COVID-19 in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Living in Lombardy, Italy
et al., Movement Disorders, doi:10.1002/mds.28176, Jun 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
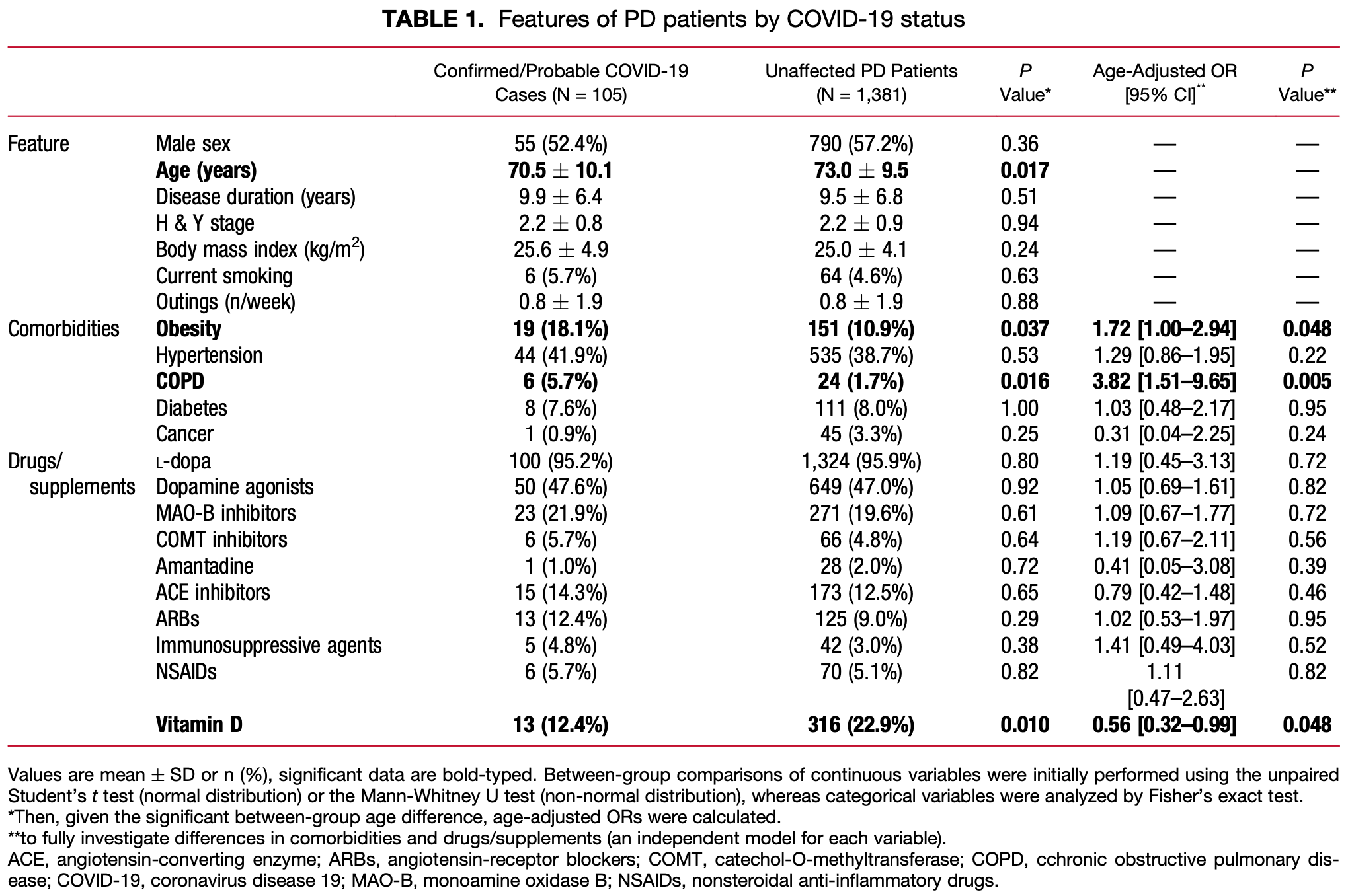
Retrospective phone survey of 1,486 Parkinson's disease patients in Italy, showing lower risk of COVID-19 cases with vitamin D supplementation. This paper also presents a case control study of PD patients and family member control patients.
This is the 39th of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of case, 42.0% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.048, treatment 13 of 329 (4.0%), control 92 of 1,157 (8.0%), NNT 25, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fasano et al., 2 Jun 2021, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, dosage not specified.
COVID‐19 in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Living in Lombardy, Italy
Movement Disorders, doi:10.1002/mds.28176
Background: It is unknown whether patients with PD are at greater risk of COVID-19, what their risk factors are, and whether their clinical manifestations differ from the general population. Objectives: The study aimed to address all these issues. Methods: In a case-controlled survey, we interviewed 1,486 PD patients attending a single tertiary center in Lombardy, Italy and 1,207 family members (controls). Results: One hundred five (7.1%) and 92 controls (7.6%) were identified as COVID-19 cases. COVID-19 patients were younger, more likely to suffer from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, to be obese, and vitamin D nonsupplemented than unaffected patients. Six patients (5.7%) and 7 family members (7.6%) died from COVID-19. Patients were less likely to report shortness of breath and require hospitalization. Conclusions: In an unselected large cohort of nonadvanced PD patients, COVID-19 risk and mortality did not differ from the general population, but symptoms appeared to be milder. The possible protective role of vitamin D supplementation warrants future studies.
Supporting Data Additional Supporting Information may be found in the online version of this article at the publisher's web-site.
References
Antonini, Leta, Teo, Chaudhuri, Outcome of Parkinson's disease patients affected by COVID-19, Mov Disord, doi:10.1002/mds.28104
Baille, Chenivesse, Perez, Dyspnea: an underestimated symptom in Parkinson's disease, Parkinsonism Relat Disord
Baille, Jesus, Perez, Ventilatory dysfunction in Parkinson's disease, J Parkinsons Dis
Carter, Baranauskas, Fly, Considerations for obesity, vitamin D, and physical activity amidst the COVID-19 pandemic, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22838
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Ddp, COVID-19 Italia-Monitoraggio della situazione
Fasano, Antonini, Katzenschlager, Management of advanced therapies in Parkinson's disease patients in times of humanitarian crisis: the COVID-19 experience, Mov Disord Clin Pract
Fasano, Elia, Dallocchio, Predictors of COVID-19 outcome in Parkinson's disease
Filatov, Sharma, Hindi, Espinosa, Neurological complications of coronavirus disease (COVID-19): encephalopathy, Cureus
Gardner, States, Bagley, The coronavirus and the risks to the elderly in long-term care, J Aging Soc Policy, doi:10.1080/08959420.2020.1750543
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, A SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction map reveals drug targets and potential drug-repurposing, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.22.002386
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA
Helmich, Bloem, The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Parkinson's disease: hidden sorrows and emerging opportunities, J Parkinsons Dis
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-Is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
Jarcho, Ingelfinger, Hamel, Agostino, Harrington, Inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMe2012924
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Kakodkar, Kaka, Baig, A comprehensive literature review on the clinical presentation, and management of the pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Cureus
Kittleson, The invisible hand-medical care during the pandemic, N Engl J Med
Ko, Kang, Lee, Levodopa-induced respiratory dysfunction confirmed by levodopa challenge test: a case report, Medicine
Little, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and covid-19, BMJ
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041
Mccartney, Byrne, Optimisation of vitamin D status for enhanced immuno-protection against Covid-19, Ir Med J
Monteiro, Souza-Machado, Valderramas, Melo, The effect of levodopa on pulmonary function in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Ther
Nataf, An alteration of the dopamine synthetic pathway is possibly involved in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25826
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4683
Papa, Brundin, Fung, Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on Parkinson's disease and movement disorders, Mov Disord Clin Pract
Postuma, Berg, Stern, MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease, Mov Disord
Prasad, Holla, Neeraja, Parkinson's disease and COVID-19: perceptions and implications in patients and caregivers, Mov Disord, doi:10.1002/mds.28088
Silberstein, Vitamin D: a simpler alternative to tocilizumab for trial in COVID-19?, Med Hypotheses
Smieszek, Przychodzen, Polymeropoulos, Amantadine disrupts lysosomal gene expression; potential therapy for COVID19, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.05.026187
Torres, Maheswari, Parthasarathy, Ng, Liu et al., Conductance and amantadine binding of a pore formed by a lysineflanked transmembrane domain of SARS coronavirus envelope protein, Protein Sci
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.28176",
"ISSN": [
"0885-3185",
"1531-8257"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mds.28176",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>It is unknown whether patients with PD are at greater risk of COVID‐19, what their risk factors are, and whether their clinical manifestations differ from the general population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>The study aimed to address all these issues.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In a case‐controlled survey, we interviewed 1,486 PD patients attending a single tertiary center in Lombardy, Italy and 1,207 family members (controls).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>One hundred five (7.1%) and 92 controls (7.6%) were identified as COVID‐19 cases. COVID‐19 patients were younger, more likely to suffer from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, to be obese, and vitamin D nonsupplemented than unaffected patients. Six patients (5.7%) and 7 family members (7.6%) died from COVID‐19. Patients were less likely to report shortness of breath and require hospitalization.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>In an unselected large cohort of nonadvanced PD patients, COVID‐19 risk and mortality did not differ from the general population, but symptoms appeared to be milder. The possible protective role of vitamin D supplementation warrants future studies. © 2020 International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/mds.28176"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-05-12"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-05-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-06-26"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5346-0180",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Edmond J. Safra Program in Parkinson’s Disease and the Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders Centre, Toronto Western Hospital, UHN, Division of Neurology University of Toronto Toronto Ontario Canada"
},
{
"name": "Krembil Brain Institute Toronto Ontario Canada"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fasano",
"given": "Alfonso",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0747-1951",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fondazione IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Pavia Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cereda",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UOS Clinical Nutrition Pini‐CTO, Milan Italy"
},
{
"name": "Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson Italy"
}
],
"family": "Barichella",
"given": "Michela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson Italy"
},
{
"name": "Parkinson Institute Pini‐CTO, Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Cassani",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson Italy"
},
{
"name": "Parkinson Institute Pini‐CTO, Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ferri",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Parkinson Institute Pini‐CTO, Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Zecchinelli",
"given": "Anna Lena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fondazione Grigioni per il Morbo di Parkinson Italy"
},
{
"name": "Parkinson Institute Pini‐CTO, Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pezzoli",
"given": "Gianni",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Movement Disorders",
"container-title-short": "Movement Disorders",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-02T14:04:45Z",
"timestamp": 1591106685000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-06T00:27:49Z",
"timestamp": 1693960069000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-27T17:58:39Z",
"timestamp": 1711562319093
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 122,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-06-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1593129600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.wiley.com/onlinelibrary/tdm/v1/articles/10.1002%2Fmds.28176",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/mds.28176",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/mds.28176",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/mds.28176",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1089-1093",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
6,
26
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4683",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mdc3.12953",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Neurological complications of coronavirus disease (COVID‐19): encephalopathy",
"author": "Filatov A",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.28104",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.28088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.08.012",
"author": "Fasano A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1",
"volume-title": "Predictors of COVID‐19 outcome in Parkinson’s disease"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1",
"unstructured": "Civile DdP. COVID‐19 Italia—Monitoraggio della situazione [online]. Available at:http://opendatadpc.maps.arcgis.com/apps/opsdashboard/index.html#/b0c68bce2cce478eaac82fe38d4138b1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mds.26424",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22838",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"article-title": "A comprehensive literature review on the clinical presentation, and management of the pandemic coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19)",
"author": "Kakodkar P",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Optimisation of vitamin D status for enhanced immuno‐protection against Covid‐19",
"author": "McCartney DM",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Ir Med J",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109767",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25826",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1"
},
{
"article-title": "A SARS‐CoV‐2‐human protein‐protein interaction map reveals drug targets and potential drug‐repurposing",
"author": "Gordon DE",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Amantadine disrupts lysosomal gene expression; potential therapy for COVID19",
"author": "Smieszek SP",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1110/ps.062730007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2012924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs and covid‐19",
"author": "Little P",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JPD-202038",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mdc3.12965",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.03.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.parkreldis.2018.09.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/JPD-160804",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000012488",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2006607",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08959420.2020.1750543",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_36_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mds.28176"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Neurology (clinical)",
"Neurology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "<scp>COVID</scp>‐19 in Parkinson’s Disease Patients Living in Lombardy, Italy",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "35"
}
