A study on the effect of aspirin on clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and outcomes in patients with COVID-19
et al., Journal of Nephropharmacology, doi:10.34172/npj.2023.10506, Feb 2023
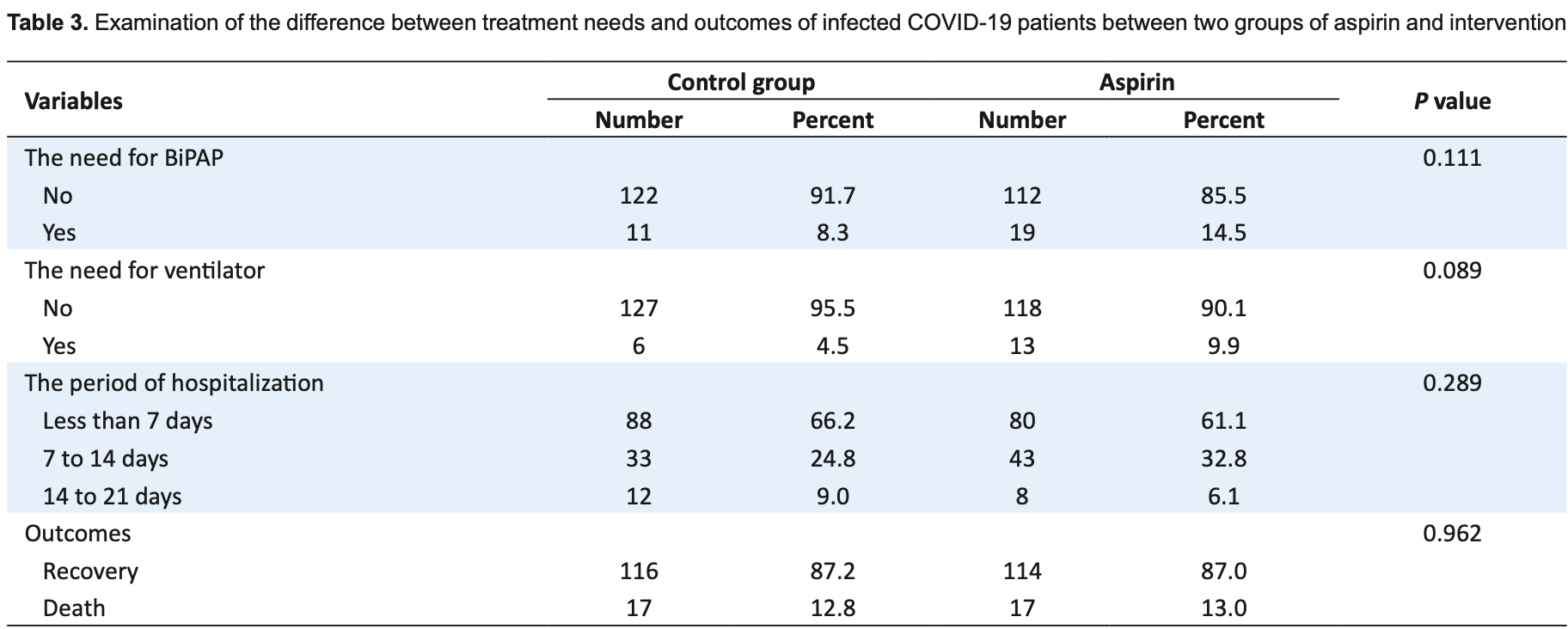
Retrospective 131 COVID-19 patients with aspirin use and 131 matched controls in Iran, showing no significant difference in outcomes, however age matching used only two categories, 40-60 and 60+, therefore matching may be very poor given the relationship between age and COVID-19 risk. The percentages given for the control group death/recovery outcomes do not match the reported counts.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
age matching based on only two categories, matching may be very poor given the relationship between age and COVID-19 risk; inconsistent data.
|
risk of death, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 17 of 131 (13.0%), control 17 of 131 (13.0%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Azizi et al., 17 Feb 2023, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
A study on the effect of aspirin on clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and outcomes in patients with COVID-19
doi:10.34172/npj.2023.10506
In a cross-sectional and observational study, the case and control groups were selected based on aspirin use, with non-users divided into two groups (131 medical records of patients with COVID-19 who administered aspirin and 131 of the group of patients with COVID-19 without aspirin administration). Aspirin was found to be ineffective in treating clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
Authors' contribution The principal investigators of the present study were RA and MDM. AM contributed to the conception and design of the study and revised and revaluated the manuscript. RG conducted data analysis. MNA and SMR collected data. In addition, all authors contributed to the final manuscript, read it, approved it, and attested to its accuracy and validity.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical issues The research adhered to the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. Patients' consent was obtained with their knowledge. The permission number of 154/99/30362 was granted by the Ethics Committee in Deputy of Treatment of Social Security Organization. Moreover, the authors have identified ethical concerns (including plagiarism, data fabrication, and double publication).
Funding/Support None.
References
Abdelhafiz, Emmerton, Sinclair, Diabetes in COVID-19 pandemic-prevalence, patient characteristics and adverse outcomes, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14112
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Yamane, Levine et al., Aspirin Use Is Associated With Decreased Mechanical Ventilation, Intensive Care Unit Admission, and In-Hospital Mortality in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019, Anesth Analg, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Arbous, Gommers et al., Confirmation of the high cumulative incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19: An updated analysis, Thromb Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.041
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Ornelas, Zacharias-Millward, Menter, Davis, Lichtenberger et al., Beyond COX-1: the effects of aspirin on platelet biology and potential mechanisms of chemoprevention, Cancer Metastasis Rev, doi:10.1007/s10555-017-9675-z
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5
Yang, Ng, Li, Thrombocytopenia in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome (review), Hematology, doi:10.1080/10245330400026170
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.34172/npj.2023.10506",
"ISSN": [
"2345-4202"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/npj.2023.10506",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction: Low-dose aspirin is one of the most widely used secondary prevention agents for cardiovascular disease and stroke. An unstable risk factor for chronic cardiovascular disease is a viral infection. Evidence suggests that the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) could increase the risk of acute cardiovascular events by inducing systemic inflammatory responses and instability in coronary plaques. Objectives: The present study aimed to examine the impact of aspirin on clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Patients and Methods: After reviewing the documents of hospitalized patients at the Dr. Shariati hospital in Isfahan, Iran, while case and control groups were selected using a cross-sectional method based on aspirin use and non-use. Following a random selection of the reference population (131 medical records of patients with COVID-19 who had aspirin use and 131 of the group of patients with COVID-19 without aspirin use). Medical records of patients with cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease with diabetes, and patients without underlying disease were evaluated. After matching the two groups based on age, gender, and medical history, the examination and results were recorded in a questionnaire. Results: The results showed that during treatment, no significant difference between the case and control groups regarding clinical symptoms, laboratory results, the need for bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP), and mechanical ventilation (P=0.0111 and P=0.089, respectively) were observed. Moreover, no significant difference in the outcome, including improvement and death was detected (P=0.962). Likewise, no significant difference in hospitalization duration between the aspirin and control groups was seen (P=0.289). Conclusion: Our study on a group of COVID-19 patients showed, aspirin is ineffective on clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and outcomes, however our results further investigation by multi-centric investigations.</jats:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Journal Owner",
"name": "journal_owner",
"value": "Society of Diabetic Nephropathy Prevention"
},
{
"label": "Journal Publisher",
"name": "journal_publisher",
"value": "Society of Diabetic Nephropathy Prevention"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-06-24"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-01-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2023-02-17"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7272-150X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Occupational Health and Safety Engineering, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Yazd, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Azizi",
"given": "Roham",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4368-3900",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Dehghani Mobarakeh",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6378-3490",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Modeling in Health Research Center, Shahrekord University of Medical Siences, Shahrekord, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Goujani",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8243-1530",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Biological Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Nabi-Afjadi",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2716-1632",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Occupational Health and Safety Engineering, Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences and Health Services, Yazd, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mousavi Rizi",
"given": "Soheil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0173-1222",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Maghsoudi",
"given": "Ahmadreza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Nephropharmacology",
"container-title-short": "J Nephropharmacol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"jnephropharmacology.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-19T08:35:13Z",
"timestamp": 1681893313000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-08T09:29:12Z",
"timestamp": 1686216552000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-07T17:16:25Z",
"timestamp": 1712510185318
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jnephropharmacology.com/PDF/npj-12-e10506.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://jnephropharmacology.com/PDF/npj-12-e10506.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "20123",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e10506",
"prefix": "10.34172",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Maad Rayan Publishing Company",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jnephropharmacology.com/Article/npj-10506"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Nephrology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A study on the effect of aspirin on clinical symptoms, laboratory indices, and outcomes in patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.34172/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "12"
}