The Clinical Significance of Vitamin D and Zinc Levels with Respect to Immune Response in COVID-19 Positive Children
et al., Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, doi:10.1093/tropej/fmac072, Aug 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
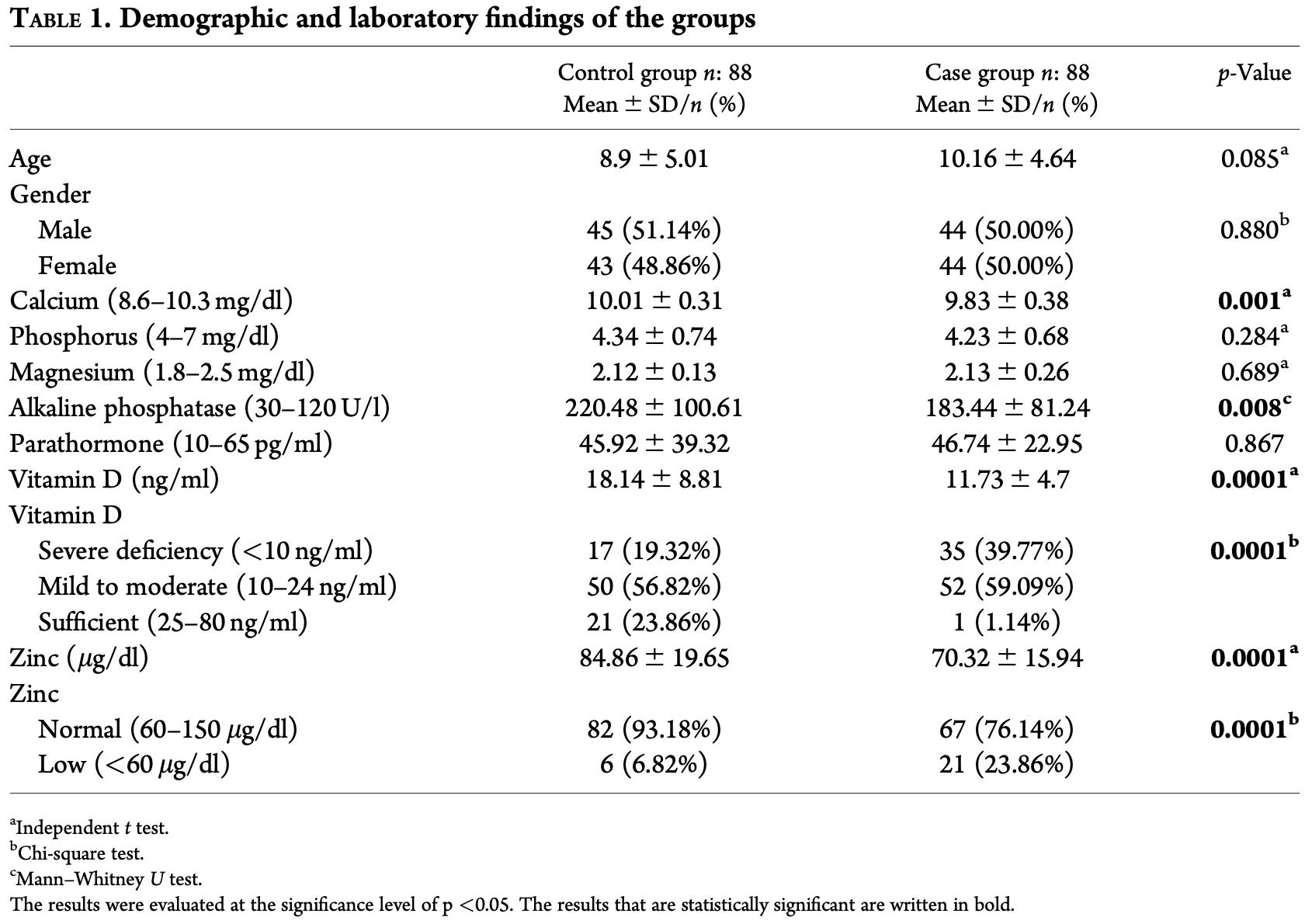
Prospective study of 88 pediatric COVID-19 patients and 88 healthy controls, showing significantly lower zinc and vitamin D levels in COVID-19 patients.
This is the 142nd of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
Study covers vitamin D and zinc.
|
risk of case, 63.7% lower, OR 0.36, p = 0.003, high D levels (≥10ng/ml) 53 of 88 (60.2%) cases,
71 of 88 (80.7%) controls, NNT 4.1, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Doğan et al., 4 Aug 2022, prospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 1 July, 2021 - 30 October, 2021.
Contact: mehmet_tolga@hotmail.com.
The Clinical Significance of Vitamin D and Zinc Levels with Respect to Immune Response in COVID-19 Positive Children
Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, doi:10.1093/tropej/fmac072
Aim: In this study, we aimed to evaluate serum vitamin D and zinc levels in children diagnosed with cor- onavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Materials and methods: In this study, 88 children with COVID-19 disease and 88 healthy children aged 1-18 years were enrolled between 01 July 2021 and 30 October 2021 in the Pediatrics Clinic of Tekirda g C ¸orlu State Hospital. Serum vitamin D and zinc levels have been measured and NCSS (Number Cruncher Statistical System) program has been utilized for statistical analysis. Results: We included 88 COVID-19 positive pediatric patients [50% (n ¼ 44) female] and 88 healthy children [48.86% (n ¼ 43) female] in this study. The mean serum vitamin D levels of COVID-19 positive patients were statistically significantly lower than the control group (p ¼ 0.0001). The zinc mean values of the study group were found to be statistically significantly lower than the control group (p ¼ 0.0001). There was a statistically significant correlation between serum vitamin D and zinc values in all patient groups (r ¼ 0.245, p ¼ 0.001).
Conclusion: As a result, zinc and vitamin D levels were observed lower in COVID-19 patients than in healthy individuals. Since there is no defined treatment protocol for COVID-19 infection on children yet, zinc and vitamin D supplementation can be used as a supportive treatment in COVID-19 infection.
References
Ako Glu, Bulut, Alemdar, Evaluation of childhood COVID-19 cases: a retrospective analysis, J Pediatr Infect Dis
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Alvares, Ribas, Miranda, Clinical prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and vitamin D levels: a systematic review, Rev Assoc Med Bras
Amos, Razzaque, Zinc and its role in vitamin D function, Curr Res Physiol
Bayramo Glu, Akkoc, The association between vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: singlecenter experience from a pandemic hospital, Eur J Pediatr
Berardi, Giardullo, Corrado, Vitamin D and connective tissue diseases, Inflamm Res
Bonaventura, Benedetti, De, Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation, Autoimmun Rev
Brown, Sarkar, Vitamin D deficiency: a factor in COVID-19, progression, severity and mortality?-an urgent call for research, MitoFit Preprint Arch
Camargo Ca, Ganmaa, Frazier, Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia, Pediatrics
Choi, Kim, Kang, Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children, Clin Exp Pediatr
Dankers, Colin, Van Hamburg, Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Front Immunol
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Dufort, Koumans, Chow, New York State and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Investigation Team. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State, N Engl J Med
Elham, Azam, Azam, Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19, Clin Nutr ESPEN
Fukada, Hojyo, Hara, Revisiting the old and learning the new of zinc in immunity, Nat Immunol
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that Vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Hawker, B cells as a target of immune modulation, Ann Indian Acad Neurol
Heaney, Dowell, Hale, Calcium absorption varies within the reference range for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, J Am Coll Nutr
Heller, Sun, Hackler, Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker, Redox Biol
Henry, Lippi, Plebani, Laboratory abnormalities in children with novel coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Chem Lab Med
Holick, Vitamin D deficiency, N Engl J Med
Kiran, Prema, Thilagavathi, Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase levels in healthy adults above the age of 20 living in Potheri Village of Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, J App Pharm Sci
Langlois, 'aragon, Manzanares, Vitamin D in the ICU: more sun for critically ill adult patients?, Nutrition
Liu, Nelson, Wang, Vitamin D modulates prostaglandin E2 synthesis and degradation in human lung fibroblasts, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol
Lysandropoulos, Jaquie ´ry, Jilek, Vitamin D has a direct immunomodulatory effect on CD8þ T cells of patients with early multiple sclerosis and healthy control subjects, J Neuroimmunol
Meral, Guven, Uslu, The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in children, adolescents and adults in a sample of Turkish population, Stud Ethno-Med
Molloy, Murphy, Vitamin D, Covid-19 and children, Ir Med J
Pal, Squitti, Picozza, Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials, Biol Trace Elem Res
Razzaque, COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance?, Tohoku J Exp Med
Razzaque, COVID-19 pandemic: can zinc supplementation provide an additional shield against the infection?, Comput Struct Biotechnol J
Razzaque, Magnesium: are we consuming enough?, Nutrients
Sacn Vitamin, Report, The Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) Recommendations on Vitamin D. Public Health England
Shaheen, Noor, Barakzai, Serum alkaline phosphatase screening for vitamin D deficiency states, J Coll Physicians Surg Pak
Shams, Afshari, Tajadini, The relationship of serum vitamin D and Zinc in a nationally representative sample of Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-III study, Med J Islam Repub Iran
Singh, Assessing the role of zinc in Covid-19 infections and mortality: is zinc deficiency a risk factor for Covid-19? medRxiv
Sun, Zhang, Zou, Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Aging
Teymoori-Rad, Shokri, Salimi, The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections, Rev Med Virol
Tezer, Demirda G T, Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children, Turk J Med Sci
Urashima, Segawa, Okazaki, Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to prevent seasonal influenza A in schoolchildren, Am J Clin Nutr
Uwitonze, Razzaque, Role of magnesium in vitamin D activation and function, J Am Osteopath Assoc
Viner, Mytton, Bonell, Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JAMA Pediatr
Vitamin, Zinc Levels in COVID-19 Positive Children
Vlieg-Boerstra, De, Meyer, Nutrient supplementation for prevention of viral respiratory tract infections in healthy subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Allergy
Wintergerst, Maggini, Hornig, Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune function, Ann Nutr Metab
Wintergerst, Maggini, Hornig, Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions, Ann Nutr Metab
Yasui, Yasui, Suzuki, Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatmentrelationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis
Yılmaz, Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?, Pediatr Pulmonol
Zu, Jiang, Xu, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China, Radiology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/tropej/fmac072",
"ISSN": [
"0142-6338",
"1465-3664"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmac072",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Aim</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this study, we aimed to evaluate serum vitamin D and zinc levels in children diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this study, 88 children with COVID-19 disease and 88 healthy children aged 1–18 years were enrolled between 01 July 2021 and 30 October 2021 in the Pediatrics Clinic of Tekirdağ Çorlu State Hospital. Serum vitamin D and zinc levels have been measured and NCSS (Number Cruncher Statistical System) program has been utilized for statistical analysis.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We included 88 COVID-19 positive pediatric patients [50% (n = 44) female] and 88 healthy children [48.86% (n = 43) female] in this study. The mean serum vitamin D levels of COVID-19 positive patients were statistically significantly lower than the control group (p = 0.0001). The zinc mean values of the study group were found to be statistically significantly lower than the control group (p = 0.0001). There was a statistically significant correlation between serum vitamin D and zinc values in all patient groups (r = 0.245, p = 0.001).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>As a result, zinc and vitamin D levels were observed lower in COVID-19 patients than in healthy individuals. Since there is no defined treatment protocol for COVID-19 infection on children yet, zinc and vitamin D supplementation can be used as a supportive treatment in COVID-19 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1691-9316",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Tekirdağ Çorlu District State Hospital, Ministry of Health , 59850 Tekirdağ, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Doğan",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3972-2460",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Tekirdağ Çorlu District State Hospital, Ministry of Health , 59850 Tekirdağ, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dumanoğlu Doğan",
"given": "İmran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7083-0454",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, Tekirdağ Çorlu District State Hospital, Ministry of Health , 59850 Tekirdağ, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uyanık",
"given": "Metin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6055-7746",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Kartal Dr. Lütfi Kırdar City Hospital, University of Health Science , 34865 Istanbul, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Köle",
"given": "Mehmet Tolga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7278-309X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Kartal Dr. Lütfi Kırdar City Hospital, University of Health Science , 34865 Istanbul, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pişmişoğlu",
"given": "Kemal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Tropical Pediatrics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T19:17:41Z",
"timestamp": 1661195861000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T19:18:16Z",
"timestamp": 1661195896000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-22T19:41:12Z",
"timestamp": 1661197272320
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1659571200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/tropej/article-pdf/68/5/fmac072/45496647/fmac072.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/tropej/article-pdf/68/5/fmac072/45496647/fmac072.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
22
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1148/radiol.2020200490",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China",
"author": "Zu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E15",
"journal-title": "Radiology",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B1",
"volume": "296",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3345/cep.2020.00535",
"article-title": "Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pediatr",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B2",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.4573",
"article-title": "Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Viner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JAMA Pediatr",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B3",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000107673",
"article-title": "Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune function",
"author": "Wintergerst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "301",
"journal-title": "Ann Nutr Metab",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B4",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential",
"author": "Dankers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B5",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B6",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.11.008",
"article-title": "Vitamin D has a direct immunomodulatory effect on CD8+ T cells of patients with early multiple sclerosis and healthy control subjects",
"author": "Lysandropoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "J Neuroimmunol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B7",
"volume": "233",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D, Covid-19 and children",
"author": "Molloy",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Ir Med J",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B8",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0972-2327.58275",
"article-title": "B cells as a target of immune modulation",
"author": "Hawker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Ann Indian Acad Neurol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-020-01337-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and connective tissue diseases",
"author": "Berardi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B10",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Brown",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2032",
"article-title": "The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections",
"author": "Teymoori-Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2032",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B12",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that Vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B13",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02437-9",
"article-title": "Zinc and COVID-19: basis of current clinical trials",
"author": "Pal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2882",
"journal-title": "Biol Trace Elem Res",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B14",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-019-0319-z",
"article-title": "Revisiting the old and learning the new of zinc in immunity",
"author": "Fukada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "248",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B15",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2014.11.008",
"article-title": "Zinc and its role in immunity and inflammation",
"author": "Bonaventura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B16",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000090495",
"article-title": "Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions",
"author": "Wintergerst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Ann Nutr Metab",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B17",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.251.175",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: can maintaining optimal zinc balance enhance host resistance?",
"author": "Razzaque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Tohoku J Exp Med",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B18",
"volume": "251",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-021-04030-1",
"article-title": "The association between vitamin D levels and the clinical severity and inflammation markers in pediatric COVID-19 patients: single-center experience from a pandemic hospital",
"author": "Bayramoğlu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2699",
"journal-title": "Eur J Pediatr",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B19",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09735070.2016.11905494",
"article-title": "The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in children, adolescents and adults in a sample of Turkish population",
"author": "Meral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "Stud Ethno-Med",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B20",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.03.040",
"article-title": "Serum vitamin D, calcium, and zinc levels in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Elham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B21",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3906/sag-2004-174",
"article-title": "Novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in children",
"author": "Tezer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "592",
"journal-title": "Turk J Med Sci",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B22",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0272",
"article-title": "Laboratory abnormalities in children with novel coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1135",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem Lab Med",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B23",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021756",
"article-title": "Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children in New York State",
"author": "Dufort",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B24",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.2009.29094",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation to prevent seasonal influenza A in schoolchildren",
"author": "Urashima",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1255",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B25",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2011-3029",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation and risk of acute respiratory infection in Mongolia",
"author": "Camargo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e561",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B26",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1806-9282.20220165",
"article-title": "Clinical prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019 in children and vitamin D levels: a systematic review",
"author": "Alvares",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "712",
"journal-title": "Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992)",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B27",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2018.11.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D in the ICU: more sun for critically ill adult patients?",
"author": "Langlois",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B28",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.25106",
"article-title": "Is vitamin D deficiency a risk factor for COVID-19 in children?",
"author": "Yılmaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3595",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Pulmonol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B29",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0041-1723957",
"article-title": "Evaluation of childhood COVID-19 cases: a retrospective analysis",
"author": "Akoğlu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "091",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B30",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2013-0211OC",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulates prostaglandin E2 synthesis and degradation in human lung fibroblasts",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "40",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B31",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07315724.2003.10719287",
"article-title": "Calcium absorption varies within the reference range for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D",
"author": "Heaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "142",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Nutr",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B32",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D, calcium, phosphorus and alkaline phosphatase levels in healthy adults above the age of 20 living in Potheri Village of Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu",
"author": "Kiran",
"first-page": "030",
"journal-title": "J App Pharm Sci",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B33",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B34",
"volume": "357",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.103526",
"article-title": "Serum calcium as a biomarker of clinical severity and prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11287",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B35",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum alkaline phosphatase screening for vitamin D deficiency states",
"author": "Shaheen",
"first-page": "424",
"journal-title": "J Coll Physicians Surg Pak",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B36",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10121863",
"article-title": "Magnesium: are we consuming enough?",
"author": "Razzaque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1863",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B37",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7556/jaoa.2018.037",
"article-title": "Role of magnesium in vitamin D activation and function",
"author": "Uwitonze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "J Am Osteopath Assoc",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B38",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "ACE2 receptor polymorphism: susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome",
"author": "Devaux",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "425",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B39",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101764",
"article-title": "Prediction of survival odds in COVID-19 by zinc, age and selenoprotein P as composite biomarker",
"author": "Heller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101764",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B40",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008",
"article-title": "Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment—relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19",
"author": "Yasui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B41",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Singh",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.15136",
"article-title": "Nutrient supplementation for prevention of viral respiratory tract infections in healthy subjects: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Vlieg-Boerstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B43",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.crphys.2022.04.001",
"article-title": "Zinc and its role in vitamin D function",
"author": "Amos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Curr Res Physiol",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B44",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "The relationship of serum vitamin D and Zinc in a nationally representative sample of Iranian children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-III study",
"author": "Shams",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Med J Islam Repub Iran",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B45",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2021.02.015",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: can zinc supplementation provide an additional shield against the infection?",
"author": "Razzaque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1371",
"journal-title": "Comput Struct Biotechnol J",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B46",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "SACN vitamin D and health report",
"first-page": "289",
"key": "2022082219173909600_fmac072-B47",
"volume-title": "The Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN) Recommendations on Vitamin D",
"year": "2016"
}
],
"reference-count": 47,
"references-count": 47,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/tropej/article/doi/10.1093/tropej/fmac072/6673384"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Clinical Significance of Vitamin D and Zinc Levels with Respect to Immune Response in COVID-19 Positive Children",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "68"
}
dogan
