COPD patients with high blood eosinophil counts exhibit a lower rate of omicron infection and milder post‐infection symptoms
et al., The Clinical Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1111/crj.13790, May 2024
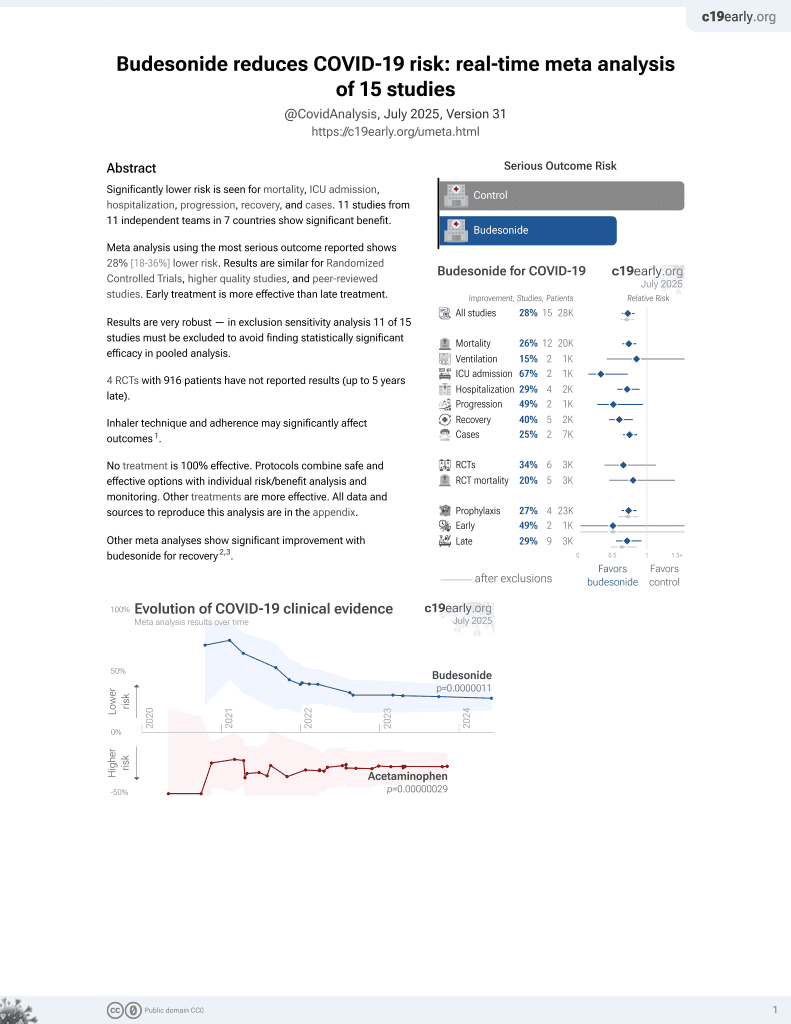
Budesonide for COVID-19
27th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2021, now with p = 0.0000042 from 14 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
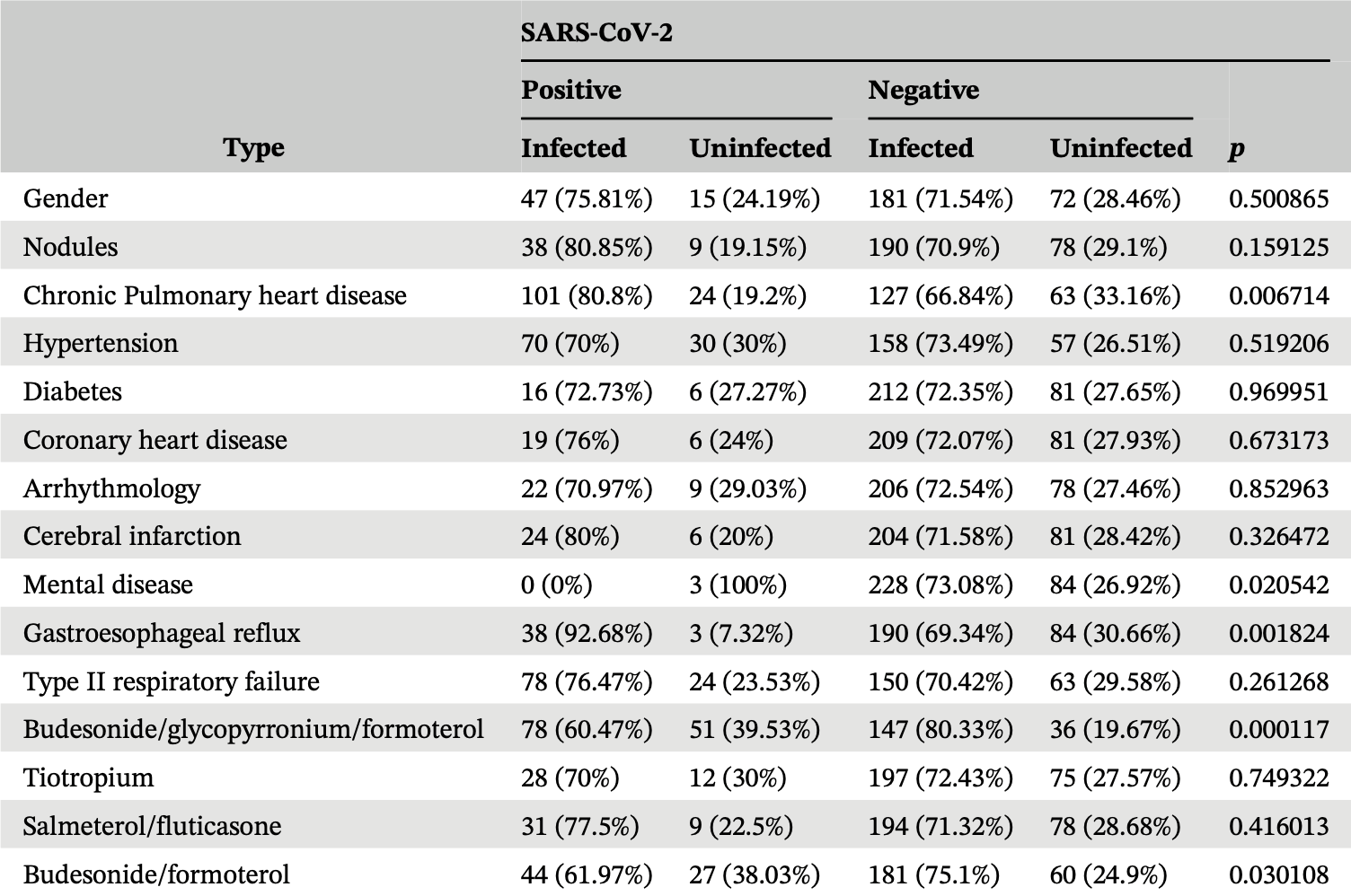
Retrospective 315 COPD patients in China showing significantly lower COVID-19 cases with budesonide/formoterol or budesonide/glycopyrronium/formoterol use. Note that Table 4 includes only infected patients, we show the COVID-19 hospitalization risk among all patients with known medication status. Minimal details are provided for the groups on these medications.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with minimal group details.
|
risk of hospitalization, 31.4% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.18, treatment 71, control 241, BF and BGF.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 50.8% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.01, treatment 10 of 71 (14.1%), control 69 of 241 (28.6%), NNT 6.9, BF.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 13.1% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.51, treatment 30 of 129 (23.3%), control 49 of 183 (26.8%), NNT 28, BF.
|
|
risk of case, 24.4% lower, RR 0.76, p < 0.001, treatment 71, control 241, BF and BGF.
|
|
risk of case, 17.5% lower, RR 0.83, p = 0.04, treatment 44 of 71 (62.0%), control 181 of 241 (75.1%), NNT 7.6, BF.
|
|
risk of case, 28.8% lower, RR 0.71, p < 0.001, treatment 78 of 129 (60.5%), control 147 of 173 (85.0%), NNT 4.1, BGF.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bai et al., 30 May 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with formoterol/glycopyrronium) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Contact: doctorliu69@126.com, wry0526@163.com.
COPD patients with high blood eosinophil counts exhibit a lower rate of omicron infection and milder post‐infection symptoms
The Clinical Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1111/crj.13790
Background: The emergence of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and its subsequent Omicron variant has raised concerns for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients due to the potential risk of disruptions to healthcare services and unknown comorbidities between COPD and Omicron. Method: In this study, we conducted a follow-up investigation of 315 COPD patients during the Omicron outbreak at Shanxi Bethune Hospital to understand the impact of the pandemic on this vulnerable population. Among all patients, 228 were infected with Omicron, of which 82 needed hospitalizations. Result: We found that COPD patients with high blood eosinophil (EOS) counts exhibited lower susceptibility to Omicron infection and were more likely to have milder symptoms that did not require hospitalization. Conversely, patients with low EOS counts showed higher rates of infection and hospitalization. Moreover, EOS count was positively correlated with T lymphocyte counts in hospitalized patients after Omicron infection, suggesting potential associations between EOS and specific immune responses in COPD patients during viral infections. Correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between EOS count and lymphocyte and T-cells, and a negative correlation between EOS count and age, neutrophil, and C-reactive protein.
Conclusion: Overall, our study contributes to the knowledge of COPD management during the COVID-19 Omicron outbreak and emphasizes the importance of considering individual immune profiles to improve care for COPD patients in the face of the ongoing global health crisis.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Ruiying Wang had the idea for and designed the study. Xiansheng Liu and Shuang Wei supervised the study. Xueli Bai, Yanan Niu, Zhifan Zhu, Min Xu, and Hu Liu did the statistical analysis. All authors contributed to acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data. Xueli Bai wrote the draft report. All authors revised the report and approved the final version before submission.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT The authors declare that there is no conflict of commercial interest related to this paper.
ETHICS STATEMENT The present study was approved by the ethics committee of Shanxi Bethune Hospital ([2022] S022), and all participants provided written informed consent.
ORCID Ruiying Wang https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6224-8480
References
Bafadhel, Mckenna, Terry, Blood eosinophils to direct corticosteroid treatment of exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized placebocontrolled trial, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:info:doi/10.1164/rccm.201108-1553OC
Barnes, Sharma, Lettis, Calverley, Blood eosinophils as a marker of response to inhaled corticosteroids in COPD, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/13993003.01370-2015
Beltramo, Cottenet, Mariet, Chronic respiratory diseases are predictors of severe outcome in COVID-19 hospitalised patients: a nationwide study, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/13993003.04474-2020
Benson, Hartl, Barnes, Galwey, Van Dyke et al., Blood eosinophil counts in the general population and airways disease: a comprehensive review and meta-analysis, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/13993003.04590-2020
Cosio, Shafiek, Toledo-Pons, Characterization of COPD admissions during the first COVID-19 outbreak, Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, doi:info:doi/10.2147/COPD.S312493
D'armiento, Scharf, Roth, Eosinophil and T cell markers predict functional decline in COPD patients, Respir Res, doi:info:doi/10.1186/1465-9921-10-113
David, Bafadhel, Koenderman, De Soyza, Eosinophilic inflammation in COPD: from an inflammatory marker to a treatable trait, Thorax, doi:info:doi/10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-215167
Decramer, Janssens, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and comorbidities, Lancet Respir Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2213-2600(12)70060-7
Divo, Cote, De Torres, None, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:info:doi/10.1164/rccm.201201-0034OC
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, COVID-19 and comorbidities: deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health, doi:info:doi/10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Fan, Li, Zhang, Wan, Zhang et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: recent progress and future perspectives, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:info:doi/10.1038/s41392-022-00997-x
Faner, Cruz, Opez-Giraldo, Agusti, Network medicine, multimorbidity and the lung in the elderly, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/09031936.00078714
Filip, Puscaselu, Anchidin-Norocel, Dimian, Savage, Global challenges to public health care systems during the COVID-19 pandemic: a review of pandemic measures and problems, J Pers Med, doi:info:doi/10.3390/jpm12081295
Gong, Sun, Stability of blood eosinophils in COPD with multiple acute exacerbations within 1 year and its relationship with prognosis, Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, doi:info:doi/10.2147/COPD.S392660
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Halpin, Faner, Sibila, Badia, Agusti, Do chronic respiratory diseases or their treatment affect the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Lancet Respir Med, doi:info:doi/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30167-3
Halpin, Vogelmeier, Agusti, COVID-19 and COPD: lessons beyond the pandemic, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:info:doi/10.1152/ajplung.00386.2021
Hansen, Moeller, Backer, Severe outcomes of COVID-19 among patients with COPD and asthma, ERJ Open Res, doi:info:doi/10.1183/23120541.00594-2020
Hogg, Chu, Utokaparch, The nature of smallairway obstruction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, N Engl J Med, doi:info:doi/10.1056/NEJMoa032158
Jayakrishnan, Nair, COVID-19, obstructive airway disease and eosinophils: a complex interplay, Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J, doi:info:doi/10.18295/squmj.1.2022.001
Leung, Niikura, Cwt, Sin, COVID-19 and COPD, Eur Respir J, doi:info:doi/10.1183/13993003.02108-2020
Mahase, Covid-19: increased demand for steroid inhalers causes "distressing" shortages, BMJ
Negewo, Gibson, Mcdonald, COPD and its comorbidities: impact, measurement and mechanisms, Respirology, doi:info:doi/10.1111/resp.12642
Oh, Lee, Hong, Blood eosinophil count as a prognostic biomarker in COPD, Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, doi:info:doi/10.2147/COPD.S179734
Organisation, Chronic Respiratory Diseases, Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Papaporfyriou, Bakakos, Hillas, Papaioannou, Loukides, Blood eosinophils in COPD: friend or foe?, Expert Rev Respir Med, doi:info:doi/10.1080/17476348.2021.2011219
Sullivan, Simonian, Falta, Oligoclonal CD4+ T cells in the lungs of patients with severe emphysema, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:info:doi/10.1164/rccm.200410-1332OC
Turato, Semenzato, Bazzan, Blood eosinophilia neither reflects tissue eosinophils nor worsens clinical outcomes in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:info:doi/10.1164/rccm.201708-1684LE
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/crj.13790",
"ISSN": [
"1752-6981",
"1752-699X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/crj.13790",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The emergence of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) and its subsequent Omicron variant has raised concerns for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients due to the potential risk of disruptions to healthcare services and unknown comorbidities between COPD and Omicron.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Method</jats:title><jats:p>In this study, we conducted a follow‐up investigation of 315 COPD patients during the Omicron outbreak at Shanxi Bethune Hospital to understand the impact of the pandemic on this vulnerable population. Among all patients, 228 were infected with Omicron, of which 82 needed hospitalizations.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Result</jats:title><jats:p>We found that COPD patients with high blood eosinophil (EOS) counts exhibited lower susceptibility to Omicron infection and were more likely to have milder symptoms that did not require hospitalization. Conversely, patients with low EOS counts showed higher rates of infection and hospitalization. Moreover, EOS count was positively correlated with T lymphocyte counts in hospitalized patients after Omicron infection, suggesting potential associations between EOS and specific immune responses in COPD patients during viral infections. Correlation analysis revealed a positive correlation between EOS count and lymphocyte and T‐cells, and a negative correlation between EOS count and age, neutrophil, and C‐reactive protein.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Overall, our study contributes to the knowledge of COPD management during the COVID‐19 Omicron outbreak and emphasizes the importance of considering individual immune profiles to improve care for COPD patients in the face of the ongoing global health crisis.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/crj.13790"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-11-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-05-11"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-05-30"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"family": "Bai",
"given": "Xueli",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"family": "Niu",
"given": "Yanan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
},
{
"name": "Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan China"
}
],
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Shuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Zhifan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Hu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
},
{
"name": "Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan China"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xiansheng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6224-8480",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Third Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Academy of Medical Sciences, Tongji Shanxi Hospital Taiyuan China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ruiying",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Clinical Respiratory Journal",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Respiratory J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-31T06:04:14Z",
"timestamp": 1717135454000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-31T06:04:18Z",
"timestamp": 1717135458000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82000053"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:25:31Z",
"timestamp": 1717201531582
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717027200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/crj.13790",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa032158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1"
},
{
"author": "Organisation, W.H",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1",
"volume-title": "Chronic Respiratory Diseases, Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201201‐0034OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213‐2600(12)70060‐7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00078714",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/resp.12642",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201108‐1553OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.04590‐2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392‐022‐00997‐x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00386.2021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213‐2600(20)30167‐3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02108‐2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.04474‐2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl‐2020‐215167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2021.2011219",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm12081295",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1393",
"article-title": "Covid‐19: increased demand for steroid inhalers causes “distressing” shortages",
"author": "Mahase E",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/COPD.S392660",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01370‐2015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/COPD.S179734",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201708‐1684LE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18295/squmj.1.2022.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/COPD.S312493",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/23120541.00594‐2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1465‐9921‐10‐113",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.200410‐1332OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/crj.13790"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COPD patients with high blood eosinophil counts exhibit a lower rate of omicron infection and milder post‐infection symptoms",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "18"
}