Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice
et al., Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005, Jul 2019
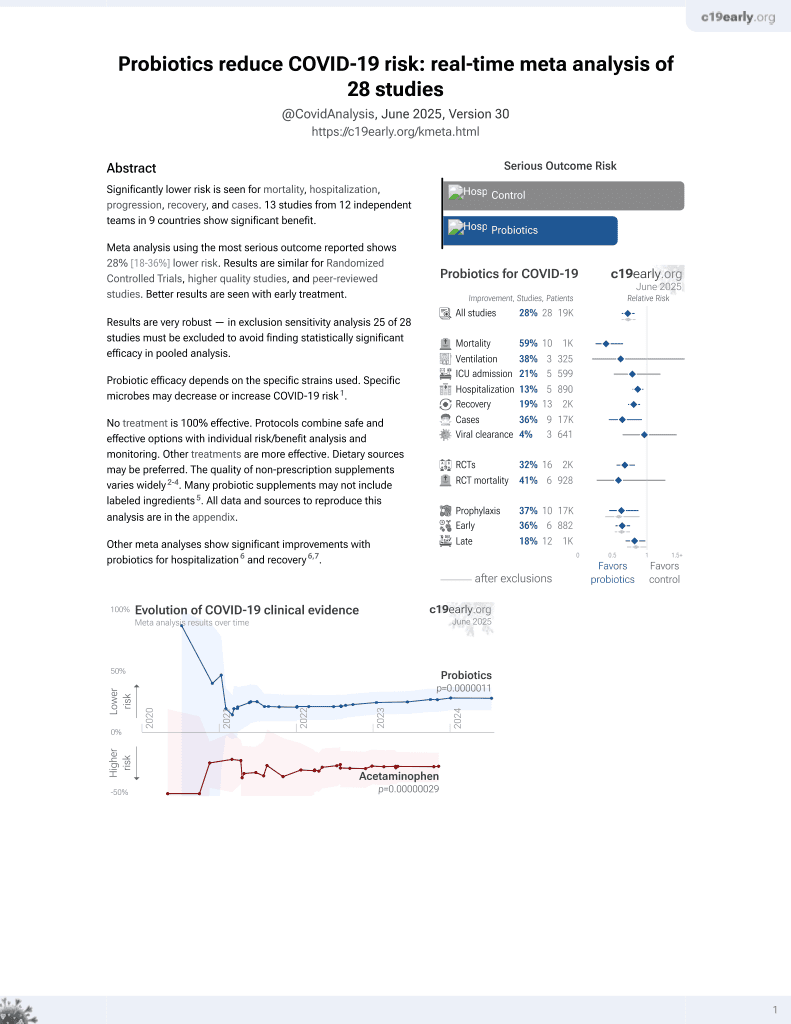
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
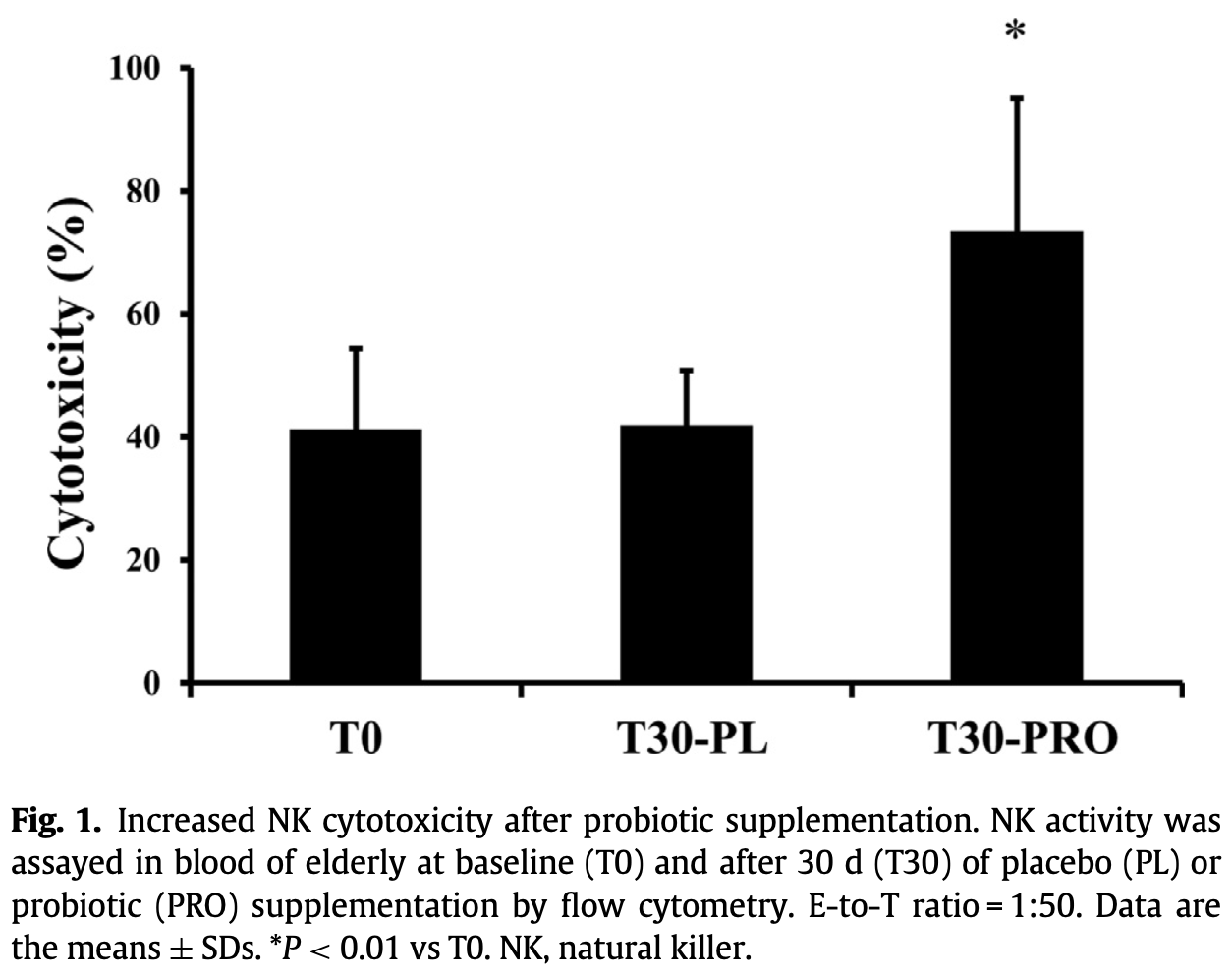
RCT 98 adults, showing that probiotics improved immune function including increased natural killer (NK) cell activity.
Graydon showed that a lower frequency of natural killer cells was associated with symptomatic COVID-19 infection.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk2.
Finamore et al., 31 Jul 2019, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Italy, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice
Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005
Aging induces several physiologic and immune changes. The usefulness of probiotics in ameliorating age-related disorders remains largely unexplored. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effectiveness of a Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture in improving the physiologic status and immunity of older adults (over 75 years). Furthermore, the possible role of such mixture in ameliorating gut immunity in aged mice was investigated. Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted with 98 adults (84.6 § 7.8 y), supplemented for 30 d with a biscuit containing a probiotic mixture of B. longum Bar33 and L. helveticus Bar13 (1:1), or no probiotics, as placebo. Blood was collected for analysis of biochemical parameters, lymphocyte subpopulations, natural killer activity, and cytokine release. Aged Balb/c mice received the same probiotic mixture or placebo daily for 28 d, then blood and intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations were analyzed. Results: The probiotic mixture ameliorated immune response in older adults by increasing naive, activated memory, regulatory T cells, B cells, and natural killer activity and decreasing memory T cells compared with placebo (P < 0.05). The biochemical parameters did not change after probiotic supplementation. In the gut of old mice, the two probiotics modulated cells crucial for gut immune homeostasis by increasing regulatory T (Treg and Tr1) and decreasing gd T cells compared with control mice (P < 0.05). In addition, B cells increased in the gut and blood of probiotic-treated mice.
Conclusion: Results from the present study data indicated that B. longum Bar33 and L. helveticus Bar13 improve immune function at intestinal and peripheral sites in aging.
References
Amati, Marzulli, Martulli, Pugliese, Caruso et al., Administration of a synbiotic to free-living elderly and evaluation of serum cytokines. A pilot study, Curr Pharm Des
Argentati, Re, Donnini, Tucci, Franceschi et al., Numerical and functional alterations of circulating T lymphocytes in aged people and centenarians, J Leukoc Biol
Asigbetse, Eigenmann, Frossard, Intestinal lamina propria TcRgam-madelta+ lymphocytes selectively express IL-10 and IL-17, J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol
Aureli, Capurso, Castellazzi, Clerici, Giovannini et al., Probiotics and health: an evidence-based review, Pharmacol Res
Brasili, Mengheri, Tomassini, Capuani, Roselli et al., Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 induce different agerelated metabolic profiles revealed by 1 H-NMR spectroscopy in urine and feces of mice, J Nutr
Bucci, Ostan, Giampieri, Cevenini, Pini et al., Immune parameters identify Italian centenarians with a longer five-year survival independent of their health and functional status, Exp Gerontol
Butcher, Chahal, Nayak, Sinclair, Henriquez et al., Senescence in innate immune responses: reduced neutrophil phagocytic capacity and CD16 expression in elderly humans, J Leukoc Biol
Calder, Bosco, Bourdet-Sicard, Capuron, Delzenne et al., Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition, Ageing Res Rev
Chang, Chen, Chang, Lin, Lin et al., Multiple strains probiotics appear to be the most effective probiotics in the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis and mortality: an updated meta-analysis, PLoS One
Chapman, Gibson, Rowland, Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains?, Eur J Nutr
Claesson, Jeffery, Conde, Power, Connor et al., Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly, Nature
Colonna-Romano, Aquino, Bulati, Lio, Candore et al., Impairment of gamma/delta T lymphocytes in elderly: Implications for immunosenescence, Exp Gerontol
Crespo, Wu, Li, Kryczek, Maj et al., Human naive T cells express functional CXCL8 and promote tumorigenesis, J Immunol
De Lafaille, Lafaille, Natural and adaptive foxp3+ regulatory T cells: more of the same or a division of labor?, Immunity
Dolati, Ahmadi, Khalili, Taheraghdam, Siahmansouri et al., Peripheral Th17/Treg imbalance in elderly patients with ischemic stroke, Neurol Sci
Donini, Poggiogalle, Molfino, Rosano, Lenzi et al., Mini-Nutritional Assessment, Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool, and Nutrition Risk Screening Tool for the nutritional evaluation of older nursing home residents, J Am Med Dir Assoc
Donini, Savina, Ricciardi, Coletti, Paolini et al., Predicting the outcome of artificial nutrition by clinical and functional indices, Nutrition
Dwivedi, Kumar, Laddha, Kemp, Induction of regulatory T cells: a role for probiotics and prebiotics to suppress autoimmunity, Autoimmun Rev
El-Bakry, Anter, Zahran, Role of some selected Bifidobacterium strains in modulating immunosenescence of aged albino rats, J Basic Appl Zool
Fagnoni, Vescovini, Passeri, Bologna, Pedrazzoni et al., Shortage of circulating naive CD8(+) T cells provides new insights on immunodeficiency in aging, Blood
Ferguson, Wikby, Maxson, Olsson, Johansson, Immune parameters in a longitudinal study of a very old population of swedish people: a comparison between survivors and nonsurvivors, J Gerontol Biol Sci
Finamore, Roselli, Britti, Merendino, Mengheri, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium animalis MB5 induce intestinal but not systemic antigen-specific hyporesponsiveness in ovalbumin-immunized rats, J Nutr
Finamore, Roselli, Britti, Monastra, Ambra et al., Intestinal and peripheral immune response to MON810 maize ingestion in weaning and old mice, J Agric Food Chem
Franceschi, Monti, Sansoni, Cossarizza, The immunology of exceptional individuals: the lesson of centenarians, Immunol Today
Fulop, Larbi, Dupuis, Page, Frost et al., Immunosenescence and inflamm-aging as two sides of the same coin: friends or foes?, Front Immunol
Garg, Delaney, Toubai, Ghosh, Reddy et al., Aging is associated with increased regulatory T-cell function, Aging Cell
Gayoso, Sanchez-Correa, Campos, Alonso, Pera et al., Immunosenescence of human natural killer cells, J Innate Immun
Gill, Rutherfurd, Cross, Gopal, Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019, Am J Clin Nutr
Gorczynski, Alexander, Bessler, Brandenburg, Fournier et al., An alteration in the levels of populations of CD4+ Treg is in part responsible for altered cytokine production by cells of aged mice which follows injection with a fetal liver extract, Immunol Lett
Gregg, Smith, Clark, Dunnion, Khan et al., The number of human peripheral blood CD4+ CD25 high regulatory T cells increases with age, Clin Exp Immunol
Hadis, Wahl, Schulz, Hardtke-Wolenski, Schippers et al., Intestinal tolerance requires gut homing and expansion of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in the lamina propria, Immunity
Hopkins, Macfarlane, Changes in predominant bacterial populations in human faeces with age and with Clostridium difficile infection, J Med Microbiol
Houh, Kim, Park, Hur, Kim et al., The effects of artemisinin on the cytolytic activity of natural killer (NK) cells, Int J Molec Sci
Jagger, Shimojima, Goronzy, Weyand, Regulatory T cells and the immune aging process: a mini-review, Gerontology
Johnstone, Parsons, Botelho, Millar, Mcneil et al., Immune biomarkers predictive of respiratory viral infection in elderly nursing home residents, PLoS One
Kwon, Lee, So, Chae, Hwang et al., Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Maneerat, Lehtinen, Childs, Forssten, Alhoniemi et al., Consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 by healthy elderly adults enhances phagocytic activity of monocytes and granulocytes, J Nutr Sci
Mañ E, Pedrosa, Lor En, Gassull, Espadaler, A mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7315 and CECT 7316 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects. A dose-response, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized pilot trial, Nutr Hosp
Merino, Ma, Rubio, Inog Es, Anchez-Ibarrola et al., Progressive decrease of CD8 high+ CD28+ CD57-cells with ageing, Clin Exp Immunol
Miyazawa, Kawase, Kubota, Yoda, Harata et al., Heatkilled Lactobacillus gasseri can enhance immunity in the elderly in a double blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Beneficial Microbes
Moro-García, Arias, Baltadjieva, Andez Benítez, Andez Barrial et al., Oral supplementation with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 8481 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects, Age
Neish, Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease, Gastroenterology
Nishioka, Shimizu, Iida, Yamazaki, Sakaguchi, CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells and CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in aged mice, J Immunol
Ogata, Shioi, Nakamura, Luo, Yokose, Association between natural killer cell activity and infection in immunologically normal elderly people, Clin Exp Immunol
Ouwehand, Invernici, Furlaneto, Messora, Effectiveness of multistrain versus single-strain probiotics: current status and recommendations for the future, J Clin Gastroenterol
Ouwehand, Tiihonen, Saarinen, Putaala, Rautonen, Influence of a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol on healthy elderly: intestinal and immune parameters, Br J Nutr
Pabst, Trafficking of regulatory T cells in the intestinal immune system, Int Immunol
Pawelec, Hallmarks of human "immunosenescence": adaptation or dysregulation?, Immun Ageing
Pellican O, Buffa, Goldeck, Bulati, Martorana et al., Evidence for less marked potential signs of T-cell immunosenescence in centenarian offspring than in the general age-matched population, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci
Przemska-Kosicka, Childs, Maidens, Dong, Todd et al., Age-related changes in the natural killer cell response to seasonal influenza vaccination are not influenced by a synbiotic: a randomised controlled trial, Front Immunol
Pu, Guo, Li, Zhu, Wang et al., Yogurt supplemented with probiotics can protect the healthy elderly from respiratory infections: a randomized controlled open-label trial, Clin Interv Aging
Rampelli, Candela, Severgnini, Biagi, Turroni et al., A probiotics-containing biscuit modulates the intestinal microbiota in the elderly, J Nutr Health Aging
Rescigno, Mucosal immunology and bacterial handling in the intestine, Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol
Roselli, Finamore, Nuccitelli, Carnevali, Brigidi et al., Prevention of TNBS-induced colitis by different Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains is associated with an expansion of gammadeltaT and regulatory T cells of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes, Inflamm Bowel Dis
Sakaguchi, Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self, Nat Immunol
Sharma, Das, Stephen-Victor, Galeotti, Karnam et al., Regulatory T cells induce activation rather than suppression of human basophils, Sci Immunol
Sharma, Dominguez, Lustgarten, High accumulation of T regulatory cells prevents the activation of immune responses in aged animals, J Immunol
Shibata, Yamada, Hara, Kishihara, Yoshikai, Resident Vdelta1+ gammadelta T cells control early infiltration of neutrophils after Escherichia coli infection via IL-17 production, J Immunol
Solana, Mariani, NK and NK/T cells in human senescence, Vaccine
Strindhall, Nilsson, L€ Ofgren, Ernerudh, Pawelec et al., No immune risk profile among individuals who reach 100 years of age: findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study, Exp Gerontol
Sun, Hurez, Thibodeaux, Kious, Liu et al., Aged regulatory T cells protect from autoimmune inflammation despite reduced STAT3 activation and decreased constraint of IL-17 producing T cells, Aging Cell
Takeda, Okumura, Effects of a fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on the human NK-cell activity, J Nutr
Valentini, Pinto, Bourdel-Marchasson, Ostan, Brigidi et al., Impact of personalized diet and probiotic supplementation on inflammation, nutritional parameters and intestinal microbiota -The "RISTOMED project": randomized controlled trial in healthy older people, Clin Nutr
Van Beek, Sovran, Hugenholtz, Meijer, Hoogerland et al., Supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 prevents decline of mucus barrier in colon of accelerated aging Ercc1-/D7 Mice, Front Immunol
Van Puyenbroeck, Hens, Coenen, Michiels, Beunckens et al., Efficacy of daily intake of Lactobacillus casei Shirota on respiratory symptoms and influenza vaccination immune response: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in healthy elderly nursing home residents, Am J Clin Nutr
Wikby, Nilsson, Forsey, Thompson, Strindhall et al., The immune risk phenotype is associated with IL-6 in the terminal decline stage: findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study of very late life functioning, Mech Ageing Dev
You, Yaqoob, Evidence of immunomodulatory effects of a novel probiotic, Bifidobacterium longum bv. infantis CCUG 52486, FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol
Yu, Gagliani, Ishigame, Huber, Zhu et al., Intestinal type 1 regulatory T cells migrate to periphery to suppress diabetogenic T cells and prevent diabetes development, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Zhao, Lin, Li, Wu, Li, Protective role of gd T cells in different pathogen infections and its potential clinical application, J Immunol Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005",
"ISSN": [
"0899-9007"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005",
"alternative-id": [
"S0899900718313078"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6869-3905",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Finamore",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2355-3241",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Roselli",
"given": "Marianna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4692-4754",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Donini",
"given": "LorenzoMaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brasili",
"given": "Dr. Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rami",
"given": "Rita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carnevali",
"given": "Paola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mistura",
"given": "Lorenza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5694-3732",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Giusti",
"given": "AnnaMaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0633-877X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mengheri",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
2,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2019-02-18T16:38:28Z",
"timestamp": 1550507908000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2019-11-17T10:51:01Z",
"timestamp": 1573987861000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100006533",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Forestry"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-06T19:44:09Z",
"timestamp": 1694029449191
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 34,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2019-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1561939200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900718313078?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0899900718313078?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "184-192",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2019,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2017.09.001",
"article-title": "Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition",
"author": "Calder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0001",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.01960",
"article-title": "Immunosenescence and inflamm-aging as two sides of the same coin: friends or foes?",
"author": "Fulop",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1960",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0002",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Senescence in innate immune responses: reduced neutrophil phagocytic capacity and CD16 expression in elderly humans",
"author": "Butcher",
"first-page": "881",
"journal-title": "J Leukoc Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0003",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.V95.9.2860.009k35_2860_2868",
"article-title": "Shortage of circulating naive CD8(+) T cells provides new insights on immunodeficiency in aging",
"author": "Fagnoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2860",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0004",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1742-4933-9-15",
"article-title": "Hallmarks of human “immunosenescence”: adaptation or dysregulation?",
"author": "Pawelec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Immun Ageing",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0005",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/50A.6.B378",
"article-title": "Immune parameters in a longitudinal study of a very old population of swedish people: a comparison between survivors and nonsurvivors",
"author": "Ferguson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "B378",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol Biol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0006",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mad.2006.04.003",
"article-title": "The immune risk phenotype is associated with IL-6 in the terminal decline stage: findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study of very late life functioning",
"author": "Wikby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "695",
"journal-title": "Mech Ageing Dev",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0007",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2007.05.001",
"article-title": "No immune risk profile among individuals who reach 100 years of age: findings from the Swedish NONA immune longitudinal study",
"author": "Strindhall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Exp Gerontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0008",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2014.01.023",
"article-title": "Immune parameters identify Italian centenarians with a longer five-year survival independent of their health and functional status",
"author": "Bucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Exp Gerontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0009",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.080",
"article-title": "Microbes in gastrointestinal health and disease",
"author": "Neish",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0010",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature11319",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly",
"author": "Claesson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "178",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0011",
"volume": "488",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/0022-1317-51-5-448",
"article-title": "Changes in predominant bacterial populations in human faeces with age and with Clostridium difficile infection",
"author": "Hopkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "448",
"journal-title": "J Med Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0012",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2011.02.006",
"article-title": "Probiotics and health: an evidence-based review",
"author": "Aureli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "366",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0013",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.113.177105",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus acidophilus La5 and Bifidobacterium lactis Bb12 induce different age-related metabolic profiles revealed by 1 H-NMR spectroscopy in urine and feces of mice",
"author": "Brasili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1549",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0014",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ibd.20961",
"article-title": "Prevention of TNBS-induced colitis by different Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains is associated with an expansion of gammadeltaT and regulatory T cells of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes",
"author": "Roselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1526",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Bowel Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0015",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2014.09.023",
"article-title": "Impact of personalized diet and probiotic supplementation on inflammation, nutritional parameters and intestinal microbiota - The \"RISTOMED project\": randomized controlled trial in healthy older people",
"author": "Valentini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0016",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/74.6.833",
"article-title": "Enhancement of immunity in the elderly by dietary supplementation with the probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis HN019",
"author": "Gill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "833",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0017",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-012-9434-6",
"article-title": "Oral supplementation with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 8481 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects",
"author": "Moro-García",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1311",
"journal-title": "Age",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0018",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114508003097",
"article-title": "Influence of a combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM and lactitol on healthy elderly: intestinal and immune parameters",
"author": "Ouwehand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0019",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/jns.2013.31",
"article-title": "Consumption of Bifidobacterium lactis Bi-07 by healthy elderly adults enhances phagocytic activity of monocytes and granulocytes",
"author": "Maneerat",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e44",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0020",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.111.026831",
"article-title": "Efficacy of daily intake of Lactobacillus casei Shirota on respiratory symptoms and influenza vaccination immune response: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in healthy elderly nursing home residents",
"author": "Van Puyenbroeck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1165",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0021",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12603-012-0372-x",
"article-title": "A probiotics-containing biscuit modulates the intestinal microbiota in the elderly",
"author": "Rampelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "166",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Health Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0022",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bpg.2013.03.004",
"article-title": "Mucosal immunology and bacterial handling in the intestine",
"author": "Rescigno",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0023",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2016.06.028",
"article-title": "Mini-Nutritional Assessment, Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool, and Nutrition Risk Screening Tool for the nutritional evaluation of older nursing home residents",
"author": "Donini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Dir Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0024",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2008.07.001",
"article-title": "Predicting the outcome of artificial nutrition by clinical and functional indices",
"author": "Donini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0025",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18071600",
"article-title": "The effects of artemisinin on the cytolytic activity of natural killer (NK) cells",
"author": "Houh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E1600",
"journal-title": "Int J Molec Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0026",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jf802059w",
"article-title": "Intestinal and peripheral immune response to MON810 maize ingestion in weaning and old mice",
"author": "Finamore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11533",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0027",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-010-0166-z",
"article-title": "Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains?",
"author": "Chapman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0028",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Multiple strains probiotics appear to be the most effective probiotics in the prevention of necrotizing enterocolitis and mortality: an updated meta-analysis",
"author": "Chang",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0029",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCG.0000000000001052",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of multistrain versus single-strain probiotics: current status and recommendations for the future",
"author": "Ouwehand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S35",
"issue": "suppl 1",
"journal-title": "J Clin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0030",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3920/BM2014.0108",
"article-title": "Heat-killed Lactobacillus gasseri can enhance immunity in the elderly in a double blind, placebo-controlled clinical study",
"author": "Miyazawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "441",
"journal-title": "Beneficial Microbes",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0031",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CIA.S141518",
"article-title": "Yogurt supplemented with probiotics can protect the healthy elderly from respiratory infections: a randomized controlled open-label trial",
"author": "Pu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1223",
"journal-title": "Clin Interv Aging",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0032",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/glt120",
"article-title": "Evidence for less marked potential signs of T-cell immunosenescence in centenarian offspring than in the general age-matched population",
"author": "Pellicanò",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "495",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0033",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00551.x",
"article-title": "Progressive decrease of CD8 high+ CD28+ CD57- cells with ageing",
"author": "Merino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0034",
"volume": "112",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "A mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum CECT 7315 and CECT 7316 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects. A dose-response, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized pilot trial",
"author": "Mañé",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Nutr Hosp",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0035",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000328005",
"article-title": "Immunosenescence of human natural killer cells",
"author": "Gayoso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "J Innate Immun",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0036",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0264-410X(99)00495-8",
"article-title": "NK and NK/T cells in human senescence",
"author": "Solana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1613",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0037",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01571.x",
"article-title": "Association between natural killer cell activity and infection in immunologically normal elderly people",
"author": "Ogata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "392",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0038",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0167-5699(95)80064-6",
"article-title": "The immunology of exceptional individuals: the lesson of centenarians",
"author": "Franceschi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Immunol Today",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0039",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/137.3.791S",
"article-title": "Effects of a fermented milk drink containing Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota on the human NK-cell activity",
"author": "Takeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "791S",
"issue": "suppl 2",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0040",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1574-695X.2012.01014.x",
"article-title": "Evidence of immunomodulatory effects of a novel probiotic, Bifidobacterium longum bv. infantis CCUG 52486",
"author": "You",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "353",
"journal-title": "FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0041",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.00591",
"article-title": "Age-related changes in the natural killer cell response to seasonal influenza vaccination are not influenced by a synbiotic: a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Przemska-Kosicka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "591",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0042",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni1178",
"article-title": "Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self",
"author": "Sakaguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "345",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0043",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000355303",
"article-title": "Regulatory T cells and the immune aging process: a mini-review",
"author": "Jagger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "130",
"journal-title": "Gerontology",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0044",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02798.x",
"article-title": "The number of human peripheral blood CD4+ CD25 high regulatory T cells increases with age",
"author": "Gregg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "540",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0045",
"volume": "140",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.177.12.8348",
"article-title": "High accumulation of T regulatory cells prevents the activation of immune responses in aged animals",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8348",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0046",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.12191",
"article-title": "Aging is associated with increased regulatory T-cell function",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "441",
"journal-title": "Aging Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0047",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6586",
"article-title": "CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ T cells and CD4+CD25-Foxp3+ T cells in aged mice",
"author": "Nishioka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6586",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0048",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2007.01.009",
"article-title": "An alteration in the levels of populations of CD4+ Treg is in part responsible for altered cytokine production by cells of aged mice which follows injection with a fetal liver extract",
"author": "Gorczynski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"journal-title": "Immunol Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0049",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1474-9726.2012.00812.x",
"article-title": "Aged regulatory T cells protect from autoimmune inflammation despite reduced STAT3 activation and decreased constraint of IL-17 producing T cells",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Aging Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0050",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10072-018-3250-4",
"article-title": "Peripheral Th17/Treg imbalance in elderly patients with ischemic stroke",
"author": "Dolati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Neurol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0051",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0108481",
"article-title": "Immune biomarkers predictive of respiratory viral infection in elderly nursing home residents",
"author": "Johnstone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0052",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0904055107",
"article-title": "Generation of regulatory dendritic cells and CD4+Foxp3+ T cells by probiotics administration suppresses immune disorders",
"author": "Kwon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2159",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0053",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.111.148924",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Bifidobacterium animalis MB5 induce intestinal but not systemic antigen-specific hyporesponsiveness in ovalbumin-immunized rats",
"author": "Finamore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "375",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0054",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2016.01.002",
"article-title": "Induction of regulatory T cells: a role for probiotics and prebiotics to suppress autoimmunity",
"author": "Dwivedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0055",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.002",
"article-title": "Natural and adaptive foxp3+ regulatory T cells: more of the same or a division of labor?",
"author": "Curotto de Lafaille",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0056",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2011.01.016",
"article-title": "Intestinal tolerance requires gut homing and expansion of FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in the lamina propria",
"author": "Hadis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0057",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxs113",
"article-title": "Trafficking of regulatory T cells in the intestinal immune system",
"author": "Pabst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Int Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0058",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1705599114",
"article-title": "Intestinal type 1 regulatory T cells migrate to periphery to suppress diabetogenic T cells and prevent diabetes development",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10443",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0059",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00408",
"article-title": "Supplementation with Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 prevents decline of mucus barrier in colon of accelerated aging Ercc1-/Δ7 Mice",
"author": "van Beek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "408",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0060",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jobaz.2013.05.002",
"article-title": "Role of some selected Bifidobacterium strains in modulating immunosenescence of aged albino rats",
"author": "El-Bakry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "J Basic Appl Zool",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0061",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Administration of a synbiotic to free-living elderly and evaluation of serum cytokines",
"author": "Amati",
"first-page": "854",
"journal-title": "A pilot study. Curr Pharm Des",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0062",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.aan0829",
"article-title": "Regulatory T cells induce activation rather than suppression of human basophils",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0063",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1700755",
"article-title": "Human naive T cells express functional CXCL8 and promote tumorigenesis",
"author": "Crespo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "814",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0064",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/5081634",
"article-title": "Protective role of γδ T cells in different pathogen infections and its potential clinical application",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0065",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Intestinal lamina propria TcRgammadelta+ lymphocytes selectively express IL-10 and IL-17",
"author": "Asigbetse",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0066",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4466",
"article-title": "Resident Vdelta1+ gammadelta T cells control early infiltration of neutrophils after Escherichia coli infection via IL-17 production",
"author": "Shibata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4466",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0067",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"article-title": "Numerical and functional alterations of circulating T lymphocytes in aged people and centenarians",
"author": "Argentati",
"first-page": "65",
"journal-title": "J Leukoc Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0068",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2004.07.005",
"article-title": "Impairment of gamma/delta T lymphocytes in elderly: Implications for immunosenescence",
"author": "Colonna-Romano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1439",
"journal-title": "Exp Gerontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.nut.2019.02.005_bib0069",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2004"
}
],
"reference-count": 69,
"references-count": 69,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0899900718313078"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "63-64"
}