Kritik COVID-19 hastalarında kullanılan N-asetilsisteinin(NAC) klinik bulgulara, inflamatuar parametrelere böbrek fonksiyonlarına olan etkileri
et al., Aksaray Üniversitesi Tıp Bilimleri Dergisi, 3:2, Oct 2022
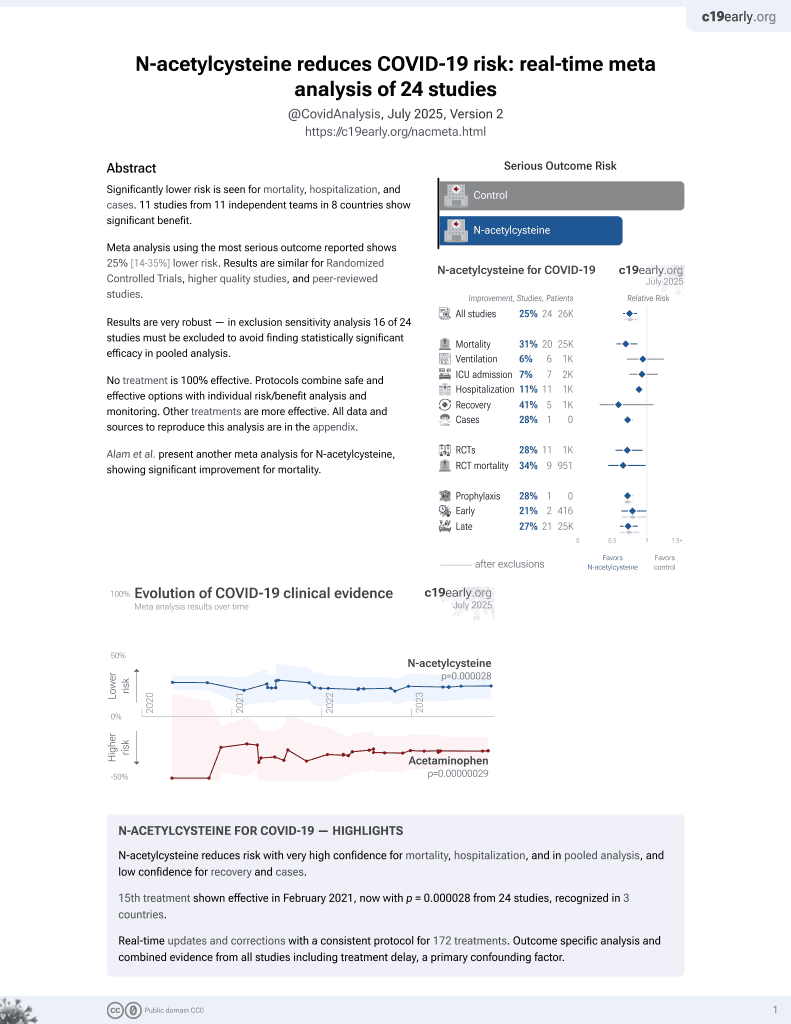
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 190 critical COVID-19 patients in Turkey, showing no significant differences with N-acetylcysteine treatment in unadjusted results with no baseline details. NAC 2400mg/day.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of death, 13.3% higher, RR 1.13, p = 0.47, treatment 52 of 97 (53.6%), control 44 of 93 (47.3%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 19.8% higher, RR 1.20, p = 0.25, treatment 55 of 97 (56.7%), control 44 of 93 (47.3%).
|
|
ICU time, 12.5% lower, relative time 0.88, p = 0.58, treatment 97, control 93.
|
|
hospitalization time, 13.3% lower, relative time 0.87, p = 0.09, treatment 97, control 93.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Çavuş et al., 25 Oct 2022, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 2 authors, study period April 2020 - September 2020.
The Effect of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on Clinical Findings, Inflammatory Parameters and Kidney Functions in Critical COVID-19 Patients
Bu çalışmada N-asetilsistein (NAC)'in COVID-19 nedeniyle üçüncü basamak yoğun bakım ihtiyacı olan kritik hastalarda; klinik bulgulara, inflamatuar parametrelere, böbrek fonksiyonlarına olan etkileri araştırıldı.
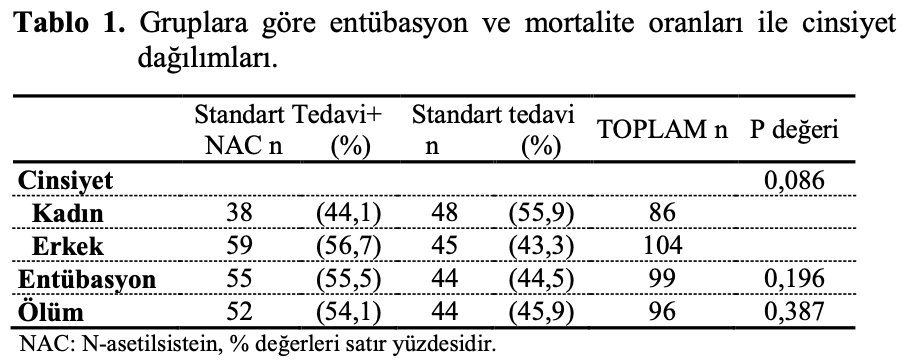
Materyal ve Metot: Bu tek merkezli retrospektif çalışmaya, Nisan-Eylül 2020 tarihleri arasında COVİD-19 PCR pozitifliği doğrulanmış 190 yetişkin hasta dahil edildi. Standart tedaviye ek olarak NAC (2400mg/gün dozda intravenöz olarak günde 1 defa) alan hastalar ile tek başına standart tedavi verilen hastaların klinik ve laboratuar bulguları karşılaştırıldı. Bulgular: Gruplar arasında yaş (p=0.423), cinsiyet (p=0.086), entübasyon (p=0,196), ölüm (p=0,387), hastane yatış (p=0,085) ve yoğun bakım yatış gün sayısı (p=0.584) açısından fark saptanmadı. Birinci gün, üçüncü gün, yedinci gün, onuncu gün ve on beşinci gün bakılan CRP (C-reactive protein), ferritin, fibrinojen, nötrofil, lenfosit sayısı, D-dimer, kreatinin değerlerinde NAC alan ve almayanlar arasında anlamlı bir fark saptanmadı (p>0.05). Sonuç: COVID-19 nedeniyle 3. Basamak yoğun bakım yatışı olan hastalarda NAC tedavisi ölümü, hastane yatış ve yoğun bakım yatış gün sayısını etkilememiştir. Aynı zamanda inflamatuar parametrelere ve böbrek fonksiyonlarına olumlu veya olumsuz bir etki göstermemiştir.
References
Aktoz, Altay, Aslanger, Atalar, Atar et al., Türk Kardiyoloji Derneği Uzlaşı Raporu: COVID-19 Pandemisi ve Kardiyovasküler Hastalıklar Konusunda Bilinmesi Gerekenler, Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars
Aldini, Altomare, Baron, Vistoli, Carini et al., N-Acetylcysteine as an antioxidant and disulphide breaking agent: the reasons why, Free Radic Res
Banerjee, Popoola, Shah, Ster, Quan et al., COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients, Kidney Int
Cazzola, Calzetta, Facciolo, Rogliani, Matera, Pharmacological investigation on the anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of N-acetylcysteine in an ex vivo model of COPD exacerbation, Respiratory Research
Chen, Aleksa, Woodland, Rieder, Koren, Prevention of ifosfamide nephrotoxicity by N-acetylcysteine: clinical pharmacokinetic considerations, Can J Clin Pharmacol
Chiba, Takahashi, Sato, Vd, Fas aracılı apoptoz, insan T hücrelerinde hücre içi glutatyon tarafından modüle edilir, Eur J Immunol
Dominari, Hathaway, Kapasi, Paul, Makkar et al., Bottom-up analysis of emergent properties of N-acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19, World J Virol
Ershad, Naji, Vearrier, N Asetilsistein
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir. Med
Geiler, Michaelis, Naczk, N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) inhibits virus replication and expression of pro-inflammatory molecules in A549 cells infected with highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza A virus, Biochem Pharmacol
Ho, Douglas, Glutathione and N-Acetylcysteine suppression of human immunodeficiency virus replication in human Monocyte/ Macrophages in vitro, AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses
Hoffmann, Fischereder, Krüger, Drobnik, Krämer, The value of Nacetylcysteine in the prevention of radiocontrast agent-induced nephropathy seems questionable, J Am Soc Nephrol
Hou, Zhang, Liang, Xu, Hu, Risk factors for disease progression in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Infect Dis (Lond)
Ibrahim, Smith, Lewis, Kon, Goldenberg et al., Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous Nacetylcysteine, Clin Immunol
Island, None
Lai, Hanczko, Bonilla, Caza, Clair et al., Nacetylcysteine reduces disease activity by blocking mammalian target of rapamycin in T cells from systemic lupus erythematosus patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Arthritis Rheum
Liu, Yao, Xu, Qiu, Cao et al., The anti-inflammatory effects of acetaminophen and N-acetylcysteine through suppression of the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in LPS-challenged piglet mononuclear phagocytes, Innate Immun
Mata, Sarrion, Armengot, Respiratory syncytial virus inhibits ciliagenesis in differentiated normal human bronchial epithelial cells: effectiveness of N-Acetylcysteine, PLoS One
Ng, Hirsch, Hazzan, Wanchoo, Shah et al., Outcomes Among Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 and Acute Kidney Injury, Am J Kidney Dis
Ocak, Erişim adresi
Porcu, Urbano, Verri, Barbosa, Baracat et al., Effects of adjunctive N-acetylcysteine on depressive symptoms: modulation by baseline high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, Psychiatry Res
Prauchner, Oxidative stress in sepsis: Pathophysiological implications justifying antioxidant co-therapy, Burns
Roederer, Ela, Staal, Herzenberg, N-acetylcysteine: a new approach to anti-HIV therapy, AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses
Sağlık Bakanlığı, Sağlığı, Müdürlüğü, Bilim kurulu çalışması, covıd-19 (sars-cOV-2 enfeksiyonu) rehberi
Shi, Puyo, N-Acetylcysteine to Combat COVID-19: An Evidence Review, Ther Clin Risk Manag
Subramaniam, Suarez-Cuervo, Wilson, Effectiveness of Prevention Strategies for Contrast-Induced Nephropathy A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis, Ann Intern Med
Suter, Domenighetti, Schaller, N-Acetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man: a randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled clinical study, Chest
Tarık, Inflammatory Regulation Effect of NAC on COVID-19 Treatment, INFECT
Tavakolpour, Rakhshandehroo, Wei, Rashidian, Lymphopenia during the COVID-19 infection: What it shows and what can be learned, Immunol Lett
Uzun, Çavdar, COVID-19 ve akut böbrek hasarı, DEU Tıp Derg
Wrotek, Jędrzejewski, Piotrowski, Kozak, N-Acetyl-l-cysteine exacerbates generation of IL-10 in cells stimulated with endotoxin in vitro and produces antipyresis via IL10 dependent pathway in vivo, Immunology Letters
Zhang, Yu, Tong, Liu, Tang, Predictive factors for disease progression in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, J. Clin. Virol
Zuin, Palamidese, Negrin, Catozzo, Scarda et al., High-dose N-acetylcysteine in patients with exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Clin. Drug Invest
Şit, Kayabaşı, SARS-CoV-2 ile İlişkili Akut Böbrek Hasarı, Dicle Tıp Dergisi
Šalamon, Kramar, Marolt, Poljšak, Milisav, Medical and Dietary Uses of N-Acetylcysteine, Antioxidants