Characterization of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients at a Brooklyn Safety-Net Hospital
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.9809, Aug 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
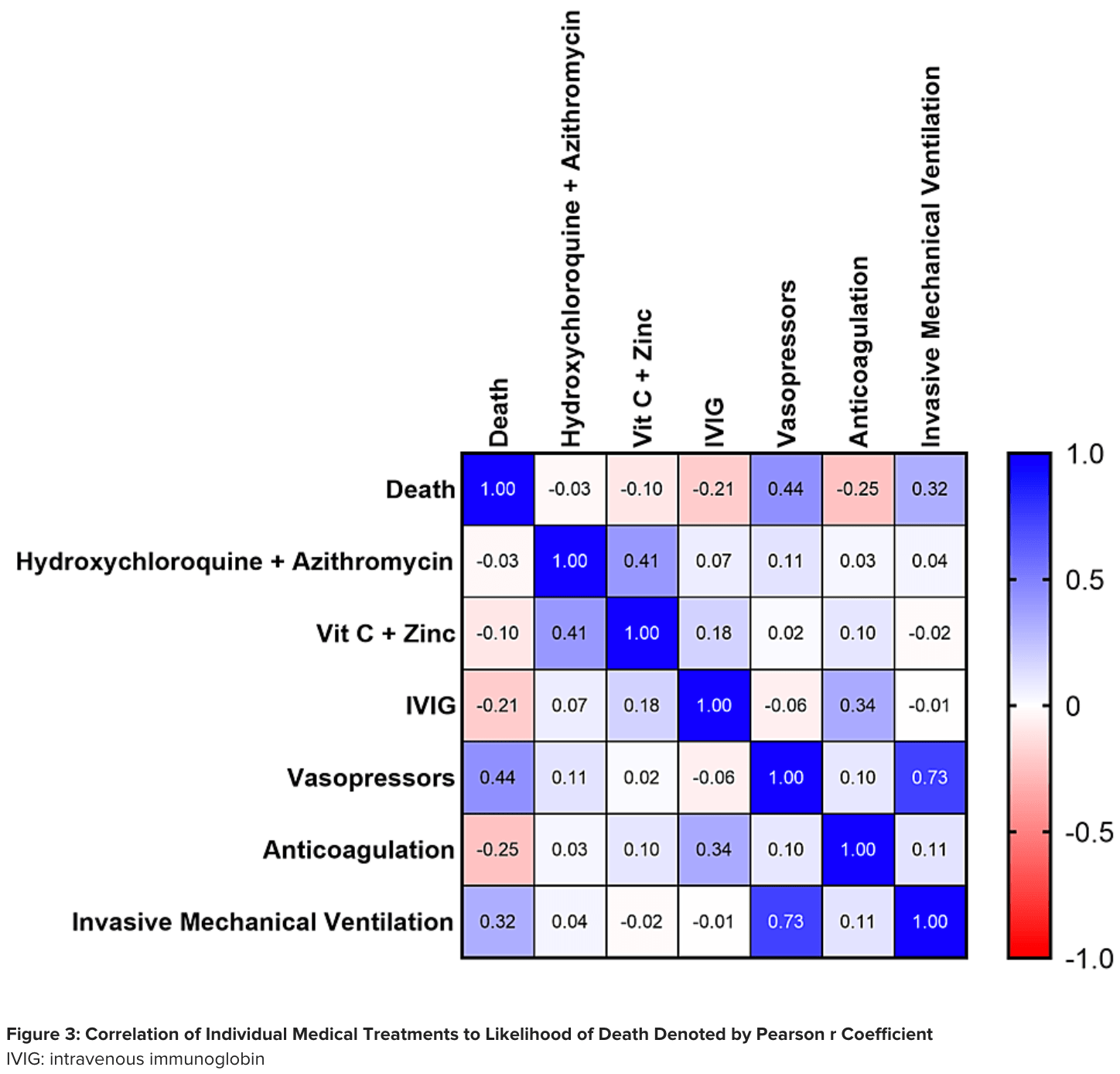
Retrospective 102 ICU patients in the USA, 73 receiving vitamin C and zinc, showing a negative correlation of treatment with mortality, but not reaching statistical significance (p = 0.31).
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
very late stage, ICU patients.
Study covers vitamin C and zinc.
Capone et al., 17 Aug 2021, USA, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Characterization of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients at a Brooklyn Safety-Net Hospital
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.9809
Background The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic continues to spread across the country with over 3 million cases and 150,000 deaths in the United States as of July 2020. Outcomes have been poor, with reported admission rates to the intensive care team of 5% in China and mortality among critically ill patients of 50% in Seattle. Here we explore the disease characteristics in a Brooklyn safety-net hospital affected by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic.
Methods A retrospective chart review of COVID-19 positive patients at The Brooklyn Hospital Center who were treated by the intensive care team prior to April 20, 2020. Data was extracted from the electronic health record, analyzed and correlated for outcome.
Results Impact of various clinical treatments was assessed, showing no change in median overall survival (OS) of both hydroxychloroquine with azithromycin or vitamin C with zinc. Supplemental therapies were used in selected patients, and some were shown to increase median OS and patients requiring vasopressor support or invasive mechanical ventilation showed decreased OS. There was no statistically significant difference in overall survival based on ethnicity, healthcare status, or individual medical comorbidities, although a negative trend exists for diabetes. Despite this, there is a trend towards increasingly poor prognosis based on the number of comorbidities and Class 3 obesity.
Conclusions Despite the fact that we show no significant differences in mortality based on ethnicity, insurance status, or individual medical comorbidities, we show a high overall mortality. There is also a trend towards increased overall mortality in Class 3 obesity, which should be further investigated. We suggest that these findings may be attributed to both socioeconomic factors and an increased incidence of total medical comorbidities in our patient population.
Additional Information Disclosures Human subjects: Consent was obtained by all participants in this study. The Brooklyn Hospital Center issued approval 1595421. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might
References
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, COVID-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region -case series, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2004500
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chronic Dis, doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2
Gattinoni, Coppola, Cressoni, Busana, Rossi et al., COVID-19 does not lead to a "typical" acute respiratory distress syndrome, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE
Gautret, Lagier, Parola, Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2012410
Goyal, Choi, Pinheiro, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2010419
Grasselli, Pesenti, Cecconi, Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4031
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2002032
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19, Thromb Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013
Magagnoli, Narendran, Pereira, Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19, doi:10.1101/2020.04.16.20065920
Mahévas, Tran, Roumier, No evidence of clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in patients hospitalised for COVID-19 infection and requiring oxygen : results of a study using routinely collected data to emulate a target trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.10.20060699
Oxley, Mocco, Majidi, Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of COVID-19 in the young, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2009787
Pan, Chen, Lu, Lung recruitability in SARS-CoV-2 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a single-center, observational study, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202003-0527LE
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospitalization and critical illness among 4,103 patients with Covid-19 disease in New, doi:10.1101/2020.04.08.20057794
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outbreak in China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2007575
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.9809",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.9809",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Capone",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abramyan",
"given": "Shogik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rosenberg",
"given": "Joshua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeibeq",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vasudevan",
"given": "Viswanath",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samad",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gerolemou",
"given": "Louis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinelis",
"given": "Evgeny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gasperino",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Orsini",
"given": "Jose",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-08-17T17:16:32Z",
"timestamp": 1597684592000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-09T19:25:20Z",
"timestamp": 1707506720000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-10T00:14:51Z",
"timestamp": 1707524091264
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 11,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
17
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/38460-characterization-of-critically-ill-covid-19-patients-at-a-brooklyn-safety-net-hospital",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
17
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan W",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, et al.. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:1708-1720. 10.1056/nejmoa2002032",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outbreak in China",
"author": "Wu Z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) outbreak in China. JAMA. 2020, 323:1239. 10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4031",
"article-title": "Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli G",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Grasselli G, Pesenti A, Cecconi M. Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA. 2020, 323:1545-1546. 10.1001/jama.2020.4031",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2004500",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region — case series",
"author": "Bhatraju PK",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Bhatraju PK, Ghassemieh BJ, Nichols M, et al.. COVID-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region — case series. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:1-11. 10.1056/nejmoa2004500",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2010419",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City",
"author": "Goyal P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, et al.. Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:2372-2374. 10.1056/NEJMc2010419",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area",
"author": "Richardson S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M, et al.. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA. 2020, 323:2052-2059. 10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Cummings MJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Cummings MJ, Baldwin MR, Abrams D, et al.. Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020, 395:1763-1770. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Louisiana coronavirus COVID-19. (2020). Accessed. May 1, 2020: http://ldh.la.gov/coronavirus/."
},
{
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus - Michigan data 2020. (2020). Accessed. May 1, 2020: https://www.michigan.gov/coronavirus/0,9753,7-406-98163_98173---,00.html."
},
{
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "New York State Department of Health NYS COVID-19 Tracker. (2020). Accessed. May 6, 2020: https://covid19tracker.health.ny.gov/views/NYS-COVID19-Tracker/NYSDOHCOVID-19Tracker-Fatalities?%3Aembed=yes&%3Atoolb...."
},
{
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Defining Adult Overweight and Obesity 2020. (2020). Accessed. May 17, 2020: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.08.20057794",
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospitalization and critical illness among 4,103 patients with Covid-19 disease in New York City [Pre-Print}",
"author": "Petrilli C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Petrilli C, Jones S, Yang J, et al.. Factors associated with hospitalization and critical illness among 4,103 patients with Covid-19 disease in New York City [Pre-Print}. medRxiv. 2020, 10.1101/2020.04.08.20057794",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson ME",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis. 1987, 40:373-83. 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID- 19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Gautret P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Antimicrob Agents",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Gautret P, Lagier J-C, Parola P, et al.. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID- 19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020, 56:105949. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.16.20065920",
"article-title": "Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19 [Pre-Print]",
"author": "Magagnoli J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Magagnoli J, Narendran S, Pereira F, et al.. Outcomes of hydroxychloroquine usage in United States veterans hospitalized with Covid-19 [Pre-Print]. medRxiv. 2020, 10.1101/2020.04.16.20065920",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.10.20060699",
"article-title": "No evidence of clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in patients hospitalised for COVID-19 infection and requiring oxygen : results of a study using routinely collected data to emulate a target trial [Pre-Print]",
"author": "Mahévas M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Mahévas M, Tran V, Roumier M, et al.. No evidence of clinical efficacy of hydroxychloroquine in patients hospitalised for COVID-19 infection and requiring oxygen : results of a study using routinely collected data to emulate a target trial [Pre-Print]. medRxiv. 2020, 1:20. 10.1101/2020.04.10.20060699",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"article-title": "Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Geleris J",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Geleris J, Sun Y, Platt J, et al.. Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:2411-2418. 10.1056/NEJMoa2012410",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013",
"article-title": "Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Klok FA",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": "Klok FA, Kruip MJHA, van der Meer NJM, et al.. Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19. Thromb Res. 2020, 191:145-147. 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2009787",
"article-title": "Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of COVID-19 in the young",
"author": "Oxley TJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Oxley TJ, Mocco J, Majidi S, et al.. Large-vessel stroke as a presenting feature of COVID-19 in the young. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:e60. 10.1056/NEJMc2009787",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2007575",
"article-title": "Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang Y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": "Zhang Y, Xiao M, Zhang S, et al.. Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med. 2020, 382:38. 10.1056/NEJMc2007575",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE",
"article-title": "COVID-19 does not lead to a “typical” acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Gattinoni L",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Gattinoni L, Coppola S, Cressoni M, Busana M, Rossi S, Chiumello D. COVID-19 does not lead to a “typical” acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020, 201:10.1164/rccm.202003-0817LE",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202003-0527LE",
"article-title": "Lung recruitability in SARS-CoV-2 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a single-center, observational study",
"author": "Pan C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": "Pan C, Chen L, Lu C, et al.. Lung recruitability in SARS-CoV-2 associated acute respiratory distress syndrome: a single-center, observational study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020, 201:10.1164/rccm.202003-0527LE",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/38460-characterization-of-critically-ill-covid-19-patients-at-a-brooklyn-safety-net-hospital"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Characterization of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients at a Brooklyn Safety-Net Hospital",
"type": "journal-article"
}
capone
