The Effect of Melatonin as an Adjuvant Therapy on COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3878090, IRCT20200408046988N1, Jul 2021
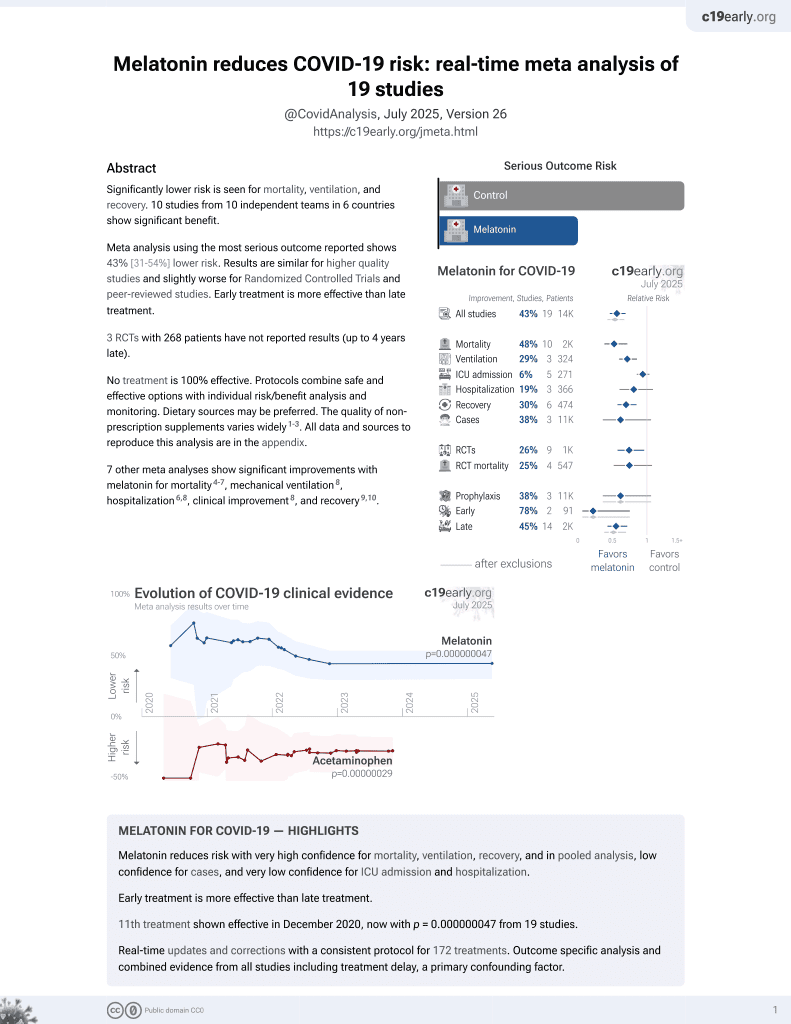
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 81 hospitalized patients in Iran, showing significantly improved oxygen saturation with treatment. Melatonin 3mg, 3x daily for 2 weeks.
Davoodian et al., 1 Jul 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, preprint, 6 authors, trial IRCT20200408046988N1.
The effect of melatonin as an adjuvant therapy on COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Background: Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland and has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. So, it is proposed to be effective in the management of Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to evaluate the effect of melatonin as adjunctive therapy for the treatment of hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Methods: In this double-blind randomized placebo controlled clinical trial, 81 mild to moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients with inclusion criteria were randomly divided to treatment (n=42) group to receive melatonin tablet 3 mg, three times daily for 2 weeks or placebo (n=39) group. Patients' symptoms and laboratory data were assessed at baseline and during the follow-up period and compared between two groups.
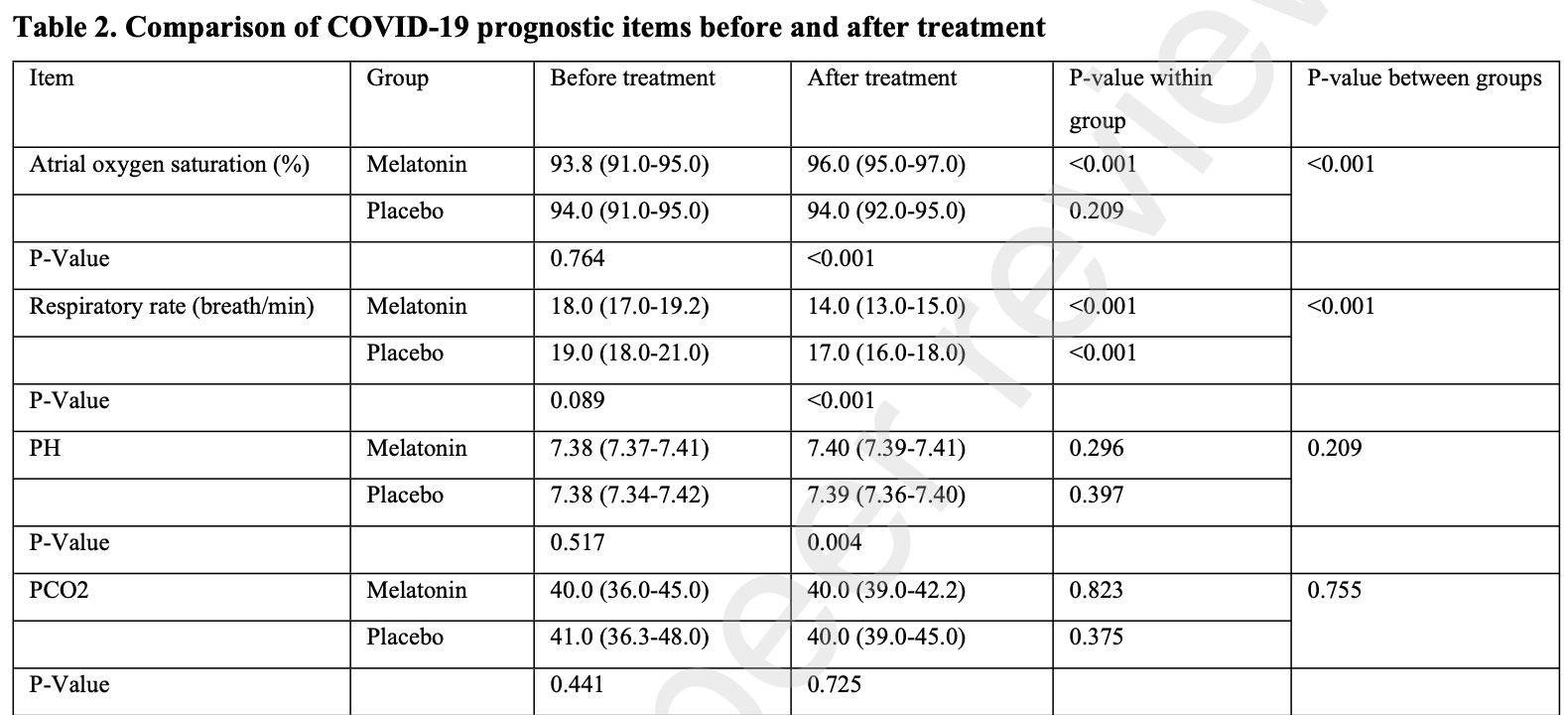
Findings: After two weeks of follow-up, the oxygen saturation and the respiratory rate significantly improved in the melatonin group. Moreover, C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), creatine phosphokinase (CPK), Ferritin, and D-Dimer levels significantly decreased in the melatonin group, but there was a considerable increase in the placebo group. Between-group comparison showed a significant difference between melatonin and placebo groups. Interpretation: the results of this randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial indicated the high efficacy and safety of melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 disease. Further study with large sample size and on other populations like severe COVID-19 is recommended.
References
Acuña-Castroviejo, Escames, Figueira, De La Oliva, Borobia et al., Clinical trial to test the efficacy of melatonin in COVID-19, Journal of pineal research
Campos, Cipolla-Neto, Amaral, Michelini, Bader et al., The Angiotensin-melatonin axis, International journal of hypertension
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies. Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents
Davoudi-Monfared, Rahmani, Khalili, Hajiabdolbaghi, Salehi et al., A Randomized Clinical Trial of the Efficacy and Safety of Interferon β-1a in Treatment of Severe COVID-19, Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, Jama
Ho, Bryson, Rumsfeld, Medication adherence: its importance in cardiovascular outcomes, Circulation
Juybari, Pourhanifeh, Hosseinzadeh, Hemati, Mehrzadi, Melatonin potentials against viral infections including COVID-19: Current evidence and new findings, Virus research
Kircheis, Haasbach, Lueftenegger, Heyken, Ocker et al., NF-κB Pathway as a Potential Target for Treatment of Critical Stage COVID-19 Patients, Frontiers in immunology
Makris, Spanou, Acute Kidney Injury: Definition, Pathophysiology and Clinical Phenotypes, The Clinical biochemist Reviews
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mokhtari, Hassani, Ghaffari, Ebrahimi, Yarahmadi et al., COVID-19 and multiorgan failure: A narrative review on potential mechanisms, Journal of molecular histology
Ni, Yang, Yang, Bao, Li et al., Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19, Critical care
Okamoto, Ichikawa, The pivotal role of the angiotensin-II-NF-κB axis in the development of COVID-19 pathophysiology, Hypertension research : official journal of the Japanese Society of Hypertension
Poursadegh, Davoudian, Mozdourian, Abdollahi, Synchronous presentation of COVID-19 pneumonia and pulmonary embolism
Reiter, Mayo, Tan, Sainz, Jimenez et al., Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers, Journal of pineal research
Rodriguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Gutiérrez-Ocampo, Villamizar-Peña, Holguin-Rivera et al., Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Travel medicine and infectious disease
Saber-Moghaddam, Salari, Hejazi, Amini, Taherzadeh et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytotherapy research
Salles, Correspondence COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life sciences
Scotton, Chambers, Molecular targets in pulmonary fibrosis: the myofibroblast in focus, Chest
Shneider, Kudriavtsev, Vakhrusheva, Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic? International reviews of immunology
Whitehead, Julious, Cooper, Campbell, Estimating the sample size for a pilot randomised trial to minimise the overall trial sample size for the external pilot and main trial for a continuous outcome variable, Statistical methods in medical research
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA internal medicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3878090",
"ISSN": [
"1556-5068"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3878090",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davoodian",
"given": "Najmeh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharifimood",
"given": "Farnoosh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salarbashi",
"given": "Davoud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elyasi",
"given": "Sepideh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baniasad",
"given": "Amir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bejestani",
"given": "Farhang Soltani",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "SSRN Electronic Journal",
"container-title-short": "SSRN Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-07T03:04:47Z",
"timestamp": 1625627087000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-07T03:05:05Z",
"timestamp": 1625627105000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-01T09:34:47Z",
"timestamp": 1648805687105
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.2139",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=3878090"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Effect of Melatonin as an Adjuvant Therapy on COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}