DYRK1A is a multifunctional host factor that regulates coronavirus replication in a kinase-independent manner
et al., Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/jvi.01239-23, Jan 2024
In vitro study showing DYRK1A (dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A) is a critical host factor for coronavirus replication in a kinase-independent manner.
Fu et al., 23 Jan 2024, USA, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Contact: sunlimeng@webmail.hzau.edu.cn, penggq@mail.hzau.edu.cn.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
DYRK1A is a multifunctional host factor that regulates coronavirus replication in a kinase-independent manner
Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/jvi.01239-23
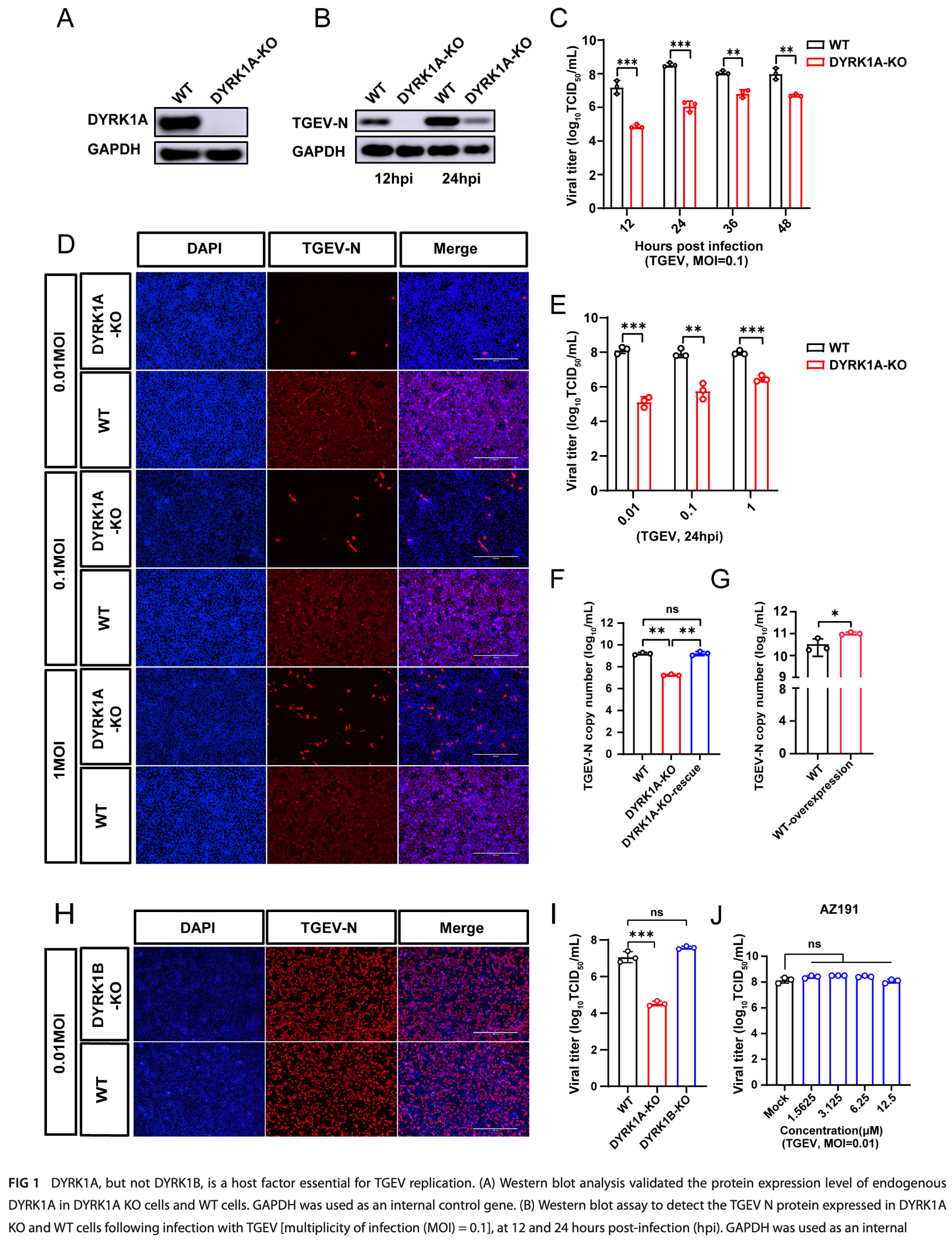
Coronaviruses (CoVs) pose a major threat to human and animal health worldwide, which complete viral replication by hijacking host factors. Identifying host factors essential for the viral life cycle can deepen our understanding of the mechanisms of virus-host interactions. Based on our previous genome-wide CRISPR screen of α-CoV transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), we identified the host factor dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A), but not DYRK1B, as a critical factor in TGEV replication. Rescue assays and kinase inhibitor experiments revealed that the effect of DYRK1A on viral replication is independent of its kinase activity. Nuclear localization signal modification experiments showed that nuclear DYRK1A facilitated virus replication. Furthermore, DYRK1A knockout significantly downregulated the expression of the TGEV receptor aminopeptidase N (ANPEP) and inhibited viral entry. Notably, we also demonstrated that DYRK1A is essential for the early stage of TGEV replication. Transmission electron microscopy results indicated that DYRK1A contributes to the formation of double-membrane vesicles in a kinase-independent manner. Finally, we validated that DYRK1A is also a proviral factor for mouse hepatitis virus, porcine deltacoronavirus, and porcine sapelovirus. In conclusion, our work demonstrated that DYRK1A is an essential host factor for the replication of multiple viruses, providing new insights into the mechanism of virus-host interactions and facilitating the development of new broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. IMPORTANCE Coronaviruses, like other positive-sense RNA viruses, can remodel the host membrane to form double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) as their replication organelles. Currently, host factors involved in DMV formation are not well defined. In this study, we used transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) as a virus model to investigate the regulatory mechanism of dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regu lated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) on coronavirus. Results showed that DYRK1A significantly inhibited TGEV replication in a kinase-independent manner. DYRK1A knockout (KO) can regulate the expression of receptor aminopeptidase N (ANPEP) and endocytic-related genes to inhibit virus entry. More importantly, our results revealed that DYRK1A KO notably inhibited the formation of DMV to regulate the virus replication. Further data proved that DYRK1A is also essential in the replication of mouse hepatitis virus, porcine deltacoronavirus, and porcine sapelovirus. Taken together, our findings demonstrated that DYRK1A is a conserved factor for positive-sense RNA viruses and provided new insights into its transcriptional regulation activity, revealing its potential as a candidate target for therapeutic design.
Confocal microscopy To observe the endocytosis of the TGEV in host cells, the same amount of DYRK1A KO cells and control cells were cultured in 35 mm Petri dishes overnight. An equivalent dose of TGEV (MOI = 5) was added to each well and incubated at 4°C for 60 minutes for complete adsorption and then transferred to 37°C and incubated for 30 minutes for endocytosis. Immunofluorescence assays were performed as described above, while the images were acquired using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Nikon). The subcellular localization of DYRK1A in DYRK1A KO cells and control cells transfected with DYRK1A-FLAG-pcDNA3.1 plasmid was observed after 24 h. Afterward, TGEV (MOI = 1) was added into these cells, incubated for 24 h, immunolabeled with a FLAG-tag antibody (Proteintech, no. 20543-1-AP; MBL, no. PM020) and dsRNA antibody (SCICONS, no. 10010200, 1:1,000), and imaged to identify double-fluorescent positive cells.
Statistical analysis Statistical significance values were assessed using GraphPad Prism 8.0. Two-tailed unpaired t-tests were used for data analysis. Unless otherwise stated, the data represent the mean ± standard deviation of experiments performed, at least, in triplicate.
AUTHOR AFFILIATIONS
ADDITIONAL FILES The following material is available online.
Supplemental Material Supplemental figures (JVI01239-23-s0001.docx). Fig. S1 and S2 .
References
Abbassi, Johns, Kassiou, Munoz, DYRK1A in neurodegen eration and cancer: molecular basis and clinical implications, Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.03.004
Adayev, Wegiel, Hwang, Harmine is an ATP-competitive inhibitor for dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A), Arch Biochem Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2010.12.024
Alvarez, Estivill, De, Luna, DYRK1A accumulates in splicing speckles through a novel targeting signal and induces speckle disassembly, J Cell Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04469-x
Aranda, Laguna, De, Luna, DYRK family of protein kinases: evolutionary relationships, biochemical properties, and functional roles, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.10-165837
Ashford, Oxley, Kettle, Hudson, Guichard et al., A novel DYRK1B inhibitor AZ191 demonstrates that DYRK1B acts independently of GSK3β to phosphorylate cyclin D1 at Thr(286), not Thr(288), Biochem J, doi:10.1042/BJ20130461
Becker, Weber, Wetzel, Eirmbter, Tejedor et al., Sequence characteristics, subcellular localization, and substrate specificity of DYRK-related kinases, a novel family of dual specificity protein kinases, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.25893
Biering, Sarnik, Wang, Zengel, Leist et al., Genome-wide bidirectional CRISPR screens identify mucins as host factors modulating SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x
Daniloski, Jordan, Wessels, Hoagland, Kasela et al., Identification of required host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection in human cells, Cell, doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x
De Graaf, Hekerman, Spelten, Herrmann, Packman et al., Characterization of Cyclin L2, a novel Cyclin with an arginine/Serine-rich domain: Phosphorylation by Dyrk1A and Colocalization with splicing factors, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M310794200
Deboever, Fistrovich, Hulme, Dunckley, The omnipresence of DYRK1A in human diseases, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23169355
Delmas, Gelfi, 'haridon, Vogel, Sjöström et al., Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV, Nature, doi:10.1038/357417a0
Deng, Peng, Characteristics of and public health responses to the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak in China, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9020575
Fernández-Martínez, Zahonero, Sánchez-Gómez, DYRK1A: the double-edged kinase as a protagonist in cell growth and tumorigen esis, Mol Cell Oncol, doi:10.4161/23723548.2014.970048
Fu, Fu, Su, Li, Yang et al., Mlst8 is essential for coronavirus replication and regulates its replication through the mTORC1 pathway, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00899-23
González, Gomez-Puertas, Cavanagh, Gorbalenya, Enjuanes, A comparative sequence analysis to revise the current taxonomy of the family coronaviridae, Arch Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-003-0162-1
Hemmila, Turbide, Olson, Jothy, Holmes et al., Ceacam1a-/-mice are completely resistant to infection by murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus A59, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.78.18.10156-10165.2004
Hille, Dierck, Kühl, Sosna, Adam-Klages et al., DYRK1A regulates the cardiomyocyte cell cycle via D-cyclin-dependent Rb/E2f-signalling, Cardiovasc Res, doi:10.1093/cvr/cvw074
Himpel, Panzer, Eirmbter, Czajkowska, Sayed et al., Identification of the autophosphorylation sites and characterization of their effects in the protein kinase DYRK1A, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3590497
Hood, Silver, In or out? Regulating nuclear transport, Curr Opin Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80032-5
Ionescu, Dufrasne, Gelbcke, Jabin, Kiss et al., DYRK1A kinase inhibitors with emphasis on cancer, Mini Rev Med Chem, doi:10.2174/13895575112091315
Kelly, Rahmani, DYRK1A enhances the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade in PC12 cells by forming a complex with Ras, B-Raf, and MEK1, Mol Biol Cell, doi:10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1085
Kentrup, Becker, Heukelbach, Wilmes, Schürmann et al., DYRK, a dual specificity protein kinase with unique structural features whose activity is dependent on tyrosine residues between subdomains VII and VIII ( * ), J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.271.7.3488
Kim, Son, Koo, Kim, Alfajaro et al., Porcine sapelovirus uses α2,3-linked sialic acid on GD1A ganglioside as a receptor, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02449-15
Knoops, Kikkert, Worm S Van Den, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Van Der Meer et al., SARS-coronavirus replication is supported by a reticulovesicular network of modified endoplasmic reticulum, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060226
Laguna, Aranda, Barallobre, Barhoum, Fernández et al., The protein kinase DYRK1A regulates caspase-9-mediated apoptosis during retina development, Dev Cell, doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.014
Lamond, Spector, Nuclear speckles: a model for nuclear organelles, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/nrm1172
Laude, Rasschaert, Delmas, Godet, Gelfi, Molecular biology of transmissible gastroenteritis virus, Vet Microbiol, doi:10.1016/0378-1135(90)90144-k
Lepagnol-Bestel, Zvara, Maussion, Quignon, Ngimbous et al., DYRK1A interacts with the REST/NRSF-SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex to deregulate gene clusters involved in the neuronal phenotypic traits of down syndrome, Hum Mol Genet, doi:10.1093/hmg/ddp047
Li, Xu, Fu, Lei, Yao et al., DYRK1A interacts with histone acetyl transferase p300 and CBP and localizes to enhancers, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1128/MCB.24.13.5821-5834.2004
Luo, Wang, Zhu, Fan, Liu et al., Aminopep tidase N-null neonatal piglets are protected from transmissible gastroenteritis virus but not porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-49838-y
Mao, Maye, Kogerman, Tejedor, Toftgard et al., Regulation of gli1 transcriptional activity in the nucleus by DYRK1, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M206743200
Masters, The molecular biology of coronaviruses, Adv Virus Res, doi:10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3
Matsuo, Ochiai, Nakashima, Taga, A new expression cloning strategy for isolation of substrate-specific kinases by using phosphorylation site-specific antibody, J Immunol Methods, doi:10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00313-6
Mc, Hr, Elzinga, Hwang, Dynamin is a minibrain kinase/dual specificity Yak1-related kinase 1A substrate, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M111101200
Miller, Mcgrath, Hu, Ariannejad, Weston et al., Coronavirus interactions with the cellular autophagy machinery, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1817280
Moon, Norman, Lambert, Age dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine (TGE). I. Clinical signs and some mucosal dimensions in small intestine, Can J Comp Med
Ogawa, Nonaka, Goto, Ohnishi, Hiramatsu et al., Development of a novel selective inhibitor of the down syndrome-related kinase DYRK1A, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/ncomms1090
Ou, Qian, Characterization of SARS-Cov-2 glycoprotein using a quantitative cell-cell fusion system
Papenfuss, Lützow, Wilms, Babendreyer, Flaßhoff et al., Differential maturation and chaperone dependence of the paralogous protein kinases DYRK1A and DYRK1, B. Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-06423-0
Park, Song, Chung, Function and regulation of Dyrk1A: Towards understanding down syndrome, Cell Mol Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-009-0123-2
Prentice, Jerome, Yoshimori, Mizushima, Denison, Coronavirus replication complex formation utilizes components of cellular autophagy, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M306124200
Rebendenne, Roy, Bonaventure, Valadão, Desmarets et al., Bidirectional genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal host factors regulating SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV and seasonal HCoVs, Nat Genet, doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x
Roingeard, Eymieux, Burlaud-Gaillard, Hourioux, Patient et al., The double-membrane vesicle (DMV): a virus-induced organelle dedicated to the replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other positivesense single-stranded RNA viruses, Cell Mol Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04469-x
Salichs, Ledda, Mularoni, Albà, De et al., Genomewide analysis of histidine repeats reveals their role in the localization of human proteins to the nuclear speckles compartment, PLoS Genet, doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000397
Schneider, Luna, Hoffmann, Sánchez-Rivera, Leal et al., Genome-scale identification of SARS-CoV-2 and pan-coronavirus host factor networks, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.006
Seifert, Allan, Clarke, DYRK1A Phosphorylates caspase 9 at an inhibitory site and is potently inhibited in human cells by Harmine, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06751.x
Shue, Chiramel, Cerikan, To, Frölich et al., Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies RACK1 as a critical host factor for flavivirus replication, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00596-21
Sitz, Tigges, Baumgärtel, Khaspekov, Lutz, DYRK1A potentiates steroid hormone-induced transcription via the chromatin remodeling factor Arip4, Mol Cell Biol, doi:10.1128/MCB.24.13.5821-5834.2004
Snijder, Van Der Meer, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Onderwater, Van Der Meulen et al., Ultrastructure and origin of membrane vesicles associated with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication complex, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02501-05
Song, Sternberg, Kasten-Sportès, Keuren, Chung et al., Isolation of human and murine homologues of the drosophila minibrain gene: human homologue maps to 21q22.2 in the down syndrome "critical region, Genomics, doi:10.1006/geno.1996.0636
Soppa, Schumacher, Ortiz, Pasqualon, Tejedor et al., The down syndrome-related protein kinase DYRK1A phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and Cyclin D1 and induces cell cycle exit and neuronal differentiation, Cell Cycle, doi:10.4161/cc.29104
Stoian, Rowland, Petrovan, Sheahan, Samuel et al., The use of cells from ANPEP knockout pigs to evaluate the role of aminopeptidase N (APN) as a receptor for porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV), Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2019.12.007
Strine, Cai, Wei, Alfajaro, Filler et al., DYRK1A promotes viral entry of highly pathogenic human coronaviruses in a kinase-independent manner, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3002097
Sun, Zhao, Fu, Fu, Su et al., Genome-scale CRISPR screen identifies TMEM41B as a multi-function host factor required for coronavirus replication, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1010113
Twu, Lee, Kim, Prasad, Cerikan et al., Contribution of autophagy machinery factors to HCV and SARS-CoV-2 replication organelle formation, Cell Rep, doi:10.1128/MCB.24.13.5821-5834.2004
Von Groote-Bidlingmaier, Schmoll, Orth, Joost, Becker et al., DYRK1 is a co-activator of FKHR (FOXO1a)-dependent glucose-6-phosphatase gene expression, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02914-5
Vona, Bezdan, Islam, Salichs, López-Bigas et al., Chromatin-wide profiling of DYRK1A reveals a role as a gene-specific RNA polymerase II CTD kinase, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.026
Walte, Rüben, Birner-Gruenberger, Preisinger, Bamberg-Lemper et al., Mechanism of dual specificity kinase activity of DYRK1A, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.12411
Wang, Liu, Ji, Yang, Liang et al., Porcine deltacoronavi rus engages the transmissible gastroenteritis virus functional receptor porcine aminopeptidase N for infectious cellular entry, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00318-18
Wang, Simoneau, Kulsuptrakul, Bouhaddou, Travisano et al., Genetic screens identify host factors for SARS-CoV-2 and common cold coronaviruses, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004
Wei, Alfajaro, Deweirdt, Hanna, Lu-Culligan et al., Genomewide CRISPR screens reveal host factors critical for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell, doi:10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x
Williams, Jiang, Holmes, Receptor for mouse hepatitis virus is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of glycopro teins, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.88.13.5533
Wong, Li, Lau, Woo, Global epidemiology of bat coronaviruses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11020174
Woo, Lau, Lam, Lau, Tsang et al., Discovery of seven novel mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.06540-11
Woods, Cohen, Becker, Jakes, Goedert et al., The kinase DYRK Phosphorylates protein-synthesis initiation factor eIF2Bɛ at Ser539 and the microtubule-associated protein tau at Thr212: potential role for DYRK as a glycogen synthase kinase 3-priming kinase, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/bj3550609
Woods, Rena, Morrice, Barthel, Becker et al., The kinase DYRK1A phosphorylates the transcription factor FKHR at Ser329 in vitro, a novel in vivo phosphorylation site, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/bj3550597
Wu, Yeh, Tsay, Shieh, Kao et al., Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates the phosphorylation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus Full-Length Text, Journal of Virology January
Yang, Liu, Wang, Chen, Wang et al., Aminopeptidase N is an entry co-factor triggering porcine deltacoronavirus entry via an endocytotic pathway, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00944-21
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2951-z
Zhu, Liu, Wang, Luo, Shi et al., Contribution of porcine aminopeptidase N to porcine deltacoronavirus infection, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1038/s41426-018-0068-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01239-23",
"ISSN": [
"0022-538X",
"1098-5514"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01239-23",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n Coronaviruses (CoVs) pose a major threat to human and animal health worldwide, which complete viral replication by hijacking host factors. Identifying host factors essential for the viral life cycle can deepen our understanding of the mechanisms of virus–host interactions. Based on our previous genome-wide CRISPR screen of α-CoV transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), we identified the host factor dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A), but not DYRK1B, as a critical factor in TGEV replication. Rescue assays and kinase inhibitor experiments revealed that the effect of DYRK1A on viral replication is independent of its kinase activity. Nuclear localization signal modification experiments showed that nuclear DYRK1A facilitated virus replication. Furthermore, DYRK1A knockout significantly downregulated the expression of the TGEV receptor aminopeptidase N (\n <jats:italic>ANPEP</jats:italic>\n ) and inhibited viral entry. Notably, we also demonstrated that DYRK1A is essential for the early stage of TGEV replication. Transmission electron microscopy results indicated that DYRK1A contributes to the formation of double-membrane vesicles in a kinase-independent manner. Finally, we validated that DYRK1A is also a proviral factor for mouse hepatitis virus, porcine deltacoronavirus, and porcine sapelovirus. In conclusion, our work demonstrated that DYRK1A is an essential host factor for the replication of multiple viruses, providing new insights into the mechanism of virus–host interactions and facilitating the development of new broad-spectrum antiviral drugs.\n </jats:p>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>IMPORTANCE</jats:title>\n <jats:p>\n Coronaviruses, like other positive-sense RNA viruses, can remodel the host membrane to form double-membrane vesicles (DMVs) as their replication organelles. Currently, host factors involved in DMV formation are not well defined. In this study, we used transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) as a virus model to investigate the regulatory mechanism of dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinase 1A (DYRK1A) on coronavirus. Results showed that DYRK1A significantly inhibited TGEV replication in a kinase-independent manner. DYRK1A knockout (KO) can regulate the expression of receptor aminopeptidase N (\n <jats:italic>ANPEP</jats:italic>\n ) and endocytic-related genes to inhibit virus entry. More importantly, our results revealed that DYRK1A KO notably inhibited the formation of DMV to regulate the virus replication. Further data proved that DYRK1A is also essential in the replication of mouse hepatitis virus, porcine deltacoronavirus, and porcine sapelovirus. Taken together, our findings demonstrated that DYRK1A is a conserved factor for positive-sense RNA viruses and provided new insights into its transcriptional regulation activity, revealing its potential as a candidate target for therapeutic design.\n </jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/jvi.01239-23"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-08-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2023-11-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-12-15"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0000-5442-9812",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Zhen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Xiang",
"given": "Yixin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Yanan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Zhelin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "Yubei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Mengfang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Yuanyuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Baghaei Daemi",
"given": "Hakimeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Yuejun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Agricultural Animal Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction of Ministry of Education & Key Lab of Swine Genetics and Breeding of Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Shengsong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3884-3428",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Limeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8813-6663",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Key Laboratory of Agricultural Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Preventive Veterinary Medicine in Hubei Province, The Cooperative Innovation Center for Sustainable Pig Production, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Key Laboratory of Prevention & Control for African Swine Fever and Other Major Pig Diseases, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Wuhan, China"
},
{
"name": "Hubei Hongshan Laboratory, Frontiers Science Center for Animal Breeding and Sustainable Production, Wuhan, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Peng",
"given": "Guiqing",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Virology",
"container-title-short": "J Virol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-15T14:00:42Z",
"timestamp": 1702648842000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-15T23:37:50Z",
"timestamp": 1715816270000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gallagher",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"32202784"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "MOST | National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"32125037"
],
"name": "MOST | NSFC | National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-30T06:09:33Z",
"timestamp": 1748585373165,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.1128/ASMCopyrightv2",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1705968000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1705968000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/jvi.01239-23",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/jvi.01239-23",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-003-0162-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_2_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0065-3527(06)66005-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11020174",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.06540-11",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9020575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2951-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0378-1135(90)90144-k",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_8_2"
},
{
"article-title": "Age dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine (TGE). I. Clinical signs and some mucosal dimensions in small intestine",
"author": "Moon HW",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Can J Comp Med",
"key": "e_1_3_4_9_2",
"unstructured": "Moon HW, Norman JO, Lambert G. 1973. Age dependent resistance to transmissible gastroenteritis of swine (TGE). I. Clinical signs and some mucosal dimensions in small intestine. Can J Comp Med 37:157–166.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "1973"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.030",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-022-01110-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41588-022-01131-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00899-23",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M805747200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00596-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.10-165837",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/0264-6021:3590497",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.12411",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.271.7.3488",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/geno.1996.0636",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-009-0123-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvw074",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/cc.29104",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06751.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2008.10.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M310794200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/23723548.2014.970048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.03.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/13895575112091315",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/357417a0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-49838-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-06423-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BJ20130461",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3550597",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M206743200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M111101200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0022-1759(00)00313-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3550609",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2010.12.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms1090",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.273.40.25893",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1242/jcs.00618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-022-04469-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.0060226",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02501-05",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23169355",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.78.18.10156-10165.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.88.13.5533",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1010113",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrm1172",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pgen.1000397",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/ddp047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0006-291x(02)02914-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_56_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3002097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_57_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0955-0674(99)80032-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_58_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2019.12.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_59_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00318-18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_60_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00944-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_61_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41426-018-0068-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_62_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02449-15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_63_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_64_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gky754",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_65_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/MCB.24.13.5821-5834.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_66_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2014.12.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_67_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e04-12-1085",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_68_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M306124200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_69_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2020.1817280",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_70_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-0716-2895-9_15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_4_71_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 70,
"references-count": 70,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/jvi.01239-23"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "DYRK1A is a multifunctional host factor that regulates coronavirus replication in a kinase-independent manner",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page",
"volume": "98"
}