Higher Scores of Ambient Temperature, Sunshine Hours and UV Index are Associated with Lower COVID-19 Mortality
, M., The Open COVID Journal, doi:10.2174/26669587-v2-e221209-2022-24, Dec 2022
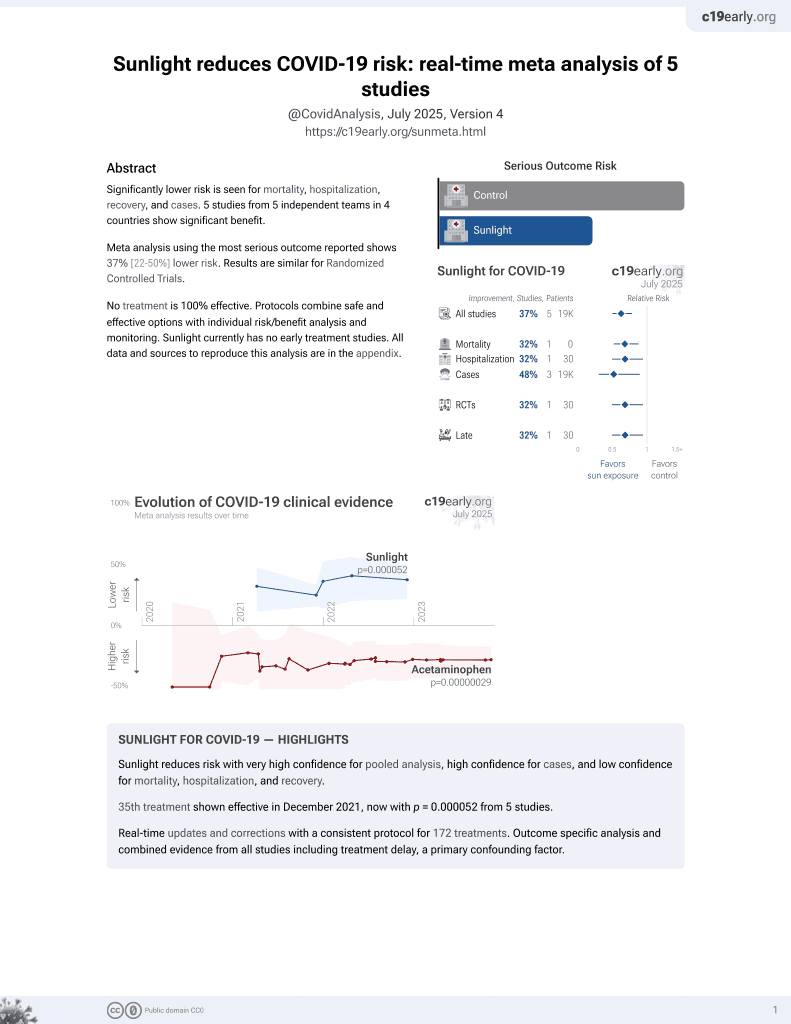
Sunlight for COVID-19
36th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2021, now with p = 0.000052 from 5 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
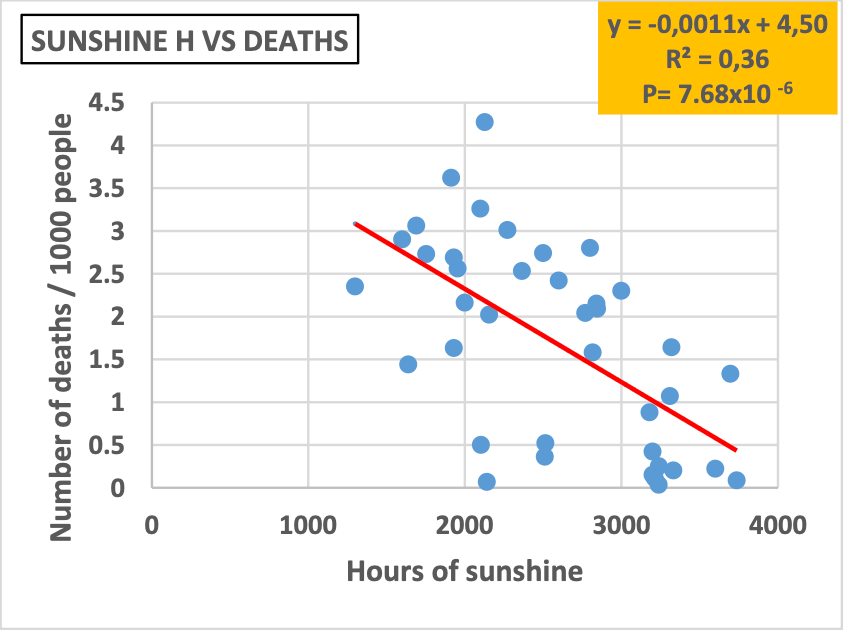
Analysis of COVID-19 deaths in 39 countries, showing mortality negatively correlated with sunshine hours.
Errasfa et al., 30 Dec 2022, Morocco, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: mourad.errasfa@usmba.ac.ma.
Higher Scores of Ambient Temperature, Sunshine Hours and UV Index are Associated with Lower COVID-19 Mortality
The Open COVID Journal, doi:10.2174/26669587-v2-e221209-2022-24
Background: Following two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, thousands of deaths were registered around the world. A question on whether climate parameters in each country could or not affect coronavirus incidence and COVID-19 death toll is under debate.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The author declares no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
AKNOWLEDGEMENTS Declared none.
References
Arumugam, Menon, Narayan, Ambient temperature and [37] COVID-19 incidence rates: An opportunity for intervention? Western Pac, Surveill Response J
Biasin, Bianco, Pareschi, UV-C irradiation is highly [22] effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2 replication, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-85425-w
Carleton, Cornetet, Huybers, Meng, Proctor, Global [21] evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2012370118
Caspi, Shalit, Kristensen, COVID-19 spread rate: An online surveillance tool, doi:10.1101/2020.03.26.20044727
Chan, Yuan, Kok, A familial cluster of pneumonia [1] associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-toperson transmission: A study of a family cluster, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9
Chen, Prettner, Cao, Revisiting the association between [17] temperature and COVID-19 transmissibility across 117 countries, ERJ Open Res, doi:10.1183/23120541.00550-2020
Chen, Prettner, Kuhn, Climate and the spread of [18] COVID-19, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-87692-z
Cherrie, Clemens, Colandrea, Ultraviolet A radiation and [23] COVID-19 deaths in the USA with replication studies in England and Italy, Br J Dermatol, doi:10.1111/bjd.20093
Chiyomaru, Takemoto, Global COVID-19 transmission rate [39] is influenced by precipitation seasonality and the speed of climate temperature warming, doi:10.1101/2020.04.10.20060459
Cui, Chen, Li, Liu, Wang, Prevalence of venous [5] thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14830
Cuschieri, The STROBE guidelines, J Anaesth
Davies, Klepac, Liu, Age-dependent effects in the [45] transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9
De Angelis, Renzetti, Volta, COVID-19 incidence and [25] mortality in Lombardy, Italy: An ecological study on the role of air pollution, meteorological factors, demographic and socioeconomic variables, Environ Res, doi:10.1016/j.envres.2021.110777
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and COVID-19 possible link and [6] implications, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018
Errasfa, Blood hemostasis dysfunction and inflammation in [10] COVID-19 patients: Viral and host active molecules as therapeutic targets, Open Toxicol J, doi:10.2174/1874340402107010001
Errasfa, Magnesium therapeutic potential against COVID-19: Could
Fontal, Bouma, San-José, López, Pascual et al., None
Gupta, Gupta, Wymant, Kendall, Effect of ambient temperature on COVID 19 [43] infection rate: Evidence from California, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3575404
Hu, Xiao, Zhu, Zhu, Liu, Correlation between local air [14] temperature and the COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, China, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.604870
Isaia, Diémoz, Maluta, Does solar ultraviolet radiation [26] play a role in COVID-19 infection and deaths? An environmental ecological study in Italy, Sci Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143757
Livadiotis, Statistical analysis of the impact of environmental [36] temperature on the exponential growth rate of cases infected by COVID-19, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233875
Ma, Pei, Shaman, Dubrow, Chen, Role of meteorological [24] factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23866-7
Meo, Abukhalaf, Alomar, Climate and COVID-19
Mourad, Milk oligosaccharides and lectins as candidates for clinical [13] trials against COVID-19, Curr Nutr Food Sci
Nakano, Chiang, Chen, Sunlight exposure and [28] phototherapy: Perspectives for healthy aging in an era of COVID-19, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph182010950
Nicastro, Sironi, Antonello, Forcing seasonality of [20] influenza-like epidemics with daily solar resonance, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2020.101605
Notari, Temperature dependence of COVID-19 transmission
Sajadi, Habibzadeh, Vintzileos, Temperature and [41] latitude analysis to predict potential spread and seasonality for COVID-19, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3550308
Tang, Liu, Ren, Sunlight ultraviolet radiation dose is [27] negatively correlated with the percent positive of SARS-CoV-2 and four other common human coronaviruses in the U, S. Sci Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141816
Tobaiqy, Qashqary, Al-Dahery, Therapeutic management
Tsai, Lin, Chang, Probiotics, prebiotics and [11] amelioration of diseases, J Biomed Sci, doi:10.1186/s12929-018-0493-6
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Estimates of the severity of
Wu, Jing, Liu, Effects of temperature and humidity on the
Wu, Zhao, Yu, A new coronavirus associated with human [2] respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3
Zhu, Zhu, Wang, The association between ambient [15] temperature and mortality of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: A time-series analysis, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-020-10131-7
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Alterations in gut microbiota of [7] patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2174/26669587-v2-e221209-2022-24",
"ISSN": [
"2666-9587"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/26669587-v2-e221209-2022-24",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Following two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, thousands of deaths were registered around the world. A question on whether climate parameters in each country could or not affect coronavirus incidence and COVID-19 death toll is under debate.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objective:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this work, we aimed to analyse possible relation between the prevalence of COVID-19 deaths and the geographic latitude. The study focused on the geographic latitudes and some of their associated climate factors, such as the average annual level of temperature, sunshine hours and UV index.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We sought the number of the deaths caused by COVID-19 in 39 countries. Latitude levels were plotted against the average annual levels of either temperature, sunshine hours or UV index. Data were analysed by simple linear regression or polynomial regression, by means of Microsoft Excel software (2016).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>When COVID-19 death numbers were plotted against geographic latitudes, we obtained inverted bell-shaped curves, for both the first and second year of the pandemic, with a coefficient of determination of (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,32) and (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,39), respectively. In addition, COVID-19 death numbers were very negatively correlated with the average annual levels of temperature (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,52, P= 4.92x10<jats:sup>-7</jats:sup>), sunshine hours (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,36, P= 7.68x10<jats:sup>-6</jats:sup>) and UV index (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,38, P= 4.16x10<jats:sup>-5</jats:sup>). Bell-shaped curves were obtained when latitude was plotted against the average annual number of temperature, sunshine hours and UV index, with a coefficient of determination of (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,85), (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,452) and (R<jats:sup>2</jats:sup> = 0,87), respectively.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion:</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In contrast to high-latitude countries, countries located at low latitudes may have suffered less COVID-19 death tolls, thanks to their elevated temperature, sunshine hours and UV index. The above climate factors, in addition to yet unknown factors, could have impaired the spread of the coronavirus and/or helped individual’s natural immunity to fight COVID-19 disease.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Peer Review Details",
"name": "peer_review_details"
},
"label": "Review Status",
"name": "review_status",
"order": 0,
"value": "Peer Reviewed"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Peer Review Details",
"name": "peer_review_details"
},
"label": "Review Process",
"name": "review_process",
"order": 1,
"value": "Single blind"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Plagiarism Screening",
"name": "plagiarism_screening"
},
"label": "Screening Status",
"name": "screening_status",
"order": 0,
"value": "Checked with iThenticate"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2022-5-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-9-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-10-13"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2022-12-30"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Errasfa",
"given": "Mourad",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "The Open COVID Journal",
"container-title-short": "TOCOVIDJ",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"opencovidjournal.com",
"benthamopen.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-09T10:14:32Z",
"timestamp": 1670580872000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T04:28:52Z",
"timestamp": 1672979332000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-07T06:01:07Z",
"timestamp": 1673071267543
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672358400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://opencovidjournal.com/contents/volumes/V2/e266695872212090/e266695872212090.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://opencovidjournal.com/contents/volumes/V2/e266695872212090/e266695872212090.xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://opencovidjournal.com/contents/volumes/V2/e266695872212090/e266695872212090.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.2174",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Bentham Science Publishers Ltd.",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Chan JFW, Yuan S, Kok KH, et al. \n A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. \n Lancet \n 2020; \n 395\n (10223)\n : 514-23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Wu F, Zhao S, Yu B, et al. \n A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. \n Nature \n 2020; \n 579\n (7798)\n : 265-9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.19.956581",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici A, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D. \n Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARSCoV- 2 spike glycoprotein. \n Cell \n 2020; \n 8674\n (20)\n : 30262-2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Verity R, Okell LC, Dorigatti I, et al. \n Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A model-based analysis. \n Lancet Infect Dis \n 2020; \n 20\n (6)\n : 669-77."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14830",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Cui S, Chen S, Li X, Liu S, Wang F. \n Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia. \n J Thromb Haemost \n 2020; \n 18\n (6)\n : 1421-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Dhar D, Mohanty A. \n Gut microbiota and COVID-19 possible link and implications. \n Virus Res \n 2020; \n 285\n : 198018."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Zuo T, Zhang F, Lui GCY, et al. \n Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization. \n Gastroenterology \n 2020; \n 159\n (3)\n : 944-55."
},
{
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Ricardo J. \n COVID-19 cytokine storm: The interplay between inflammation and coagulation. \n Lancet Respir Med \n 2020; \n (20): \n 30216-2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.infpip.2020.100061",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Tobaiqy M, Qashqary M, Al-Dahery S, et al. \n Therapeutic management of patients with COVID-19: A systematic review. \n Infect Prev Pract \n 2020; \n 2\n (3)\n : 100061."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1874340402107010001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Errasfa M. \n Blood hemostasis dysfunction and inflammation in COVID-19 patients: Viral and host active molecules as therapeutic targets. \n Open Toxicol J \n 2021; \n 7\n (1)\n : 1-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12929-018-0493-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Tsai YL, Lin TL, Chang CJ, et al. \n Probiotics, prebiotics and amelioration of diseases. \n J Biomed Sci \n 2019; \n 26\n (1)\n : 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/mrh.2020.0474",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Errasfa M. \n Magnesium therapeutic potential against COVID-19: Could it be an “All-in-one” therapy? \n Magnes Res \n 2021; \n 34\n (1)\n : 32-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573401316999200819125355",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Mourad E. \n Milk oligosaccharides and lectins as candidates for clinical trials against COVID-19. \n Curr Nutr Food Sci \n 2021; \n 17\n (3)\n : 246-8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.604870",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Hu C, Xiao L, Zhu H, Zhu H, Liu L. \n Correlation between local air temperature and the COVID-19 pandemic in Hubei, China. \n Front Public Health \n 2021; \n 8\n : 604870."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-020-10131-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Zhu G, Zhu Y, Wang Z, et al. \n The association between ambient temperature and mortality of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China: A time-series analysis. \n BMC Public Health \n 2021; \n 21\n (1)\n : 117."
},
{
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Meo SA, Abukhalaf AA, Alomar AA, et al. \n Climate and COVID-19 pandemic: Effect of heat and humidity on the incidence and mortality in world’s top ten hottest and top ten coldest countries. \n Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci \n 2020; \n 24\n (15)\n : 8232-8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/23120541.00550-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Chen S, Prettner K, Cao B, et al. \n Revisiting the association between temperature and COVID-19 transmissibility across 117 countries. \n ERJ Open Res \n 2020; \n 6\n (4)\n : 00550-2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-87692-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Chen S, Prettner K, Kuhn M, et al. \n Climate and the spread of COVID-19. \n Sci Rep \n 2021; \n 11\n (1)\n : 9042."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43588-021-00136-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Fontal A, Bouma MJ, San-José A, López L, Pascual M, Rodó X. \n Climatic signatures in the different COVID-19 pandemic waves across both hemispheres. \n Nature Computational Science \n 2021; \n 1\n (10)\n : 655-65."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2020.101605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Nicastro F, Sironi G, Antonello E, et al. \n Forcing seasonality of influenza-like epidemics with daily solar resonance. \n iScience \n 2020; \n 23\n (10)\n : 101605."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012370118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Carleton T, Cornetet J, Huybers P, Meng KC, Proctor J. \n Global evidence for ultraviolet radiation decreasing COVID-19 growth rates. \n Proc Natl Acad Sci USA \n 2021; \n 118\n (1)\n : e2012370118."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85425-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Biasin M, Bianco A, Pareschi G, et al. \n UV-C irradiation is highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2 replication. \n Sci Rep \n 2021; \n 11\n (1)\n : 6260."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjd.20093",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23",
"unstructured": "Cherrie M, Clemens T, Colandrea C, et al. \n Ultraviolet A radiation and COVID‐19 deaths in the USA with replication studies in England and Italy. \n Br J Dermatol \n 2021; \n 185\n (2)\n : 363-70."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23866-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24",
"unstructured": "Ma Y, Pei S, Shaman J, Dubrow R, Chen K. \n Role of meteorological factors in the transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States. \n Nat Commun \n 2021; \n 12\n (1)\n : 3602."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2021.110777",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25",
"unstructured": "De Angelis E, Renzetti S, Volta M, et al. \n COVID-19 incidence and mortality in Lombardy, Italy: An ecological study on the role of air pollution, meteorological factors, demographic and socioeconomic variables. \n Environ Res \n 2021; \n 195\n : 110777."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.143757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26",
"unstructured": "Isaia G, Diémoz H, Maluta F, et al. \n Does solar ultraviolet radiation play a role in COVID-19 infection and deaths? An environmental ecological study in Italy. \n Sci Total Environ \n 2021; \n 757\n : 143757."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141816",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27",
"unstructured": "Tang L, Liu M, Ren B, et al. \n Sunlight ultraviolet radiation dose is negatively correlated with the percent positive of SARS-CoV-2 and four other common human coronaviruses in the U.S. \n Sci Total Environ \n 2021; \n 751\n : 141816."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph182010950",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28",
"unstructured": "Nakano T, Chiang KC, Chen CC, et al. \n Sunlight exposure and phototherapy: Perspectives for healthy aging in an era of COVID-19. \n Int J Environ Res Public Health \n 2021; \n 18\n (20)\n : 10950."
},
{
"key": "ref29",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). \n \n Available from: https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus"
},
{
"key": "ref30",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). \n \n Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html"
},
{
"key": "ref31",
"unstructured": "Esotc. \n Climate \n Spotlight On, Sunshine duration \n 2018.\n \n Available from: https://climate.copernicus.eu/sunshine-duration"
},
{
"key": "ref32",
"unstructured": "UV Index worldwide. \n \n Available from: https://www.bfs.de/EN/topics/opt/uv/index/worldwide/worldwide.html"
},
{
"key": "ref33",
"unstructured": "Ultraviolet radiation: global solar UV index. \n \n Available from: https://allcountries.org/health/ultraviolet_radiation_global_solar_uv_index.html"
},
{
"key": "ref34",
"unstructured": "Current Climate, Climatology. \n \n Available from: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/country/guinea/climate-data-historical"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/sja.SJA_543_18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35",
"unstructured": "Cuschieri S. \n The STROBE guidelines. \n Saudi J Anaesth \n 2019; \n 13\n (5)\n : 31."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0233875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36",
"unstructured": "Livadiotis G. \n Statistical analysis of the impact of environmental temperature on the exponential growth rate of cases infected by COVID-19. \n PLoS One \n 2020; \n 15\n (5)\n : e0233875."
},
{
"key": "ref37",
"unstructured": "Arumugam M, Menon B, Narayan SK. \n Ambient temperature and COVID-19 incidence rates: An opportunity for intervention? \n Western Pac Surveill Response J \n 2020; \n 17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.26.20044727",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38",
"unstructured": "Caspi G, Shalit U, Kristensen SL, et al. \n 2020.\n Climate effect on COVID-19 spread rate: An online surveillance tool. \n medRxiv"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.10.20060459",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39",
"unstructured": "Chiyomaru K, Takemoto K. \n 2020.\n Global COVID-19 transmission rate is influenced by precipitation seasonality and the speed of climate temperature warming. \n medRxiv"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.26.20044529",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40",
"unstructured": "Notari A. \n 2020.\n Temperature dependence of COVID-19 transmission. \n medRxiv"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3550308",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41",
"unstructured": "Sajadi MM, Habibzadeh P, Vintzileos A, et al. \n \n Temperature and latitude analysis to predict potential spread and seasonality for COVID-19. \n SSRN \n 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42",
"unstructured": "Wu Y, Jing W, Liu J, et al. \n Effects of temperature and humidity on the daily new cases and new deaths of COVID-19 in 166 countries. \n Sci Total Environ \n 2020; \n 729\n : 139051."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3575404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref43",
"unstructured": "Gupta D, Gupta A. \n \n Effect of ambient temperature on COVID 19 infection rate: Evidence from California. \n SSRN \n 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb6936",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44",
"unstructured": "Ferretti L, Wymant C, Kendall M, et al. \n Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing. \n Science \n 2020; \n 368\n (6491)\n : eabb6936."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0962-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45",
"unstructured": "Davies NG, Klepac P, Liu Y, et al. \n Age-dependent effects in the transmission and control of COVID-19 epidemics. \n Nat Med \n 2020; \n 26\n (8)\n : 1205-11."
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://opencovidjournal.com/VOLUME/2/ELOCATOR/e266695872212090/"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Higher Scores of Ambient Temperature, Sunshine Hours and UV Index are Associated with Lower COVID-19 Mortality",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2174/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "2"
}