The Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Generating Lozenges on Outcome in Newly Diagnosed COVID-19 Patients of African American and Hispanic Origin
et al., The American Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021, NCT04601077, Jun 2023
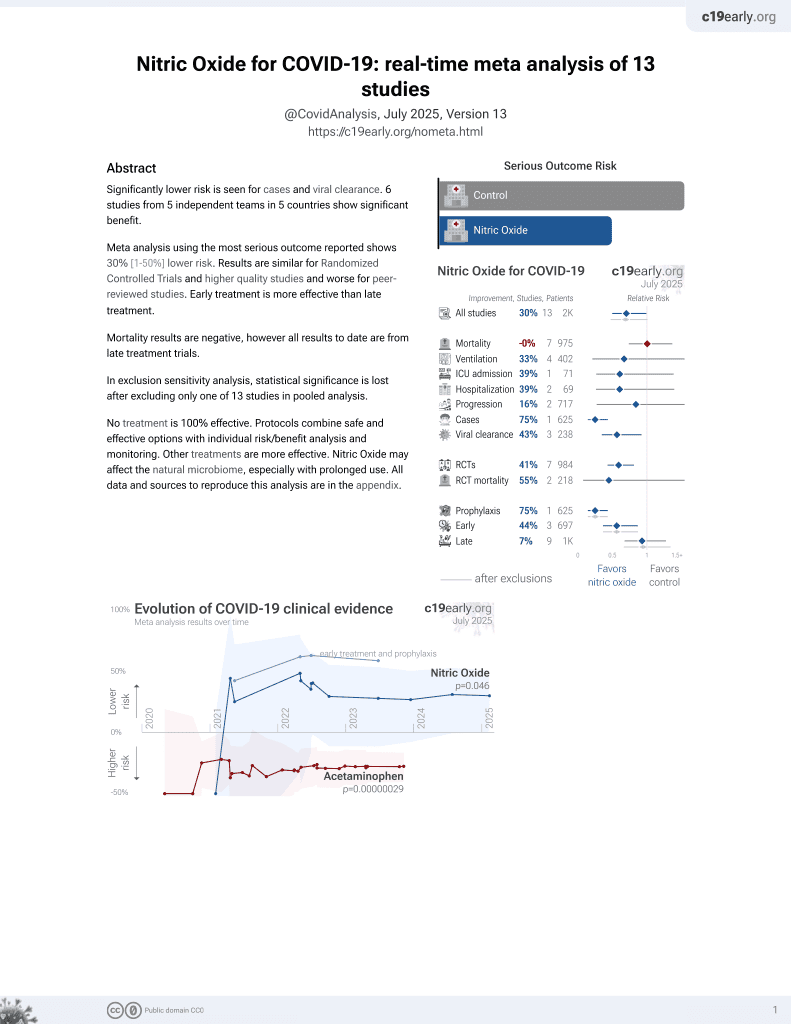
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
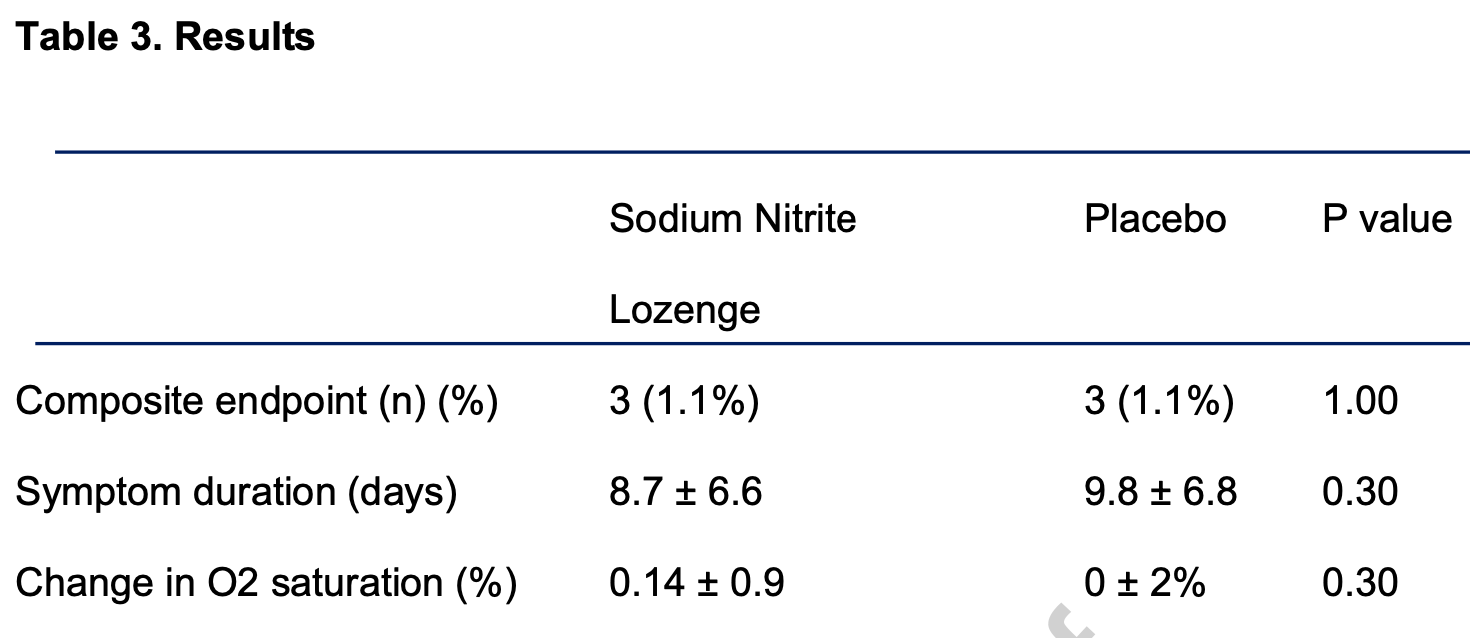
RCT 524 outpatients in the USA for a nitric oxide generating lozenge, showing no significant difference in combined hospitalization, ICU admission, intubation, dialysis, and death. There were only 3 events in each arm, all occuring in 2020, with zero events in 2021 or 2022. Recovery was 11% faster with treatment, without statistical significance. Authors note that a higher dose may have been more effective. Trials showing greater efficacy have used a nasal spray.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of progression, 0.8% higher, RR 1.01, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 261 (1.1%), control 3 of 263 (1.1%), combined hospitalization, ICU admission, intubation, dialysis, and death.
|
|
recovery time, 11.2% lower, relative time 0.89, p = 0.30, treatment 261, control 263.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bryan et al., 24 Jun 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, study period 1 November, 2020 - 30 November, 2022, trial NCT04601077 (history).
Contact: johnsomberg@comcast.net.
The Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Generating Lozenges on Outcome in Newly Diagnosed COVID-19 Patients of African American and Hispanic Origin
The American Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Å. Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol
Akerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
Allen, Stamler, Piantadosi, Hemoglobin, nitric oxide and molecular mechanisms of hypoxic vasodilation, Trends Mol Med
Alqahtani, Aldhahir, Ghamdi, Inhaled Nitric Oxide for Clinical Management of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Bagate, Tuffet, Masi, Perier, Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Intensive Care
Benedetto, Romano, Baca, Inhaled nitric oxide in cardiac surgery: Evidence or tradition?, Nitric Oxide
Bryan, Tribble, Angelov, Oral Microbiome and Nitric Oxide: the Missing Link in the Management of Blood Pressure, Curr Hypertens Rep
Carnethon, Pu, Howard, Cardiovascular Health in African Americans: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association
Covid, Tracker, None
Covid, Tracker, None
Dellinger, Zimmerman, Taylor, Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: results of a randomized phase II trial. Inhaled nitric oxide in ARDS study group, Crit Care Med
Ferrari, Santini, Protti, Inhaled nitric oxide in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19, J Crit Care
Furchgott, Zawadzki, The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine, Nature
Garfield, Mcfadyen, Briar, Potential for personalised application of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 pneumonia, Br J Anaesth
Gebistorf, Karam, Wetterslev, Afshari, Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Higgins, Berry, Lorenzi, Murthy, Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP Randomized Clinical Trial
Ignarro, Inhaled NO and COVID-19, Br J Pharmacol
Inomax, gas, for inhalation. FDA approved label
Lotz, Muellenbach, Meybohm, Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19-induced ARDS -Is it worthwhile?, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand
Marletta, Yoon, Iyengar, Leaf, Wishnok, Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate, Biochemistry
Mcknight, Smith, Drummond, Duncan, Golden et al., Chemical synthesis of nitric oxide in the stomach from dietary nitrate in humans, Gut
Moncada, Higgs, The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology, Br J Pharmacol
Radomski, Palmer, Moncada, The anti-aggregating properties of vascular endothelium: interactions between prostacyclin and nitric oxide, Br J Pharmacol
Schmid, Bürki, Engel, Schmidlin, Tornic et al., Inhaled nitric oxide versus intravenous vasodilators in severe pulmonary hypertension after cardiac surgery, Anesth Analg
Shi, Qin, Shen, Association of Cardiac Injury With Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, JAMA Cardiol
Sulaiman, Korayem, Altebainawi, Evaluation of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment for moderate-to-severe ARDS in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study, Crit Care
Vives, Gascó, Pla, Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Severe Pulmonary Hypertension and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Secondary to COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report, Am J Case Rep
Welker, Huang, Gil, Ramakrishna, 2021 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Update, With Coronavirus Disease, J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth
Witek, Lakhkar, Nitric Oxide
Yancy, COVID-19 and African Americans, JAMA
Zhang, Hess, Qian, Hemoglobin βCys93 is essential for cardiovascular function and integrated response to hypoxia, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021",
"ISSN": [
"0002-9343"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021",
"alternative-id": [
"S0002934323003911"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Generating Lozenges on Outcome in Newly Diagnosed COVID-19 Patients of African American and Hispanic Origin"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The American Journal of Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bryan",
"given": "Nathan S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Molnar",
"given": "Janos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Somberg",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The American Journal of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "The American Journal of Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"amjmed.com",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T13:52:23Z",
"timestamp": 1687614743000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T13:52:44Z",
"timestamp": 1687614764000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-25T04:35:59Z",
"timestamp": 1687667759078
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0002934323003911?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0002934323003911?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0001",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID Data Tracker. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#datatracker-home Last acessed: 01 02 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950",
"article-title": "Association of Cardiac Injury With Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "802",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0002",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0003",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID Data Tracker./Underlying Medical Conditions. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#underlying-med-conditions Last acessed: 01 02 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.23257",
"article-title": "Long-term (180-Day) Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0004",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Witek",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0005",
"series-title": "StatPearls [Internet]",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0006",
"unstructured": "INOMAX (nitric oxide) gas, for inhalation. FDA approved label. Available at: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2015/020845s016s017lbl.pdf Last acessed: 01 02 2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.jvca.2021.02.053",
"article-title": "2021 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Update, With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Focus",
"author": "Welker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1188",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0007",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199801000-00011",
"article-title": "Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: results of a randomized phase II trial. Inhaled nitric oxide in ARDS study group",
"author": "Dellinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0008",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults",
"author": "Gebistorf",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0009",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2015.06.002",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide in cardiac surgery: Evidence or tradition?",
"author": "Benedetto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0010",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide versus intravenous vasodilators in severe pulmonary hypertension after cardiac surgery",
"author": "Schmid",
"first-page": "1108",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Anesth Analg",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0011",
"volume": "89",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-022-04158-y",
"article-title": "Evaluation of inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) treatment for moderate-to-severe ARDS in critically ill patients with COVID-19: a multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Al Sulaiman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "304",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0012",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00769-2",
"article-title": "A. Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Bagate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aas.13757",
"article-title": "Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19-induced ARDS - Is it worthwhile?",
"author": "Lotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "629",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Acta Anaesthesiol Scand",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0014",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.006",
"article-title": "Potential for personalised application of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 pneumonia",
"author": "Garfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e72",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Br J Anaesth",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0015",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph191912803",
"article-title": "Inhaled Nitric Oxide for Clinical Management of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Alqahtani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12803",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0016",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12659/AJCR.937147",
"article-title": "Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Acute Severe Pulmonary Hypertension and Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Secondary to COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Case Report",
"author": "Vives",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Case Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0017",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0706458",
"article-title": "The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology",
"author": "Moncada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S193",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0018",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15085",
"article-title": "Inhaled NO and COVID-19",
"author": "Ignarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3848",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0019",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.08.007",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0020",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1502285112",
"article-title": "Hemoglobin βCys93 is essential for cardiovascular function and integrated response to hypoxia",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6425",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0021",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected",
"author": "Akerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0022",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11367.x",
"article-title": "The anti-aggregating properties of vascular endothelium: interactions between prostacyclin and nitric oxide",
"author": "Radomski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0023",
"volume": "92",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6548",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and African Americans",
"author": "Yancy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1891",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0024",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIR.0000000000000534",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular Health in African Americans: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association",
"author": "Carnethon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e393",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0025",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0026",
"unstructured": "CDC COVID Data Tracker/COVID-19 Weekly Cases and Deaths per 100,000 Population by Age, Race/Ethnicity, and Sex. Available at: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#demographicsovertime Last accessed 01/02/2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"article-title": "Å. Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro",
"author": "Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0027",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmed.2009.08.002",
"article-title": "Hemoglobin, nitric oxide and molecular mechanisms of hypoxic vasodilation",
"author": "Allen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Trends Mol Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0028",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/288373a0",
"article-title": "The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine",
"author": "Furchgott",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"issue": "5789",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0029",
"volume": "288",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi00424a003",
"article-title": "Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate",
"author": "Marletta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8706",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "Biochemistry",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0030",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gut.40.2.211",
"article-title": "Chemical synthesis of nitric oxide in the stomach from dietary nitrate in humans",
"author": "McKnight",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0031",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11906-017-0725-2",
"article-title": "Oral Microbiome and Nitric Oxide: the Missing Link in the Management of Blood Pressure",
"author": "Bryan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Curr Hypertens Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2023.05.021_bib0032",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2017"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0002934323003911"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Generating Lozenges on Outcome in Newly Diagnosed COVID-19 Patients of African American and Hispanic Origin",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}