Preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor RAY1216 shows improved pharmacokinetics compared with nirmatrelvir
et al., Nature Microbiology, doi:10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9, Mar 2024
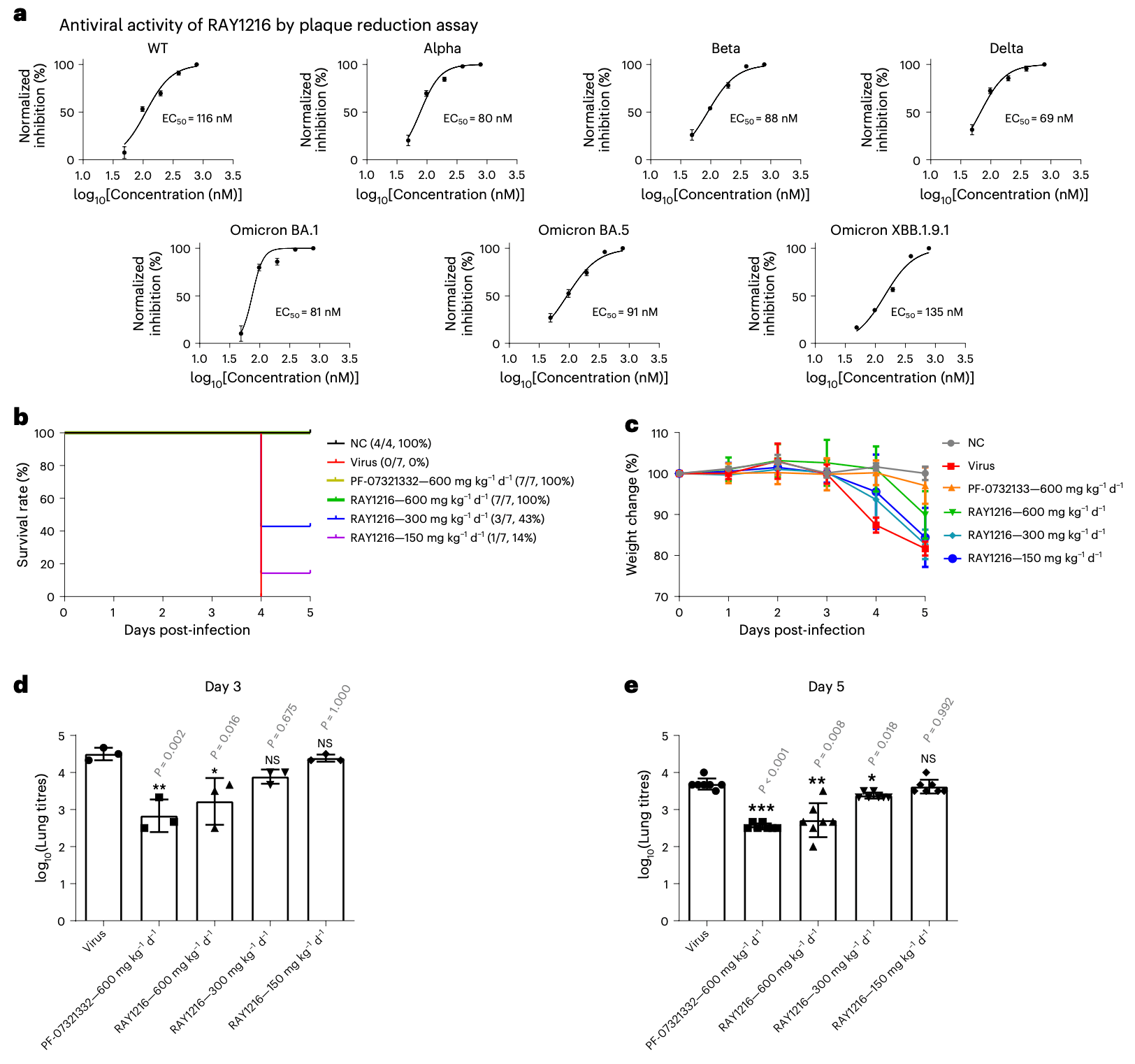
In vitro and K18-hACE2 transgenic mouse study showing the preclinical efficacy of RAY1216, an inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants. RAY1216 forms a covalent bond with the catalytic cysteine of Mpro and has improved pharmacokinetic properties compared to nirmatrelvir. The crystal structure of the RAY1216:Mpro complex shows that RAY1216 binds in the Mpro active site. Authors demonstrate that RAY1216 inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 variants, including omicron subvariants BA.1, BA.5, and XBB.1.9.1, in Vero E6 cells with EC50 values ranging from 69-135 nM. In K18-hACE2 transgenic mice challenged with a lethal dose of SARS-CoV-2 delta variant, oral RAY1216 treatment improved survival in a dose-dependent manner. RAY1216 also reduced lung viral titers and alleviated lung histopathology in mice infected with a non-lethal dose of SARS-CoV-2. The pharmacokinetics of RAY1216 in mice and rats were superior to those of nirmatrelvir, with slower plasma clearance and longer elimination half-lives. RAY1216 has been approved as a COVID-19 treatment in China under the generic name leritrelvir.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of leritrelvir for COVID-19:
Chen et al., 29 Mar 2024, peer-reviewed, 33 authors.
Contact: jeffyah@163.com, chen_shuhui@wuxiapptec.com, nanshan@vip.163.com, xiong_xiaoli@gibh.ac.cn.
Preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor RAY1216 shows improved pharmacokinetics compared with nirmatrelvir
Nature Microbiology, doi:10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9
Although vaccines are available for SARS-CoV-2, antiviral drugs such as nirmatrelvir are still needed, particularly for individuals in whom vaccines are less effective, such as the immunocompromised, to prevent severe COVID-19. Here we report an α-ketoamide-based peptidomimetic inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro ), designated RAY1216. Enzyme inhibition kinetic analysis shows that RAY1216 has an inhibition constant of 8.4 nM and suggests that it dissociates about 12 times slower from M pro compared with nirmatrelvir. The crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 M pro :RAY1216 complex shows that RAY1216 covalently binds to the catalytic Cys145 through the α-ketoamide group. In vitro and using human ACE2 transgenic mouse models, RAY1216 shows antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 variants comparable to those of nirmatrelvir. It also shows improved pharmacokinetics in mice and rats, suggesting that RAY1216 could be used without ritonavir, which is co-administered with nirmatrelvir. RAY1216 has been approved as a single-component drug named 'leritrelvir' for COVID-19 treatment in China. SARS-CoV-2 has become established in the human population through the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and is likely to remain in circulation. Owing to multinational efforts, vaccines were rapidly rolled out in the early stage of the pandemic and proved successful in saving lives. However, probably due to population immune pressures established by infections and vaccinations, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants with highly mutated spike proteins quickly emerged 1 . Rapid emergence of highly mutated variants has shown the extraordinary capacity of the virus to escape humoral immunity, representing a great challenge to vaccines and therapeutic antibodies 2,3 . A number of small-molecule SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics have been developed 4 . This therapeutic strategy may be part of a solution to combat SARS-CoV-2 immune escape. Of note, the orally available drugs molnupiravir and Paxlovid have been approved for COVID-19 treatment
Article https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9 before administration; the p.o. formulation was the same as that of the mice, and the rats were fed 4 h post-dose. Blood samples were taken via jugular vein cannula at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 24 h after dosing and collected into tubes containing sodium heparin. Plasma samples were obtained and stored in the same manner as described in the mouse section above.
K18-hACE2 mouse pharmacokinetics To evaluate the pharmacokinetics of RAY1216 and PF-07321332 in the K18-hACE2 mouse, RAY1216 and PF-07321332 groups were set up and each group had five SPF-grade female 6-week-old K18-hACE2 mice (purchased from GemPharmatech). Each mouse was administrated with a single dose of 600 mg kg -1 RAY1216 or PF-07321332 p.o. daily for 5 days (the same dose used in the antiviral animal experiment). On the fifth day, blood samples were taken from the cheek at 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 24 h. The blood samples were processed and analysed with the same protocol as the ICR mouse samples.
LC-MS/MS analysis of mouse plasma samples For the mouse pharmacokinetic studies, 20 μl plasma samples (the blank sample used 20 μl blank plasma) were mixed with 200 μl of 50% methanol acetonitrile solution (50 ng ml -1 tolbutamide in MeOH); a double blank sample was prepared with 200 μl 50% methanol acetonitrile solution. Samples were centrifugated at 1,790 × g for 10 min at 4 °C. Then, 100 μl of the supernatant was transferred to a clean tube..
References
Bao, The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice, Nature
Boras, Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19, Nat. Commun
Bradshaw, Prolonged and tunable residence time using reversible covalent kinase inhibitors, Nat. Chem. Biol
Breidenbach, Targeting the main protease of SARS-CoV-2: from the establishment of high throughput screening to the design of tailored inhibitors, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed
Cha, Agarwal, Parks, Tight-binding inhibitors-II: non-steady state nature of inhibition of milk xanthine oxidase by allopurinol and alloxanthine and of human erythrocytic adenosine deaminase by coformycin, Biochem. Pharmacol
Cha, Tight-binding inhibitors-I: kinetic behavior, Biochem. Pharmacol
Cha, Tight-binding inhibitors-III: a new approach for the determination of competition between tight-binding inhibitors and substrates-inhibition of adenosine deaminase by coformycin, Biochem. Pharmacol
Chen, Experimental crystal structure of RAY1216, doi:10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc2fl1ps
Chen, Huang, Ma, Kuzmič, Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 variants by RAY1216 and PF-07321332 as assessed by qPCR. Viral gene in the supernatants of Vero E6 cell infected by wildtype (a), Alpha (b), Beta (c), Delta (d), Omicron BA.1 (e) and Omicron BA.5 (f) SARS-CoV-2 authentic viruses in the presence of different concentrations of RAY1216/PF-07321332 was measured by quantitative real-time PCR assay, nanshan, doi:10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9ExtendedDataFig.2
Chen, Tan, Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of HCV NS3-4A protease as potential therapeutic agents against HCV infection, Curr. Med. Chem
Copeland, Evaluation of Enzyme Inhibitors in Drug Discovery: A Guide for Medicinal Chemists and Pharmacologists 2nd edn
Copeland, Pompliano, Meek, Drug-target residence time and its implications for lead optimization, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov
Cox, SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Dahl, Akerud, Pharmacokinetics and the drug-target residence time concept, Drug Discov. Today
Dai, Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Science
Dragovich, Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of irreversible human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitors. 4. Incorporation of P1 lactam moieties as l-glutamine replacements, J. Med. Chem
Drayman, Masitinib is a broad coronavirus 3CL inhibitor that blocks replication of SARS-CoV-2, Science
Emsley, Cowtan, Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics, Acta Crystallogr. D
Fenton, Keam, Emerging small molecule antivirals may fit neatly into COVID-19 treatment, Drugs Ther. Perspect
Gao, Discovery and crystallographic studies of trisubstituted piperazine derivatives as non-covalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with high target specificity and low toxicity, J. Med. Chem
Greasley, Structural basis for the in vitro efficacy of nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 variants, J. Biol. Chem
Grum-Tokars, Ratia, Begaye, Baker, Mesecar, Evaluating the 3C-like protease activity of SARS-coronavirus: recommendations for standardized assays for drug discovery, Virus Res
Harvey, SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Ip, Global prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease mutations associated with nirmatrelvir or ensitrelvir resistance, eBioMedicine
Jin, Structure of M pro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors, Nature
Jochmans, The substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro are selected by a protease inhibitor in vitro and confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, mBio
Kabsch, Xds, None, Acta Crystallogr. D
Kitamura, Expedited approach toward the rational design of noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors, J. Med. Chem
Kneller, Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL M pro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography, Nat. Commun
Kuzmic, DynaFit-a software package for enzymology, Methods Enzymol
Kuzmic, Program DYNAFIT for the analysis of enzyme kinetic data: application to HIV proteinase, Anal. Biochem
Kwong, Kauffman, Hurter, Mueller, Discovery and development of telaprevir: an NS3-4A protease inhibitor for treating genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C virus, Nat. Biotechnol
Lee, Genetic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 M pro reveals high sequence and structural conservation prior to the introduction of protease inhibitor Paxlovid, mBio
Lin, Kwong, Perni, Discovery and development of VX-950, a novel, covalent, and reversible inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3.4A serine protease, Infect. Disord. Drug Targets
Ltd, None
Lu, Tonge, Drug-target residence time: critical information for lead optimization, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol
Luo, Engineering a reliable and convenient SARS-CoV-2 replicon system for analysis of viral RNA synthesis and screening of antiviral inhibitors, mBio
Ma, Boceprevir, GC-376, and calpain inhibitors II, XII inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral replication by targeting the viral main protease, Cell Res
Ma, Discovery of di-and trihaloacetamides as covalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with high target specificity, J. Am. Chem. Soc
Ma, Liushen Capsules, a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19, alleviates SARS-CoV-2-induced pulmonary in vivo and inhibits the proliferation of the variant virus strains in vitro, Chin. Med
Mccoy, Phaser crystallographic software, J. Appl. Crystallogr
Morrison, The slow-binding and slow, tight-binding inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions, Trends Biochem. Sci
Morrison, Walsh, None, Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology
Murshudov, Vagin, Dodson, Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method, Acta Crystallogr. D
Owen, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Park, Korean Scutellaria baicalensis water extract inhibits cell cycle G1/S transition by suppressing cyclin D1 expression and matrix-metalloproteinase-2 activity in human lung cancer cells, J. Ethnopharmacol
Qiao, SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitors with antiviral activity in a transgenic mouse model, Science
Quan, An orally available M pro inhibitor is effective against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and variants including Omicron, Nat. Microbiol
Rut, SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitors and activity-based probes for patient-sample imaging, Nat. Chem. Biol
Sacco, Structure and inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease reveal strategy for developing dual inhibitors against M pro and cathepsin, L. Sci. Adv
Tan, 3C protease of enterovirus 68: structure-based design of Michael acceptor inhibitors and their broad-spectrum antiviral effects against picornaviruses, J. Virol
Tian, Sun, Xu, Ye, The emergence and epidemic characteristics of the highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, J. Med. Virol
Unoh, Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19, J. Med. Chem
Winn, Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments, Acta Crystallogr. D
Xiong, What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: from structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design, Med. Res. Rev
Yip, Discovery of a novel bicycloproline P2 bearing peptidyl alpha-ketoamide LY514962 as HCV protease inhibitor, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett
Yip, P4 and P1′ optimization of bicycloproline P2 bearing tetrapeptidyl alpha-ketoamides as HCV protease inhibitors, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett
Zaidman, An automatic pipeline for the design of irreversible derivatives identifies a potent SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor, Cell Chem. Biol
Zhan, Leritrelvir for the treatment of mild or moderate COVID-19 without co-administered ritonavir: a multicentre randomised double-blind placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, eClinicalMedicine
Zhang, Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors, Science
Zhao, Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with protease inhibitor PF-07321332, Protein Cell
Zhou, β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 through lethal mutagenesis but is also mutagenic to mammalian cells, J. Infect. Dis
Zhu, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med
Zhu, Identification of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitors by a quantitative high-throughput screening, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci
Zhu, Peptide aldehyde inhibitors challenge the substrate specificity of the SARS-coronavirus main protease, Antiviral Res
Ziebuhr, Snijder, Gorbalenya, Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in the Nidovirales, J. Gen. Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9",
"ISSN": [
"2058-5276"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41564-024-01618-9",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Although vaccines are available for SARS-CoV-2, antiviral drugs such as nirmatrelvir are still needed, particularly for individuals in whom vaccines are less effective, such as the immunocompromised, to prevent severe COVID-19. Here we report an α-ketoamide-based peptidomimetic inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M<jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>), designated RAY1216. Enzyme inhibition kinetic analysis shows that RAY1216 has an inhibition constant of 8.4 nM and suggests that it dissociates about 12 times slower from M<jats:sup>pro</jats:sup> compared with nirmatrelvir. The crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 M<jats:sup>pro</jats:sup>:RAY1216 complex shows that RAY1216 covalently binds to the catalytic Cys145 through the α-ketoamide group. In vitro and using human ACE2 transgenic mouse models, RAY1216 shows antiviral activities against SARS-CoV-2 variants comparable to those of nirmatrelvir. It also shows improved pharmacokinetics in mice and rats, suggesting that RAY1216 could be used without ritonavir, which is co-administered with nirmatrelvir. RAY1216 has been approved as a single-component drug named ‘leritrelvir’ for COVID-19 treatment in China.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"1618"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "27 February 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "22 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "29 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "Xiaoxin Chen, J.H., H.L. and C.L. are employees of Guangdong Raynovent Biotech, which holds the patent of RAY1216. Guangdong Raynovent Biotech provided the RAY1216 molecule used in this study and was responsible for the chemical characterization of RAY1216 and the in vivo and in vitro pharmacokinetic studies. The Raynovent company is not involved in the interpretation of the other results reported in this study and provides no funding to the other parties. P.K. is the author and distributor of the software package DynaFit. DynaFit licenses are available free of charge to all academic, educational and non-profit research institutions. The other authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xiaoxin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0898-1352",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Xiaodong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Qinhai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5250-8381",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kuzmič",
"given": "Petr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Biao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Sai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jizheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1680-7533",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Jinxin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Bin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Haiming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Wenjie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Chunguang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Shiguan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Jianzhou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Haijun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Long",
"given": "Chaofeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Hongrui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheng",
"given": "Yanan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guo",
"given": "Yaoting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Niu",
"given": "Chuanying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xue",
"given": "Lu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2317-0558",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Jinsong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5647-6014",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Tianyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4602-0571",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Zhenzhen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8897-4891",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Deng",
"given": "Wenbin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Xinwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0009-0002-8375-7975",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Shu-Hui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2274-1427",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "Nanshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4632-9122",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xiong",
"given": "Xiaoli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2681-4171",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Zifeng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "Nat Microbiol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-29T11:01:54Z",
"timestamp": 1711710114000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T22:02:33Z",
"timestamp": 1712268153000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T11:50:14Z",
"timestamp": 1712663414949
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1711670400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1711670400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01618-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01618-9",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01618-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1075-1088",
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27643",
"author": "D Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2376",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "1618_CR1",
"unstructured": "Tian, D., Sun, Y., Xu, H. & Ye, Q. The emergence and epidemic characteristics of the highly mutated SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. J. Med. Virol. 94, 2376–2383 (2022).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00809-7",
"author": "M Cox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "1618_CR2",
"unstructured": "Cox, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant evasion of monoclonal antibodies based on in vitro studies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 112–124 (2023).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"author": "WT Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "1618_CR3",
"unstructured": "Harvey, W. T. et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 409–424 (2021).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40267-022-00897-8",
"author": "C Fenton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Drugs Ther. Perspect.",
"key": "1618_CR4",
"unstructured": "Fenton, C. & Keam, S. J. Emerging small molecule antivirals may fit neatly into COVID-19 treatment. Drugs Ther. Perspect. 38, 112–126 (2022).",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab247",
"author": "S Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "1618_CR5",
"unstructured": "Zhou, S. et al. β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 through lethal mutagenesis but is also mutagenic to mammalian cells. J. Infect. Dis. 224, 415–419 (2021).",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"author": "DR Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1618_CR6",
"unstructured": "Owen, D. R. et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 374, 1586–1593 (2021).",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13238-021-00883-2",
"author": "Y Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Protein Cell",
"key": "1618_CR7",
"unstructured": "Zhao, Y. et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease in complex with protease inhibitor PF-07321332. Protein Cell 13, 689–693 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/0022-1317-81-4-853",
"author": "J Ziebuhr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "853",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "1618_CR8",
"unstructured": "Ziebuhr, J., Snijder, E. J. & Gorbalenya, A. E. Virus-encoded proteinases and proteolytic processing in the Nidovirales. J. Gen. Virol. 81, 853–879 (2000).",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abg5827",
"author": "N Drayman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1618_CR9",
"unstructured": "Drayman, N. et al. Masitinib is a broad coronavirus 3CL inhibitor that blocks replication of SARS-CoV-2. Science 373, 931–936 (2021).",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.0c00108",
"author": "W Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1008",
"journal-title": "ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "1618_CR10",
"unstructured": "Zhu, W. et al. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitors by a quantitative high-throughput screening. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 3, 1008–1016 (2020).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117",
"author": "Y Unoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6499",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR11",
"unstructured": "Unoh, Y. et al. Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19. J. Med. Chem. 65, 6499–6512 (2022).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jacs.1c08060",
"author": "C Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20697",
"journal-title": "J. Am. Chem. Soc.",
"key": "1618_CR12",
"unstructured": "Ma, C. et al. Discovery of di- and trihaloacetamides as covalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with high target specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 143, 20697–20709 (2021).",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01146",
"author": "S Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13343",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gao, S. et al. Discovery and crystallographic studies of trisubstituted piperazine derivatives as non-covalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors with high target specificity and low toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 65, 13343–13364 (2022).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.05.018",
"author": "D Zaidman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1795",
"journal-title": "Cell Chem. Biol.",
"key": "1618_CR14",
"unstructured": "Zaidman, D. et al. An automatic pipeline for the design of irreversible derivatives identifies a potent SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor. Cell Chem. Biol. 28, 1795–1806.e5 (2021).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c00509",
"author": "N Kitamura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2848",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR15",
"unstructured": "Kitamura, N. et al. Expedited approach toward the rational design of noncovalent SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 65, 2848–2865 (2022).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abf1611",
"author": "J Qiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1374",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1618_CR16",
"unstructured": "Qiao, J. et al. SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors with antiviral activity in a transgenic mouse model. Science 371, 1374–1378 (2021).",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26239-2",
"author": "B Boras",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "1618_CR17",
"unstructured": "Boras, B. et al. Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19. Nat. Commun. 12, 6055 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb4489",
"author": "W Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1331",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1618_CR18",
"unstructured": "Dai, W. et al. Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Science 368, 1331–1335 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y",
"author": "Z Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1618_CR19",
"unstructured": "Jin, Z. et al. Structure of Mpro from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors. Nature 582, 289–293 (2020).",
"volume": "582",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01119-7",
"author": "BX Quan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "716",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "1618_CR20",
"unstructured": "Quan, B. X. et al. An orally available Mpro inhibitor is effective against wild-type SARS-CoV-2 and variants including Omicron. Nat. Microbiol. 7, 716–725 (2022).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb3405",
"author": "L Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "1618_CR21",
"unstructured": "Zhang, L. et al. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 main protease provides a basis for design of improved α-ketoamide inhibitors. Science 368, 409–412 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0356-z",
"author": "C Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "678",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "1618_CR22",
"unstructured": "Ma, C. et al. Boceprevir, GC-376, and calpain inhibitors II, XII inhibit SARS-CoV-2 viral replication by targeting the viral main protease. Cell Res 30, 678–692 (2020).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/anie.202016961",
"author": "J Breidenbach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10423",
"journal-title": "Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.",
"key": "1618_CR23",
"unstructured": "Breidenbach, J. et al. Targeting the main protease of SARS-CoV-2: from the establishment of high throughput screening to the design of tailored inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 60, 10423–10429 (2021).",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2003.09.074",
"author": "Y Yip",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "251",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "1618_CR24",
"unstructured": "Yip, Y. et al. Discovery of a novel bicycloproline P2 bearing peptidyl alpha-ketoamide LY514962 as HCV protease inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 251–256 (2004).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2004.07.007",
"author": "Y Yip",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5007",
"journal-title": "Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "1618_CR25",
"unstructured": "Yip, Y. et al. P4 and P1′ optimization of bicycloproline P2 bearing tetrapeptidyl alpha-ketoamides as HCV protease inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 14, 5007–5011 (2004).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867054864769",
"author": "SH Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2317",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR26",
"unstructured": "Chen, S. H. & Tan, S. L. Discovery of small-molecule inhibitors of HCV NS3-4A protease as potential therapeutic agents against HCV infection. Curr. Med. Chem. 12, 2317–2342 (2005).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nbt.2020",
"author": "AD Kwong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "993",
"journal-title": "Nat. Biotechnol.",
"key": "1618_CR27",
"unstructured": "Kwong, A. D., Kauffman, R. S., Hurter, P. & Mueller, P. Discovery and development of telaprevir: an NS3-4A protease inhibitor for treating genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C virus. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 993–1003 (2011).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21783",
"author": "M Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1965",
"journal-title": "Med. Res. Rev.",
"key": "1618_CR28",
"unstructured": "Xiong, M. et al. What coronavirus 3C-like protease tells us: from structure, substrate selectivity, to inhibitor design. Med. Res. Rev. 41, 1965–1998 (2021).",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.015",
"author": "V Grum-Tokars",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "63",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "1618_CR29",
"unstructured": "Grum-Tokars, V., Ratia, K., Begaye, A., Baker, S. C. & Mesecar, A. D. Evaluating the 3C-like protease activity of SARS-coronavirus: recommendations for standardized assays for drug discovery. Virus Res. 133, 63–73 (2008).",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0968-0004(82)90157-8",
"author": "JF Morrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "1618_CR30",
"unstructured": "Morrison, J. F. The slow-binding and slow, tight-binding inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 7, 102–105 (1982).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1982"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9780470123072.ch5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1618_CR31",
"unstructured": "Morrison, J. F. & Walsh, C. T. in Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology Vol. 61 (ed. Meister, A.) 201–301 (Wiley, 1988)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(75)90051-9",
"author": "S Cha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2187",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "1618_CR32",
"unstructured": "Cha, S., Agarwal, R. P. & Parks, R. E. Tight-binding inhibitors—II: non-steady state nature of inhibition of milk xanthine oxidase by allopurinol and alloxanthine and of human erythrocytic adenosine deaminase by coformycin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 24, 2187–2197 (1975).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1975"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(75)90050-7",
"author": "S Cha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2177",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "1618_CR33",
"unstructured": "Cha, S. Tight-binding inhibitors—I: kinetic behavior. Biochem. Pharmacol. 24, 2177–2185 (1975).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1975"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0006-2952(76)90259-8",
"author": "S Cha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2695",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "1618_CR34",
"unstructured": "Cha, S. Tight-binding inhibitors—III: a new approach for the determination of competition between tight-binding inhibitors and substrates—inhibition of adenosine deaminase by coformycin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 25, 2695–2702 (1976).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1976"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9781118540398",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1618_CR35",
"unstructured": "Copeland, R. A. Evaluation of Enzyme Inhibitors in Drug Discovery: A Guide for Medicinal Chemists and Pharmacologists 2nd edn (Wiley, 2013)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/abio.1996.0238",
"author": "P Kuzmic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "260",
"journal-title": "Anal. Biochem.",
"key": "1618_CR36",
"unstructured": "Kuzmic, P. Program DYNAFIT for the analysis of enzyme kinetic data: application to HIV proteinase. Anal. Biochem. 237, 260–273 (1996).",
"volume": "237",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0076-6879(09)67010-5",
"author": "P Kuzmic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "247",
"journal-title": "Methods Enzymol.",
"key": "1618_CR37",
"unstructured": "Kuzmic, P. DynaFit—a software package for enzymology. Methods Enzymol. 467, 247–280 (2009).",
"volume": "467",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nchembio.1817",
"author": "JM Bradshaw",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "525",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "1618_CR38",
"unstructured": "Bradshaw, J. M. et al. Prolonged and tunable residence time using reversible covalent kinase inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 11, 525–531 (2015).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd2082",
"author": "RA Copeland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "730",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "1618_CR39",
"unstructured": "Copeland, R. A., Pompliano, D. L. & Meek, T. D. Drug-target residence time and its implications for lead optimization. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 730–739 (2006).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.08.001",
"author": "L Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "204",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "1618_CR40",
"unstructured": "Zhu, L. et al. Peptide aldehyde inhibitors challenge the substrate specificity of the SARS-coronavirus main protease. Antiviral Res. 92, 204–212 (2011).",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01123-12",
"author": "J Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4339",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "1618_CR41",
"unstructured": "Tan, J. et al. 3C protease of enterovirus 68: structure-based design of Michael acceptor inhibitors and their broad-spectrum antiviral effects against picornaviruses. J. Virol. 87, 4339–4351 (2013).",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187152606776056706",
"author": "C Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Infect. Disord. Drug Targets",
"key": "1618_CR42",
"unstructured": "Lin, C., Kwong, A. D. & Perni, R. B. Discovery and development of VX-950, a novel, covalent, and reversible inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3.4A serine protease. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 6, 3–16 (2006).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-16954-7",
"author": "DW Kneller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "1618_CR43",
"unstructured": "Kneller, D. W. et al. Structural plasticity of SARS-CoV-2 3CL Mpro active site cavity revealed by room temperature X-ray crystallography. Nat. Commun. 11, 3202 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abe0751",
"author": "MD Sacco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabe0751",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "1618_CR44",
"unstructured": "Sacco, M. D. et al. Structure and inhibition of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease reveal strategy for developing dual inhibitors against Mpro and cathepsin L. Sci. Adv. 6, eabe0751 (2020).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-020-00689-z",
"author": "W Rut",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "1618_CR45",
"unstructured": "Rut, W. et al. SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitors and activity-based probes for patient-sample imaging. Nat. Chem. Biol. 17, 222–228 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm9805384",
"author": "PS Dragovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1213",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR46",
"unstructured": "Dragovich, P. S. et al. Structure-based design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of irreversible human rhinovirus 3C protease inhibitors. 4. Incorporation of P1 lactam moieties as l-glutamine replacements. J. Med. Chem. 42, 1213–1224 (1999).",
"volume": "42",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2312-y",
"author": "L Bao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "830",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "1618_CR47",
"unstructured": "Bao, L. et al. The pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 in hACE2 transgenic mice. Nature 583, 830–833 (2020).",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00869-22",
"author": "JT Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "1618_CR48",
"unstructured": "Lee, J. T. et al. Genetic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2 Mpro reveals high sequence and structural conservation prior to the introduction of protease inhibitor Paxlovid. mBio 13, e0086922 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101972",
"author": "SE Greasley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "1618_CR49",
"unstructured": "Greasley, S. E. et al. Structural basis for the in vitro efficacy of nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 variants. J. Biol. Chem. 298, 101972 (2022).",
"volume": "298",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2023.104559",
"author": "JD Ip",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104559",
"journal-title": "eBioMedicine",
"key": "1618_CR50",
"unstructured": "Ip, J. D. et al. Global prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease mutations associated with nirmatrelvir or ensitrelvir resistance. eBioMedicine 91, 104559 (2023).",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02754-20",
"author": "Y Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e02754",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "1618_CR51",
"unstructured": "Luo, Y. et al. Engineering a reliable and convenient SARS-CoV-2 replicon system for analysis of viral RNA synthesis and screening of antiviral inhibitors. mBio 12, e02754–20 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.02815-22",
"author": "D Jochmans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "1618_CR52",
"unstructured": "Jochmans, D. et al. The substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro are selected by a protease inhibitor in vitro and confer resistance to nirmatrelvir. mBio 14, e0281522 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drudis.2013.02.010",
"author": "G Dahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Drug Discov. Today",
"key": "1618_CR53",
"unstructured": "Dahl, G. & Akerud, T. Pharmacokinetics and the drug-target residence time concept. Drug Discov. Today 18, 697–707 (2013).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbpa.2010.06.176",
"author": "H Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "1618_CR54",
"unstructured": "Lu, H. & Tonge, P. J. Drug-target residence time: critical information for lead optimization. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 14, 467–474 (2010).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "Y Zhan",
"first-page": "102359",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "1618_CR55",
"unstructured": "Zhan, Y. et al. Leritrelvir for the treatment of mild or moderate COVID-19 without co-administered ritonavir: a multicentre randomised double-blind placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. eClinicalMedicine 14, 102359 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444909047337",
"author": "W Kabsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D",
"key": "1618_CR56",
"unstructured": "Kabsch, W. XDS. Acta Crystallogr. D 66, 125–132 (2010).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0021889807021206",
"author": "AJ McCoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "658",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Crystallogr.",
"key": "1618_CR57",
"unstructured": "McCoy, A. J. et al. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 40, 658–674 (2007).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444910045749",
"author": "MD Winn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D",
"key": "1618_CR58",
"unstructured": "Winn, M. D. et al. Overview of the CCP4 suite and current developments. Acta Crystallogr. D 67, 235–242 (2011).",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444904019158",
"author": "P Emsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2126",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D",
"key": "1618_CR59",
"unstructured": "Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 2126–2132 (2004).",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444996012255",
"author": "GN Murshudov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D",
"key": "1618_CR60",
"unstructured": "Murshudov, G. N., Vagin, A. A. & Dodson, E. J. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta Crystallogr. D 53, 240–255 (1997).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"author": "N Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "1618_CR61",
"unstructured": "Zhu, N. et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020).",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2010.10.057",
"author": "KI Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "634",
"journal-title": "J. Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "1618_CR62",
"unstructured": "Park, K. I. et al. Korean Scutellaria baicalensis water extract inhibits cell cycle G1/S transition by suppressing cyclin D1 expression and matrix-metalloproteinase-2 activity in human lung cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 133, 634–641 (2011).",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13020-022-00598-4",
"author": "Q Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Chin. Med",
"key": "1618_CR63",
"unstructured": "Ma, Q. et al. Liushen Capsules, a promising clinical candidate for COVID-19, alleviates SARS-CoV-2-induced pulmonary in vivo and inhibits the proliferation of the variant virus strains in vitro. Chin. Med 17, 40 (2022).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc2fl1ps",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1618_CR64",
"unstructured": "Chen, X. et al. Experimental crystal structure of RAY1216. CCDC https://doi.org/10.5517/ccdc.csd.cc2fl1ps (2023)."
}
],
"reference-count": 64,
"references-count": 64,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2634509/v1",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-024-01618-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"Genetics",
"Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology",
"Immunology",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Preclinical evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor RAY1216 shows improved pharmacokinetics compared with nirmatrelvir",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "9"
}