Sep 30 2022 |
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1020123 | Atovaquone for treatment of COVID-19: A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial |
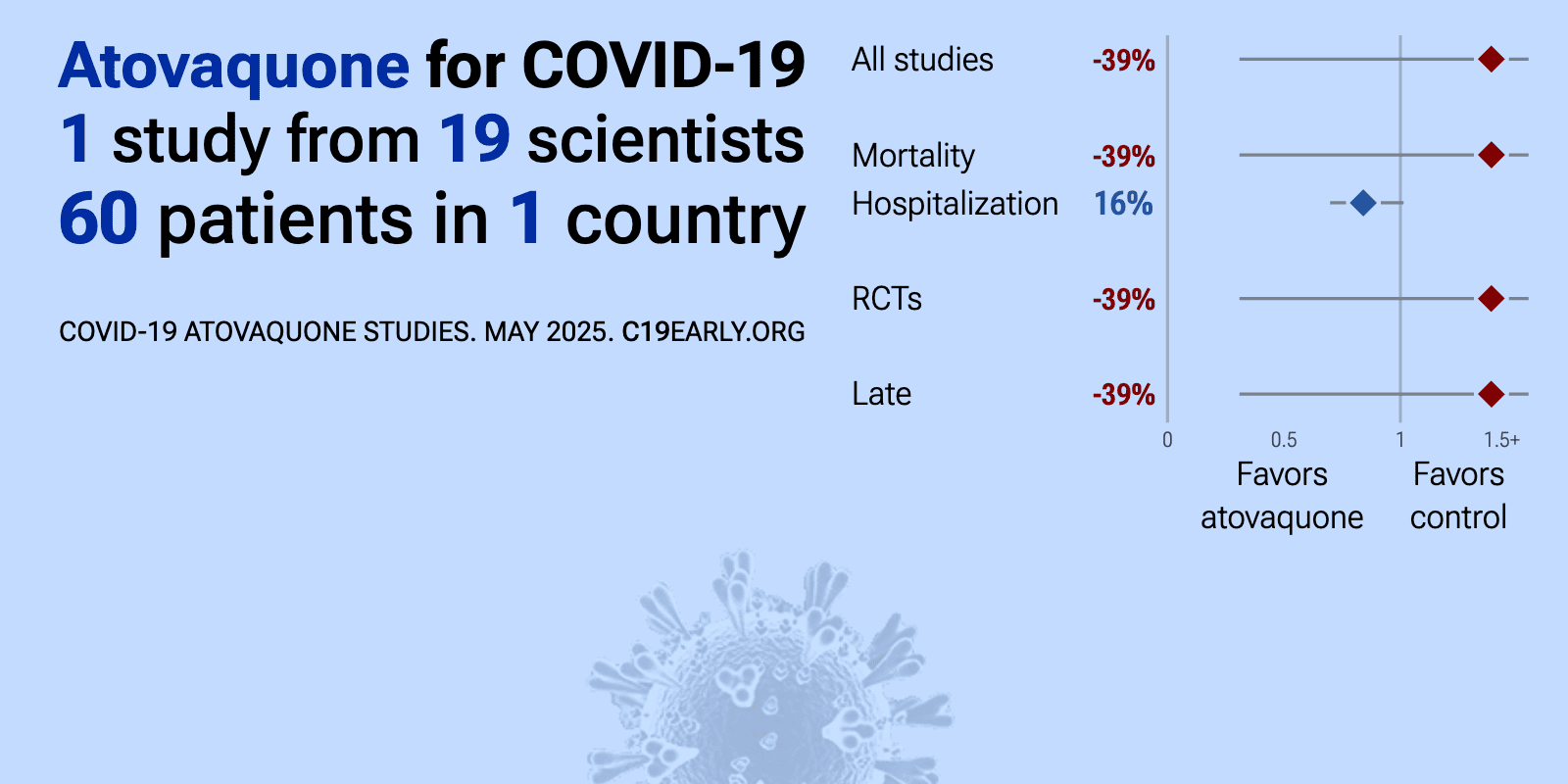
| 39% higher mortality (p=1), 20% greater improvement (p=0.56), and 16% shorter hospitalization (p=0.07). RCT 60 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in viral clearance with atovaquone. Patients were randomized 2:1 to receive atovaquone 1500mg BID or placebo for up to 10 days, with both groups receiving standard of.. | ||
Sep 9 2021 |
et al., PLOS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009840 | Discovery of re-purposed drugs that slow SARS-CoV-2 replication in human cells |
| In vitro studying identifying 35 compounds that inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in Vero cells and hepatocytes when treated prior to infection, and several compounds that slow replication when treated after infection: vitamin D, amodiaquine, atovaquone.. | ||
Jul 8 2021 |
et al., Journal of Virology & Antiviral Research | Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Anti-Parasitic Drugs Inhibiting the Receptor Binding Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein |
| In silico study identifying 32 anti-parisitic compounds effectively inhibiting the RBD of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, showing ivermectin and atovaquone among the top compounds. | ||