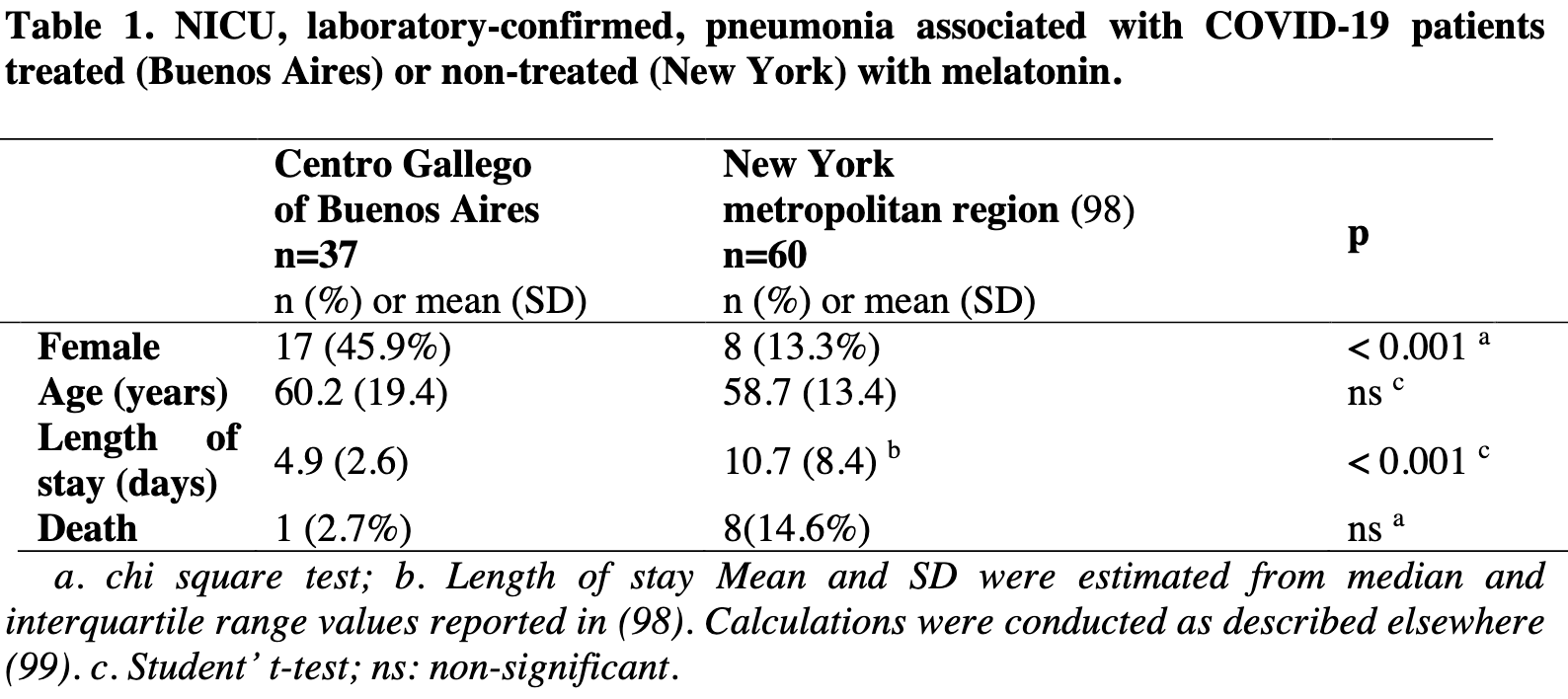
Efficacy of melatonin in non-intensive care unit patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and sleep dysregulation
et al., Melatonin Research, doi:10.32794/mr11250089, Dec 2020
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of melatonin for COVID-19 along with preliminary data suggesting efficacy of melatonin for COVID-19 pneumonia patients.
Brusco et al., 23 Dec 2020, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.32794/mr11250089",
"ISSN": [
"2641-0281"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.32794/mr11250089",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The association of sleep disruption with a higher vulnerability to
\nCOVID-19 infection is a subject of major clinical importance. In patients with
\npneumonia associated with COVID-19 admitted to non-intensive care unit (NICU) several
\nfactors, like the disrupting influence of respiratory distress, medication, greater
\nstress due to social isolation, and lack of appropriate exposure to environmental
\nlight can be instrumental to disrupt sleep/wake cycle. The
\ntherapeutic potential of melatonin to counteract the consequences of COVID-19
\ninfection has been advocated. Because of its wide-ranging effects as an
\nantioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory compound, melatonin could
\nbe unique in impairing the consequences of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Melatonin is
\nalso an effective chronobiotic agent to reverse the circadian disruption of social
\nisolation and to control delirium in severely affected patients. Properly
\nadministered, melatonin may restore the optimal circadian pattern of the
\nsleep-wake cycle and improve clinical condition in pneumonia associated with COVID-19
\npatients. The present review article discusses the importance of maintaining
\nnormal sleep and circadian rhythmicity in NICU patients and provides
\npreliminary data suggesting the efficacy of melatonin (9 mg/day) to reduce
\nlength of stay of pneumonia patients associated with COVID-19 in NICU. </jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brusco",
"given": "Luis I.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruz",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cangas",
"given": "Alicia V",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rojas",
"given": "Carmen González",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vigo",
"given": "Daniel E",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cardinali",
"given": "Daniel Pedro",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Melatonin Research",
"container-title-short": "Melatonin Res.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-04T02:01:11Z",
"timestamp": 1609725671000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-04T02:01:34Z",
"timestamp": 1609725694000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-19T08:19:23Z",
"timestamp": 1681892363197
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
3
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"member": "18079",
"original-title": [],
"page": "173-188",
"prefix": "10.32794",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "ST Bio-life",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.melatonin-research.net/index.php/MR/article/view/125"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of melatonin in non-intensive care unit patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and sleep dysregulation",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}