Lifestyle and quality of life in children and adolescents during the covid-19 social distancing period
et al., Jornal de Pediatria, doi:10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006, Aug 2023
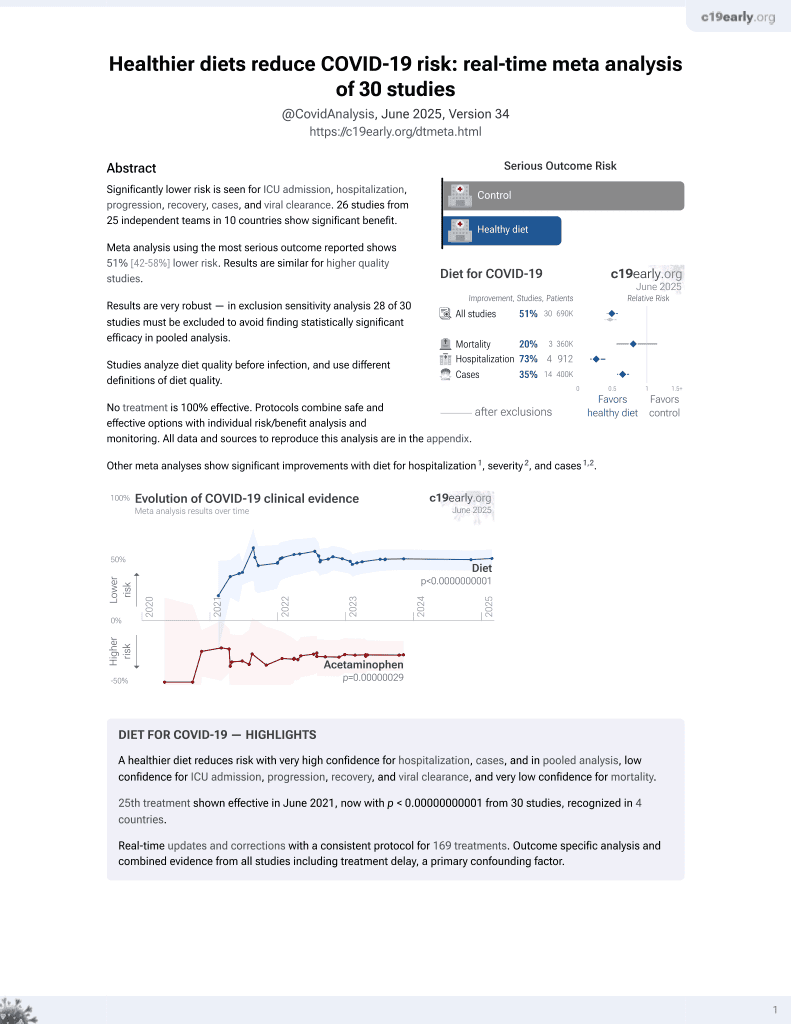
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
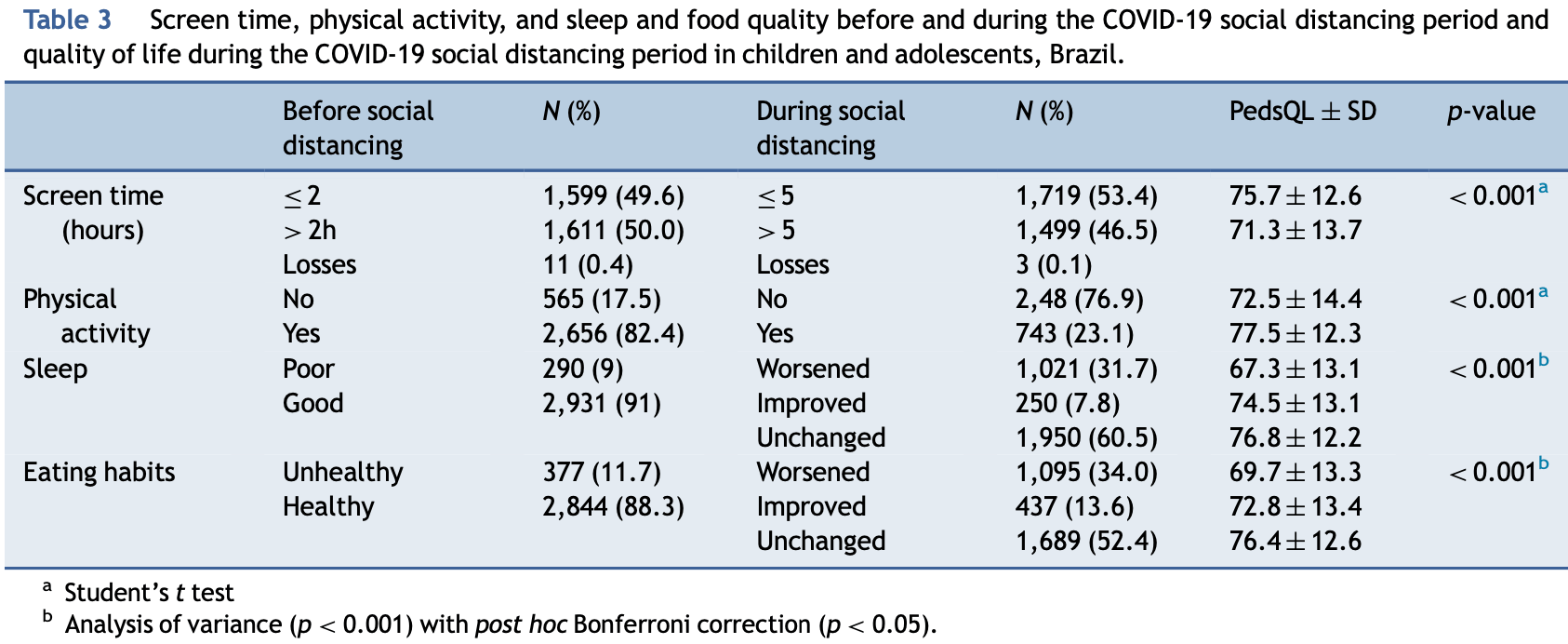
Cross-sectional analysis of 2,574 families in Brazil, showing that pandemic social distancing caused negative changes in exercise, diet, and sleep for children.
Araujo et al., 14 Aug 2023, Brazil, peer-reviewed, survey, 7 authors, study period 23 June, 2020 - 12 July, 2020.
Contact: catherinee.pires@gmail.com.
Lifestyle and quality of life in children and adolescents during the covid-19 social distancing period
Jornal de Pediatria, doi:10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006
Objective: To evaluate the lifestyle and quality of life in Brazilian children and adolescents during the COVID-19 social distancing period in 2020. Methods: This cross-sectional study evaluated children and adolescents (2-18 years of age) and their parents, who voluntarily participated in an online survey. Snowball sampling was used to recruit participants during the first 6 months of the pandemic. A questionnaire was used to characterize the study population. The PedsQL 4.0 and the EUROHIS-QOL 8-item index were used to assess the quality of life (QoL) in children/adolescents and parents, respectively. Data were analyzed using SPSS 18.0 statistical program through the ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni analysis, student's t test, and the generalized estimating equation. Results: Mean screen time increased from 2h pre-pandemic to 5h during the pandemic (p < 0.001), which was associated with a decline in PedSQL4.0 scores (from 75.7 § 2.6 to 71.3 § 13.7, p < 0.001). Unhealthy eating habits increased from 11% to 34% and were associated with worse QoL scores compared with improved or unchanged eating habits during the pandemic (69.7 § 13.3 vs 72.80 § 13.4 vs 76.4 § 12.6; p < 0.001). Poor sleep quality increased from 9% to 31.7% and was associated with worse QoL scores compared to improved or unchanged sleep quality during the pandemic (67.3 § 13.1 vs 74.5 § 13.1 vs 76.8 § 12.2; p < 0.05). Physical exercise was associated with better PedSQL4.0 scores (77.5 § 12.3 vs 72.5 § 14.4; p < 0.001). Children aged 2-4y old had the best QoLscores.
Conflicts of interest 374 The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Barton, Food and beverage offerings by parents of preschoolers: a daily survey study of dinner offerings during COVID-19, Appetite
Choi, Hui, Wan, Kwok, Tam et al., COVID-19 and health-related quality of life: a community-based online survey in Hong Kong, Int J Environ Res Public Health
Cremeens, Eiser, Blades, Factors influencing agreement between child self-report and parent proxy-reports on the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory TM 4.0 (PedsQL TM ) generic core scales, Health Qual Life Outcomes
Dong, Mo, Hu, Qi, Jiang et al., Epidemiology of 380 COVID-19 among children in China, Pediatrics
Han, Hart, Stiglic N, Viner RM. Effects of screentime on the health and 439 well-being of children and adolescents: a systematic review of 440 reviews, Soc Sci Q
Jansen, Thapaliya, Aghababian, Sadler, Smith et al., Parental stress, food parenting practices and child snack intake during the COVID-19 pandemic, Appetite
Johnson, Warburton DE, Bredin SS. Health benefits of physical activity: a 445 systematic review of current systematic reviews, Curr Opin Car-446 diol
Kharel, Sakamoto, Carandang, Ulambayar, Shibanuma 417 et al., Impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown 418 on movement behaviours of children and adolescents: a system-419 atic review, BMJ Glob Health
Kirschbaum, Working paper: Repercussões da pandemia 398 de COVID-19 no desenvolvimento infantil [Internet]
Klatchoian, Len, Terreri, Silva, Itamoto et al., Quality of life of children and adolescents from São 426 Paulo: reliability and validity of the Brazilian version of the 427 Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 Generic Core 428 Scales, J Pediatr (Rio J)
Krumbein, Ls, Fragkou, Th€ Olken C, None, H€ unerbein BL
Liu, Tang, Wang, Yang, Chen, Sleep of preschoolers during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak, J Sleep Res
Ludvigsson, Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows 386 milder cases and a better prognosis than adults, Acta Paediatr
Manitto, Chiesa, Da Cunha, Abuchaim, Biderman, None
Meade, Mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on 410 children and adolescents: a review of the current research, Pediatr Clin North Am
Muros, Ortega, Vm, The associa-421 tion between healthy lifestyle behaviors and health-related 422 quality of life among adolescents, J Pediatr (Rio J)
Okely, Kariippanon, Guan, Taylor, Suesse et al., Global effect of COVID-19 pandemic on physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep among 3-to 5-year-old children: a longitudinal study of 14 countries
Patrick, Henkhaus, Zickafoose, Lovell, Halvorson et al., Well-being of parents and children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national survey, Pediatrics
Penna, De Aquino, Pinheiro, Do Nascimento, Unez et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mental health, early childhood development, and parental practices: a global scoping review
Pires, Fleck, Power, Da Rocha, Carroll et al., 433 The Impact of COVID-19 on health behavior, stress, financial 434 and food security among middle to high income Canadian fami-435 lies with young children, Braz J Psychiatry
Reiter, Respiratory viral co-infections in patients with 394 COVID-19 and associated outcomes: a systematic review and 395 meta-analysis, Rev Med Virol
Singhal, Mcmillan, Savich, Matovelo, Santorino et al., COVID-19 and parent-child psychological well-being, Pediatrics
Stockwell, Trott, Tully, Shin, Barnett et al., Changes in physical activity and sedentary behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: a systematic review, BMJ BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med
Sultana, Tasnim, Hossain, Bhattacharya, Purohit, None
Wang, Pan, Tan, Xu, Mcintyre, A longitu-413 dinal study on the mental health of general population during 414 the COVID-19 epidemic in China, Brain Behav Immun
Wu, Han, Zhang, Luo, Hu et al., The influence of 448 physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: a systematic review, PLoS One
Xiang, Zhang, Kuwahara, Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on
Zheng, Zeng, Yuan, Tian, Yang et al., Preva-389 lence and risk factor for long COVID in children and adolescents
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006",
"ISSN": [
"0021-7557"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006",
"alternative-id": [
"S002175572300089X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Lifestyle and quality of life in children and adolescents during the covid-19 social distancing period"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Jornal de Pediatria"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Sociedade Brasileira de Pediatria. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8991-2062",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Araujo",
"given": "Catherine Pires de",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5859-6239",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Piva",
"given": "Jefferson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7260-3033",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rocha",
"given": "Neusa Sica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9535-0307",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nicoladeli",
"given": "Amanda Vettoretti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9792-2604",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vieira",
"given": "Ana Paula Radunz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8477-7383",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hartwig",
"given": "Jessica Paniz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7849-8732",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rocha",
"given": "Tais Sica",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Jornal de Pediatria",
"container-title-short": "Jornal de Pediatria",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-14T13:26:04Z",
"timestamp": 1692019564000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-17T01:41:01Z",
"timestamp": 1692236461000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-17T04:10:18Z",
"timestamp": 1692245418505
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1690848000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 9,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691625600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S002175572300089X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S002175572300089X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-0702",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of COVID-19 among children in China",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0001",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0002",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 confirmed cases and deaths - UNICEF DATA [Internet]. [cited 2023 May 6]. Available from:https://data.unicef.org/resources/covid-19-confirmed-cases-and-deaths-dashboard/"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apa.15270",
"article-title": "Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults",
"author": "Ludvigsson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1088",
"journal-title": "Acta Paediatr",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0003",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2023.03.005",
"article-title": "Prevalence and risk factor for long COVID in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis and systematic review",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0004",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2365",
"article-title": "Respiratory viral co-infections in patients with COVID-19 and associated outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Krumbein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2365",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0005",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0006",
"unstructured": "Manitto AM, Chiesa AM, da Cunha AJ, Abuchaim B, Biderman C, Kirschbaum C, et al. Working paper: Repercussões da pandemia de COVID-19 no desenvolvimento infantil [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2022 Jan 5]. Available from:https://ncpi.org.br/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Working-Paper-Repercussoes-da-pandemia-no-desenvolvimento-infantil-3.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2020.04.013",
"article-title": "Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on children and adolescents’ lifestyle behavior larger than expected",
"author": "Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Prog Cardiovasc Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0007",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8",
"article-title": "The psychological impact of quarantine and how to reduce it: rapid review of the evidence",
"author": "Brooks",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "912",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0008",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcl.2021.05.003",
"article-title": "Mental health effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on children and adolescents: a review of the current research",
"author": "Meade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "945",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Clin North Am",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0009",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.028",
"article-title": "A longitudinal study on the mental health of general population during the COVID-19 epidemic in China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "40",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0010",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2021-007190",
"article-title": "Impact of COVID-19 pandemic lockdown on movement behaviours of children and adolescents: a systematic review",
"author": "Kharel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7190",
"journal-title": "BMJ Glob Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0011",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jped.2016.10.005",
"article-title": "The association between healthy lifestyle behaviors and health-related quality of life among adolescents",
"author": "Muros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "406",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr (Rio J)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0012",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S0021-75572008000400005",
"article-title": "Quality of life of children and adolescents from São Paulo: reliability and validity of the Brazilian version of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory version 4.0 Generic Core Scales",
"author": "Klatchoian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "308",
"journal-title": "J Pediatr (Rio J)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0013",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1516-4446-2017-2297",
"article-title": "Psychometric properties of the EUROHIS-QOL 8-item index (WHOQOL-8) in a Brazilian sample",
"author": "Pires",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "Braz J Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0014",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082352",
"article-title": "The Impact of COVID-19 on health behavior, stress, financial and food security among middle to high income Canadian families with young children",
"author": "Carroll",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2352",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0015",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ssqu.13031",
"article-title": "Job precarity and economic prospects during the COVID-19 public health crisis",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2394",
"journal-title": "Soc Sci Q",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0016",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2018-023191",
"article-title": "Effects of screentime on the health and well-being of children and adolescents: a systematic review of reviews",
"author": "Stiglic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0017",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.50880.1",
"article-title": "Digital screen time during the COVID-19 pandemic: a public health concern",
"author": "Sultana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "81",
"journal-title": "F1000Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0018",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HCO.0000000000000437",
"article-title": "Health benefits of physical activity: a systematic review of current systematic reviews",
"author": "Warburton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "541",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0019",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0187668",
"article-title": "The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: a systematic review",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0020",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Changes in physical activity and sedentary behaviours from before to during the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown: a systematic review",
"author": "Stockwell",
"first-page": "960",
"journal-title": "BMJ BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0021",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.appet.2021.105119",
"article-title": "Parental stress, food parenting practices and child snack intake during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Jansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Appetite",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0022",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.appet.2022.106047",
"article-title": "Food and beverage offerings by parents of preschoolers: a daily survey study of dinner offerings during COVID-19",
"author": "Barton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Appetite",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0023",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-021-10852-3",
"article-title": "Global effect of COVID-19 pandemic on physical activity, sedentary behaviour and sleep among 3- to 5-year-old children: a longitudinal study of 14 countries",
"author": "Okely",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "940",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0024",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-023-15003-4",
"article-title": "Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mental health, early childhood development, and parental practices: a global scoping review",
"author": "Penna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "388",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0025",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jsr.13142",
"article-title": "Sleep of preschoolers during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13142",
"journal-title": "J Sleep Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0026",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18063228",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and health-related quality of life: a community-based online survey in Hong Kong",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3228",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0027",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-016824",
"article-title": "Well-being of parents and children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a national survey",
"author": "Patrick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0028",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2020-016915E",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and parent-child psychological well-being",
"author": "Singhal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S123",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0029",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1477-7525-4-58",
"article-title": "Factors influencing agreement between child self-report and parent proxy-reports on the Pediatric Quality of Life InventoryTM 4.0 (PedsQLTM) generic core scales",
"author": "Cremeens",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Health Qual Life Outcomes",
"key": "10.1016/j.jped.2023.07.006_bib0030",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2006"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S002175572300089X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Lifestyle and quality of life in children and adolescents during the covid-19 social distancing period",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
araujo