Exploration of shared gene signatures and molecular mechanisms between psoriasis and COVID-19: evidence from transcriptome data
et al., Mammalian Genome, doi:10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8, Jan 2026
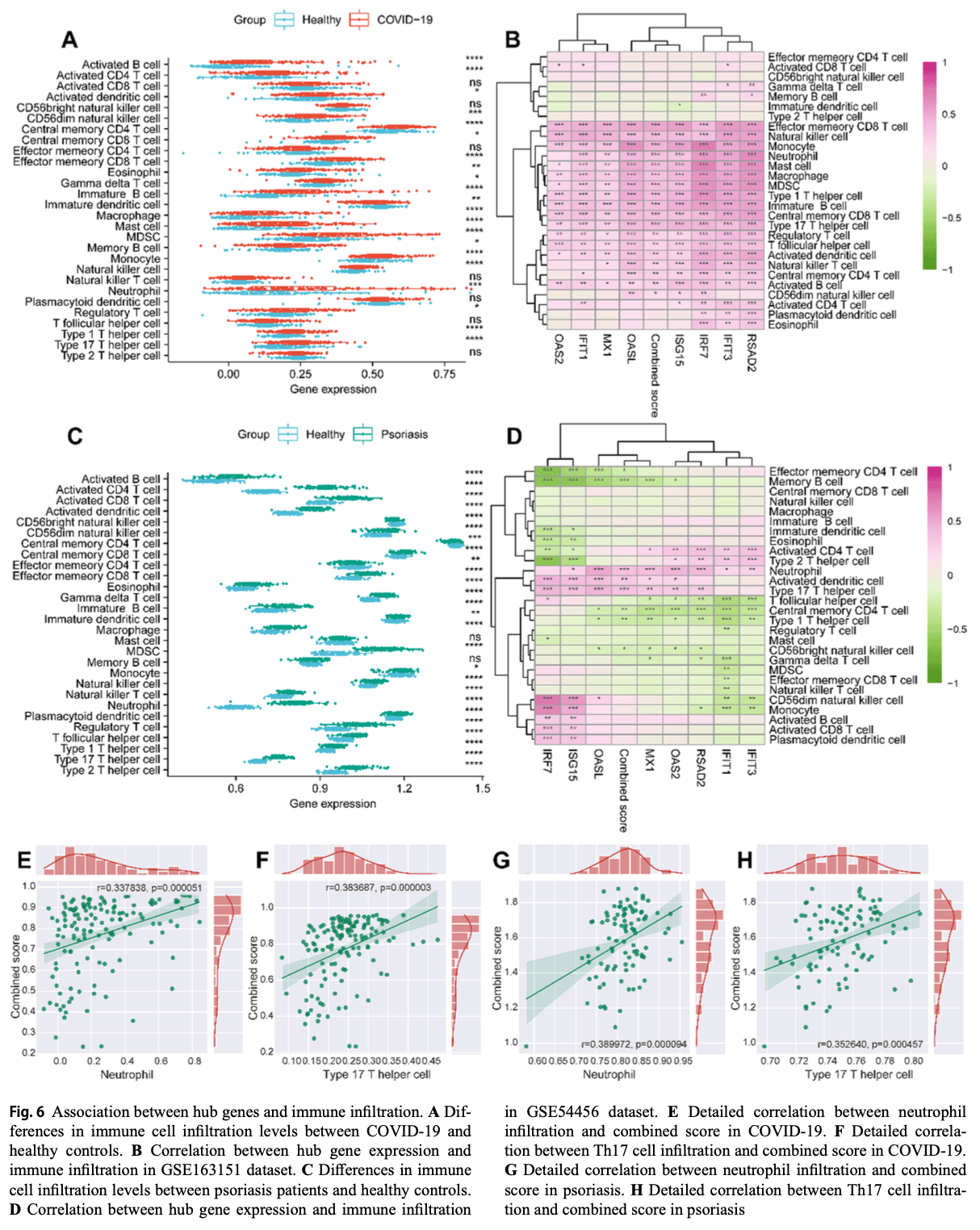
In silico study showing shared molecular mechanisms between COVID-19 and psoriasis through transcriptomic analysis. Authors identified 66 common upregulated genes between the two conditions, with eight hub genes (OAS2, MX1, IRF7, RSAD2, OASL, IFIT1, IFIT3, and ISG15) showing high diagnostic accuracy (AUC >0.7 for COVID-19, AUC >0.9 for psoriasis).
Dong et al., 13 Jan 2026, China, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: yyeli2000@126.com, youwanglu@163.com.
Exploration of shared gene signatures and molecular mechanisms between psoriasis and COVID-19: evidence from transcriptome data
Mammalian Genome, doi:10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8
Emerging evidence suggests that the onset or worsening of psoriasis can occur following COVID-19 infection or vaccination. Additionally, individuals with psoriasis may be more susceptible to COVID-19. However, the underlying mechanisms driving this phenomenon remain unclear. This study aims to explore the potential shared mechanisms and the complex interplay between psoriasis and COVID-19. Gene expression profiles for COVID-19 (GSE162183) and psoriasis (GSE54456) were obtained from the Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Common differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, followed by functional annotation, protein-protein interaction (PPI) network construction, and hub gene identification. Validation of hub genes was performed using independent datasets (GSE152075 and GSE157103 for COVID-19; GSE121212 and GSE78097 for psoriasis). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to assess the predictive value of the hub genes. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) and immune infiltration analysis were conducted, and expression patterns of the hub genes were further explored using a single-cell RNA sequencing dataset. A total of 66 common DEGs (all upregulated) were identified. The influenza A and NOD-like receptor signaling pathways were enriched in both COVID-19 and psoriasis. OAS2, MX1, IRF7, RSAD2, OASL, IFIT1, IFIT3, and ISG15 were identified as hub genes after validation, with all are under the curve (AUC) > 0.7 for COVID-19 and AUC > 0.9 for psoriasis. Upregulation of these hub genes was associated with increased infiltration of neutrophils and Th17 cells. Singlecell analysis showed that the hub genes were primarily expressed in epithelial cells in COVID-19 and keratinocytes in psoriasis. This study reveals shared pathogenic mechanisms between psoriasis and COVID-19 and provides insights into how COVID-19 may exacerbate psoriasis. The identified common pathways, hub genes, and associated cell types offer valuable guidance for future research and potential therapeutic targets.
Author contributions Conceptualization, Data curation, YWL; Formal analysis, YWL; Funding acquisition, YYL, RJD, and YWL; Investigation, Methodology, LHY; Supervision, YYL; Visualization, Writing -original draft, RJD; Writing -review & editing, all authors.
Declarations Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval Not applicable. Consent to participate Not applicable.
Consent for publication Not applicable. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit h t t p : / / c r e a t i v e c o m m o n s . o r g / l i c e n s e s..
References
Aibar, SCENIC: single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering, Nat Methods
Amerio, COVID-19 and psoriasis: should we fear for patients treated with biologics?, Dermatol Ther
Antunes, Microbiota-derived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response, Nat Commun
Ardoin, Pisetsky, Developments in the scientific Understanding of lupus, Arthritis Res Ther
Chen, Liu, Cao, Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: a comprehensive review, J Autoimmun
Criado, COVID-19 and skin diseases: results from a survey of 843 patients with atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, vitiligo and chronic urticaria, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Crow, Stetson, The type I interferonopathies: 10 years on, Nat Rev Immunol
Dong, Identification of key molecules in COVID-19 patients significantly correlated with clinical outcomes by analyzing transcriptomic data, Front Immunol
Dupire, Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Ebrahimi, Sayad, Rahimi, COVID-19 and psoriasis: biologic treatment and challenges, J Dermatolog Treat
Galeotti, Bayry, Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases following COVID-19, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Gao, Single cell transcriptional zonation of human psoriasis skin identifies an alternative immunoregulatory axis conducted by skin resident cells, Cell Death Dis
Griffiths, Barker, Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis, Lancet
Griffiths, None, Psoriasis. Lancet
Gunes, Possible triggering effect of influenza vaccination on psoriasis, J Immunol Res
Hall, Rosen, Type i interferons: crucial participants in disease amplification in autoimmunity, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Hao, Wang, Li, FKBP5 regulates RIG-I-mediated NF-kappaB activation and influenza A virus infection, Viruses. h t t p s, doi:10.3390/v12060672
Hu, Identification of hub genes and molecular subtypes in COVID-19 based on WGCNA, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kalliolias, Ivashkiv, Overview of the biology of type I interferons, Arthritis Res Ther
Kim, The spectrum of mild to severe psoriasis vulgaris is defined by a common activation of IL-17 pathway genes, but with key differences in immune regulatory genes, J Invest Dermatol
Krajewski, Matusiak, Szepietowski, Psoriasis flareup associated with second dose of Pfizer-BioNTech BNT16B2b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Kuang, Association of outdoor activity restriction and income loss with patient-reported outcomes of psoriasis during the COVID-19 pandemic: A web-based survey, J Am Acad Dermatol
Kutlu, Metin, Dermatological diseases presented before COVID-19: are patients with psoriasis and superficial fungal infections more vulnerable to the COVID-19?, Dermatol Ther
Li, Transcriptome analysis of psoriasis in a large casecontrol sample: RNA-seq provides insights into disease mechanisms, J Invest Dermatol
Lieberman, In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age, PLoS Biol
Liu, Sawalha, Lu, COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases, Curr Opin Rheumatol
Lu, L36G is associated with cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis, Front Immunol
Macias, Cunha, Psoriasis triggered by tetanus-diphtheria vaccination, Cutan Ocul Toxicol
Melero, Deciphering psoriasis. A bioinformatic approach, J Dermatol Sci
Miladi, Pustular psoriasis flare-up in a patient with COVID-19, J Cosmet Dermatol
Nasiri, A challenging case of psoriasis flare-up after COVID-19 infection, J Dermatolog Treat
Nehar-Belaid, Mapping systemic lupus erythematosus heterogeneity at the single-cell level, Nat Immunol
Overmyer, Large-Scale Multi-omic analysis of COVID-19 severity, Cell Syst
Ozaras, Covid-19 and exacerbation of psoriasis, Dermatol Ther
Phillips, Lymphatic type 1 interferon responses are critical for control of systemic reovirus dissemination, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02167-20
Picard, Belot, Does type-I interferon drive systemic autoimmunity?, Autoimmun Rev
Raposo, Antiviral gene expression in psoriasis, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Sachs, plotROC: a tool for plotting ROC curves, J Stat Softw. h t t p s, doi:10.18637/jss.v079.c02
Schoggins, Interferon-stimulated genes: what do they all do?, Annu Rev Virol
Singh, SARS-CoV-2 and its beta variant of concern infect human conjunctival epithelial cells and induce differential antiviral innate immune response, Ocul Surf
Skaug, Assassi, Type I interferon dysregulation in systemic sclerosis, Cytokine
Sotiriou, Psoriasis exacerbation after COVID-19 vaccination: a report of 14 cases from a single centre, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Stallmach, Infliximab against severe COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome with organ failure-a cautionary case series, Crit Care
Takeshita, Risk of serious Infection, opportunistic Infection, and herpes Zoster among patients with psoriasis in the united Kingdom, J Invest Dermatol
Tsoi, Atopic dermatitis is an IL-13-Dominant disease with greater molecular heterogeneity compared to psoriasis, J Invest Dermatol
Wahadat, Type I IFN signature in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: a conspiracy of DNA-and RNAsensing receptors?, Arthritis Res Ther
Wolk, IL-29 is produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis, Sci Transl Med
Wu, New onset and exacerbations of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccines: a systematic review, Am J Clin Dermatol
Wu, Yang, TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: an emerging target of JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Yan, The role of the skin and gut Microbiome in psoriatic disease, Curr Dermatol Rep
Zhang, Integrated bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways in plaque psoriasis, Mol Med Rep
Zhang, Transcriptional profiling and machine learning unveil a concordant biosignature of type I Interferon-Inducible host response across nasal swab and pulmonary tissue for COVID-19 diagnosis, Front Immunol
Zhou, Heightened innate immune responses in the respiratory tract of COVID-19 patients, Cell Host Microbe
Zhou, Yao, Roles of infection in psoriasis, Int J Mol Sci. h t t, doi:10.3390/ijms23136955
Zumla, Reducing mortality from 2019-nCoV: host-directed therapies should be an option, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8",
"ISSN": [
"0938-8990",
"1432-1777"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8",
"alternative-id": [
"10194"
],
"article-number": "23",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "19 August 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "3 January 2026"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "13 January 2026"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 5,
"value": "Not applicable."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dong",
"given": "Rong-Jing",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Lu-Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Yu-Ye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "You-Wang",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Mammalian Genome",
"container-title-short": "Mamm Genome",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-13T21:12:29Z",
"timestamp": 1768338749000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-14T09:05:38Z",
"timestamp": 1768381538000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82203934"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"82203934"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "the National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82272356"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"82272356"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "the National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"21xjz33R"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"21xjz33R"
]
}
],
"name": "the Talent Introduction Project of Hubei Polytechnic University"
},
{
"award": [
"21xjz34R"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"21xjz34R"
]
}
],
"name": "the Talent Introduction Project of Hubei Polytechnic University"
},
{
"award": [
"202403AC100011"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"202403AC100011"
]
}
],
"name": "the Key research and development program of Yunnan Province"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-14T15:05:11Z",
"timestamp": 1768403111024,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768262400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768262400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4463",
"author": "S Aibar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1083",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Methods",
"key": "10194_CR1",
"unstructured": "Aibar S et al (2017) SCENIC: single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering. Nat Methods 14(11):1083–1086",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13434",
"author": "P Amerio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13434",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Ther",
"key": "10194_CR2",
"unstructured": "Amerio P et al (2020) COVID-19 and psoriasis: should we fear for patients treated with biologics? Dermatol Ther 33(4):e13434",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-019-11152-6",
"author": "KH Antunes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3273",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10194_CR3",
"unstructured": "Antunes KH et al (2019) Microbiota-derived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response. Nat Commun 10(1):3273",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar2488",
"author": "SP Ardoin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "218",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res Ther",
"key": "10194_CR4",
"unstructured": "Ardoin SP, Pisetsky DS (2008) Developments in the scientific Understanding of lupus. Arthritis Res Ther 10(5):218",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2017.03.008",
"author": "K Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "10194_CR5",
"unstructured": "Chen K, Liu J, Cao X (2017) Regulation of type I interferon signaling in immunity and inflammation: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun 83:1–11",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.17635",
"author": "PR Criado",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10194_CR6",
"unstructured": "Criado PR et al (2022) COVID-19 and skin diseases: results from a survey of 843 patients with atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, vitiligo and chronic urticaria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 36(1):e1–e3",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00633-9",
"author": "YJ Crow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "471",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10194_CR7",
"unstructured": "Crow YJ, Stetson DB (2022) The type I interferonopathies: 10 years on. Nat Rev Immunol 22(8):471–483",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2014.532",
"author": "AM D’Erme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1025",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Invest Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR8",
"unstructured": "D’Erme AM et al (2015) IL-36γ (IL-1F9) is a biomarker for psoriasis skin lesions. J Invest Dermatol 135(4):1025–1032",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.930866",
"author": "Z Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "930866",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10194_CR9",
"unstructured": "Dong Z et al (2022) Identification of key molecules in COVID-19 patients significantly correlated with clinical outcomes by analyzing transcriptomic data. Front Immunol 13:930866",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "G Dupire",
"first-page": "CD011571",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10194_CR10",
"unstructured": "Dupire G et al (2019) Antistreptococcal interventions for guttate and chronic plaque psoriasis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3(3):CD011571",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09546634.2020.1789051",
"author": "A Ebrahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "699",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Dermatolog Treat",
"key": "10194_CR11",
"unstructured": "Ebrahimi A, Sayad B, Rahimi Z (2022) COVID-19 and psoriasis: biologic treatment and challenges. J Dermatolog Treat 33(2):699–703",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-0448-7",
"author": "C Galeotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "10194_CR12",
"unstructured": "Galeotti C, Bayry J (2020) Autoimmune and inflammatory diseases following COVID-19. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16(8):413–414",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-021-03724-6",
"author": "Y Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "450",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "10194_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gao Y et al (2021) Single cell transcriptional zonation of human psoriasis skin identifies an alternative immunoregulatory axis conducted by skin resident cells. Cell Death Dis 12(5):450",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61128-3",
"author": "CE Griffiths",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "263",
"issue": "9583",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10194_CR14",
"unstructured": "Griffiths CE, Barker JN (2007) Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370(9583):263–271",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32549-6",
"author": "CEM Griffiths",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1301",
"issue": "10281",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10194_CR15",
"unstructured": "Griffiths CEM et al (2021) Psoriasis. Lancet 397(10281):1301–1315",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/258430",
"author": "AT Gunes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "258430",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "10194_CR16",
"unstructured": "Gunes AT et al (2015) Possible triggering effect of influenza vaccination on psoriasis. J Immunol Res 2015:258430",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2009.237",
"author": "JC Hall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "40",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "10194_CR17",
"unstructured": "Hall JC, Rosen A (2010) Type i interferons: crucial participants in disease amplification in autoimmunity. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6(1):40–49",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12060672",
"author": "W Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10194_CR18",
"unstructured": "Hao W, Wang L, Li S (2020) FKBP5 regulates RIG-I-mediated NF-kappaB activation and influenza A virus infection. Viruses. https://doi.org/10.3390/v12060672",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "RW Hu",
"first-page": "6411",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10194_CR19",
"unstructured": "Hu RW et al (2021) Identification of hub genes and molecular subtypes in COVID-19 based on WGCNA. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(20):6411–6424",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10194_CR20",
"unstructured": "Huang C et al (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 395(10223):497–506",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/ar2881",
"author": "GD Kalliolias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res Ther",
"key": "10194_CR21",
"unstructured": "Kalliolias GD, Ivashkiv LB (2010) Overview of the biology of type I interferons. Arthritis Res Ther 12(1):S1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jid.2016.04.032",
"author": "J Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2173",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Invest Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR22",
"unstructured": "Kim J et al (2016) The spectrum of mild to severe psoriasis vulgaris is defined by a common activation of IL-17 pathway genes, but with key differences in immune regulatory genes. J Invest Dermatol 136(11):2173–2182",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "PK Krajewski",
"first-page": "e632",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10194_CR23",
"unstructured": "Krajewski PK, Matusiak L, Szepietowski JC (2021) Psoriasis flare-up associated with second dose of Pfizer-BioNTech BNT16B2b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 35(10):e632–e634",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaad.2020.05.018",
"author": "Y Kuang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "670",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Am Acad Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR24",
"unstructured": "Kuang Y et al (2020) Association of outdoor activity restriction and income loss with patient-reported outcomes of psoriasis during the COVID-19 pandemic: A web-based survey. J Am Acad Dermatol 83(2):670–672",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13509",
"author": "Ö Kutlu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Ther",
"key": "10194_CR25",
"unstructured": "Kutlu Ö, Metin A (2020) Dermatological diseases presented before COVID-19: are patients with psoriasis and superficial fungal infections more vulnerable to the COVID-19? Dermatol Ther 33(4):e13509",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/jid.2014.28",
"author": "B Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1828",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Invest Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR26",
"unstructured": "Li B et al (2014) Transcriptome analysis of psoriasis in a large case-control sample: RNA-seq provides insights into disease mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol 134(7):1828–1838",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000849",
"author": "NAP Lieberman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3000849",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol",
"key": "10194_CR27",
"unstructured": "Lieberman NAP et al (2020) In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age. PLoS Biol 18(9):e3000849",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/BOR.0000000000000776",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Rheumatol",
"key": "10194_CR28",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Sawalha AH, Lu Q (2021) COVID-19 and autoimmune diseases. Curr Opin Rheumatol 33(2):155–162",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.971071",
"author": "YW Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "971071",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10194_CR29",
"unstructured": "Lu YW et al (2022) L36G is associated with cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis. Front Immunol 13:971071",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/15569527.2012.727936",
"author": "VC Macias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cutan Ocul Toxicol",
"key": "10194_CR30",
"unstructured": "Macias VC, Cunha D (2013) Psoriasis triggered by tetanus-diphtheria vaccination. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 32(2):164–165",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2021.04.008",
"author": "L Martin-Sancho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2656",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell",
"key": "10194_CR31",
"unstructured": "Martin-Sancho L et al (2021) Functional landscape of SARS-CoV-2 cellular restriction. Mol Cell 81(12):2656–2668e8",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdermsci.2017.11.010",
"author": "JL Melero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Dermatol Sci",
"key": "10194_CR32",
"unstructured": "Melero JL et al (2018) Deciphering psoriasis. A bioinformatic approach. J Dermatol Sci 89(2):120–126",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jocd.14508",
"author": "R Miladi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3364",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Cosmet Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR33",
"unstructured": "Miladi R et al (2021) Pustular psoriasis flare-up in a patient with COVID-19. J Cosmet Dermatol 20(11):3364–3368",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09546634.2020.1764904",
"author": "S Nasiri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "448",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Dermatolog Treat",
"key": "10194_CR34",
"unstructured": "Nasiri S et al (2020) A challenging case of psoriasis flare-up after COVID-19 infection. J Dermatolog Treat 31(5):448–449",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0743-0",
"author": "D Nehar-Belaid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1094",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "10194_CR35",
"unstructured": "Nehar-Belaid D et al (2020) Mapping systemic lupus erythematosus heterogeneity at the single-cell level. Nat Immunol 21(9):1094–1106",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cels.2020.10.003",
"author": "KA Overmyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Syst",
"key": "10194_CR36",
"unstructured": "Overmyer KA et al (2021) Large-Scale Multi-omic analysis of COVID-19 severity. Cell Syst 12(1):23–40e7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13632",
"author": "R Ozaras",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13632",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Dermatol Ther",
"key": "10194_CR37",
"unstructured": "Ozaras R et al (2020) Covid-19 and exacerbation of psoriasis. Dermatol Ther 33(4):e13632",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02167-20",
"author": "MB Phillips",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "10194_CR38",
"unstructured": "Phillips MB et al (2021) Lymphatic type 1 interferon responses are critical for control of systemic reovirus dissemination. J Virol. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02167-20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2017.07.001",
"author": "C Picard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "897",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "10194_CR39",
"unstructured": "Picard C, Belot A (2017) Does type-I interferon drive systemic autoimmunity? Autoimmun Rev 16(9):897–902",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.13091",
"author": "RA Raposo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1951",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10194_CR40",
"unstructured": "Raposo RA et al (2015) Antiviral gene expression in psoriasis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 29(10):1951–1957",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v079.c02",
"author": "MC Sachs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Stat Softw",
"key": "10194_CR41",
"unstructured": "Sachs MC (2017) plotROC: a tool for plotting ROC curves. J Stat Softw. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v079.c02",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-virology-092818-015756",
"author": "JW Schoggins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "567",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Virol",
"key": "10194_CR42",
"unstructured": "Schoggins JW (2019) Interferon-stimulated genes: what do they all do? Annu Rev Virol 6(1):567–584",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtos.2021.09.007",
"author": "S Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Ocul Surf",
"key": "10194_CR43",
"unstructured": "Singh S et al (2022) SARS-CoV-2 and its beta variant of concern infect human conjunctival epithelial cells and induce differential antiviral innate immune response. Ocul Surf 23:184–194",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2018.12.018",
"author": "B Skaug",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "154635",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "10194_CR44",
"unstructured": "Skaug B, Assassi S (2020) Type I interferon dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Cytokine 132:154635",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.17582",
"author": "E Sotiriou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e857",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol",
"key": "10194_CR45",
"unstructured": "Sotiriou E et al (2021) Psoriasis exacerbation after COVID-19 vaccination: a report of 14 cases from a single centre. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 35(12):e857–e859",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03158-0",
"author": "A Stallmach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "444",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10194_CR46",
"unstructured": "Stallmach A et al (2020) Infliximab against severe COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome with organ failure-a cautionary case series. Crit Care 24(1):444",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jid.2018.01.039",
"author": "J Takeshita",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1726",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Invest Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR47",
"unstructured": "Takeshita J et al (2018) Risk of serious Infection, opportunistic Infection, and herpes Zoster among patients with psoriasis in the united Kingdom. J Invest Dermatol 138(8):1726–1735",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jid.2018.12.018",
"author": "LC Tsoi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1480",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Invest Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR48",
"unstructured": "Tsoi LC et al (2019) Atopic dermatitis is an IL-13-Dominant disease with greater molecular heterogeneity compared to psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol 139(7):1480–1489",
"volume": "139",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13075-017-1501-z",
"author": "MJ Wahadat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Res Ther",
"key": "10194_CR49",
"unstructured": "Wahadat MJ et al (2018) Type I IFN signature in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus: a conspiracy of DNA- and RNA-sensing receptors? Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):4",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.3006245",
"author": "K Wolk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "204ra129",
"issue": "204",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10194_CR50",
"unstructured": "Wolk K et al (2013) IL-29 is produced by T(H)17 cells and mediates the cutaneous antiviral competence in psoriasis. Sci Transl Med 5(204):204ra129",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "10194_CR51",
"unstructured": "Worldometer (2022) Covid-19 coronavirus pandemic. https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/#countries"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.005",
"author": "D Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "368",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "10194_CR52",
"unstructured": "Wu D, Yang XO (2020) TH17 responses in cytokine storm of COVID-19: an emerging target of JAK2 inhibitor fedratinib. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 53(3):368–370",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40257-022-00721-z",
"author": "PC Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "775",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Dermatol",
"key": "10194_CR53",
"unstructured": "Wu PC et al (2022) New onset and exacerbations of psoriasis following COVID-19 vaccines: a systematic review. Am J Clin Dermatol 23(6):775–799",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13671-017-0178-5",
"author": "D Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "94",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Curr Dermatol Rep",
"key": "10194_CR54",
"unstructured": "Yan D et al (2017) The role of the skin and gut Microbiome in psoriatic disease. Curr Dermatol Rep 6(2):94–103",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "YJ Zhang",
"first-page": "225",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "10194_CR55",
"unstructured": "Zhang YJ et al (2019) Integrated bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes and signaling pathways in plaque psoriasis. Mol Med Rep 20(1):225–235",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.733171",
"author": "C Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "733171",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10194_CR56",
"unstructured": "Zhang C et al (2021) Transcriptional profiling and machine learning unveil a concordant biosignature of type I Interferon-Inducible host response across nasal swab and pulmonary tissue for COVID-19 diagnosis. Front Immunol 12:733171",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23136955",
"author": "S Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10194_CR57",
"unstructured": "Zhou S, Yao Z (2022) Roles of infection in psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23136955",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.017",
"author": "Z Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "883",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "10194_CR58",
"unstructured": "Zhou Z et al (2020) Heightened innate immune responses in the respiratory tract of COVID-19 patients. Cell Host Microbe 27(6):883–890e2",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30305-6",
"author": "A Zumla",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e35",
"issue": "10224",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10194_CR59",
"unstructured": "Zumla A et al (2020) Reducing mortality from 2019-nCoV: host-directed therapies should be an option. Lancet 395(10224):e35–e36",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 59,
"references-count": 59,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s00335-026-10194-8"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Exploration of shared gene signatures and molecular mechanisms between psoriasis and COVID-19: evidence from transcriptome data",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "37"
}