Clinical Investigation of Leukocyte DNA Damage in COVID-19 Patients
et al., Current Issues in Molecular Biology, doi:10.3390/cimb45020062, Jan 2023
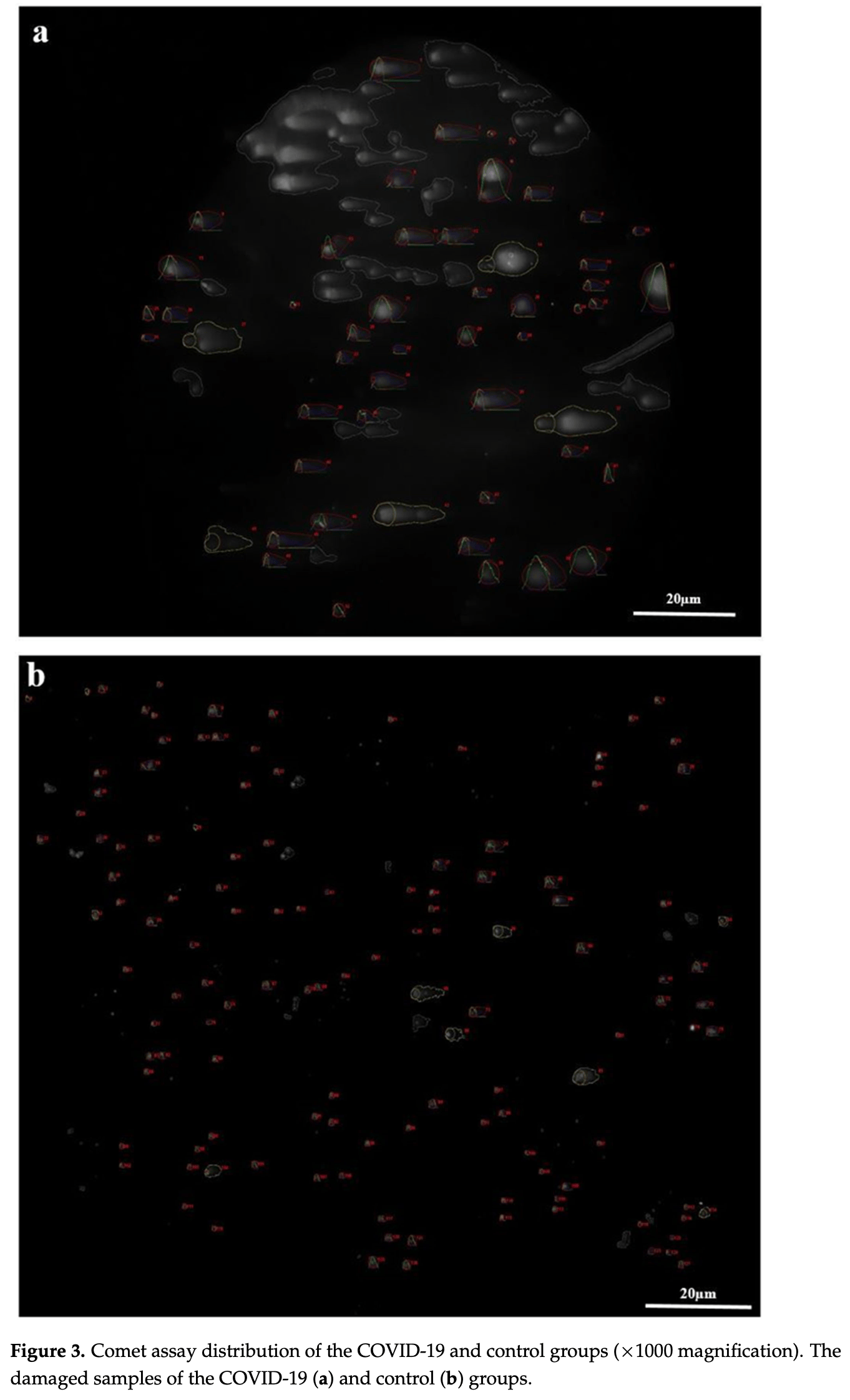
Cross-sectional study of 50 COVID-19 patients and 42 controls showing significantly increased DNA damage in leukocytes of COVID-19 patients. Authors hypothesize that SARS-CoV-2 causes DNA damage through cytokine storm-induced reactive oxygen species production and inflammatory processes that disrupt cellular DNA repair mechanisms.
Doğan et al., 19 Jan 2023, prospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: dthdogan@gmail.com (corresponding author), dthdogan@atauni.edu.tr.
Clinical Investigation of Leukocyte DNA Damage in COVID-19 Patients
Current Issues in Molecular Biology, doi:10.3390/cimb45020062
This prospective cross-sectional study aimed to evaluate leukocyte DNA damage in coronavirus disease patients. In this study, 50 COVID-19-positive patients attending the Erzurum City Hospital Internal Medicine Outpatient Clinic and 42 control group patients were included. DNA damage was detected in living cells through leukocyte isolation in 50 COVID-19positive patients using the comet assay method. DNA tail/head (olive) moments were evaluated and compared. White blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (HGB), neutrophils (NEU), lymphocytes (LYM), eosinophils (EO), monocytes (MONO), basophils (BASO), platelets (PLT), and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were analyzed. The RBC, lymphocyte, eosinophil, and monocyte means were significantly higher in the control group (p < 0.05), whereas the HGB and neutrophile means were significantly higher in the study group (p < 0.05). There were significant negative correlations between COVID-19 and RBC (r = -0.863), LYM (r = -0.542), EO (r = -0.686), and MONO (r = -0.385). Meanwhile, there were significant positive correlations between COVID-19 and HGB (r = 0.863), NEU (r = 0.307), tail moment (r = 0.598), and olive moment (r = 0.582). Both the tail and olive moment mean differences were significantly higher in the study group, with higher ranges (p < 0.05). COVID-19 infection caused statistically significant increases in both the tail and olive damage percentage in patients, causing DNA damage. Lastly, the NLR rate was associated with the presence and progression of COVID-19.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Ahmad, Haque, Surviving the Storm: Cytokine Biosignature in SARS-CoV-2 Severity Prediction, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10040614
Basheer, Saad, Kananeh, Asad, Khayat et al., Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against?, Curr. Issues Mol. Biol, doi:10.3390/cimb44100323
Bhargava, Khan, Panwar, Pathak, Punde et al., Occult hepatitis B virus infection with low viremia induces DNA damage, apoptosis and oxidative stress in peripheral blood lymphocytes, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.023
Cameron, Ran, Xu, Danesh, Bermejo-Martin et al., Interferon-mediated immunopathological events are associated with atypical innate and adaptive immune responses in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00527-07
Diao, Wang, Tan, Chen, Liu et al., Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827
El-Amine, Germini, Zakharova, Tsfasman, Sheval et al., HIV-1 Tat protein induces DNA damage in human peripheral blood B-lymphocytes via mitochondrial ROS production, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.024
Fathi, Rezaei, Lymphopenia in COVID-19: Therapeutic opportunities, Cell Biol. Int, doi:10.1002/cbin.11403
Gao, Li, Han, Li, Wu et al., Diagnostic utility of clinical laboratory data determinations for patients with the severe COVID-19, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25770
Ghaebi, Tahmasebi, Jozghorbani, Sadeghi, Thangavelu et al., Risk factors for adverse outcomes of COVID-19 patients: Possible basis for diverse responses to the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119503
Gu, Sha, Zhang, Shen, Zhao et al., Neutrophils and Lymphocytes Can Help Distinguish Asymptomatic COVID-19 From Moderate COVID-19, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2021.654272
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Han, Xu, Cheng, Zhong, Yuan et al., Retrospective Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients, mSphere, doi:10.1128/mSphere.00922-20
Harper, Elledge, The DNA damage response: Ten years after, Mol. Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.015
Henry, COVID-19, ECMO, and lymphopenia: A word of caution, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30119-3
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jackson, Bartek, The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature08467
Jia, Gong, Will Mutations in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Lead to the Failure of COVID-19 Vaccines?, J. Korean Med. Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e124
Karaşör, Bucak, Cenariu, Bodu, Taşpınar et al., The Effects of Different Doses of ROCK Inhibitor, Antifreeze Protein III, and Boron Added to Semen Extender on Semen Freezeability of Ankara Bucks, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27228070
Kerget, Çelik, Kerget, Aksakal, Uçar et al., Evaluation of 3-month follow-up of patients with postacute COVID-19 syndrome, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27579
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/M20-0504
Lee, Hui, Wu, Chan, Cameron et al., A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa030685
Liu, Tao, Wang, Yuan, Liu et al., Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease, Chin. Med. J. (Engl, doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000000775
Liu, Yang, Zhang, Huang, Wang et al., Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury, Sci. China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8
Machhi, Herskovitz, Senan, Dutta, Nath et al., The Natural History, Pathobiology, and Clinical Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infections, J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/s11481-020-09944-5
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Mo, Xing, Xiao, Deng, Zhao et al., Clinical Characteristics of Refractory Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa270
Papanikolaou, Rapti, Stellas, Stefanou, Syrigos et al., Delineating the SARS-CoV-2 Induced Interplay between the Host Immune System and the DNA Damage Response Network, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10101764
Parker, Brigham, Connolly, Mcpeake, Agranovich et al., Addressing the post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multidisciplinary model of care, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00385-4
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Villamizar-Peña, Holguin-Rivera et al., Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Travel. Med. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Sharma, Ahmad Farouk, Lal, A Review on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Evolution, Transmission, Detection, Control and Prevention, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13020202
Singh, Mittal, Gollapudi, Butzmann, Kumar et al., A meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 patients identifies the combinatorial significance of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, lymphocyte, and neutrophil values as a predictor of disease severity, Int. J. Lab. Hematol, doi:10.1111/ijlh.13354
Tan, Wang, Zhang, Ding, Huang et al., Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: A descriptive and predictive study, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-020-0148-4
Thevarajan, Nguyen, Koutsakos, Druce, Caly et al., Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: A case report of non-severe COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0819-2
Tomo, Karli, Dharmalingam, Yadav, Sharma, The Clinical Laboratory: A Key Player in Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19, EJIFCC
Wang, Yang, Li, Wen, Zhang, Clinical Features of 69 Cases With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa272
Wang, Yang, Post-acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Neglected Public Health Issue, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.908757
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Zella, Giovanetti, Cella, Borsetti, Ciotti et al., The importance of genomic analysis in cracking the coronavirus pandemic, Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn, doi:10.1080/14737159.2021.1917998
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Yuan, Yang et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
Zheng, Gao, Wang, Song, Liu et al., Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients, Cell. Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cimb45020062",
"ISSN": [
"1467-3045"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/cimb45020062",
"abstract": "<jats:p>This prospective cross-sectional study aimed to evaluate leukocyte DNA damage in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients. In this study, 50 COVID-19-positive patients attending the Erzurum City Hospital Internal Medicine Outpatient Clinic and 42 control group patients were included. DNA damage was detected in living cells through leukocyte isolation in 50 COVID-19-positive patients using the comet assay method. DNA tail/head (olive) moments were evaluated and compared. White blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), hemoglobin (HGB), neutrophils (NEU), lymphocytes (LYM), eosinophils (EO), monocytes (MONO), basophils (BASO), platelets (PLT), and the neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were analyzed. The RBC, lymphocyte, eosinophil, and monocyte means were significantly higher in the control group (p < 0.05), whereas the HGB and neutrophile means were significantly higher in the study group (p < 0.05). There were significant negative correlations between COVID-19 and RBC (r = −0.863), LYM (r = −0.542), EO (r = −0.686), and MONO (r = −0.385). Meanwhile, there were significant positive correlations between COVID-19 and HGB (r = 0.863), NEU (r = 0.307), tail moment (r = 0.598), and olive moment (r = 0.582). Both the tail and olive moment mean differences were significantly higher in the study group, with higher ranges (p < 0.05). COVID-19 infection caused statistically significant increases in both the tail and olive damage percentage in patients, causing DNA damage. Lastly, the NLR rate was associated with the presence and progression of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"cimb45020062"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5232-4336",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Doğan",
"given": "Hasan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Erzurum Regional Training and Research Hospital, Health Sciences University, Erzurum 25100, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Kara",
"given": "Aslı",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3971-3318",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nephrology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Çankaya",
"given": "Erdem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Balkan",
"given": "Eda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Histology and Embryology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Gürbüz",
"given": "Muhammet Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Kızılkaya",
"given": "Murat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Ataturk University, Erzurum 25240, Turkey"
}
],
"family": "Aykaç",
"given": "Merve",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Current Issues in Molecular Biology",
"container-title-short": "CIMB",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-20T07:52:21Z",
"timestamp": 1674201141000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-25T09:50:43Z",
"timestamp": 1724579443000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004951",
"award": [
"TSA-2021-8869"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100004951",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Atatürk University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-19T16:54:53Z",
"timestamp": 1742403293023,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1674086400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1467-3045/45/2/62/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "963-974",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-0504",
"article-title": "The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application",
"author": "Lauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101623",
"article-title": "Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101623",
"journal-title": "Travel. Med. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6912e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID-19 Response Team (2020). Severe Outcomes Among Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-United States, February 12-March 16, 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep., 69, 343–346."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00385-4",
"article-title": "Addressing the post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A multidisciplinary model of care",
"author": "Parker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1328",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.908757",
"article-title": "Post-acute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Neglected Public Health Issue",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "908757",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30119-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19, ECMO, and lymphopenia: A word of caution",
"author": "Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e24",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A single-centered, retrospective, observational study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000775",
"article-title": "Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1032",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med. J. (Engl.)",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8",
"article-title": "Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "364",
"journal-title": "Sci. China Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0819-2",
"article-title": "Breadth of concomitant immune responses prior to patient recovery: A case report of non-severe COVID-19",
"author": "Thevarajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "453",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"article-title": "Functional exhaustion of antiviral lymphocytes in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "533",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827",
"article-title": "Reduction and Functional Exhaustion of T Cells in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Diao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "827",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27579",
"article-title": "Evaluation of 3-month follow-up of patients with postacute COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Kerget",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2026",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10040614",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Ahmad, R., and Haque, M. (2022). Surviving the Storm: Cytokine Biosignature in SARS-CoV-2 Severity Prediction. Vaccines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbin.11403",
"article-title": "Lymphopenia in COVID-19: Therapeutic opportunities",
"author": "Fathi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1792",
"journal-title": "Cell Biol. Int.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cimb44100323",
"article-title": "Cytokine Patterns in COVID-19 Patients: Which Cytokines Predict Mortality and Which Protect Against?",
"author": "Basheer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4735",
"journal-title": "Curr. Issues Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa272",
"article-title": "Clinical Features of 69 Cases With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "769",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25770",
"article-title": "Diagnostic utility of clinical laboratory data determinations for patients with the severe COVID-19",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "791",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa270",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Refractory Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Mo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e4208",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00527-07",
"article-title": "Interferon-mediated immunopathological events are associated with atypical innate and adaptive immune responses in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8692",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa030685",
"article-title": "A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1986",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "348",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-0148-4",
"article-title": "Lymphopenia predicts disease severity of COVID-19: A descriptive and predictive study",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.024",
"article-title": "HIV-1 Tat protein induces DNA damage in human peripheral blood B-lymphocytes via mitochondrial ROS production",
"author": "Germini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2010.07.023",
"article-title": "Occult hepatitis B virus infection with low viremia induces DNA damage, apoptosis and oxidative stress in peripheral blood lymphocytes",
"author": "Bhargava",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2007.11.015",
"article-title": "The DNA damage response: Ten years after",
"author": "Harper",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "739",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature08467",
"article-title": "The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1071",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "461",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27228070",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Karaşör, Ö.F., Bucak, M.N., Cenariu, M., Bodu, M., Taşpınar, M., and Taşpınar, F. (2022). The Effects of Different Doses of ROCK Inhibitor, Antifreeze Protein III, and Boron Added to Semen Extender on Semen Freezeability of Ankara Bucks. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10101764",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Papanikolaou, C., Rapti, V., Stellas, D., Stefanou, D.T., Syrigos, K., Pavlakis, G.N., and Souliotis, V.L. (2022). Delineating the SARS-CoV-2 Induced Interplay between the Host Immune System and the DNA Damage Response Network. Vaccines, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119503",
"article-title": "Risk factors for adverse outcomes of COVID-19 patients: Possible basis for diverse responses to the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Ghaebi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119503",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2021.654272",
"article-title": "Neutrophils and Lymphocytes Can Help Distinguish Asymptomatic COVID-19 From Moderate COVID-19",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "654272",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijlh.13354",
"article-title": "A meta-analysis of SARS-CoV-2 patients identifies the combinatorial significance of D-dimer, C-reactive protein, lymphocyte, and neutrophil values as a predictor of disease severity",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "324",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Lab. Hematol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSphere.00922-20",
"article-title": "Descriptive, Retrospective Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Asymptomatic COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00922-20",
"journal-title": "mSphere",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The Clinical Laboratory: A Key Player in Diagnosis and Management of COVID-19",
"author": "Tomo",
"first-page": "326",
"journal-title": "EJIFCC",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e124",
"article-title": "Will Mutations in the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Lead to the Failure of COVID-19 Vaccines?",
"author": "Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e124",
"journal-title": "J. Korean Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13020202",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Sharma, A., Ahmad Farouk, I., and Lal, S.K. (2021). COVID-19: A Review on the Novel Coronavirus Disease Evolution, Transmission, Detection, Control and Prevention. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14737159.2021.1917998",
"article-title": "The importance of genomic analysis in cracking the coronavirus pandemic",
"author": "Zella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "547",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11481-020-09944-5",
"article-title": "The Natural History, Pathobiology, and Clinical Manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 Infections",
"author": "Machhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "359",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1467-3045/45/2/62"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical Investigation of Leukocyte DNA Damage in COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "45"
}