Antiinflammatory potential of nano-curcumin as an alternative therapeutic agent for the treatment of mild-to-moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a placebo-controlled clinical trial
et al., Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7375, Jan 2022
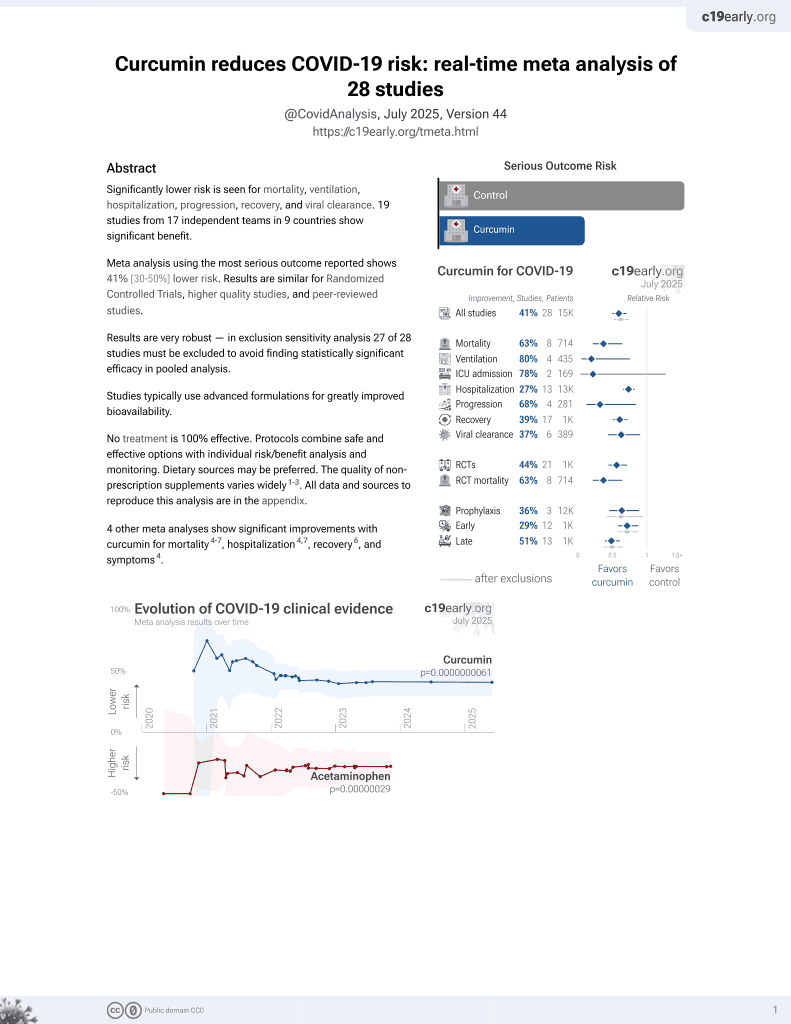
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 60 hospitalized patients in Iran, 30 treated with nano-curcumin, showing significant improvements in inflammatory cytokines, and improvements in clinical outcomes without statistical significance. 240 mg/day nano-curcumin for 7 days.
This is the 8th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
This is the 11th of 28 COVID-19 controlled studies for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
|
risk of death, 25.9% lower, RR 0.74, p = 0.74, treatment 5 of 27 (18.5%), control 6 of 24 (25.0%), NNT 15, excluding patients that stopped treatment due to progression - 3 for curcumin and 6 for control.
|
|
risk of progression, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.47, treatment 3 of 30 (10.0%), control 6 of 30 (20.0%), NNT 10.0.
|
|
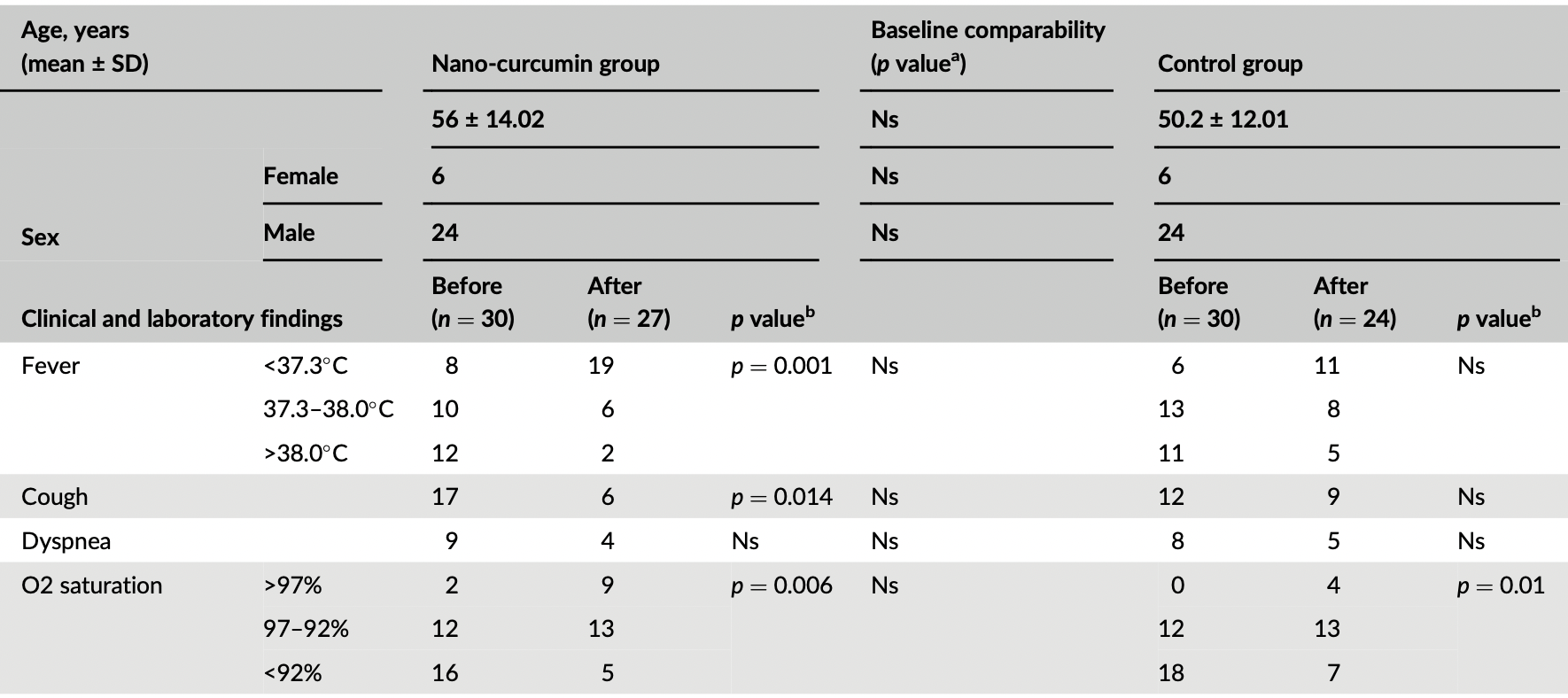
risk of unresolved fever, 45.3% lower, RR 0.55, p = 0.09, treatment 8 of 27 (29.6%), control 13 of 24 (54.2%), NNT 4.1.
|
|
risk of unresolved dyspnea, 28.9% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.72, treatment 4 of 27 (14.8%), control 5 of 24 (20.8%), NNT 17.
|
|
risk of unresolved cough, 40.7% lower, RR 0.59, p = 0.36, treatment 6 of 27 (22.2%), control 9 of 24 (37.5%), NNT 6.5.
|
|
risk of O2 <92%, 36.5% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.51, treatment 5 of 27 (18.5%), control 7 of 24 (29.2%), NNT 9.4.
|
|
risk of O2 <97%, 20.0% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.21, treatment 18 of 27 (66.7%), control 20 of 24 (83.3%), NNT 6.0.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Asadirad et al., 17 Jan 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period June 2020 - July 2020.
Antiinflammatory potential of nano‐curcumin as an alternative therapeutic agent for the treatment of mild‐to‐moderate hospitalized COVID‐19 patients in a placebo‐controlled clinical trial
Phytotherapy Research, doi:10.1002/ptr.7375
The present study conducted a placebo-controlled clinical trial to evaluate the impact of nano-curcumin on the inflammatory cytokines in mild-to-moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients. A total of 60 COVID-19 patients were randomly divided into nano-curcumin and control groups, and then they received 240 mg/day nano-curcumin for 7 days. The clinical manifestation and laboratory parameters in patients were recorded on days 0 and seven. Also, SYBR Green real-time PCR and ELISA techniques were implicated in assessing the mRNA expression of IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, MCP-1, and TNF-α and the serum levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α inflammatory mediators, respectively. Although the clinical manifestations and laboratory parameters improved via the nano-curcumin treatment, the mRNA expression of IFN-γ (p = 0.006) and TNF-α (p = 0.04) were significantly reduced. Besides, a considerable difference was observed between the nano-curcumin and control groups in the expression of IFN-γ (p = 0.001), IL-1β (p = 0.0002), and IL-6 (p = 0.008). In addition, there was a significant difference between the nano-curcumin and control groups in the serum levels of IL-1β (p = 0.042). The evidence demonstrated that nano-curcumin could be implicated as a complementary medication to act as an antiinflammatory agent and inhibit inflammatory complications.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflict of interest.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
References
Ahmadi, Salari, Sharifi, Reihani, Rostamiani et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in the management of mild to moderate outpatient COVID-19: A randomized triple-blind placebocontrolled clinical trial, Food Science & Nutrition
Avasarala, Zhang, Liu, Wang, London et al., Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, PLoS One
Babaei, Nassiri-Asl, Hosseinzadeh, Curcumin (a constituent of turmeric): New treatment option against COVID-19, Food Science & Nutrition
Bahrami, Kamalinejad, Latifi, Seif, Dadmehr, Cytokine storm in COVID-19 and parthenolide: Preclinical evidence, Phytotherapy Research
Barnard, Kumaki, Recent developments in anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus chemotherapy, Future Virology
Cao, COVID-19: Immunopathology and its implications for therapy, Nature Reviews Immunology
Derosa, Maffioli, Simental-Mendia, Bo, Sahebkar, Effect of curcumin on circulating interleukin-6 concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Pharmacological Research
Fan, Yao, Li, Hu, Shao et al., Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin on acute lung injury in a rodent model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion by inhibiting the pathway of NF-kb, International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology
Henry, Oliveira, Santos, Benoit, Plebani et al., Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A meta-analysis, Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM)
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The Lancet
Karimian, Pirro, Majeed, Sahebkar, Curcumin as a natural regulator of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews
Kunnumakkara, Bordoloi, Padmavathi, Monisha, Roy et al., Curcumin, the golden nutraceutical: Multitargeting for multiple chronic diseases, British Journal of Pharmacology
Kunnumakkara, Harsha, Banik, Vikkurthi, Sailo et al., Is curcumin bioavailability a problem in humans: Lessons from clinical trials, Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology
Li, Fan, Lai, Han, Li et al., Coronavirus infections and immune responses, Journal of Medical Virology
Li, Ma, Acute respiratory failure in COVID-19: Is it "typical, ARDS? Critical Care
Liu, Huang, Law, Tian, Leung et al., Preventive effect of curcumin against chemotherapy-induced side-effects, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Mani, Johnson, Steel, Broszczak, Neilsen et al., Natural product-derived phytochemicals as potential agents against coronaviruses: A review, Virus Research
Mckee, Sternberg, Stange, Laufer, Naujokat, Candidate drugs against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Pharmacological Research
Okabayashi, Kariwa, Yokota, Iki, Indoh et al., Cytokine regulation in SARS coronavirus infection compared to other respiratory virus infections, Journal of Medical Virology
Pawar, Mastud, Pawar, Pawar, Bhoite et al., Oral Curcumin with Piperine as adjuvant therapy for the treatment of COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Roshanravan, Seif, Ostadrahimi, Pouraghaei, Ghaffari, Targeting cytokine storm to manage patients with COVID-19: A mini-review, Archives of Medical Research
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Medicine
Saber-Moghaddam, Salari, Hejazi, Amini, Taherzadeh et al., Oral nano-curcumin formulation efficacy in management of mild to moderate hospitalized coronavirus disease-19 patients: An open label nonrandomized clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research
Sahebkar, Cicero, Simental-Mendía, Aggarwal, Gupta, Curcumin downregulates human tumor necrosis factor-α levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis ofrandomized controlled trials, Pharmacological Research
Seif, Aazami, Khoshmirsafa, Kamali, Mohsenzadegan et al., JAK inhibition as a new treatment strategy for patients with COVID-19, International Archives of Allergy and Immunology
Shanmugam, Rane, Kanchi, Arfuso, Chinnathambi et al., The multifaceted role of curcumin in cancer prevention and treatment, Molecules
Song, Ge, Cai, Zhang, Curcumin protects mice from coxsackievirus B3-induced myocarditis by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/Akt/nuclear factor-κB pathway, Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics
Soni, Mehta, Ratre, Tiwari, Amit et al., Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19?, European Journal of Pharmacology
Valizadeh, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Danshina, Gencer, Ammari et al., Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, International Immunopharmacology
Vitali, Bagri, Wessels, Arora, Ganugula et al., Curcumin can decrease tissue inflammation and the severity of HSV-2 infection in the female reproductive mucosa, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Wang, Yang, Li, Wen, Zhang, Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Xu, Liu, Curcumin alleviates macrophage activation and lung inflammation induced by influenza virus infection through inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway, Influenza and Other Respiratory Viruses
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Zahedipour, Hosseini, Sathyapalan, Majeed, Jamialahmadi et al., Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytotherapy Research
Zhang, Swamy, Balijepalli, Panicker, Mooliyil et al., Direct pulmonary delivery of solubilized curcumin reduces severity of lethal pneumonia, The FASEB Journal
Zhu, Yang, Chen, Jiang, Wang et al., Antiinflammatory potential of nano-curcumin as an alternative therapeutic agent for the treatment of mild-to-moderate hospitalized COVID-19 patients in a placebo-controlled clinical trial, Phytotherapy Research
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7375",
"ISSN": [
"0951-418X",
"1099-1573"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ptr.7375",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ptr.7375"
],
"archive": [
"Portico"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-07-14"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-12-22"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-01-17"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7203-343X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
},
{
"name": "Cancer, Petroleum and Environmental Pollutants Research Center Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Asadirad",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious and Tropical Diseases Research Center, Health Research Institute Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Nashibi",
"given": "Roohangiz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
},
{
"name": "Cancer, Petroleum and Environmental Pollutants Research Center Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Khodadadi",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghadiri",
"given": "Ata A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
},
{
"name": "Student Research Committee Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"family": "Sadeghi",
"given": "Mahvash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cancer, Petroleum and Environmental Pollutants Research Center Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery Ilam University of Medical Sciences Ilam Iran"
}
],
"family": "Aminian",
"given": "Azam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8442-0584",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Immunology, School of Medicine Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences Ahvaz Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Dehnavi",
"given": "Sajad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Phytotherapy Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T02:23:30Z",
"timestamp": 1642472610000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T02:23:36Z",
"timestamp": 1642472616000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-18T05:40:50Z",
"timestamp": 1642484450180
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0951-418X"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1099-1573"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
17
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642377600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642377600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7375",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/ptr.7375",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ptr.7375",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_2_1",
"unstructured": "Food Science & Nutrition 9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0057285",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.1858",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6776",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl.11.33",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0308-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2016.07.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_8_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Anti‐inflammatory and antioxidant effects of curcumin on acute lung injury in a rodent model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion by inhibiting the pathway of NF‐kb",
"author": "Fan Z.",
"first-page": "3451",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology",
"key": "e_1_2_11_9_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_10_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_11_1",
"unstructured": "The Lancet 395"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.13621",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_13_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_14_1",
"unstructured": "Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology 15"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_15_1",
"unstructured": "Journal of Medical Virology 92"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02911-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2018.01374",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.197989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104859",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_19_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_11_20_1",
"unstructured": "Journal of Medical Virology 78 4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.669362",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.00912",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000508247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules20022728",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1074248413503044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21010337",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12459",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.201901047RR",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.5791",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_11_38_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Phytotherapy Research"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Antiinflammatory potential of nano‐curcumin as an alternative therapeutic agent for the treatment of mild‐to‐moderate hospitalized COVID‐19 patients in a placebo‐controlled clinical trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}