Effect of calcifediol supplementation as add-on therapy on the immune repertoire in recipients of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine: A prospective open-label, placebo-controlled, clinical trial
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004, CTRI/2021/08/035709, Mar 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
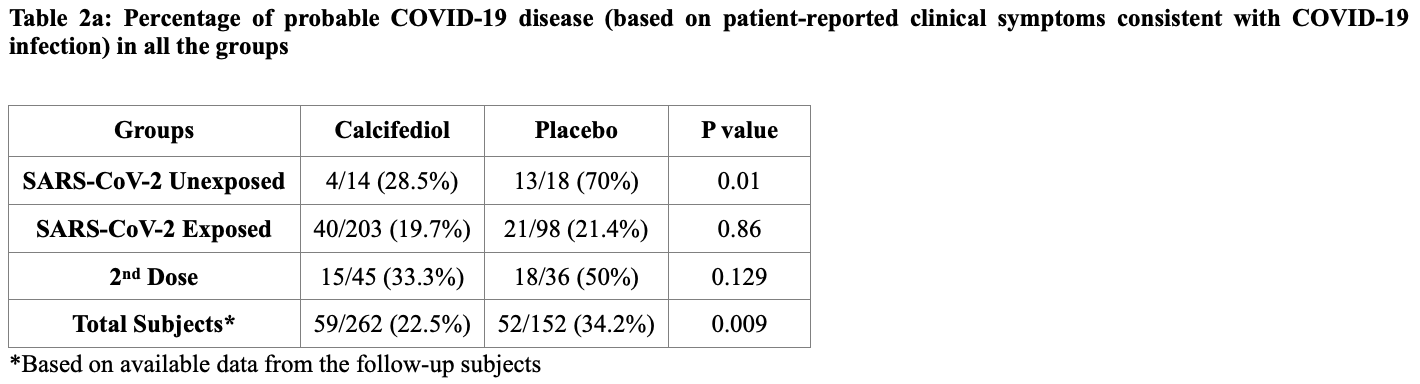
Prospective study of 580 ChAdOx1 recipients, 262 treated with calcifediol (patient choice), showing lower cases with treatment. Supplementation did not significantly affect antibody levels following ChAdOx1 receipt. Calcifediol patients were older (31 vs. 26 in the exposed subgroup containing most patients). 50μg/day calcifediol.
This is the 112th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of symptomatic case, 34.2% lower, RR 0.66, p = 0.01, treatment 59 of 262 (22.5%), control 52 of 152 (34.2%), NNT 8.6.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bhat et al., 6 Mar 2023, prospective, placebo-controlled, India, peer-reviewed, 13 authors, dosage calcifediol 50μg days 1-180, trial CTRI/2021/08/035709.
Abstract: Journal of Infection xxx (xxxx) xxx–xxx
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Journal of Infection
journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jinf
Letter to the Editor
Effect of calcifediol supplementation as add-on therapy on the
immune repertoire in recipients of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19
vaccine: A prospective open-label, placebo-controlled, clinical
trial
Dear Editor,
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused formidable
global health crisis, and multiple vaccination programs have been
rolled out to curb the spread of the pandemic. Genetic disorders like
primary immunodeficiency diseases severely compromise the gen
eration of protective immunity following vaccinations. The spectrum
also includes those genetic disorders that have a lesser impact on
immunological memory such as Down Syndrome (DS). In a recent
study, Valentini et al.1 confirmed that the serological efficacy of
COVID-19 vaccination is least affected by DS. The authors included a
substantial number of subjects and further observed that the older
subjects exhibit lower anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers 6 months
after vaccination. Earlier, Yarci-Carrion et al.2 had also reported that
DS and non-DS subjects develop similar anti-SARS-CoV-2 titers after
the third dose of vaccine that decline with age. However, the same
group demonstrated that DS subjects develop milder T cell responses
to the standard 2-dose vaccine.3 Valentini et al.1 further denote that
the factors modifying immune responses to vaccination in such
disorders are less explored. This may include nutritional deficiencies
like vitamin D [25(OH)D]. Indeed, reports have shown that hypovi
taminosis D is quite frequent in subjects with DS.4
It is also known that individuals with low 25(OH)D levels have a
higher risk of acquiring severe COVID-19 and stimulation of vitamin
D receptor can reduce COVID-19-associated hospitalization and
mortality.5,6 However, studies on vitamin D supplementation in
COVID-19 vaccination have yielded conflicting results with some
reporting improvement, while others observing lack of association
between 25(OH)D status and antibody titers post vaccination.7,8
Most of these studies, however, did not assess cellular immune re
sponses, which are more likely to be influenced by vitamin D. Cal
cifediol [25(OH)D3], the immediate precursor of 1,25(OH)2D3 leads
to a faster achievement of desired levels and biodistribution of cir
culating 1,25(OH)2D3 as compared to cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).9
There are reports on favorable outcomes of calcifediol supple
mentation in COVID-19,10 but there are no data on its utility in im
proving efficacy of COVID-19 vaccines. Therefore, we evaluated the
efficacy of calcifediol supplementation on cell-mediated immune
responses besides anti-SARS-CoV-2 titers post COVID-19 vaccina
tion. We carried an open-label, placebo-controlled clinical trial to
assess the impact of calcifediol supplementation on the efficacy of
ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine in terms of, protection from break
through infection and COVID-19 disease, anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody
titers, SARS-CoV-2 specific lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine
secretion.
Herein 580 adult subjects receiving ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine
were recruited at the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education
and Research (PGIMER), Chandigarh, India. The subjects received
either calcifediol (50 µg/day) or placebo, orally for 6 months
(Supplementary Fig. 1, Supplementary Table 1) and divided in 3
groups [SARS-CoV-2 unexposed,..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4453"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004",
"alternative-id": [
"S0163445323001317"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of calcifediol supplementation as add-on therapy on the immune repertoire in recipients of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine: A prospective open-label, placebo-controlled, clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The British Infection Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhat",
"given": "Swati",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Das",
"given": "Liza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maheshwari",
"given": "Deep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badal",
"given": "Darshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sarkar",
"given": "Roman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Madhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandav",
"given": "Surinder Singh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padhi",
"given": "Bijaya Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bhadada",
"given": "Sanjay Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holick",
"given": "Michael F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dutta",
"given": "Pinaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sachdeva",
"given": "Naresh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marwaha",
"given": "Raman Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"journalofinfection.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-06T20:58:46Z",
"timestamp": 1678136326000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-12T12:02:53Z",
"timestamp": 1678622573000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-13T04:33:29Z",
"timestamp": 1678682009291
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001317?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0163445323001317?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Factor associated with SARS-CoV-2 vaccination serological efficacy in adolescents and adults with Down syndrome: data from an international, collaborative initiative of the Trisomy 21 Research Society",
"author": "Valentini",
"first-page": "00090",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib1",
"volume": "4453",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.11.014",
"article-title": "Effect of a SARS-CoV-2 booster vaccine dose on the immune response of adults with Down syndrome",
"author": "Yarci-Carrión",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib2",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac590",
"article-title": "Development of an effective immune response in adults with down syndrome after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination",
"author": "Esparcia-Pinedo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e155",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib3",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2015/896758",
"article-title": "Determinants of vitamin D levels in children and adolescents with Down syndrome",
"author": "Stagi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "896758",
"journal-title": "Int J Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib4",
"volume": "2015",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14245329",
"article-title": "The impact of serum levels of vitamin D3 and its metabolites on the prognosis and disease severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Fabbri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5329",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib5",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor stimulation to reduce acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in patients with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections: revised Ms SBMB 2020_166",
"author": "Quesada-Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib6",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14183821",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation does not influence SARS-CoV-2 vaccine efficacy or immunogenicity: sub-studies nested within the CORONAVIT randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3821",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib7",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.retram.2022.103344",
"article-title": "Age and vitamin D affect the magnitude of the antibody response to the first dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine",
"author": "Piec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Res Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib8",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbmr.4387",
"article-title": "Calcifediol is superior to cholecalciferol in improving vitamin D status in postmenopausal women: a randomized trial",
"author": "Pérez-Castrillón",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1967",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Bone Miner Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib9",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2022.111899",
"article-title": "REsCue trial: randomized controlled clinical trial with extended-release calcifediol in symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients",
"author": "Bishop",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2023.03.004_bib10",
"volume": "107",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 10,
"references-count": 10,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0163445323001317"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of calcifediol supplementation as add-on therapy on the immune repertoire in recipients of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine: A prospective open-label, placebo-controlled, clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
