj",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref39",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.07.009",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal prophylaxis for COVID-19: an illustration of severe bias arising from inappropriate comparators in observational studies",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref40",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40360-022-00549-7",
"article-title": "Comparative risk of incidence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 among proton pump inhibitor and histamine-2 receptor antagonist short-term users: a nationwide retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "BMC Pharmacol Toxicol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref41",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.007",
"article-title": "Association between preadmission acid suppressive medication exposure and severity of illness in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "Elmunzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1417",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref42",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-021-00397-z",
"article-title": "Therapeutic prevention of COVID-19 in elderly: a case-control study",
"author": "Blanc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2333",
"journal-title": "Geroscience",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref43",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-022-03319-w",
"article-title": "Non-peer-reviewed data, effect measures, and meta-regression analysis on proton pump inhibitor use and COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1351",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref44",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2021.08.013",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality: the culprit may not be proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref45",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.03.012",
"article-title": "The associations between pharmacologic gastric acid suppression and adverse outcomes in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1722",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref46",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-017-0519-y",
"article-title": "Acid-suppressive therapy and risk of infections: pros and cons",
"author": "Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "587",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref47",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20236031",
"article-title": "The phylogeny and biological function of gastric juice—microbiological consequences of removing gastric acid",
"author": "Martinsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6031",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref48",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.006",
"article-title": "Inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV",
"author": "Darnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "J Virol Methods",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref49",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310861",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors alter the composition of the gut microbiota",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref50",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2015-310376",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors affect the gut microbiome",
"author": "Imhann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref51",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Human gut microbiota and its metabolites impact immune responses in COVID-19 and its complications",
"author": "Nagata",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref52",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.12846",
"article-title": "Iron deficiency anaemia due to proton pump inhibitors: clinical impact revealed",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "245",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref53",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "The effects of proton pump inhibitors in acid hypersecretion-induced vitamin B12 deficiency: a systematic review (2022)",
"author": "Swarnakari",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref54",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11894-010-0141-0",
"article-title": "Association of long-term proton pump inhibitor therapy with bone fractures and effects on absorption of calcium, vitamin B12, iron, and magnesium",
"author": "Ito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "448",
"journal-title": "Curr Gastroenterol Rep",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref55",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.841532",
"article-title": "Ingestion, immunity, and infection: nutrition and viral respiratory tract infections",
"author": "Govers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref56",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuab092",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin B12 in viral infections: a comprehensive review of its relationship with the muscle-gut-brain axis and implications for SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Batista",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref57",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-200205000-00026",
"article-title": "Omeprazole treatment diminishes intra- and extracellular neutrophil reactive oxygen production and bactericidal activity",
"author": "Zedtwitz-Liebenstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1118",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref58",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0306-3623(94)00301-3",
"article-title": "The effect of omeprazole on human natural killer cell activity",
"author": "Aybay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1413",
"journal-title": "Gen Pharmacol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref59",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24021191",
"article-title": "Proton-pump inhibitors suppress T cell response by shifting intracellular zinc distribution",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1191",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref60",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.292.16.1955",
"article-title": "Risk of community-acquired pneumonia and use of gastric acid-suppressive drugs",
"author": "Laheij",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1955",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref61",
"volume": "292",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107915",
"article-title": "Potential causes and consequences of gastrointestinal disorders during a SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Trottein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref62",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055",
"article-title": "Evidence for gastrointestinal infection of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1831",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref63",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12862",
"article-title": "Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in kidney tissue",
"author": "Saheb Sharif-Askari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1048",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref64",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.637885",
"article-title": "Acid pH increases SARS-CoV-2 infection and the risk of death by COVID-19",
"author": "Jimenez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "637885",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref65",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref66",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.098",
"article-title": "Association between famotidine use and COVID-19 severity in Hong Kong: a territory-wide study",
"author": "Cheung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1898",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref67",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-326952",
"article-title": "Oral famotidine versus placebo in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, data-intense, phase 2 clinical trial",
"author": "Brennan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "879",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref68",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04773-6",
"article-title": "The efficacy of famotidine in improvement of outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Samimagham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "848",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref69",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of oral famotidine in patients hospitalized with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2",
"author": "Pahwani",
"first-page": "e22404",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref70",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.022",
"article-title": "No evidence of clinical efficacy of famotidine for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheema",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref71",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-021-03255-1",
"article-title": "Acid suppressant use in association with incidence and severe outcomes of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref72",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ckj/sfab158",
"article-title": "An introduction to inverse probability of treatment weighting in observational research",
"author": "Chesnaye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Clin Kidney J",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref73",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00273171.2011.568786",
"article-title": "An introduction to propensity score methods for reducing the effects of confounding in observational studies",
"author": "Austin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"journal-title": "Multivariate Behav Res",
"key": "2024041510492095900_ref74",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2011"
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ageing/article/doi/10.1093/ageing/afae082/7645558"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Proton pump inhibitors and risk of severe COVID-19 in older people",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "53"
}