An open-label prospective observational study of antiandrogen and non-antiandrogen early pharmacological approaches in females with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The Pre-AndroCoV Female Trial
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870, Oct 2020
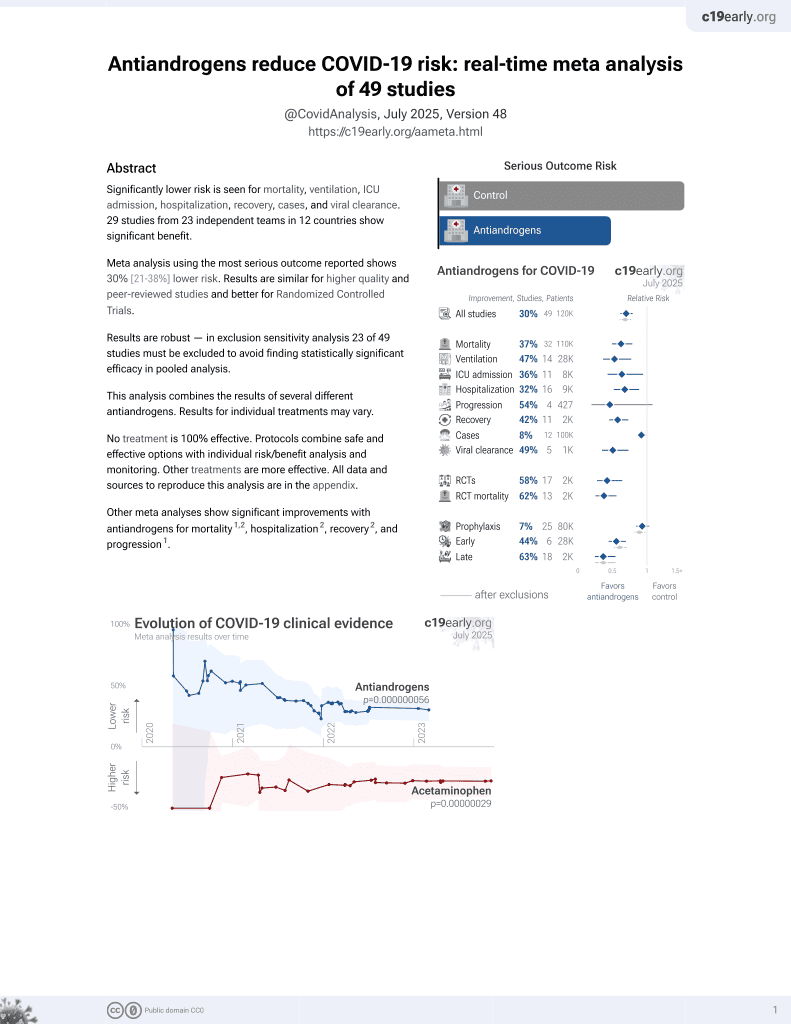
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
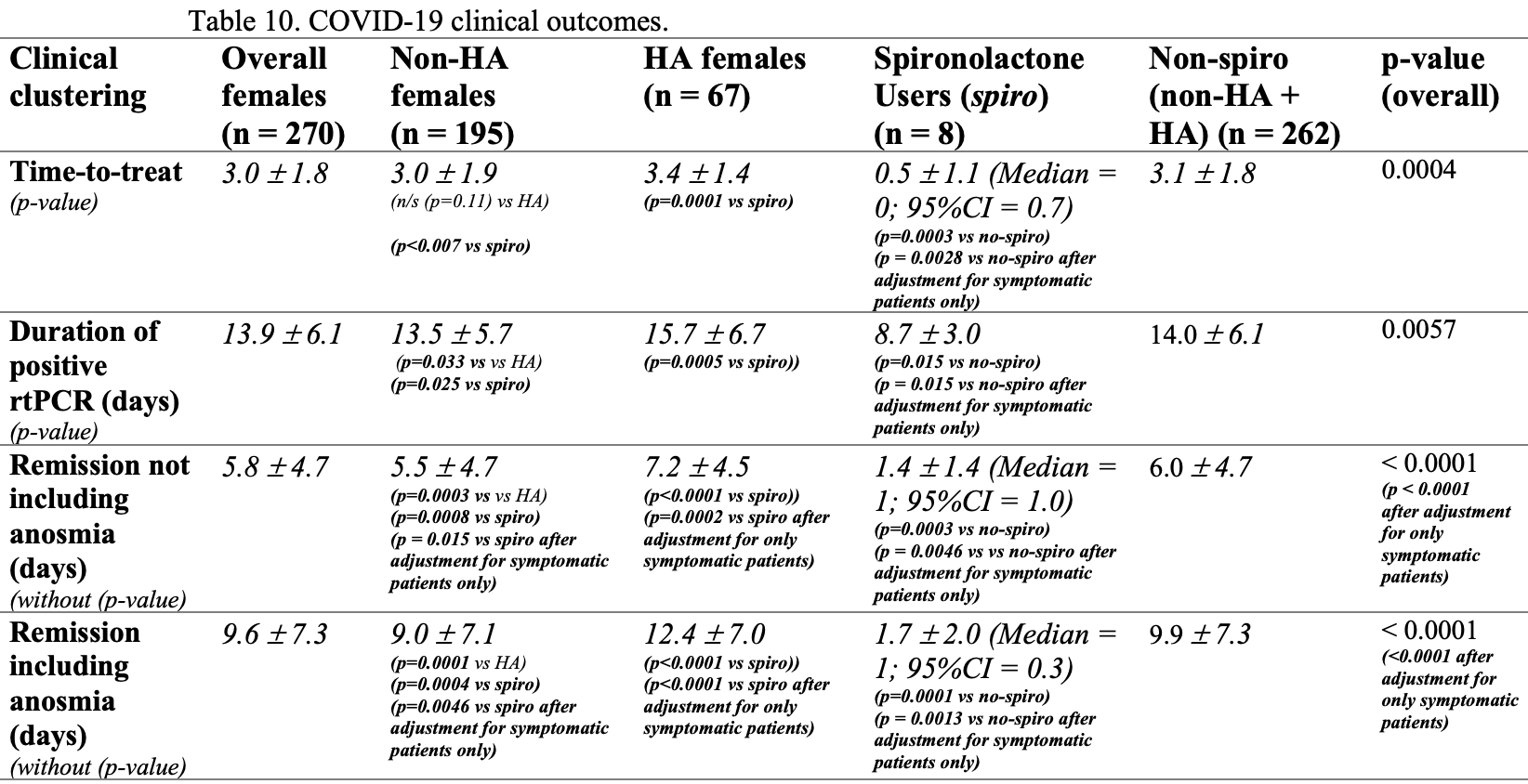
Prospective study of 270 female COVID-19 patients in Brazil, 75 with hyperandrogenism, of which 8 were on spironolactone. Results suggest that HA patients may be at increased risk, and that spironolactone use may reduce the risk compared to both other HA patients and non-HA patients. SOC included other treatments and there was no mortality or hospitalization.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
significant unadjusted differences between groups.
|
recovery time, 76.7% lower, relative time 0.23, p = 0.006, treatment 8, control 262, excluding anosmia.
|
|
recovery time, 82.8% lower, relative time 0.17, p = 0.002, treatment 8, control 262, including anosmia.
|
|
time to viral-, 37.9% lower, relative time 0.62, p = 0.02, treatment 8, control 262.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cadegiani et al., 6 Oct 2020, prospective, Brazil, preprint, 4 authors, average treatment delay 3.0 days.
An open-label prospective observational study of antiandrogen and non-antiandrogen early pharmacological approaches in females with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The Pre-AndroCoV Female Trial
doi:10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870
Background: While COVID-19 remains largely unclear and mortality continues to raise, early effective approaches prior to complications lack, as well as researches for characterization and therapeutical potential options in actual early COVID-19. Although females seem to be less affected than females, hyperandrogenic (HA) phenotype, like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), idiopathic hirsutism, congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) female androgenetic alopecia (AGA), or idiopathic HA may be at higher risk due to its inherent enhanced androgenic activity. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of any early pharmacological approach to females diagnosed with COVID-19 .
References
Cadegiani, Can spironolactone be used to prevent COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in patients with hypertension?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00136.2020
Cadegiani, Goren, Wambier, Spironolactone may provide protection from SARS-CoV-2: Targeting androgens, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112
Cadegiani, Repurposing existing drugs for COVID-19: an endocrinology perspective, BMC Endocr Disord, doi:10.1186/s12902-020-00626-0
Cadegiani, Wambier, Goren, Spironolactone: An Anti-androgenic and Anti-hypertensive Drug That May Provide Protection Against the Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19
Cavalcanti, Zampieri, Rosa, Azevedo, Veiga et al., Hydroxychloroquine with or without Azithromycin in Mild-to-Moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2019014
Clauw, Häuser, Cohen, Fitzcharles, Considering the potential for an increase in chronic pain after the COVID-19 pandemic, Pain, doi:10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001950
Goren, Mccoy, Wambier, What does androgenetic alopecia have to do with COVID-19? An insight into a potential new therapy
Goren, Vano-Galvan, Wambier, A preliminary observation: male pattern hair loss among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain -A potential clue to the role of androgens in COVID-19 severity
Goren, Wambier, Herrera, Mccoy, Vaño-Galván et al., Anti-androgens may protect against severe COVID-19 outcomes: results from a prospective cohort study of 77 hospitalized men, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16953
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hajifathalian, Kumar, Newberry, Obesity is associated with worse outcomes in COVID-19: Analysis of Early Data From New York City, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22923
Kalligeros, Shehadeh, Mylona, Association of Obesity with Disease Severity among Patients with COVID-19, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22859
Kim, Kim, Ra, Lee, Bae et al., Clinical characteristics of asymptomatic and symptomatic patients with mild COVID-19, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.040
Kragholm, Andersen, Gerds, Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) -a Danish nationwide, register-based study, Clin Infect Dis
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease
Lechien, Chiesa-Estomba, Siati, Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1
Mccoy, Wambier, Herrera, Vaño-Galván, Gioia et al., Androgen Receptor Genetic Variant Predicts COVID-19 Disease Severity: A Prospective Longitudinal Study of Hospitalized COVID-19 Male Patients, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Novak, Post COVID-19 syndrome associated with orthostatic cerebral hypoperfusion syndrome, small fiber neuropathy and benefit of immunotherapy: a case report, eNeurologicalSci, doi:10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100276
Palaiodimos, Kokkinidis, Li, Severe obesity, increasing age and male sex are independently associated with worse in-hospital outcomes, and higher in-hospital mortality, in a cohort of patients with COVID-19 in the Bronx, Metabolism
Pascarella, Strumia, Piliego, Bruno, Buono et al., COVID-19 diagnosis and management: a comprehensive review, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13091
Stokes, Zambrano, Anderson, Coronavirus Disease 2019 Case Surveillance -United States, January 22, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Tong, Wong, Zhu, Fastenberg, Tham, The Prevalence of Olfactory and Gustatory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Metaanalysis, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1177/0194599820926473
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>While COVID-19 remains largely unclear and mortality continues to raise, early effective approaches prior to complications lack, as well as researches for characterization and therapeutical potential options in actual early COVID-19. Although females seem to be less affected than females, hyperandrogenic (HA) phenotype, like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), idiopathic hirsutism, congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) female androgenetic alopecia (AGA), or idiopathic HA may be at higher risk due to its inherent enhanced androgenic activity. The present study aimed to evaluate the effects of any early pharmacological approach to females diagnosed with COVID-19 before seven days of symptoms, as well as investigate whether HA is an additional risk factor in this population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title><jats:p>Females with symptoms for less than seven days confirmed for COVID-19 through positive real-time polymerase chain reaction (rtPCR-SARS-CoV-2) were classified and divided as non-HA, HA, and HA using spironolactone (HA-spiro) groups. Patients were questioned for baseline characteristics, 23 different diseases, 44 drug classes and vaccines, 28 different symptoms, and eight different parameters to measure COVID-19 related clinical outcomes. Treatment was then provided, including azithromycin 500mg/day for five days in all cases, associated with hydroxychloroquine 400mg/day for five days, nitazoxanide 500mg twice a day for six days, or ivermectin 0.2mg/kg/day por three days, and optionally spironolactone 100mg twice a day until cure. Patients were assessed for COVID-19 clinical course, clinical and viral duration, and disease progression.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In total, 270 females were enrolled, including 195, 67, and eight in non-HA, HA, and HA-spiro groups, respectively. Prevailing symptoms were anosmia (71.1%), ageusia (67.0%), headache (48.1%), myalgia (37.4%), dry cough (36.3%), nasal congestion or rhinorrhea (34.1%), fatigue (33.3%), weakness (29.5%), hyporexia (27.8%), thoracic pain (24.8%), diarrhea (24.1%) and dizziness (21.5%). Earliest symptoms (days) were dizziness (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>0 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>2 day), abdominal pain</jats:italic> (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>1 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>3);</jats:italic> conjunctival hyperemia (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>1 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5)</jats:italic>, nasal congestion or rhinorrhea (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>2 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5)</jats:italic>, headache (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>2 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5), dry cough</jats:italic> (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>2 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5)</jats:italic>, myalgia (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>2 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>4)</jats:italic>, nauseas (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>3 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5)</jats:italic> and weakness (<jats:italic>1</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>3 ± 0</jats:italic>.<jats:italic>5)</jats:italic>. Time-to-treat, positive rtPCR, and duration of symptoms with and without anosmia and ageusia were significantly lower in HA-spiro than non-HA, HA, and overall non-users. Time-to-treat was similar while all duration of symptoms and positive rtPCR-SARS-CoV-2 were significantly shorter in non-HA than HA. Spironolactone users were more likely to be asymptomatic than non-users during COVID-19. Fewer non-HA than HA females were affected by anosmia, ageusia, dry cough, fatigue, weakness and hyporexia. Ageusia, weakness and myalgia lasted shorter in non-HA than HA. None of the patients needed hospitalization or any other COVID-19 complication.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>A sensitive, early detection of COVID-19 followed by a pharmaceutical approach with different drug combinations yielded irrefutable differences compared to sex-, age-, body mass index (BMI)-, and disease-matched non-treated controls in terms of clinical outcomes, ethically disallowing placebo-control randomized clinical trials in the early stage of COVID-19 due to the marked improvements. HA females presented more severe and prolonged clinical manifestations, although none progressed to worse outcomes. Spironolactone mitigated the additional risks due to HA.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
6
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2699-4344",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cadegiani",
"given": "Flavio A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goren",
"given": "Andy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4636-4489",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wambier",
"given": "Carlos G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "McCoy",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-06T17:55:16Z",
"timestamp": 1602006916000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-19T22:40:23Z",
"timestamp": 1603147223000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-08T12:23:36Z",
"timestamp": 1709900616169
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
6
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
6
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.1",
"unstructured": "Guan W , Ni Z , Hu Y , et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 2020; Feb 28."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22923",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22859",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154262",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2019014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.5"
},
{
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.6",
"unstructured": "Zhou F , Yu T , Du R , et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 11] [published correction appears in Lancet. 2020 Mar 12;:]. Lancet. 2020;S0140-6736(20)30566-3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-0504",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.7",
"unstructured": "Lauer SA , Grantz KH , Bi Q , et al. The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 10]. Ann Intern Med. 2020;10. 7326/M20-0504."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.9"
},
{
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.10",
"unstructured": "https://www.who.int/teams/health-care-readiness-clinical-unit/covid-19/data-platform (Last accessed September 29th, 2020)"
},
{
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.11",
"unstructured": "https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html (Last accessed September 29th, 2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6924e2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12902-020-00626-0",
"article-title": "Repurposing existing drugs for COVID-19: an endocrinology perspective",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "BMC Endocr Disord",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.13",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13091",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jocd.13443",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.15",
"unstructured": "Goren A , Vano-Galvan S , Wambier CG , et al. A preliminary observation: male pattern hair loss among hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Spain - A potential clue to the role of androgens in COVID-19 severity [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 16]. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2020;10. 1111/jocd.13443."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13365",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.16",
"unstructured": "Goren A , McCoy J , Wambier CG , et al. What does androgenetic alopecia have to do with COVID-19? An insight into a potential new therapy [published online ahead of print, 2020 Apr 1]. Dermatol Ther. 2020;e13365."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.16956",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.17",
"unstructured": "McCoy J , Wambier CG , Herrera S , Vaño-Galván S , Gioia F , Comeche B , Ron R , Serrano-Villar S , Iwasiow RM , Tayeb MA , Cadegiani FA , Mesinkovska NA , Shapiro J , Sinclair R , Goren A. Androgen Receptor Genetic Variant Predicts COVID-19 Disease Severity: A Prospective Longitudinal Study of Hospitalized COVID-19 Male Patients. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Sep 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa924",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.18",
"unstructured": "Kragholm K , Andersen MP , Gerds TA , et al. Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) - a Danish nationwide, register-based study. Clin Infect Dis 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jdv.16953",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00136.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00453",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.22"
},
{
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.23",
"unstructured": "https://www.uptodate.com/contents/coronavirus-disease-2019-covid-19-clinicalfeatures?topicRef=126981&source=see_link (Last accessed September 29th, 2020)"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.040",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0194599820926473",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100276",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001950",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020101915400542000_2020.10.05.20206870v1.28"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.10.05.20206870"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "An open-label prospective observational study of antiandrogen and non-antiandrogen early pharmacological approaches in females with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The Pre-AndroCoV Female Trial",
"type": "posted-content"
}