Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody-containing plasma improves outcome in patients with hematologic or solid cancer and severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
et al., Nature Cancer, doi:10.1038/s43018-022-00503-w, Dec 2022
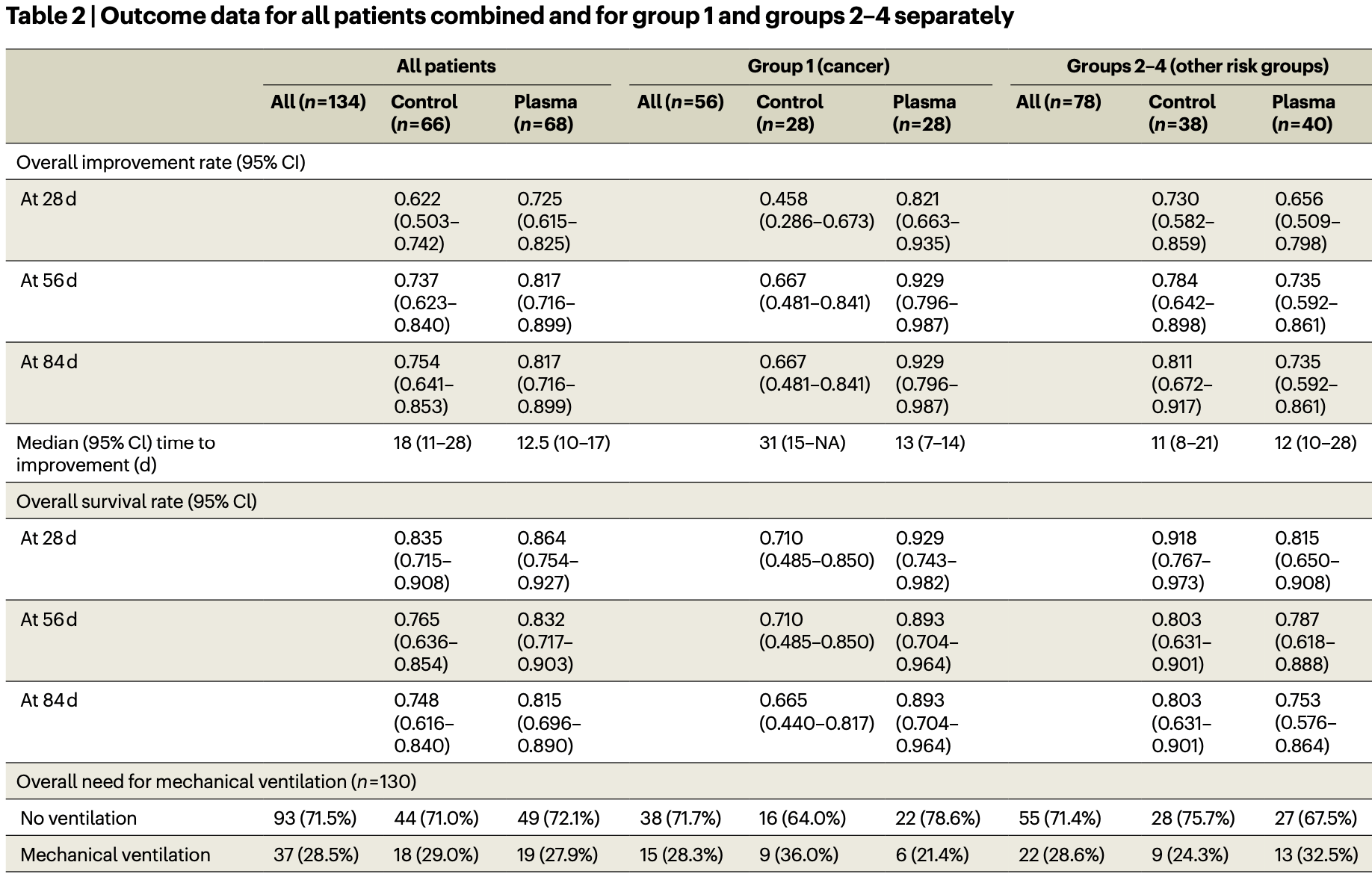
RCT 134 hospitalized patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with convalescent plasma for all patients, however significantly improved mortality and time to improvement was seen for patients with cancer.
|
risk of death, 8.2% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.39, treatment 68, control 66, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, day 84.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 2.5% higher, RR 1.02, p = 1.00, treatment 19 of 68 (27.9%), control 18 of 66 (27.3%).
|
|
risk of 7-point scale, 22.5% lower, HR 0.78, p = 0.22, treatment 68, control 66, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Denkinger et al., 29 Dec 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Germany, peer-reviewed, 54 authors, study period 3 September, 2020 - 20 January, 2022, average treatment delay 7.0 days.
Contact: claudia.denkinger@uni-heidelberg.de, carsten.mueller-tidow@med.uni-heidelberg.de.
Abstract: nature cancer
Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00503-w
Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody-containing
plasma improves outcome in patients with
hematologic or solid cancer and severe
COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial
Received: 16 September 2022
A list of authors and their affiliations appears at the end of the paper
Accepted: 29 November 2022
Published online: xx xx xxxx
Check for updates
Patients with cancer are at high risk of severe coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19), with high morbidity and mortality. Furthermore, impaired
humoral response renders severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines less effective and treatment options are scarce.
Randomized trials using convalescent plasma are missing for high-risk
patients. Here, we performed a randomized, open-label, multicenter trial
(https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2020-001632-10/DE)
in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 (n = 134) within four risk groups
((1) cancer (n = 56); (2) immunosuppression (n = 16); (3) laboratory-based
risk factors (n = 36); and (4) advanced age (n = 26)) randomized to standard
of care (control arm) or standard of care plus convalescent/vaccinated
anti-SARS-CoV-2 plasma (plasma arm). No serious adverse events were
observed related to the plasma treatment. Clinical improvement as the
primary outcome was assessed using a seven-point ordinal scale. Secondary
outcomes were time to discharge and overall survival. For the four groups
combined, those receiving plasma did not improve clinically compared
with those in the control arm (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.29; P = 0.205). However,
patients with cancer experienced a shortened median time to improvement
(HR = 2.50; P = 0.003) and superior survival with plasma treatment versus the
control arm (HR = 0.28; P = 0.042). Neutralizing antibody activity increased
in the plasma cohort but not in the control cohort of patients with cancer
(P = 0.001). Taken together, convalescent/vaccinated plasma may improve
COVID-19 outcomes in patients with cancer who are unable to intrinsically
generate an adequate immune response.
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated risk of death is particularly high for patients with hematologic or solid cancer1–3, advanced
age4,5 and other conditions6,7. Both humoral8 and cellular9 immunodeficiency contribute to unfavorable outcomes. Despite this, severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine availability
and waning vaccine efficacy in these patients remain concerning10,11.
Few therapies improve outcomes in severe COVID-19 with
impaired oxygenation12. Monoclonal antibodies as pre- or postexposure prophylaxis or as early treatment can reduce the risk of severe
COVID-19 (refs. 13,14). Evidence for the benefit of monoclonal antibodies in patients requiring oxygen supplementation is missing15
or pending16.
e-mail: Claudia.Denkinger@uni-heidelberg.de; carsten.mueller-tidow@med.uni-heidelberg.de
Nature Cancer
Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00503-w
Randomized (n = 134)a
Allocation
Allocated to plasma (n = 68)
- All received the allocated intervention
(n = 68)
Allocated to standard of care (n = 66)
- All received the allocated intervention
(n = 66)
Follow-up
Lost to follow-up (n = 10)b
- At day 14 (n = 1)
- At day 28 (n = 2)
- At day 56 (n = 2)
- At day 84 (n = 5)
Lost to follow-up (n = 4)b
- At day 14 (n = 1)
- At day 56 (n = 3)
Discontinued intervention (received only
one infusion of..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s43018-022-00503-w",
"ISSN": [
"2662-1347"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00503-w",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Patients with cancer are at high risk of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), with high morbidity and mortality. Furthermore, impaired humoral response renders severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccines less effective and treatment options are scarce. Randomized trials using convalescent plasma are missing for high-risk patients. Here, we performed a randomized, open-label, multicenter trial (<jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2020-001632-10/DE\">https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2020-001632-10/DE</jats:ext-link>) in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 134) within four risk groups ((1) cancer (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 56); (2) immunosuppression (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 16); (3) laboratory-based risk factors (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 36); and (4) advanced age (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 26)) randomized to standard of care (control arm) or standard of care plus convalescent/vaccinated anti-SARS-CoV-2 plasma (plasma arm). No serious adverse events were observed related to the plasma treatment. Clinical improvement as the primary outcome was assessed using a seven-point ordinal scale. Secondary outcomes were time to discharge and overall survival. For the four groups combined, those receiving plasma did not improve clinically compared with those in the control arm (hazard ratio (HR) = 1.29; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.205). However, patients with cancer experienced a shortened median time to improvement (HR = 2.50; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.003) and superior survival with plasma treatment versus the control arm (HR = 0.28; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.042). Neutralizing antibody activity increased in the plasma cohort but not in the control cohort of patients with cancer (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.001). Taken together, convalescent/vaccinated plasma may improve COVID-19 outcomes in patients with cancer who are unable to intrinsically generate an adequate immune response.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"503"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "16 September 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "29 November 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "29 December 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7216-7067",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Denkinger",
"given": "Claudia M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Janssen",
"given": "Maike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schäkel",
"given": "Ulrike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gall",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leo",
"given": "Albrecht",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stelmach",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weber",
"given": "Stefan F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krisam",
"given": "Johannes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baumann",
"given": "Lukas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stermann",
"given": "Jacek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1386-3350",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Merle",
"given": "Uta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weigand",
"given": "Markus A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nusshag",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bullinger",
"given": "Lars",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schrezenmeier",
"given": "Jens-Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5916-3029",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bornhäuser",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alakel",
"given": "Nael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Witzke",
"given": "Oliver",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3819-9540",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wolf",
"given": "Timo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vehreschild",
"given": "Maria J. G. T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmiedel",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2836-9224",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Addo",
"given": "Marylyn M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Herth",
"given": "Felix",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kreuter",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tepasse",
"given": "Phil-Robin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hertenstein",
"given": "Bernd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hänel",
"given": "Mathias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Morgner",
"given": "Anke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kiehl",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hopfer",
"given": "Olaf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wattad",
"given": "Mohammad-Amen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schimanski",
"given": "Carl C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Celik",
"given": "Cihan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pohle",
"given": "Thorsten",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruhe",
"given": "Matthias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kern",
"given": "Winfried V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmitt",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lorenz",
"given": "Hanns-Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6923-0590",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Souto-Carneiro",
"given": "Margarida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaeddert",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Halama",
"given": "Niels",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meuer",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kräusslich",
"given": "Hans-Georg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Müller",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schnitzler",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parthé",
"given": "Sylvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5601-9307",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bartenschlager",
"given": "Ralf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gronkowski",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Klemmer",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1579-1509",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schmitt",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dreger",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kriegsmann",
"given": "Katharina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2215-2059",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schlenk",
"given": "Richard F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7166-5232",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Müller-Tidow",
"given": "Carsten",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Cancer",
"container-title-short": "Nat Cancer",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-29T17:06:50Z",
"timestamp": 1672333610000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-12T11:39:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673523540000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "The Federal Ministry of Education and Research, Germany"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-13T05:54:39Z",
"timestamp": 1673589279324
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672272000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672272000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00503-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00503-w",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00503-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020008824",
"author": "A Vijenthira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2881",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "503_CR1",
"unstructured": "Vijenthira, A. et al. Outcomes of patients with hematologic malignancies and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 3377 patients. Blood 136, 2881–2892 (2020).",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01177-0",
"author": "L Pagano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "J. Hematol. Oncol.",
"key": "503_CR2",
"unstructured": "Pagano, L. et al. COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: a European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA). J. Hematol. Oncol. 14, 168 (2021).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0979-0",
"author": "EV Robilotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1218",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "503_CR3",
"unstructured": "Robilotti, E. V. et al. Determinants of COVID-19 disease severity in patients with cancer. Nat. Med. 26, 1218–1223 (2020).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0255154",
"author": "S Katzenschlager",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0255154",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "503_CR4",
"unstructured": "Katzenschlager, S. et al. Can we predict the severe course of COVID-19—a systematic review and meta-analysis of indicators of clinical outcome? PLoS ONE 16, e0255154 (2021).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1",
"author": "AT Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1123",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Epidemiol.",
"key": "503_CR5",
"unstructured": "Levin, A. T. et al. Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 35, 1123–1138 (2020).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.12.620",
"author": "AM Shields",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "503_CR6",
"unstructured": "Shields, A. M., Burns, S. O., Savic, S. & Richter, A. G. COVID-19 in patients with primary and secondary immunodeficiency: the United Kingdom experience. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 147, 870–875.e1 (2021).",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0000000000003523",
"author": "Y Azzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Transplantation",
"key": "503_CR7",
"unstructured": "Azzi, Y., Bartash, R., Scalea, J., Loarte-Campos, P. & Akalin, E. COVID-19 and solid organ transplantation: a review article. Transplantation 105, 37–55 (2021).",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00059-X",
"author": "J Avouac",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e419",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "503_CR8",
"unstructured": "Avouac, J. et al. COVID-19 outcomes in patients with inflammatory rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases treated with rituximab: a cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 3, e419–e426 (2021).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0191",
"author": "T Bilich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1982",
"journal-title": "Cancer Discov.",
"key": "503_CR9",
"unstructured": "Bilich, T. et al. Preexisting and post-COVID-19 immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with cancer. Cancer Discov. 11, 1982–1995 (2021).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41408-021-00534-z",
"author": "F Malard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Blood Cancer J",
"key": "503_CR10",
"unstructured": "Malard, F. et al. Weak immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 11, 142 (2021).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2114583",
"author": "EG Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e84",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR11",
"unstructured": "Levin, E. G. et al. Waning immune humoral response to BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine over 6 months. N. Engl. J. Med. 385, e84 (2021).",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa478",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "503_CR12",
"unstructured": "Bhimraj, A. et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa478 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.005",
"author": "D Corti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3086",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "503_CR13",
"unstructured": "Corti, D., Purcell, L. A., Snell, G. & Veesler, D. Tackling COVID-19 with neutralizing monoclonal antibodies. Cell 184, 3086–3108 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hon.2974",
"author": "B Weinbergerová",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "280",
"journal-title": "Hematol. Oncol.",
"key": "503_CR14",
"unstructured": "Weinbergerová, B.Successful early use of anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal neutralizing antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 infected hematological patients—a Czech multicenter experience. Hematol. Oncol. 40, 280–286 (2022).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08923973.2021.1993894",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol.",
"key": "503_CR15",
"unstructured": "Kow, C. S., Ramachandram, D. S. & Hasan, S. S. The use of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies and risk of hospital admission and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 44, 28–34 (2022).",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0270196",
"author": "S Saha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0270196",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "503_CR16",
"unstructured": "Saha, S. Death and invasive mechanical ventilation risk in hospitalized COVID-19 patients treated with anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies and/or antiviral agents: a systematic review and network meta-analysis protocol. PLoS ONE 17, e0270196 (2022).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2049",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "503_CR17",
"unstructured": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial. Lancet 397, 2049–2059 (2021).",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"author": "R Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "610",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR18",
"unstructured": "Libster, R. et al. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe COVID-19 in older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 610–618 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "V Piechotta",
"first-page": "CD013600",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "503_CR19",
"unstructured": "Piechotta, V. et al. Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID‐19: a living systematic review. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 7, CD013600 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"author": "VA Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR20",
"unstructured": "Simonovich, V. A. et al. A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in COVID-19 severe pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 619–629 (2020).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"author": "L Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "503_CR21",
"unstructured": "Li, L. et al. Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 324, 460–470 (2020).",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055189",
"author": "M Bajpai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e055189",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "503_CR22",
"unstructured": "Bajpai, M. et al. Efficacy of convalescent plasma therapy in the patient with COVID-19: a randomised control trial (COPLA-II trial). BMJ Open 12, e055189 (2022).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI150646",
"author": "MR O’Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e150646",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "503_CR23",
"unstructured": "O’Donnell, M. R. et al. A randomized double-blind controlled trial of convalescent plasma in adults with severe COVID-19. J. Clin. Invest. 131, e150646 (2021).",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01488-2",
"author": "P Bégin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2012",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "503_CR24",
"unstructured": "Bégin, P. et al. Convalescent plasma for hospitalized patients with COVID-19: an open-label, randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med. 27, 2012–2024 (2021).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.06.034",
"author": "FW Hamilton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "503_CR25",
"unstructured": "Hamilton, F. W., Lee, T., Arnold, D. T., Lilford, R. & Hemming, K. Is convalescent plasma futile in COVID-19? A Bayesian re-analysis of the RECOVERY randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 109, 114–117 (2021).",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.18178",
"author": "Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1690",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "503_CR26",
"unstructured": "Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators Effect of convalescent plasma on organ support-free days in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 326, 1690–1702 (2021).",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41375-022-01511-6",
"author": "T Hueso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "Leukemia",
"key": "503_CR27",
"unstructured": "Hueso, T. et al. Convalescent plasma improves overall survival in patients with B-cell lymphoid malignancy and COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort and propensity score analysis. Leukemia 36, 1025–1034 (2022).",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1799",
"author": "MA Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1167",
"journal-title": "JAMA Oncol.",
"key": "503_CR28",
"unstructured": "Thompson, M. A. et al. Association of convalescent plasma therapy with survival in patients with hematologic cancers and COVID-19. JAMA Oncol. 7, 1167–1175 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"author": "AB Cavalcanti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2041",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR29",
"unstructured": "Cavalcanti, A. B. et al. Hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin in mild-to-moderate COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 383, 2041–2052 (2020).",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2028700",
"author": "IO Rosas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1503",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR30",
"unstructured": "Rosas, I. O. et al. Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 1503–1516 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04735-y",
"author": "M Janssen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "503_CR31",
"unstructured": "Janssen, M. et al. A randomized open label phase-II clinical trial with or without infusion of plasma from subjects after convalescence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in high-risk patients with confirmed severe SARS-CoV-2 disease (RECOVER): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 21, 828 (2020).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119657",
"author": "DJ Sullivan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1700",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR32",
"unstructured": "Sullivan, D. J. et al. Early outpatient treatment for COVID-19 with convalescent plasma. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1700–1711 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"author": "LA VanBlargan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "503_CR33",
"unstructured": "VanBlargan, L. A. et al. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 28, 490–495 (2022).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-06629-2",
"author": "Y Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "503_CR34",
"unstructured": "Yu, Y. et al. mRNA vaccine-induced antibodies more effective than natural immunity in neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 and its high affinity variants. Sci. Rep. 12, 2628 (2022).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102898",
"author": "P De Candia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102898",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "503_CR35",
"unstructured": "De Candia, P. et al. Effect of time and titer in convalescent plasma therapy for COVID-19. iScience 24, 102898 (2021).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"author": "B Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "503_CR36",
"unstructured": "Cao, B. et al. A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 1787–1799 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.17054",
"author": "L Benning",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1873",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Transplant.",
"key": "503_CR37",
"unstructured": "Benning, L. et al. Neutralizing antibody response against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) and the B.1.1.529 (Omicron) variants after a third mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine dose in kidney transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 22, 1873–1883 (2022).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00503-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cancer Research",
"Oncology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody-containing plasma improves outcome in patients with hematologic or solid cancer and severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}