The association between dietary intakes of zinc, vitamin C and COVID-19 severity and related symptoms: A cross-sectional study
et al., Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.013, Mar 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
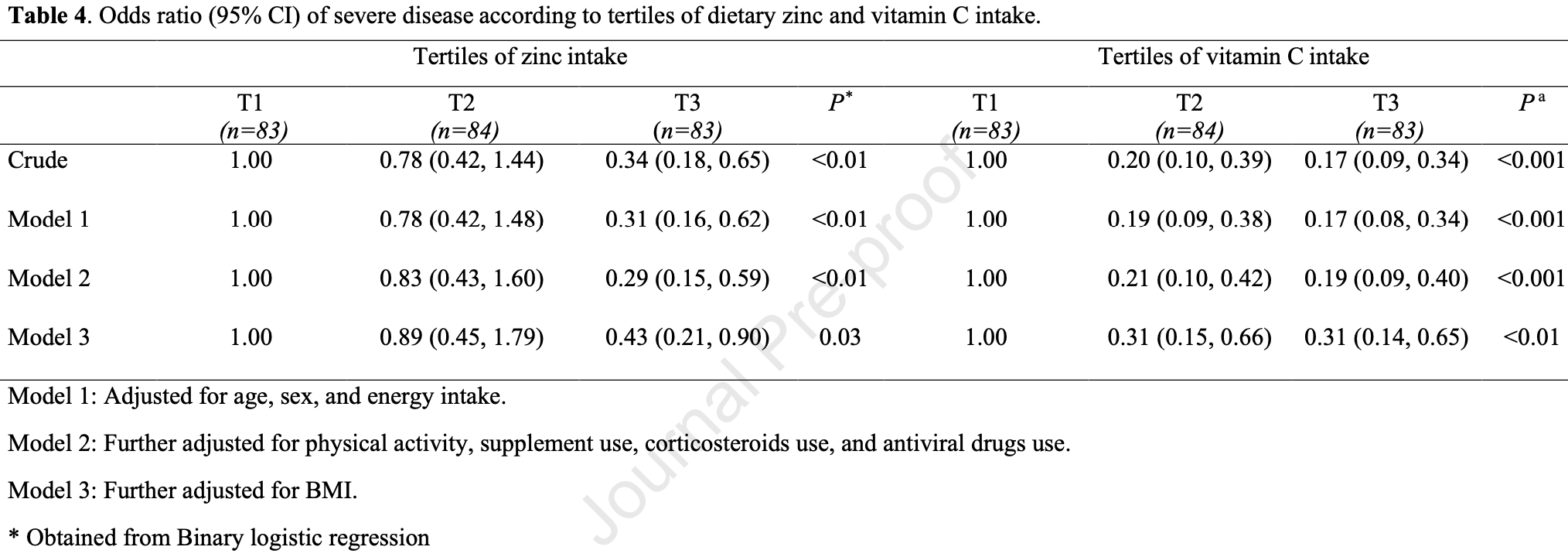
Retrospective 250 recovered COVID-19 patients, showing lower risk of severe cases with higher vitamin C intake.
This is the 56th of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
20 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0016.
Study covers zinc and vitamin C.
|
risk of severe case, 69.0% lower, OR 0.31, p = 0.003, adjusted per study, T3 vs. T1, multivariable, model 3, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Asoudeh et al., 21 Mar 2023, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period June 2021 - September 2021.
The association between dietary intakes of zinc, vitamin C and COVID-19 severity and related symptoms: A cross-sectional study
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.013
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Conflict of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Author contributions: FA, SMM, SMG, NZ, SR and EP contributed to the conception and design of the study, data collection, and statistical analysis and drafting of the manuscript; AM and MT contributed in data collection and manuscript drafting. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f 0.23 Vitamin B6 (mg/day)
References
Aadahl, Jørgensen, Validation of a new self-report instrument for measuring physical activity. Medicine and science in sports and exercise
Beigmohammadi, Bitarafan, Abdollahi, Amoozadeh, Salahshour et al., The association between serum levels of micronutrients and the severity of disease in patients with COVID-19, Nutrition
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Carr, Rowe, The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19
Chen, Shao, Hsu, Wu, Hung et al., Incidence of acute kidney injury in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Critical care
Chilvers, Mckean, Rutman, Myint, Silverman et al., The effects of coronavirus on human nasal ciliated respiratory epithelium, European Respiratory Journal
Darma, Ranuh, Merbawani, Setyoningrum, Hidajat et al., Zinc supplementation effect on the bronchial cilia length, the number of cilia, and the number of intact bronchial cell in zinc deficiency rats, The Indonesian Biomedical Journal
Dong, Guo, Zhang, Sun, Bjpo, The effects of low-carbohydrate diets on cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis, PLoS One
Esfahani, Asghari, Mirmiran, Azizi, Reproducibility and relative validity of food group intake in a food frequency questionnaire developed for the Tehran Lipid and Glucose Study, Journal of epidemiology
Forman, Nutritional Epidemiology
Frassinetti, Bronzetti, Caltavuturo, Cini, Croce, The role of zinc in life: a review, Journal of environmental pathology, toxicology and oncology
Galán, Stroke as a complication and prognostic factor of COVID-19, Neurología
Ghaffarpour, Houshiar-Rad, Kianfar, The manual for household measures, cooking yields factors and edible portion of foods. Tehran: Nashre, Olume Keshavarzy
Golabi, Adelipour, Mobarak, Piri, Seyedtabib et al., The Association between Vitamin D and Zinc Status and the Progression of Clinical Symptoms among Outpatients Infected with SARS-CoV-2 and Potentially Non-Infected Participants: A Cross-Sectional Study, Nutrients
Holford, Carr, Jovic, Ali, Whitaker et al., Vitamin C-An adjunctive therapy for respiratory infection, sepsis and COVID-19, Nutrients
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The lancet
Jahromi, Tabriz, Togha, Ariyanfar, Ghorbani et al., The correlation between serum selenium, zinc, and COVID-19 severity: An observational study, BMC Infectious Diseases
Jung, Kim, Choi, The relationship between zinc status and inflammatory marker levels in rural Korean adults aged 40 and older, PloS one
Kim, Lee, Regulatory Role of Zinc in Immune Cell Signaling, Molecules and Cells
Kümel, Schrader, Zentgraf, Daus, Brendel, The mechanism of the antiherpetic activity of zinc sulphate, Journal of general virology
Ligthart-Melis, Luiking, Kakourou, Cederholm, Maier et al., None
Lin, Caffrey, Chang, Dowling, Lin, Cigarette smoking, cadmium exposure, and zinc intake on obstructive lung disorder, Respiratory research
Lu, Chen, Chang, Potential therapeutic agents against COVID-19: What we know so far, Journal of the Chinese Medical Association
Manning, Mitchell, Appadurai, Shakya, Pierce et al., Vitamin C promotes maturation of T-cells. Antioxidants & redox signaling
Marasco, Maida, Morreale, Licata, Renzulli et al., Gastrointestinal Bleeding in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis, Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Massey, The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for goodness of fit, Journal of the American statistical Association
Mousavi, Djafarian, Mojtahed, Varkaneh, Shab-Bidar, The effect of zinc supplementation on plasma C-reactive protein concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, European journal of pharmacology
Mousavi, Hajishafiee, Clark, Do Nascimento, Milajerdi et al., Clinical effectiveness of zinc supplementation on the biomarkers of oxidative stress: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Pharmacological Research
Mousavi, Mofrad, Do Nascimento, Milajerdi, Mokhtari et al., The effect of zinc supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials, European journal of nutrition
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE open medicine
Nouri-Majd, Ebrahimzadeh, Mousavi, Zargarzadeh, Eslami et al., Higher Intake of Dietary Magnesium Is Inversely Associated With COVID-19 Severity and Symptoms in Hospitalized Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study, Frontiers in nutrition
Novick, Godfrey, Pollack, Wilder, Zinc-induced suppression of inflammation in the respiratory tract, caused by infection with human rhinovirus and other irritants, Medical hypotheses
Park, Byun, Kim, Kim, Kim et al., Dietary vitamin C intake protects against COPD: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in, International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Advances in nutrition
Roscioli, Jersmann, Lester, Badiei, Fon et al., Zinc deficiency as a codeterminant for airway epithelial barrier dysfunction in an ex vivo model of COPD. International journal of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Scientific, Heymann, Shindo, COVID-19: what is next for public health?, Lancet
Shakeri, Azimian, Ghasemzadeh-Moghaddam, Safdari, Haresabadi et al., Evaluation of the relationship between serum levels of zinc, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19, Journal of medical virology
Shoenfeld, Ryabkova, Scheibenbogen, Brinth, Martinez-Lavin et al., Complex syndromes of chronic pain, fatigue and cognitive impairment linked to autoimmune dysautonomia and small fiber neuropathy, Clinical Immunology
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19, International journal of molecular medicine
Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc, Vitamin D and Vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Frontiers in Nutrition
Suara, Jr, Effect of zinc salts on respiratory syncytial virus replication. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy
Vajargah, Zargarzadeh, Ebrahimzadeh, Mousavi, Mobasheran et al., Association of fruits, vegetables, and fiber intake with COVID-19 severity and symptoms in hospitalized patients: A cross-sectional study, Frontiers in Nutrition
Wannamethee, Lowe, Rumley, Bruckdorfer, Whincup, Associations of vitamin C status, fruit and vegetable intakes, and markers of inflammation and hemostasis, The American journal of clinical nutrition
Wong, Lam, Wu, Ip, Lee et al., Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome, Clinical & Experimental Immunology
Wong, Magnusson, Sharpton, Ho, Effects of zinc status on age-related T cell dysfunction and chronic inflammation, Biometals
Woodworth, Zhang, Tamashiro, Bhargave, Palmer et al., Zinc increases ciliary beat frequency in a calcium-dependent manner, American journal of rhinology & allergy
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jama
Youssef, Hussein, Attia, Elshazli, Zora, COVID-19 and liver dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of retrospective studies, Journal of medical virology
Zargarzadeh, Vajargah, Ebrahimzadeh, Mousavi, Khodaveisi et al., Higher Adherence to the Mediterranean dietary pattern is inversely associated with severity of COVID-19 and related symptoms: A Cross-Sectional Study, Frontiers in Medicine
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.013",
"ISSN": [
"2405-4577"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.013",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405457723000803"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The association between dietary intakes of zinc, vitamin C and COVID-19 severity and related symptoms: A cross-sectional study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2023.03.013"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5083-376X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Asoudeh",
"given": "Farzaneh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ebrahimzadeh",
"given": "Armin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghoreishy",
"given": "Seyed Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imani",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mousavi",
"given": "Seyed Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zargarzadeh",
"given": "Nikan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rigi",
"given": "Somaye",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Persad",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taghizadeh",
"given": "Mohsen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Milajerdi",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalnutritionespen.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-21T07:21:44Z",
"timestamp": 1679383304000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-21T07:21:45Z",
"timestamp": 1679383305000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-22T05:18:23Z",
"timestamp": 1679462303960
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457723000803?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457723000803?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405457723000803"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The association between dietary intakes of zinc, vitamin C and COVID-19 severity and related symptoms: A cross-sectional study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
