Low serum levels of zinc and 25-hydroxyvitmain D as potential risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility: a pilot case-control study
et al., European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1038/s41430-022-01095-5, Mar 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
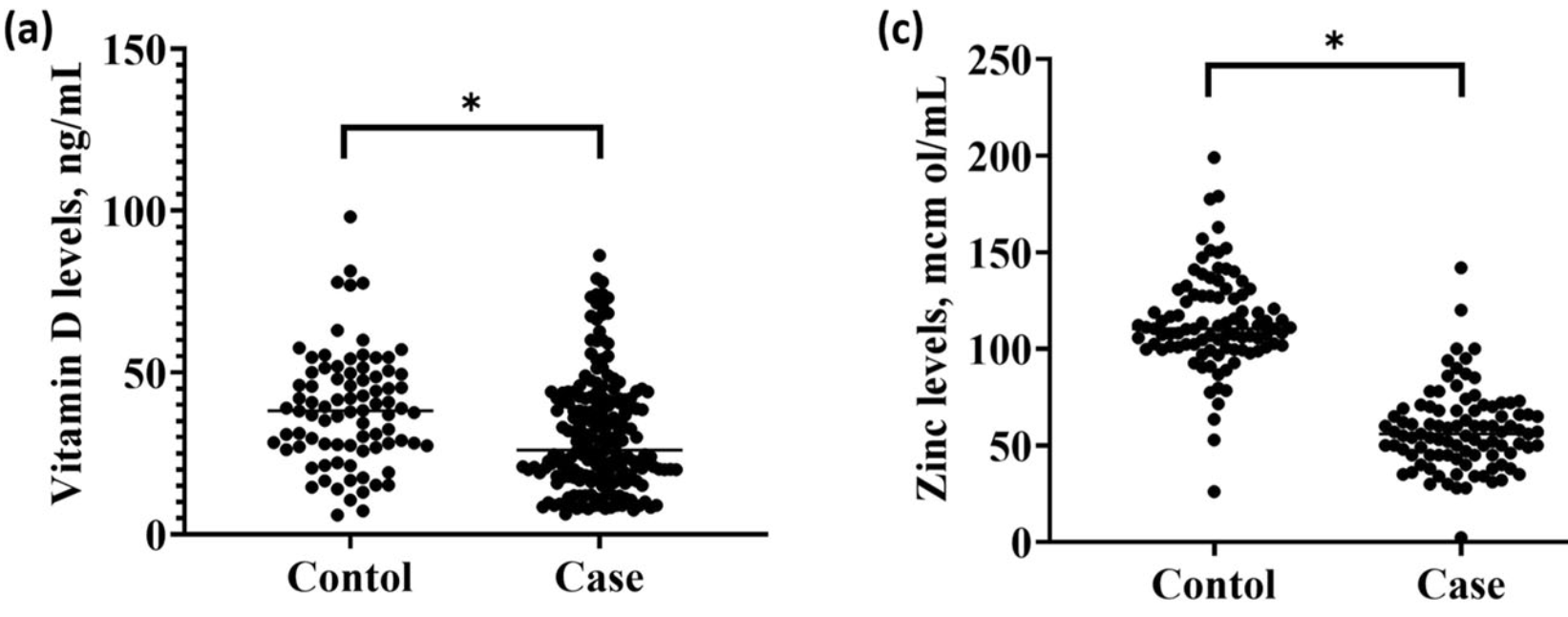
Case control study with 90 COVID-19 cases and 95 matched controls in Iran, showing significantly lower zinc levels for cases.
Study covers vitamin D and zinc.
Ghanei et al., 23 Mar 2022, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 20 March, 2020 - 20 January, 2021.
Low serum levels of zinc and 25-hydroxyvitmain D as potential risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility: a pilot case-control study
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition, doi:10.1038/s41430-022-01095-5
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: This study aimed to evaluate serum 25-hydroxyvitmain D and zinc levels in coronavirus disease 2019 patients in comparison to healthy subjects. METHODS: This was a single-center case-control study performed from March 20, 2020, to January 20, 2021, in Tehran, Iran. All patients diagnosed with COVID-19 based on a positive nasopharyngeal swab polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test were included in the case group. Controls were selected from patients referred for routine checkups who had a negative COVID-19 PCR test. Age, sex, marital and educational status, comorbidities, and serum 25-hydroxyvitmain D and zinc levels of patients were recorded. RESULTS: Ninety patients in the case group and 95 subjects in the control group who were sex and age-matched were studied. 25hydroxyvitmain D levels higher than 20 ng/ml were observed in 58 (64%) cases and 72 (76%) controls (P = 0.09). The median 25hydroxyvitmain D level in the case group was significantly lower than controls (26 (interquartile range [IQR] = 24) ng/ml vs. 38 (IQR = 22) ng/ml, respectively, P < 0.01). The median zinc level in the case group was 56 (IQR = 23) mcg/dL, while it was 110 (IQR = 27) mcg/dL among the controls (P < 0.01). There was no significant difference in the level of 25-hydroxyvitmain D and zinc between cases with and without comorbidities (P > 0.05). Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection could be predicted by serum 25hydroxyvitmain D levels below 25.2 ng/ml (81% sensitivity; 48% specificity) or zinc levels below 86.3 mcg/dL (93% sensitivity; 92% specificity). CONCLUSIONS: Low serum zinc and 25-hydroxyvitmain D levels appear to be risk factors for COVID-19 affliction; thus, the treatment of individuals with such deficiencies is recommended.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS EG and FA contributed to the conception of the work. HM, EG, MB, AB and FA contributed to the acquisition of data and AT contributed to the analysis, and interpretation of data for the work. AB, MB and FA drafted the manuscript. FA and EG and HM critically revised the manuscript. All authors gave final approval and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work ensuring integrity and accuracy. This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare no competing interests.
ETHICAL APPROVAL The study protocol was approved by our institute's Ethics Committee in Biomedical Research with reference code IR.SBMU.SRC.REC.1399.007.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-022-01095-5. Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Ayda bahmanjahromi or Fahimeh Abdollahimajd. Reprints and permission information is available at http://www.nature.com/ reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Berg, Bolt, Andersen, Owen, Zinc potentiates the antiviral action of human IFN-α tenfold, J Interferon Cytokines Res
Biesalski, Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients-A fatal relationship?, NFS J
Buyukuslu, Esin, Hizli, Sunal, Yigit et al., Clothing preference affects vitamin D status of young women, Nutr Res
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Rajagopalan, Jones et al., Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Microbiol
Carr, Micronutrient status of COVID-19 patients: a critical consideration, Crit Care
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolò et al., 25-hydroxyvitmain D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients, Aging Clin Exp Res
Dankers, Colin, Van Hamburg, Lubberts, Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Front Immunol
Darling, Ahmadi, Ward, Harvey, Alves et al., Vitamin D status, body mass index, ethnicity and COVID-19: initial analysis of the first
Gasmi, Noor, Tippairote, Dadar, Menzel et al., Individual risk management strategy and potential therapeutic options for the COVID-19 pandemic, Clin Immunol
Gasmi, Tippairote, Mujawdiya, Peana, Menzel et al., Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management, Clin Immunol
Ghazi, Zadeh, Pezeshk, Azizi, Cacicedo, Seasonal variation of serum 25 hydroxy D3 in residents of Tehran, J Endocrinol Invest
Giannini, Passeri, Tripepi, Sella, Fusaro et al., Effectiveness of in-hospital cholecalciferol use on clinical outcomes in comorbid COVID-19 patients: a hypothesis-generating study, Nutrients
Gombart, Borregaard, Koeffler, Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly upregulated in myeloid cells by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, FASEB
Gorji, Ghadiri, Potential roles of micronutrient deficiency and immune system dysfunction in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Nutrition
Grant, Lordan, Vitamin D for COVID-19 on trial: An update on prevention and therapeutic application, Endocr Pract
Greiller, Martineau, Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D, Nutrients
Gröber, Holick, The coronavirus disease (COVID-19)-A supportive approach with selected micronutrients, Int J Vitam Nutr Res
Han, Chang, Juo, Lee, Yeh et al., Papain-like protease 2 (PLP2) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV): expression, purification, characterization, and inhibition, Biochem
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Hurst, Mellanby, Handel, Griffith, Rossi et al., Vitamin D insufficiency in COVID-19 and influenza A, and critical illness survivors: a crosssectional study, BMJ
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Infante, Ricordi, Sanchez, Salzler, Padilla et al., Influence of vitamin D on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes, Nutrients
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis
Junaid, Ejaz, Abdalla, Abosalif, Ullah et al., Effective immune functions of micronutrients against SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Khalighi, Jahangirimehr, Labibzadeh, Bahmanyari, Najafi et al., Calcium, and Zinc Levels Patients with COVID-19, Clin Nutr ESPEN
Larijani, Tehrani, Hamidi, Soltani, Pajouhi, Osteoporosis, global and Iranian aspects, Iran J Public Health
Lordan, Notable developments for vitamin D amid the COVID-19 pandemic, but caution warranted overall: A narrative review, Nutrients
Lordan, Rando, Greene, Dietary supplements and nutraceuticals under investigation for COVID-19 prevention and treatment, Msystems
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Jamali-Moghadam, Asadi, Zendehdel et al., Treatment with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a pilot, multicenter, randomized, placebocontrolled double blind clinical trial, Endocr Pract
Mcauliffe, Ray, Fallon, Bradfield, Eden et al., Dietary micronutrients in the wake of COVID-19: an appraisal of evidence with a focus on highrisk groups and preventative healthcare, BMJ Nutr Prev Health
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results, JAMA
Mendes, Charlton, Thakur, Ribeiro, Lanham-New et al., Future perspectives in addressing the global issue of vitamin D deficiency, Proc Nutr Soc
Muszkat, Camargo, Griz, Lazaretti-Castro, Evidence-based nonskeletal actions of vitamin D, Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab
Orces, The association between body mass index and vitamin D supplement use among adults in the United States, Cureus
Pecora, Persico, Argentiero, Neglia, Esposito, The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections, Nutrients
Pinzon, Pradana, Vitamin D deficiency among patients with COVID-19: case series and recent literature review, Trop Med Health
Richardson, Lovegrove, Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: a UK perspective, Brit J Nutr
Rios-Lugo, Madrigal-Arellano, Gaytán-Hernández, Hernández-Mendoza, Romero-Guzmán, Association of serum zinc levels in overweight and obesity, Biol Trace Elem Res
Smet, Smet, Herroelen, Gryspeerdt, Martens, Vitamin D deficiency as risk factor for severe COVID-19: a convergence of two pandemics
Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front Nutr
Tang, Wang, Gao, The short form of the zinc finger antiviral protein inhibits influenza A virus protein expression and is antagonized by the virus-encoded NS1, J Virol
Tellinghuisen, Marcotrigiano, Rice, Structure of the zinc-binding domain of an essential component of the hepatitis C virus replicase, Nature
Thomas, Patel, Bittel, Wolski, Wang et al., Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Wang, Dabbas, Laperriere, Bitton, Soualhine et al., Direct and indirect induction by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 of the NOD2/ CARD15-defensin β2 innate immune pathway defective in Crohn disease, J Biol Chem
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Front Immunol
Yao, Paguio, Dee, Tan, Moulick et al., The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study, Chest
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-022-01095-5",
"ISSN": [
"0954-3007",
"1476-5640"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41430-022-01095-5",
"alternative-id": [
"1095"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "7 October 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 2,
"value": "21 January 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 3,
"value": "3 February 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 4,
"value": "23 March 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study protocol was approved by our institute’s Ethics Committee in Biomedical Research with reference code IR.SBMU.SRC.REC.1399.007."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghanei",
"given": "Esmat",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baghani",
"given": "Moein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moravvej",
"given": "Hamideh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Talebi",
"given": "Atefeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2742-0040",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "bahmanjahromi",
"given": "Ayda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9463-0665",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abdollahimajd",
"given": "Fahimeh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"European Journal of Clinical Nutrition"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-23T13:11:43Z",
"timestamp": 1648041103000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-23T15:07:04Z",
"timestamp": 1648048024000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-23T15:42:34Z",
"timestamp": 1648050154483
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0954-3007"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1476-5640"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1647993600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1647993600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-022-01095-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-022-01095-5",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-022-01095-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song J, et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:727–33."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108545",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR2",
"unstructured": "Gasmi A, Tippairote T, Mujawdiya PK, Peana M, Menzel A, Dadar M, et al. Micronutrients as immunomodulatory tools for COVID-19 management. Clin Immunol. 2020;220:108545."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2683-3",
"author": "AC Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "1095_CR3",
"unstructured": "Carr AC. Micronutrient status of COVID-19 patients: a critical consideration. Crit Care. 2020;24:1–2.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111047",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR4",
"unstructured": "Gorji A, Khaleghi Ghadiri M. Potential roles of micronutrient deficiency and immune system dysfunction in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Nutrition. 2021;82:111047."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000100",
"author": "S McAuliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutr Prev Health",
"key": "1095_CR5",
"unstructured": "McAuliffe S, Ray S, Fallon E, Bradfield J, Eden T, Kohlmeier M. Dietary micronutrients in the wake of COVID-19: an appraisal of evidence with a focus on high-risk groups and preventative healthcare. BMJ Nutr Prev Health. 2020;3:93.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12103198",
"author": "F Pecora",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3198",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR6",
"unstructured": "Pecora F, Persico F, Argentiero A, Neglia C, Esposito S. The role of micronutrients in support of the immune response against viral infections. Nutrients. 2020;12:3198.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711452000330X",
"author": "DP Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "678",
"journal-title": "Brit J Nutr",
"key": "1095_CR7",
"unstructured": "Richardson DP, Lovegrove JA. Nutritional status of micronutrients as a possible and modifiable risk factor for COVID-19: a UK perspective. Brit J Nutr. 2021;125:678–84.",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12102992",
"author": "K Junaid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2992",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR8",
"unstructured": "Junaid K, Ejaz H, Abdalla AE, Abosalif KOA, Ullah MI, Yasmeen H, et al. Effective immune functions of micronutrients against SARS-CoV-2. Nutrients. 2020;12:2992.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831/a000693",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR9",
"unstructured": "Gröber U, Holick MF. The coronavirus disease (COVID-19)–A supportive approach with selected micronutrients. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2022;92:13–34."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"author": "PC Calder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1181",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR10",
"unstructured": "Calder PC, Carr AC, Gombart AF, Eggersdorfer M. Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections. Nutrients. 2020;12:1181.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"author": "MF Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1911",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "1095_CR11",
"unstructured": "Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, et al. Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011;96:1911–30.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S0004-27302010000200005",
"author": "P Muszkat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "1095_CR12",
"unstructured": "Muszkat P, Camargo MBR, Griz LHM, Lazaretti-Castro M. Evidence-based non-skeletal actions of vitamin D. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab. 2010;54:110–7.",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665119001538",
"author": "MM Mendes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "Proc Nutr Soc",
"key": "1095_CR13",
"unstructured": "Mendes MM, Charlton K, Thakur S, Ribeiro H, Lanham-New SA. Future perspectives in addressing the global issue of vitamin D deficiency. Proc Nutr Soc. 2020;79:246–51.",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF03347502",
"author": "AAM Ghazi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"key": "1095_CR14",
"unstructured": "Ghazi AAM, Zadeh FR, Pezeshk P, Azizi F, Cacicedo L. Seasonal variation of serum 25 hydroxy D3 in residents of Tehran. J Endocrinol Invest. 2004;27:676–9.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"author": "B Larijani",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Iran J Public Health",
"key": "1095_CR15",
"unstructured": "Larijani B, Tehrani MRM, Hamidi Z, Soltani A, Pajouhi M. Osteoporosis, global and Iranian aspects. Iran J Public Health. 2004;33:1–17.",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697",
"author": "W Dankers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1095_CR16",
"unstructured": "Dankers W, Colin EM, van Hamburg JP, Lubberts E. Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front Immunol. 2017;7:697.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092185",
"author": "M Infante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2185",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR17",
"unstructured": "Infante M, Ricordi C, Sanchez J, Clare-Salzler MJ, Padilla N, Fuenmayor V, et al. Influence of vitamin D on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes. Nutrients. 2019;11:2185.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7064240",
"author": "CL Greiller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4240",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR18",
"unstructured": "Greiller CL, Martineau AR. Modulation of the immune response to respiratory viruses by vitamin D. Nutrients. 2015;7:4240–70.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.04-3284com",
"author": "AF Gombart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1067",
"journal-title": "FASEB",
"key": "1095_CR19",
"unstructured": "Gombart AF, Borregaard N, Koeffler HP. Human cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide (CAMP) gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor and is strongly up‐regulated in myeloid cells by 1, 25‐dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB. 2005;19:1067–77.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.C109.071225",
"author": "T-T Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2227",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "1095_CR20",
"unstructured": "Wang T-T, Dabbas B, Laperriere D, Bitton AJ, Soualhine H, Tavera-Mendoza LE, et al. Direct and indirect induction by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 of the NOD2/CARD15-defensin β2 innate immune pathway defective in Crohn disease. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:2227–31.",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01677-y",
"author": "A Daneshkhah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2141",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "1095_CR21",
"unstructured": "Daneshkhah A, Agrawal V, Eshein A, Subramanian H, Roy HK, Backman V. Evidence for possible association of vitamin D status with cytokine storm and unregulated inflammation in COVID-19 patients. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32:2141–58.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.29.20084277",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR22",
"unstructured": "Darling AL, Ahmadi KR, Ward KA, Harvey NC, Alves AC, Dunn-Waters DK, et al. Vitamin D status, body mass index, ethnicity and COVID-19: initial analysis of the first-reported UK Biobank COVID-19 positive cases (n 580) compared with negative controls (n 723). MedRxiv. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.01.20079376",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR23",
"unstructured": "De Smet D, De Smet K, Herroelen P, Gryspeerdt S, Martens GA. Vitamin D deficiency as risk factor for severe COVID-19: a convergence of two pandemics. MedRxiv. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"author": "PC Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1195",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "1095_CR24",
"unstructured": "Ilie PC, Stefanescu S, Smith L. The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2020;32:1195–8.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "EA Hurst",
"first-page": "e055435",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1095_CR25",
"unstructured": "Hurst EA, Mellanby RJ, Handel I, Griffith DM, Rossi AG, Walsh TS, et al. Vitamin D insufficiency in COVID-19 and influenza A, and critical illness survivors: a cross-sectional study. BMJ. 2021;11:e055435.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030740",
"author": "R Lordan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "740",
"journal-title": "Nutrients.",
"key": "1095_CR26",
"unstructured": "Lordan R. Notable developments for vitamin D amid the COVID-19 pandemic, but caution warranted overall: A narrative review. Nutrients. 2021;13:740.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Q Tang",
"first-page": "e01909",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "1095_CR27",
"unstructured": "Tang Q, Wang X, Gao G. The short form of the zinc finger antiviral protein inhibits influenza A virus protein expression and is antagonized by the virus-encoded NS1. J Virol. 2017;91:e01909–16.",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/10799900152434330",
"author": "K Berg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "471",
"journal-title": "J Interferon Cytokines Res",
"key": "1095_CR28",
"unstructured": "Berg K, Bolt G, Andersen H, Owen TC. Zinc potentiates the antiviral action of human IFN-α tenfold. J Interferon Cytokines Res. 2001;21:471–4.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03580",
"author": "TL Tellinghuisen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "374",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1095_CR29",
"unstructured": "Tellinghuisen TL, Marcotrigiano J, Rice CM. Structure of the zinc-binding domain of an essential component of the hepatitis C virus replicase. Nature 2005;435:374–9.",
"volume": "435",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712",
"author": "I Wessels",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1712",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1095_CR30",
"unstructured": "Wessels I, Rolles B, Rink L. The potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1712.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"author": "D Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "1095_CR31",
"unstructured": "Jothimani D, Kailasam E, Danielraj S, Nallathambi B, Ramachandran H, Sekar P, et al. COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency. Int J Infect Dis. 2020;100:343–9.",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108409",
"author": "A Gasmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108409",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "1095_CR32",
"unstructured": "Gasmi A, Noor S, Tippairote T, Dadar M, Menzel A, Bjørklund G. Individual risk management strategy and potential therapeutic options for the COVID-19 pandemic. Clin Immunol. 2020;215:108409.",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"author": "A D’Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1359",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR33",
"unstructured": "D’Avolio A, Avataneo V, Manca A, Cusato J, De Nicolò A, Lucchini R, et al. 25-hydroxyvitmain D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2. Nutrients. 2020;12:1359.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2014.07.012",
"author": "N Buyukuslu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "688",
"journal-title": "Nutr Res",
"key": "1095_CR34",
"unstructured": "Buyukuslu N, Esin K, Hizli H, Sunal N, Yigit P, Garipagaoglu M. Clothing preference affects vitamin D status of young women. Nutr Res. 2014;34:688–93.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR35",
"unstructured": "Grant WB, Lordan R. Vitamin D for COVID-19 on trial: An update on prevention and therapeutic application. Endocr Pract. 2021;27:1266–8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR36",
"unstructured": "Meltzer DO, Best TJ, Zhang H, Vokes T, Arora V, Solway J. Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results. JAMA. 2020;3:e2019722."
},
{
"author": "ACR Souza",
"first-page": "295",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "1095_CR37",
"unstructured": "Souza ACR, Vasconcelos AR, Prado PS, Pereira CPM. Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity. Front Nutr. 2020;7:295.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eprac.2021.09.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR38",
"unstructured": "Maghbooli Z, Sahraian MA, Jamali-Moghadam SR, Asadi A, Zendehdel A, Varzandi T, et al. Treatment with 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcifediol) is associated with a reduction in the blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio marker of disease severity in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: a pilot, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled double blind clinical trial. Endocr Pract. 2021;27:1242–51."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001",
"author": "HK Biesalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "NFS J",
"key": "1095_CR39",
"unstructured": "Biesalski HK. Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients–A fatal relationship? NFS J. 2020;20:10.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13010219",
"author": "S Giannini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1095_CR40",
"unstructured": "Giannini S, Passeri G, Tripepi G, Sella S, Fusaro M, Arcidiacono G, et al. Effectiveness of in-hospital cholecalciferol use on clinical outcomes in comorbid COVID-19 patients: a hypothesis-generating study. Nutrients. 2021;13:219.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41182-020-00277-w",
"author": "RT Pinzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Trop Med Health",
"key": "1095_CR41",
"unstructured": "Pinzon RT, Pradana AW. Vitamin D deficiency among patients with COVID-19: case series and recent literature review. Trop Med Health. 2020;48:1–7.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.082",
"author": "JS Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "1095_CR42",
"unstructured": "Yao JS, Paguio JA, Dee EC, Tan HC, Moulick A, Milazzo C, et al. The minimal effect of zinc on the survival of hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an observational study. Chest. 2021;159:108–11.",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR43",
"unstructured": "Khalighi A, Jahangirimehr A, Labibzadeh M, Bahmanyari N, Najafi M Serum Vitamin D, Calcium, and Zinc Levels in Patients with COVID-19. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2021;43:276."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"author": "PM Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1228",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol",
"key": "1095_CR44",
"unstructured": "Carlucci PM, Ahuja T, Petrilli C, Rajagopalan H, Jones S, Rahimian J. Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. J Med Microbiol. 2020;69:1228.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1095_CR45",
"unstructured": "Thomas S, Patel D, Bittel B, Wolski K, Wang Q, Kumar A, et al. Effect of high-dose zinc and ascorbic acid supplementation vs usual care on symptom length and reduction among ambulatory patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: the COVID A to Z randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4:e210369."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSystems.00122-21",
"author": "R Lordan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00122",
"journal-title": "Msystems",
"key": "1095_CR46",
"unstructured": "Lordan R, Rando HM, Greene CS. Dietary supplements and nutraceuticals under investigation for COVID-19 prevention and treatment. Msystems. 2021;6:e00122–21.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi0504761",
"author": "Y-S Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10349",
"journal-title": "Biochem",
"key": "1095_CR47",
"unstructured": "Han Y-S, Chang G-G, Juo C-G, Lee H-J, Yeh S-H, Hsu JT-A, et al. Papain-like protease 2 (PLP2) from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV): expression, purification, characterization, and inhibition. Biochem. 2005;44:10349–59.",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02060-8",
"author": "MJ Rios-Lugo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "1095_CR48",
"unstructured": "Rios-Lugo MJ, Madrigal-Arellano C, Gaytán-Hernández D, Hernández-Mendoza H, Romero-Guzmán ET. Association of serum zinc levels in overweight and obesity. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2020;198:51–7.",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "C Orces",
"first-page": "e5721",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "1095_CR49",
"unstructured": "Orces C. The association between body mass index and vitamin D supplement use among adults in the United States. Cureus. 2019;11:e5721.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41430-022-01095-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Eur J Clin Nutr"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Low serum levels of zinc and 25-hydroxyvitmain D as potential risk factors for COVID-19 susceptibility: a pilot case-control study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}
ghanei
