Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial
et al., Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028, NCT04352959, Oct 2021
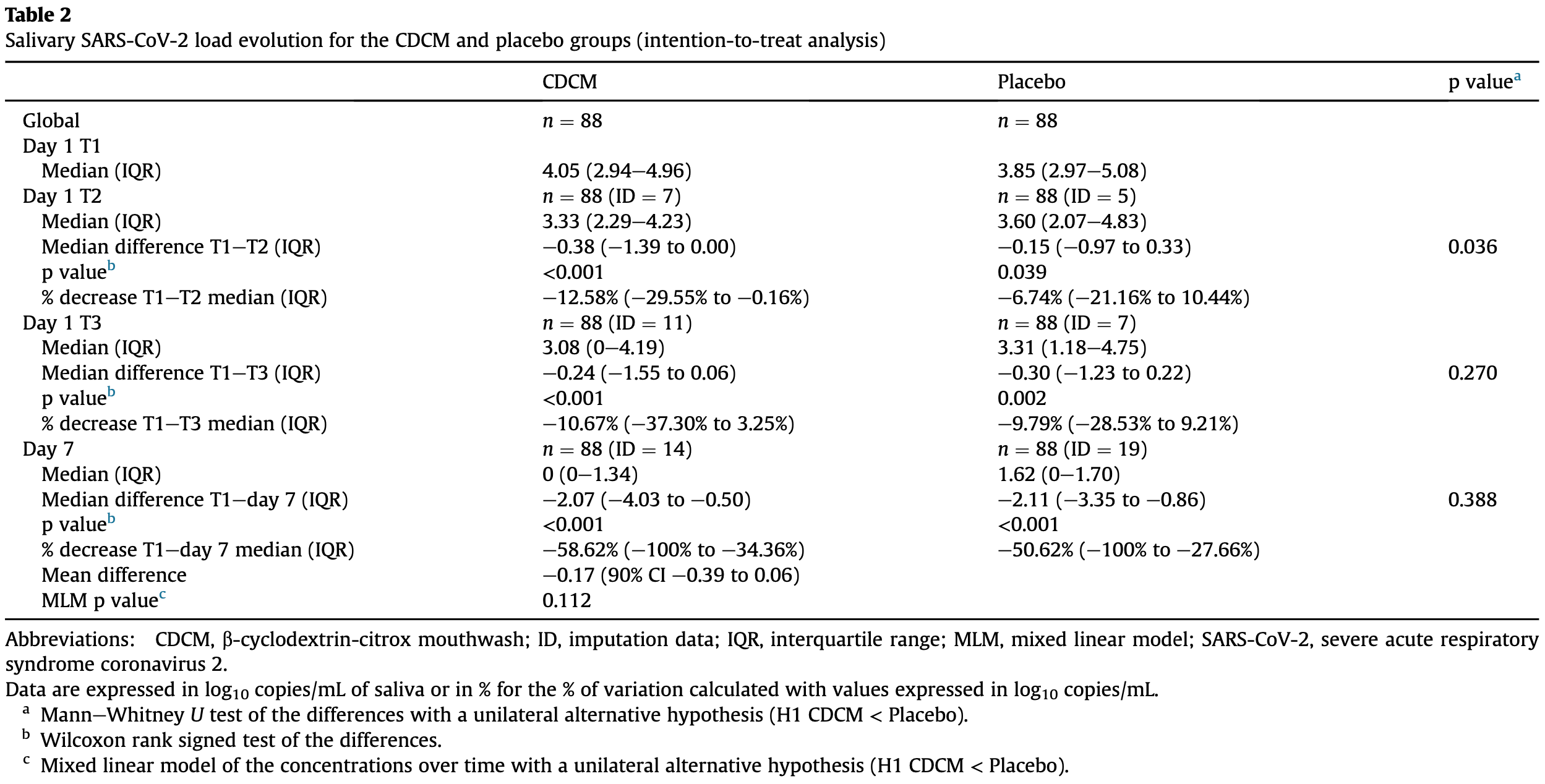
RCT 176 outpatients with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19 in France showing a significant reduction in SARS-CoV-2 salivary viral load with β-cyclodextrin-citrox mouthwash (CDCM) compared to placebo 4 hours after the first dose. Over 7 days, CDCM provided a modest benefit in reducing viral load, with a greater effect seen in those with higher baseline viral loads.
Carrouel et al., 31 Oct 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, France, peer-reviewed, mean age 43.1, 12 authors, study period 9 June, 2020 - 11 December, 2020, trial NCT04352959 (history).
Contact: carrouel@univ-lyon1.fr.
Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial
Clinical Microbiology and Infection, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028
Objectives: To determine if commercially available mouthwash with b-cyclodextrin and citrox (bioflavonoids) (CDCM) could decrease the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) salivary viral load. Methods: In this randomized controlled trial, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) PCR-positive patients aged 18e85 years with asymptomatic to mild coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms for <8 days were recruited. A total of 176 eligible patients were randomly assigned (1:1) to CDCM or placebo. Three rinses daily were performed for 7 days. Saliva sampling was performed on day 1 at 09.00 (T1), 13.00 (T2) and 18.00 (T3). On the following 6 days, one sample was taken at 15.00. Quantitative RT-PCR was used to detect SARS-CoV-2. Results: The intention-to-treat analysis demonstrated that, over the course of 1 day, CDCM was significantly more effective than placebo 4 hours after the first dose (p 0.036), with a median percentage (log 10 copies/mL) decrease T1eT2 of e12.58% (IQR e29.55% to e0.16%). The second dose maintained the low median value for the CDCM (3.08 log 10 copies/mL; IQR 0e4.19), compared with placebo (3.31 log 10 copies/mL; IQR 1.18e4.75). At day 7, there was still a greater median percentage (log 10 copies/mL) decrease in salivary viral load over time in the CDCM group (e58.62%; IQR e100% to e34.36%) compared with the placebo group (e50.62%; IQR e100% to e27.66%). These results were confirmed by the per-protocol analysis. Conclusions: This trial supports the relevance of using CDCM on day 1 (4 hours after the initial dose) to reduce the SARS-CoV-2 viral load in saliva. For long-term effect (7 days), CDMC appears to provide a modest benefit compared with placebo in reducing viral load in saliva.
Authors contributions FC, DB and CD proposed the original study idea. FC was the coordinating officer of this trial. FC, PT, CD and DB designed the trial and study protocol. MV, PT, MR and FC contributed to the data interpretation and PT, FC, MV and HP verified the data. EGD, AE, MEL and GI were responsible for the site work including the recruitment, follow up and data collection. HP monitored the trial. MBD and MV were responsible for the laboratory analysis. PT and MR did the main analysis. FC and DB wrote the first draft the manuscript and CD, MBD, MR, MV and PT contributed to the revision of the manuscript. All authors reviewed and accepted the paper before submission.
Access to data Florence Carrouel has full access to the data and is the guarantor for the data.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028 .
References
Braga, Barbosa, Santos, El-Saleh, Paz, Cyclodextrins in antiviral therapeutics and vaccines, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13030409
Braga, Cyclodextrins: emerging medicines of the new millennium, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom9120801
Carrouel, Conte, Fisher, Gonçalves, Dussart et al., COVID-19: a recommendation to examine the effect of mouthrinses with b-cyclodextrin combined with citrox in preventing infection and progression, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9041126
Carrouel, Gonçalves, Conte, Campus, Fisher et al., Antiviral activity of reagents in mouth rinses against SARS-CoV-2, J Dent Res
Carrouel, Viennot, Valette, Cohen, Dussart et al., Salivary and nasal detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus after antiviral mouthrinses (BBCovid): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials
Fini, Oral saliva and COVID-19, Oral Oncol
Goncharova, Kostyro, Ivanov, Zenkova, A Novel sulfonated derivative of b-cyclodextrin effectively inhibits influenza A virus infection in vitro and in vivo, Acta Naturae
Gülsen, Simple classification of COVID-19 patients, J Lung Pulm Respir Res
He, Lau, Wu, Deng, Wang et al., Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19, Nat Med
Herrera, Serrano, Rold An, Sanz, Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?, Clin Oral Investig, doi:10.1007/s00784-020-03413-2
Jayaweera, Perera, Gunawardana, Manatunge, Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: a critical review on the unresolved dichotomy, Environ Res
Johansson, Quandelacy, Kada, Prasad, Steele et al., SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms, JAMA Netw Open
Jones, Cagno, Ortiz, Gasilova, Piret, Modified cyclodextrins as broad-spectrum antivirals, Sci Adv
Kampf, Todt, Pfaender, Steinmann, Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents, J Hosp Infect
Lalani, Poh, Flavonoids as antiviral agents for enterovirus A71 (EV-A71), Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12020184
Li, Fu, Dongyan, Mikovits, Ruscetti et al., Flavonoid baicalin inhibits HIV-1 infection at the level of viral entry, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Meyers, Robison, Milici, Alam, Quillen et al., Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus, J Med Virol
O'donnell, Thomas, Stanton, Maillard, Murphy et al., Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Function, doi:10.1093/function/zqaa002
Pottel, Armstrong, Zou, Fekete, Huang et al., The activities of drug inactive ingredients on biological targets, Science
Pullano, Domenico, Sabbatini, Valdano, Turbelin et al., Underdetection of cases of COVID-19 in France threatens epidemic control, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03095-6
To, Tsang, Chik-Yan Yip, Chan, Wu et al., Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa149
To, Yip, Lai, Wong, Ho et al., Saliva as a diagnostic specimen for testing respiratory virus by a point-of-care molecular assay: a diagnostic validity study, Clin Microbiol Infect
Xu, Cui, Duan, Zhang, Zhou et al., Saliva: potential diagnostic value and transmission of 2019-nCoV, Int J Oral Sci
Yoon, Yoon, Song, Yoon, Lim et al., Clinical significance of a high SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the saliva, J Korean Med Sci
Zou, Liu, Li, Yao, Chen et al., Structure-activity relationship of flavonoid bifunctional inhibitors against Zika virus infection, Biochem Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028",
"ISSN": [
"1198-743X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028",
"alternative-id": [
"S1198743X21002688"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carrouel",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valette",
"given": "Martine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gadea",
"given": "Emilie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esparcieux",
"given": "Aurélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Illes",
"given": "Gabriela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Langlois",
"given": "Marie Elodie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Perrier",
"given": "Hervé",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dussart",
"given": "Claude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tramini",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ribaud",
"given": "Mélina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bouscambert-Duchamp",
"given": "Maude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourgeois",
"given": "Denis",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Microbiology and Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-24T16:32:31Z",
"timestamp": 1621873951000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-04T23:14:13Z",
"timestamp": 1633389253000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-10T01:39:42Z",
"timestamp": 1723253982289
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 27,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621555200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21002688?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1198743X21002688?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1494-1501",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41368-020-0080-z",
"article-title": "Saliva: potential diagnostic value and transmission of 2019-nCoV",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Oral Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104821",
"article-title": "Oral saliva and COVID-19",
"author": "Baghizadeh Fini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104821",
"journal-title": "Oral Oncol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib2",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2018.06.009",
"article-title": "Saliva as a diagnostic specimen for testing respiratory virus by a point-of-care molecular assay: a diagnostic validity study",
"author": "To",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "372",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib3",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa149",
"article-title": "Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva",
"author": "To",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e195",
"article-title": "Clinical significance of a high SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the saliva",
"author": "Yoon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Korean Med Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib5",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "National Academies of Sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib6",
"series-title": "Rapid expert consultation on the possibility of bioaerosol spread of SARS-CoV-2 for the COVID-19 pandemic (April 1, 2020)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envres.2020.109819",
"article-title": "Transmission of COVID-19 virus by droplets and aerosols: a critical review on the unresolved dichotomy",
"author": "Jayaweera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109819",
"journal-title": "Environ Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib7",
"volume": "188",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2020.01.022",
"article-title": "Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents",
"author": "Kampf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib8",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: a recommendation to examine the effect of mouthrinses with β-cyclodextrin combined with citrox in preventing infection and progression",
"author": "Carrouel",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib9",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0022034520967933",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of reagents in mouth rinses against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Carrouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib10",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/function/zqaa002",
"article-title": "Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "O’Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Function",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26514",
"article-title": "Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus",
"author": "Meyers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib12",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-020-03413-2",
"article-title": "Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?",
"author": "Herrera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12020184",
"article-title": "Flavonoids as antiviral agents for enterovirus A71 (EV-A71)",
"author": "Lalani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113962",
"article-title": "Structure-activity relationship of flavonoid bifunctional inhibitors against Zika virus infection",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113962",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib15",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom9120801",
"article-title": "Cyclodextrins: emerging medicines of the new millennium",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Biomolecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/bbrc.2000.3485",
"article-title": "Flavonoid baicalin inhibits HIV-1 infection at the level of viral entry",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "534",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib17",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.aax9318",
"article-title": "Modified cyclodextrins as broad-spectrum antivirals",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32607/20758251-2019-11-3-20-30",
"article-title": "A Novel sulfonated derivative of β-cyclodextrin effectively inhibits influenza A virus infection in vitro and in vivo",
"author": "Goncharova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Acta Naturae",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib19",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics13030409",
"article-title": "Cyclodextrins in antiviral therapeutics and vaccines",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04846-6",
"article-title": "Salivary and nasal detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus after antiviral mouthrinses (BBCovid): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Carrouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "906",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib21",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Simple classification of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Gülsen",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "J Lung Pulm Respir Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib22",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aaz9906",
"article-title": "The activities of drug inactive ingredients on biological targets",
"author": "Pottel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib23",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 transmission from people without COVID-19 symptoms",
"author": "Johansson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib24",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Underdetection of cases of COVID-19 in France threatens epidemic control",
"author": "Pullano",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5",
"article-title": "Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028_bib26",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1198743X21002688"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "27"
}