Effect of fluvoxamine on preventing neuropsychiatric symptoms of post COVID syndrome in mild to moderate patients, a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5, Mar 2023
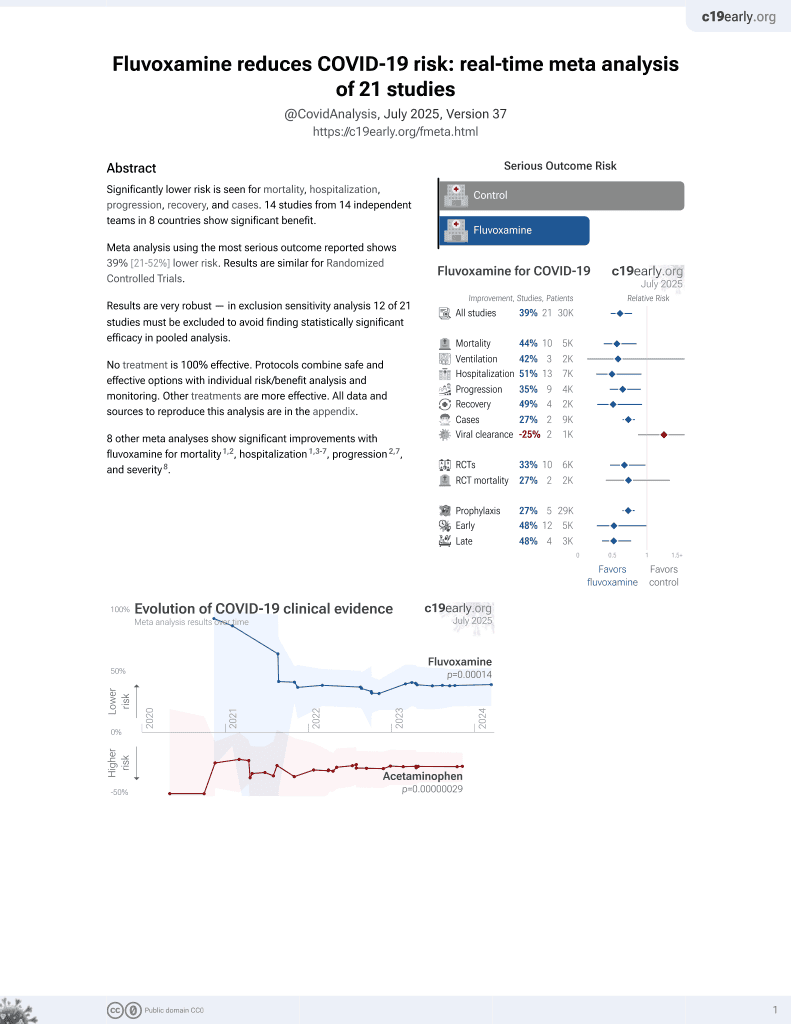
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
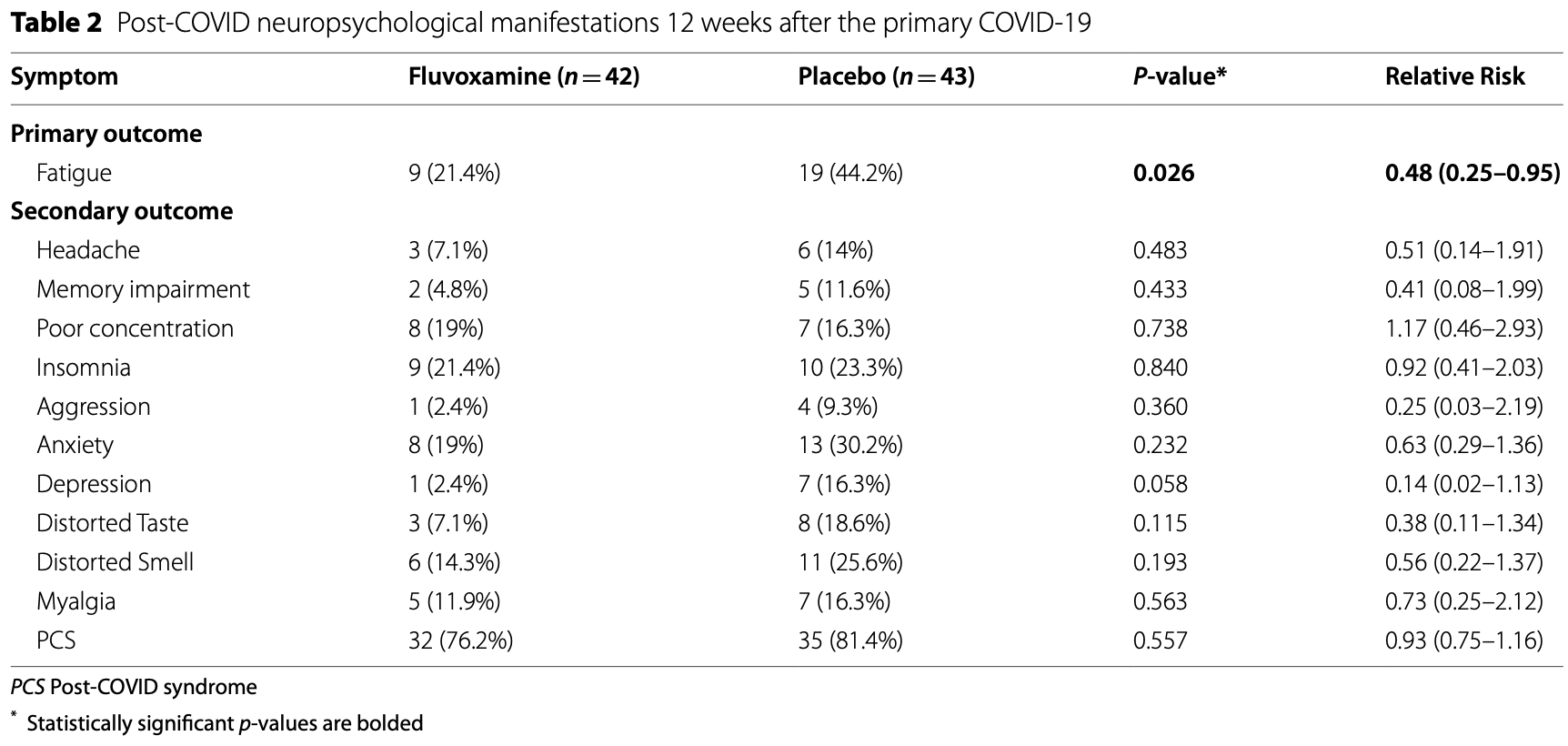
RCT 100 mild/moderate COVID-19 outpatients in Iran, showing lower post COVID symptoms 12 weeks after infection, statistically significant only for fatigue with the small sample size. All symptoms may occur for non-COVID-19 reasons, smell/taste disorder may be the most likely to be related to COVID-19 infection. Fluvoxamine 100mg daily for 10 days.
|
risk of long COVID, 50.8% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.06, treatment 42, control 43, smell and taste disturbance combined.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 44.2% lower, RR 0.56, p = 0.28, treatment 6 of 42 (14.3%), control 11 of 43 (25.6%), NNT 8.9, smell.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 61.6% lower, RR 0.38, p = 0.20, treatment 3 of 42 (7.1%), control 8 of 43 (18.6%), NNT 8.7, taste.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 51.5% lower, RR 0.48, p = 0.04, treatment 9 of 42 (21.4%), control 19 of 43 (44.2%), NNT 4.4, fatigue, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 48.8% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.48, treatment 3 of 42 (7.1%), control 6 of 43 (14.0%), NNT 15, headache.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 59.0% lower, RR 0.41, p = 0.43, treatment 2 of 42 (4.8%), control 5 of 43 (11.6%), NNT 15, memory impairment.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 17.0% higher, RR 1.17, p = 0.78, treatment 8 of 42 (19.0%), control 7 of 43 (16.3%), poor concentration.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 7.9% lower, RR 0.92, p = 1.00, treatment 9 of 42 (21.4%), control 10 of 43 (23.3%), NNT 55, insomnia.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 74.4% lower, RR 0.26, p = 0.36, treatment 1 of 42 (2.4%), control 4 of 43 (9.3%), NNT 14, aggression.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 85.4% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.06, treatment 1 of 42 (2.4%), control 7 of 43 (16.3%), NNT 7.2, depression.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 37.0% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.32, treatment 8 of 42 (19.0%), control 13 of 43 (30.2%), NNT 8.9, anxiety.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 26.9% lower, RR 0.73, p = 0.76, treatment 5 of 42 (11.9%), control 7 of 43 (16.3%), NNT 23, myalgia.
|
|
risk of long COVID, 6.4% lower, RR 0.94, p = 0.60, treatment 32 of 42 (76.2%), control 35 of 43 (81.4%), NNT 19, PCS.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Farahani et al., 31 Mar 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 38.5, 3 authors, study period March 2022 - June 2022.
Contact: ranjbar1382@yahoo.com.
Effect of fluvoxamine on preventing neuropsychiatric symptoms of post COVID syndrome in mild to moderate patients, a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial
BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5
Background Shortly after the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a considerable number of recovered patients reported persisting symptoms, especially neuropsychological manifestations, which were later named post-COVID syndrome (PCS). Immune dysregulation was suggested as one of the main mechanisms for PCS. Fluvoxamine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that is mostly used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessivecompulsive disorder, has been suggested as an anti-COVID drug due to its anti-inflammatory effects, mainly through the sigma-1 receptor. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate fluvoxamine's effect on PCS neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Method In this double-blind randomized clinical trial, we included confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 outpatients using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by an infectious disease specialist. The presence of severe COVID-19 symptoms was evaluated by the infectious disease specialist and included dyspnea, SpO2 < 94% on room air, PaO2/ FiO2 < 300 mm Hg, a respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min, and lung infiltrates > 50%. Then we performed permuted block randomization and assigned patients 1:1 into two groups to either receive fluvoxamine 100 mg tablet or a placebo daily for 10 days. Eligible patients were evaluated after 12 weeks for the presence of fatigue, as the primary, and other PCS symptoms as secondary outcomes.
Results We screened a total of 486 patients from March to June 2022. After 12 weeks, 42 patients receiving fluvoxamine and 43 patients receiving Placebo were evaluated for PCS. Patients had a mean age of 38.5 ± 14.1 and 48% of them were women. Fatigue was significantly lower in the fluvoxamine group (p-value 0.026). No significant differences were observed in other symptoms.
Conclusion We concluded that taking fluvoxamine during active COVID-19 can reduce the chance of fatigue but the advantage of fluvoxamine was not observed for other symptoms. Further studies are necessary to confirm these preliminary results.
Authors' contributions A. Ajam contributed to interpreting the data, draft writing, and final editing. A. Ranjbar Naeini contributed to research design and final editing. R. Hamidi Farahani contributed to the research design and revised it critically. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding All funding support was provided by the AJAUMS.
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate Informed consent was obtained from all study participants. The protocol of this study is by the 2013 Helsinki declaration and was approved by the Ethics Committee of AJA University of Medical Sciences (AJAUMS), Ethics ID: IR.AJAUMS.REC.1400.302. This RCT was registered in the Iranian registry of clinical trials (IRCT), a primary registry in the WHO registry network (registration number: IRCT20220526054990N1) on 01/06/2022.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Bech, Rasmussen, Olsen, Noerholm, Abildgaard, The sensitivity and specificity of the Major Depression Inventory, using the Present State Examination as the index of diagnostic validity, J Affect Disord
Cao, Liu, Xiong, Cai, Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and metaanalysis, J Med Virol
Carfì, Bernabei, Landi, Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19, JAMA
Carroll, Neumann, Aguero-Rosenfeld, Lighter, Czeisler et al., Post-COVID-19 inflammatory syndrome manifesting as refractory status epilepticus, Epilepsia
Chow, Shao, Wang, Lokhnygina, Sample Size Calculations in Clinical Research, doi:10.1201/9781315183084
Davido, Seang, Tubiana, De Truchis, Post-COVID-19 chronic symptoms: a postinfectious entity?, Clin Microbiol Infect
De, Michielsen, Heck, Drent, Measuring fatigue in sarcoidosis: the Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS), Br J Health Psychol
Desgranges, Tadini, Munting, Regina, Filippidis et al., PostCOVID19 syndrome in outpatients: a Cohort Study, J Gen Intern Med
Fernandez-De-Las-Penas, Palacios-Cena, Gomez-Mayordomo, Cuadrado, Florencio, Defining Post-COVID Symptoms (Post-Acute COVID, Long COVID, Persistent Post-COVID): An Integrative Classification, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Hamilton, The assessment of anxiety states by rating, Br J Med Psychol
Hashimoto, Suzuki, Hashimoto, Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review, Mol Psychiatry
Kamal, Omirah, Hussein, Saeed, Assessment and characterisation of post-COVID-19 manifestations, Int J Clin Pract
Kayaaslan, Eser, Kalem, Kaya, Kaplan et al., Post-COVID syndrome: A single-center questionnaire study on 1007 participants recovered from COVID-19, J Med Virol
Lee, Vigod, Bortolussi-Courval, Hanula, Boulware et al., Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization: A systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Mazza, Lorenzo, Conte, Poletti, Vai et al., Anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors: Role of inflammatory and clinical predictors, Brain Behav Immun
Mccain, Antidepressants and suicide in adolescents and adults: a public health experiment with unintended consequences?, P T
Moreno-Perez, Merino, Leon-Ramirez, Andres, Ramos et al., Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Incidence and risk factors: A Mediterranean cohort study, J Infect
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Madhavan, Mcgroder et al., Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat Med
Nasserie, Hittle, Goodman, Assessment of the frequency and variety of persistent symptoms among patients with COVID-19: A systematic review, JAMA Netw Open
Papakostas, Perlis, Scalia, Petersen, Fava, A meta-analysis of early sustained response rates between antidepressants and placebo for the treatment of major depressive disorder, J Clin Psychopharmacol
Posternak, Zimmerman, Is there a delay in the antidepressant effect? A meta-analysis, J Clin Psychiatry
Reis, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane, Milagres et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health
Rosen, Seki, Fernández-Castañeda, Beiter, Eccles et al., Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor-IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis, Sci Transl Med
Salehi, Abedi, Balakrishnan, Gholamrezanezhad, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients, AJR Am J Roentgenol
Sayed, Shokry, Gomaa, Post-COVID-19 fatigue and anhedonia: A cross-sectional study and their correlation to post-recovery period, Neuropsychopharmacol Rep
Sukhatme, Reiersen, Vayttaden, Sukhatme, Fluvoxamine: A review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19, Front Pharmacol
Szegedi, Jansen, Van Willigenburg, Van Der Meulen, Stassen et al., Early improvement in the first 2 weeks as a predictor of treatment outcome in patients with major depressive disorder: a metaanalysis including 6562 patients, J Clin Psychiatry
Taylor, Freemantle, Geddes, Bhagwagar, Early onset of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant action: systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Gen Psychiatry
Tenforde, Kim, Lindsell, Rose, Shapiro et al., Symptom duration and risk factors for delayed return to usual health among outpatients with Covid-19 in a multistate health care systems network -United States, March, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Wijeratne, Crewther, Post-COVID 19 Neurological Syndrome (PCNS); a novel syndrome with challenges for the global neurology community, J Neurol Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2334"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Shortly after the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, a considerable number of recovered patients reported persisting symptoms, especially neuropsychological manifestations, which were later named post-COVID syndrome (PCS). Immune dysregulation was suggested as one of the main mechanisms for PCS. Fluvoxamine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) that is mostly used to treat depression, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder, has been suggested as an anti-COVID drug due to its anti-inflammatory effects, mainly through the sigma-1 receptor. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate fluvoxamine's effect on PCS neuropsychiatric symptoms.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Method</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this double-blind randomized clinical trial, we included confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 outpatients using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) by an infectious disease specialist. The presence of severe COVID-19 symptoms was evaluated by the infectious disease specialist and included dyspnea, SpO2 < 94% on room air, PaO2/FiO2 < 300 mm Hg, a respiratory rate > 30 breaths/min, and lung infiltrates > 50%. Then we performed permuted block randomization and assigned patients 1:1 into two groups to either receive fluvoxamine 100 mg tablet or a placebo daily for 10 days. Eligible patients were evaluated after 12 weeks for the presence of fatigue, as the primary, and other PCS symptoms as secondary outcomes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We screened a total of 486 patients from March to June 2022. After 12 weeks, 42 patients receiving fluvoxamine and 43 patients receiving Placebo were evaluated for PCS. Patients had a mean age of 38.5 ± 14.1 and 48% of them were women. Fatigue was significantly lower in the fluvoxamine group (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic>-value 0.026). No significant differences were observed in other symptoms.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We concluded that taking fluvoxamine during active COVID-19 can reduce the chance of fatigue but the advantage of fluvoxamine was not observed for other symptoms. Further studies are necessary to confirm these preliminary results.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"8172"
],
"article-number": "197",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "24 July 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "31 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Informed consent was obtained from all study participants. The protocol of this study is by the 2013 Helsinki declaration and was approved by the Ethics Committee of AJA University of Medical Sciences (AJAUMS), Ethics ID: IR.AJAUMS.REC.1400.302. This RCT was registered in the Iranian registry of clinical trials (IRCT), a primary registry in the WHO registry network (registration number: IRCT20220526054990N1) on 01/06/2022."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farahani",
"given": "Ramin Hamidi",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ajam",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naeini",
"given": "Alireza Ranjbar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "BMC Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T13:03:25Z",
"timestamp": 1680267805000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T13:05:48Z",
"timestamp": 1680267948000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013778",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Aja University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-01T04:55:27Z",
"timestamp": 1680324927459
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680220800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680220800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.2214/AJR.20.23034",
"author": "S Salehi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "AJR Am J Roentgenol",
"key": "8172_CR1",
"unstructured": "Salehi S, Abedi A, Balakrishnan S, Gholamrezanezhad A. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review of imaging findings in 919 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215(1):87–93.",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25822",
"author": "Y Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1449",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "8172_CR2",
"unstructured": "Cao Y, Liu X, Xiong L, Cai K. Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Med Virol. 2020;92(9):1449–59.",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"author": "A Nalbandian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "601",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "8172_CR3",
"unstructured": "Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan MV, McGroder C, Stevens JS, et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):601–15.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"author": "A Carfì",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "603",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "8172_CR4",
"unstructured": "Carfì A, Bernabei R, Landi F. Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19. JAMA. 2020;324(6):603–5.",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6930e1",
"author": "MW Tenforde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "993",
"issue": "30",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "8172_CR5",
"unstructured": "Tenforde MW, Kim SS, Lindsell CJ, Billig Rose E, Shapiro NI, Files DC, et al. Symptom duration and risk factors for delayed return to usual health among outpatients with Covid-19 in a multistate health care systems network - United States, March-June 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(30):993–8.",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "8172_CR6",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Long COVID or Post-COVID Conditions. 2022. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html. "
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18052621",
"author": "C Fernandez-de-Las-Penas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2621",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "8172_CR7",
"unstructured": "Fernandez-de-Las-Penas C, Palacios-Cena D, Gomez-Mayordomo V, Cuadrado ML, Florencio LL. Defining Post-COVID Symptoms (Post-Acute COVID, Long COVID, Persistent Post-COVID): An Integrative Classification. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(5):2621.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2020.117179",
"author": "T Wijeratne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "117179",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci",
"key": "8172_CR8",
"unstructured": "Wijeratne T, Crewther S. Post-COVID 19 Neurological Syndrome (PCNS); a novel syndrome with challenges for the global neurology community. J Neurol Sci. 2020;419:117179.",
"volume": "419",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11417",
"author": "T Nasserie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2111417",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "8172_CR9",
"unstructured": "Nasserie T, Hittle M, Goodman SN. Assessment of the frequency and variety of persistent symptoms among patients with COVID-19: A systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(5):e2111417.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13746",
"author": "M Kamal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13746",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "8172_CR10",
"unstructured": "Kamal M, Abo Omirah M, Hussein A, Saeed H. Assessment and characterisation of post-COVID-19 manifestations. Int J Clin Pract. 2021;75(3):e13746.",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.07.037",
"author": "MG Mazza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "594",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "8172_CR11",
"unstructured": "Mazza MG, De Lorenzo R, Conte C, Poletti S, Vai B, Bollettini I, et al. Anxiety and depression in COVID-19 survivors: Role of inflammatory and clinical predictors. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;89:594–600.",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "JA McCain",
"first-page": "355",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "P T",
"key": "8172_CR12",
"unstructured": "McCain JA. Antidepressants and suicide in adolescents and adults: a public health experiment with unintended consequences? P T. 2009;34(7):355–78.",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aau5266",
"author": "DA Rosen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5266",
"issue": "478",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "8172_CR13",
"unstructured": "Rosen DA, Seki SM, Fernández-Castañeda A, Beiter RM, Eccles JD, Woodfolk JA, et al. Modulation of the sigma-1 receptor–IRE1 pathway is beneficial in preclinical models of inflammation and sepsis. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(478):5266.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"author": "EJ Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "8172_CR14",
"unstructured": "Lenze EJ, Mattar C, Zorumski CF, Stevens A, Schweiger J, Nicol GE, et al. Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;324(22):2292–300.",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01432-3",
"author": "Y Hashimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1898",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "8172_CR15",
"unstructured": "Hashimoto Y, Suzuki T, Hashimoto K. Mechanisms of action of fluvoxamine for COVID-19: a historical review. Mol Psychiatry. 2022;27(4):1898–907.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.652688",
"author": "VP Sukhatme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "652688",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "8172_CR16",
"unstructured": "Sukhatme VP, Reiersen AM, Vayttaden SJ, Sukhatme VV. Fluvoxamine: A review of its mechanism of action and its role in COVID-19. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:652688.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "8172_CR17",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health. Available at https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/. Accessed 08 Apr 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"author": "World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2191",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "8172_CR18",
"unstructured": "World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA. 2013;310(20):2191–4.",
"volume": "310",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.6269",
"author": "TC Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e226269",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "8172_CR19",
"unstructured": "Lee TC, Vigod S, Bortolussi-Courval E, Hanula R, Boulware DR, Lenze EJ, et al. Fluvoxamine for outpatient management of COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5(4):e226269.",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27198",
"author": "B Kayaaslan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6566",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "8172_CR20",
"unstructured": "Kayaaslan B, Eser F, Kalem AK, Kaya G, Kaplan B, Kacar D, et al. Post-COVID syndrome: A single-center questionnaire study on 1007 participants recovered from COVID-19. J Med Virol. 2021;93(12):6566–74.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11606-021-07242-1",
"author": "F Desgranges",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1943",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Gen Intern Med",
"key": "8172_CR21",
"unstructured": "Desgranges F, Tadini E, Munting A, Regina J, Filippidis P, Viala B, et al. PostCOVID19 syndrome in outpatients: a Cohort Study. J Gen Intern Med. 2022;37(8):1943–52.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1348/1359107041557048",
"author": "De Vries",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "279",
"journal-title": "Br J Health Psychol",
"key": "8172_CR22",
"unstructured": "Vries De, Michielsen H, Van Heck GL, Drent M. Measuring fatigue in sarcoidosis: the Fatigue Assessment Scale (FAS). Br J Health Psychol. 2004;9:279–91. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15296678.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/epi.16683",
"author": "E Carroll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e135",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Epilepsia",
"key": "8172_CR23",
"unstructured": "Carroll E, Neumann H, Aguero-Rosenfeld ME, Lighter J, Czeisler BM, Melmed K, et al. Post-COVID-19 inflammatory syndrome manifesting as refractory status epilepticus. Epilepsia. 2020;61(10):e135–9.",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.028",
"author": "B Davido",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1448",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "8172_CR24",
"unstructured": "Davido B, Seang S, Tubiana R, de Truchis P. Post-COVID-19 chronic symptoms: a postinfectious entity? Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020;26(11):1448–9.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/npr2.12154",
"author": "S El Sayed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychopharmacol Rep",
"key": "8172_CR25",
"unstructured": "El Sayed S, Shokry D, Gomaa SM. Post-COVID-19 fatigue and anhedonia: A cross-sectional study and their correlation to post-recovery period. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep. 2021;41(1):50–5.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.004",
"author": "O Moreno-Perez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "378",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "8172_CR26",
"unstructured": "Moreno-Perez O, Merino E, Leon-Ramirez JM, Andres M, Ramos JM, Arenas-Jimenez J, et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Incidence and risk factors: A Mediterranean cohort study. J Infect. 2021;82(3):378–83.",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x",
"author": "M Hamilton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "50",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Br J Med Psychol",
"key": "8172_CR27",
"unstructured": "Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32(1):50–5.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1959"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0165-0327(00)00309-8",
"author": "P Bech",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "159",
"issue": "2–3",
"journal-title": "J Affect Disord",
"key": "8172_CR28",
"unstructured": "Bech P, Rasmussen NA, Olsen LR, Noerholm V, Abildgaard W. The sensitivity and specificity of the Major Depression Inventory, using the Present State Examination as the index of diagnostic validity. J Affect Disord. 2001;66(2–3):159–64.",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1201/9781315183084",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "8172_CR29",
"unstructured": "Chow S-C, Shao J, Wang H, Lokhnygina Y. Sample Size Calculations in Clinical Research (3rd ed.). Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781315183084."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"author": "G Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e42",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "8172_CR30",
"unstructured": "Reis G, dos Santos Moreira-Silva EA, Silva DCM, Thabane L, Milagres AC, Ferreira TS, et al. Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial. Lancet Glob Health. 2022;10(1):e42–51.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.jcp.0000195042.62724.76",
"author": "GI Papakostas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "56",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Clin Psychopharmacol",
"key": "8172_CR31",
"unstructured": "Papakostas GI, Perlis RH, Scalia MJ, Petersen TJ, Fava M. A meta-analysis of early sustained response rates between antidepressants and placebo for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2006;26(1):56–60.",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4088/JCP.07m03780",
"author": "A Szegedi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "344",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Psychiatry",
"key": "8172_CR32",
"unstructured": "Szegedi A, Jansen WT, van Willigenburg AP, van der Meulen E, Stassen HH, Thase ME. Early improvement in the first 2 weeks as a predictor of treatment outcome in patients with major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis including 6562 patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(3):344–53.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archpsyc.63.11.1217",
"author": "MJ Taylor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1217",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Arch Gen Psychiatry",
"key": "8172_CR33",
"unstructured": "Taylor MJ, Freemantle N, Geddes JR, Bhagwagar Z. Early onset of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressant action: systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(11):1217–23.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4088/JCP.v66n0201",
"author": "MA Posternak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "148",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "A meta-analysis J Clin Psychiatry",
"key": "8172_CR34",
"unstructured": "Posternak MA, Zimmerman M. Is there a delay in the antidepressant effect? A meta-analysis J Clin Psychiatry. 2005;66(2):148–58.",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2005"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-023-08172-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of fluvoxamine on preventing neuropsychiatric symptoms of post COVID syndrome in mild to moderate patients, a randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "23"
}