HTRF-based identification of small molecules targeting SARS-CoV-2 E protein interaction with ZO-1 PDZ2
et al., Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31755-y, Dec 2025
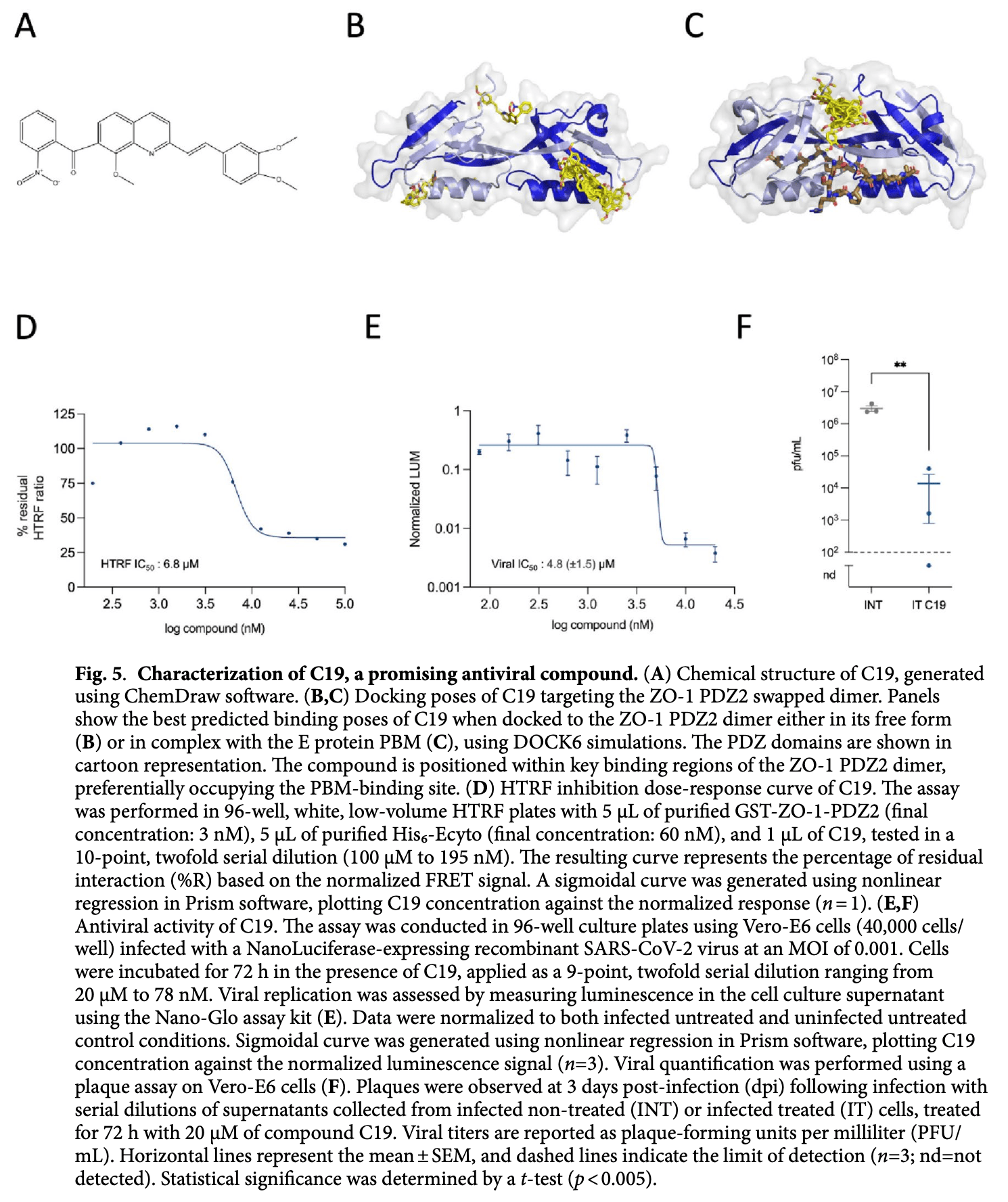
In vitro study showing that compound C19 significantly reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication by targeting the interaction between viral E protein and host ZO-1 PDZ2 domain.
Alvarez et al., 28 Dec 2025, France, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Contact: a.flavio2cg@gmail.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
HTRF-based identification of small molecules targeting SARS-CoV-2 E protein interaction with ZO-1 PDZ2
Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-31755-y
The SARS-CoV-2 E protein through its C-terminal PDZ-binding motif (PBM) interacts with several host PDZ-containing proteins, including Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) protein via its PDZ2 domain, thereby contributing to viral pathogenesis. Targeting this interaction represents a potential therapeutic strategy. In this study, we determined the X-ray structure of the E PBM peptide in complex with the ZO-1 PDZ2 domain at 1.7 Å resolution. The structure revealed a domain-swapped dimer conformation of ZO-1 PDZ2, with the E PBM peptide conventionally bound within the PDZ domain's canonical binding groove, exhibiting key interactions characteristic of type II PBM/PDZ interactions. To identify potential inhibitors of the E PBM/ZO-1 PDZ2 interaction, we performed a Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence (HTRF) screening using a protein-protein interaction-focused library of 1000 compounds. This led to the identification of 36 hits that disrupted this interaction. Subsequent cytotoxicity and dose-response assays narrowed the selection to 14 promising compounds. Docking simulations showed that some compounds bind within or near the PBM-binding pocket, supporting a competitive mechanism of interaction inhibition, while others bind at a central interface between the two PDZ monomers, suggesting an inhibition of dimerization, which in turn prevents PBM binding. Thus, the E PBM/ZO-1 PDZ2 interaction can be inhibited through both direct and indirect mechanisms. Finally, antiviral assays using a NanoLuciferase-expressing recombinant SARS-CoV-2 demonstrated that one compound, C19, significantly reduced viral replication, highlighting its potential as a candidate for further therapeutic development.
Author contributions
Declarations
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0 . 1 0 3 8 / s 4 1 5 9 8 -0 2 5 -3 1 7 5 5 -y . Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to F.A. Reprints and permissions information is available at www.nature.com/reprints . Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from..
References
Adams, PHENIX: a comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr
Alvarez, The SARS-CoV-2 envelope PDZ Binding Motif acts as a virulence factor disrupting host's epithelial cell-cell junctions, doi:10.1101/2024.12.10.627528
Baell, Holloway, New substructure filters for removal of Pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays, J. Med. Chem
Bosc, Fr-PPIChem: an academic compound library dedicated to Protein-Protein interactions, ACS Chem. Biol
Butina, Unsupervised data base clustering based on daylight's fingerprint and Tanimoto similarity: A fast and automated way to cluster small and large data sets, J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci
Caillet-Saguy, Host PDZ-containing proteins targeted by SARS-CoV-2, FEBS J
Carabelli, SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: immune escape, transmission and fitness, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Cdc, Types of COVID-19 Treatment
Chai, Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1, Nat. Commun
Chen, Pan, Wei, Zhao, Zhang, Domain-swapped dimerization of ZO-1 PDZ2 generates specific and regulatory connexin43-binding sites, EMBO J
Chen, The connexin 43/ZO-1 complex regulates cerebral endothelial F-actin architecture and migration, Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol
Chen, Yang, Chen, Cui, COVID-19 and cognitive impairment: neuroinvasive and blood-brain barrier dysfunction, J. Neuroinflammation
De Melo, Neuroinvasion and anosmia are independent phenomena upon infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants, Nat. Commun
Deinhardt-Emmer, SARS-CoV-2 causes severe epithelial inflammation and barrier dysfunction, J. Virol
Emsley, Lohkamp, Scott, Cowtan, Features and development of Coot, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr
Errico, Adams, Fremont, Antibody-mediated immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Adv. Immunol
Fanning, Lye, Anderson, Lavie, Domain swapping within PDZ2 is responsible for dimerization of ZO proteins, J. Biol. Chem
Focosi, Maggi, Neutralising antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein: risk assessment for antibody-based Covid-19 therapeutics and vaccines, Rev. Med. Virol
Focosi, Monoclonal antibody therapies against SARS-CoV-2, Lancet Infect. Dis
Gally, Bourg, Do, Aci-Sèche, Bonnet et al., A general KNIME workflow for the Preparation of molecules for virtual screening, Mol. Inform
Gally, VSPrep: A KNIME workflow for the preparation of molecular databases for virtual screening, Curr. Med. Chem
Glem, Circular fingerprints: flexible molecular descriptors with applications from physical chemistry to ADME, IDrugs Investig. Drugs J
Gupta, Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat. Med
Hamon, 2P2IHUNTER: a tool for filtering orthosteric protein-protein interaction modulators via a dedicated support vector machine, J. R Soc. Interface
Honrubia, SARS-CoV-2-mediated lung edema and replication are diminished by cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators, mBio
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J. Med. Virol
Huang, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet Lond. Engl
Javorsky, Humbert, Kvansakul, Structural basis of coronavirus E protein interactions with human PALS1 PDZ domain, Commun. Biol
Jimenez-Guardeño, The PDZ-binding motif of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein is a determinant of viral pathogenesis, PLoS Pathog
Kabsch, None, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr
Lamers, Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Lang, DOCK 6: combining techniques to model RNA-small molecule complexes, RNA
Liao, Single-cell landscape of Bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19, Nat. Med
Liu, Coronavirus envelope protein activates TMED10-mediated unconventional secretion of inflammatory factors, Nat. Commun
Markov, The evolution of SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Mccoy, Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with phaser, Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr
O'boyle, Open babel: an open chemical toolbox, J. Cheminform
Pettersen, UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J. Comput. Chem
Planès, Bert, Tairi, Benmohamed, Bahraoui, SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein binds and activates TLR2 pathway: A novel molecular target for COVID-19 interventions, Viruses
Robinot, SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the dedifferentiation of multiciliated cells and impairs mucociliary clearance, Nat. Commun
Schnittler, Structural and functional aspects of intercellular junctions in vascular endothelium, Basic. Res. Cardiol
Schoeman, Fielding, Coronavirus envelope protein: current, Virol. J
Shepley-Mctaggart, SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein interacts with PDZ-Domain-2 of host tight junction protein ZO1, BioRxiv Prepr Serv. Biol, doi:10.1101/2020.12.22.422708
Teoh, The SARS coronavirus E protein interacts with PALS1 and alters tight junction formation and epithelial morphogenesis, Mol. Biol. Cell
Troyano-Hernáez, Reinosa, Holguín, Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 envelope, membrane, nucleocapsid, and spike structural proteins from the beginning of the pandemic to September 2020: A global and regional approach by epidemiological week, Viruses
Vann, Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope E protein to human BRD4 is essential for infection, Struct. Lond. Engl
Weber, High-Throughput crystallization pipeline at the crystallography core facility of the Institut Pasteur, Mol. Basel Switz
Xia, SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein causes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)-like pathological damages and constitutes an antiviral target, Cell. Res
Xu, SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein impairs airway epithelial barrier function and exacerbates airway inflammation via increased intracellular Cl-concentration, Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther
Zhang, Chung, Oldenburg, A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays, J. Biomol. Screen
Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 E protein: pathogenesis and potential therapeutic development, Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother
Zhu, Interactions of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 protein E with cell junctions and Polarity PSD-95/ Dlg/ZO-1-Containing proteins, Front. Microbiol
Ávila-Flores, Identification of host PDZ-based interactions with the SARS-CoV-2 E protein in human monocytes, Int. J. Mol. Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-025-31755-y",
"ISSN": [
"2045-2322"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-31755-y",
"alternative-id": [
"31755"
],
"article-number": "2034",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "13 October 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "4 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "28 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarez",
"given": "Flavio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Larrous",
"given": "Florence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mechaly",
"given": "Ariel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bardiaux",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goor",
"given": "Quentin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Haouz",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Séon-Méniel",
"given": "Blandine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Sousa",
"given": "Rodolphe Alves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bourg",
"given": "Stéphane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Desmaële",
"given": "Didier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Figadère",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wolff",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Munier-Lehmann",
"given": "Hélène",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caillet-Saguy",
"given": "Célia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Scientific Reports",
"container-title-short": "Sci Rep",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-28T11:44:30Z",
"timestamp": 1766922270000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-15T14:05:40Z",
"timestamp": 1768485940000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "PFR-1 Reverse Genetics"
},
{
"name": "TASK FORCE COVID"
},
{
"name": "PFR-5 Functional Genomics of the Viral Cycle"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-16T07:32:53Z",
"timestamp": 1768548773483,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2025-12-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1766880000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 18,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768435200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-31755-y",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-31755-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-31755-y.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"author": "AM Carabelli",
"first-page": "162",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "31755_CR1",
"unstructured": "Carabelli, A. M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: immune escape, transmission and fitness. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 162–177 (2023).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-023-00878-2",
"author": "PV Markov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "361",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "31755_CR2",
"unstructured": "Markov, P. V. et al. The evolution of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 21, 361–379 (2023).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet Lond. Engl.",
"key": "31755_CR3",
"unstructured": "Huang, C. et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet Lond. Engl. 395, 497–506 (2020).",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0901-9",
"author": "M Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "842",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "31755_CR4",
"unstructured": "Liao, M. et al. Single-cell landscape of Bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 842–844 (2020).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26232",
"author": "B Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "31755_CR5",
"unstructured": "Hu, B., Huang, S. & Yin, L. The cytokine storm and COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 93, 250–256 (2021).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "31755_CR6",
"unstructured": "CDC. Types of COVID-19 Treatment. COVID-19 (2024). https://www.cdc.gov/covid/treatment/index.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00311-5",
"author": "D Focosi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e311",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "31755_CR7",
"unstructured": "Focosi, D. et al. Monoclonal antibody therapies against SARS-CoV-2. Lancet Infect. Dis. 22, e311–e326 (2022).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2231",
"author": "D Focosi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2231",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "31755_CR8",
"unstructured": "Focosi, D. & Maggi, F. Neutralising antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein: risk assessment for antibody-based Covid-19 therapeutics and vaccines. Rev. Med. Virol. 31, e2231 (2021).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.ai.2022.07.001",
"author": "JM Errico",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv. Immunol.",
"key": "31755_CR9",
"unstructured": "Errico, J. M., Adams, L. J. & Fremont, D. H. Antibody-mediated immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Adv. Immunol. 154, 1–69 (2022).",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-019-1182-0",
"author": "D Schoeman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "31755_CR10",
"unstructured": "Schoeman, D. & Fielding, B. C. Coronavirus envelope protein: current knowledge. Virol. J. 16, 69 (2019).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00519-4",
"author": "B Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "847",
"journal-title": "Cell. Res.",
"key": "31755_CR11",
"unstructured": "Xia, B. et al. SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein causes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)-like pathological damages and constitutes an antiviral target. Cell. Res. 31, 847–860 (2021).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114242",
"author": "S Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "114242",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "31755_CR12",
"unstructured": "Zhou, S. et al. SARS-CoV-2 E protein: pathogenesis and potential therapeutic development. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 159, 114242 (2023).",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13020243",
"author": "P Troyano-Hernáez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "31755_CR13",
"unstructured": "Troyano-Hernáez, P., Reinosa, R. & Holguín, Á. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 envelope, membrane, nucleocapsid, and spike structural proteins from the beginning of the pandemic to September 2020: A global and regional approach by epidemiological week. Viruses. 13, 243 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "KR Vann",
"first-page": "1224",
"journal-title": "Struct. Lond. Engl. 1993",
"key": "31755_CR14",
"unstructured": "Vann, K. R. et al. Binding of the SARS-CoV-2 envelope E protein to human BRD4 is essential for infection. Struct. Lond. Engl. 1993. 30, 1224–1232e5 (2022).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15881",
"author": "C Caillet-Saguy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5148",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "31755_CR15",
"unstructured": "Caillet-Saguy, C. et al. Host PDZ-containing proteins targeted by SARS-CoV-2. FEBS J. 288, 5148–5162 (2021).",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms241612793",
"author": "A Ávila-Flores",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12793",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "31755_CR16",
"unstructured": "Ávila-Flores, A. et al. Identification of host PDZ-based interactions with the SARS-CoV-2 E protein in human monocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 12793 (2023).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-52818-0",
"author": "L Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8708",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "31755_CR17",
"unstructured": "Liu, L. et al. Coronavirus envelope protein activates TMED10-mediated unconventional secretion of inflammatory factors. Nat. Commun. 15, 8708 (2024).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14050999",
"author": "R Planès",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "999",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "31755_CR18",
"unstructured": "Planès, R., Bert, J. B., Tairi, S., BenMohamed, L. & Bahraoui, E. SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein binds and activates TLR2 pathway: A novel molecular target for COVID-19 interventions. Viruses 14, 999 (2022).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e10-04-0338",
"author": "KT Teoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3838",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell.",
"key": "31755_CR19",
"unstructured": "Teoh, K. T. et al. The SARS coronavirus E protein interacts with PALS1 and alters tight junction formation and epithelial morphogenesis. Mol. Biol. Cell. 21, 3838–3852 (2010).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.22.422708",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "31755_CR20",
"unstructured": "Shepley-McTaggart, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 envelope (E) protein interacts with PDZ-Domain-2 of host tight junction protein ZO1. BioRxiv Prepr Serv. Biol. 2020.12.22.422708 https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.22.422708 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1004320",
"author": "JM Jimenez-Guardeño",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1004320",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "31755_CR21",
"unstructured": "Jimenez-Guardeño, J. M. et al. The PDZ-binding motif of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus envelope protein is a determinant of viral pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 10, e1004320 (2014).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2024.12.10.627528",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "31755_CR22",
"unstructured": "Alvarez, F. et al. The SARS-CoV-2 envelope PDZ Binding Motif acts as a virulence factor disrupting host’s epithelial cell-cell junctions. 12.10.627528 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.10.627528 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.03136-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "31755_CR23",
"unstructured": "Honrubia, J. M. et al. SARS-CoV-2-mediated lung edema and replication are diminished by cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator modulators. mBio. 14, e0313622 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.829094",
"author": "Y Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "829094",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "31755_CR24",
"unstructured": "Zhu, Y. et al. Interactions of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 protein E with cell junctions and Polarity PSD-95/Dlg/ZO-1-Containing proteins. Front. Microbiol. 13, 829094 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-021-02250-7",
"author": "A Javorsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "724",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "31755_CR25",
"unstructured": "Javorsky, A., Humbert, P. O. & Kvansakul, M. Structural basis of coronavirus E protein interactions with human PALS1 PDZ domain. Commun. Biol. 4, 724 (2021).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-23533-x",
"author": "J Chai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3433",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "31755_CR26",
"unstructured": "Chai, J. et al. Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein recognition of human cell junction protein PALS1. Nat. Commun. 12, 3433 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00110-21",
"author": "S Deinhardt-Emmer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00110",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "31755_CR27",
"unstructured": "Deinhardt-Emmer, S. et al. SARS-CoV-2 causes severe epithelial inflammation and barrier dysfunction. J. Virol. 95, e00110–e00121 (2021). JVI.00110 – 21.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24521-x",
"author": "R Robinot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4354",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "31755_CR28",
"unstructured": "Robinot, R. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the dedifferentiation of multiciliated cells and impairs mucociliary clearance. Nat. Commun. 12, 4354 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0",
"author": "MM Lamers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "31755_CR29",
"unstructured": "Lamers, M. M. & Haagmans, B. L. SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 270–284 (2022).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-024-01753-z",
"author": "JB Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "74",
"journal-title": "Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "31755_CR30",
"unstructured": "Xu, J. B. et al. SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein impairs airway epithelial barrier function and exacerbates airway inflammation via increased intracellular Cl- concentration. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 9, 74 (2024).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acschembio.0c00179",
"author": "N Bosc",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1566",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Biol.",
"key": "31755_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bosc, N. et al. Fr-PPIChem: an academic compound library dedicated to Protein-Protein interactions. ACS Chem. Biol. 15, 1566–1574 (2020).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M707255200",
"author": "AS Fanning",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "37710",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "31755_CR32",
"unstructured": "Fanning, A. S., Lye, M. F., Anderson, J. M. & Lavie, A. Domain swapping within PDZ2 is responsible for dimerization of ZO proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 37710–37716 (2007).",
"volume": "282",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/emboj.2008.138",
"author": "J Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2113",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "31755_CR33",
"unstructured": "Chen, J., Pan, L., Wei, Z., Zhao, Y. & Zhang, M. Domain-swapped dimerization of ZO-1 PDZ2 generates specific and regulatory connexin43-binding sites. EMBO J. 27, 2113–2123 (2008).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/108705719900400206",
"author": "JH Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "J. Biomol. Screen.",
"key": "31755_CR34",
"unstructured": "Zhang, J. H., Chung, T. D. & Oldenburg, K. R. A simple statistical parameter for use in evaluation and validation of high throughput screening assays. J. Biomol. Screen. 4, 67–73 (1999).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1261/rna.1563609",
"author": "PT Lang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1219",
"journal-title": "RNA",
"key": "31755_CR35",
"unstructured": "Lang, P. T. et al. DOCK 6: combining techniques to model RNA–small molecule complexes. RNA 15, 1219–1230 (2009).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"author": "A Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "31755_CR36",
"unstructured": "Gupta, A. et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Med. 26, 1017–1032 (2020).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12974-022-02579-8",
"author": "Y Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "222",
"journal-title": "J. Neuroinflammation",
"key": "31755_CR37",
"unstructured": "Chen, Y., Yang, W., Chen, F. & Cui, L. COVID-19 and cognitive impairment: neuroinvasive and blood–brain barrier dysfunction. J. Neuroinflammation. 19, 222 (2022).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s003950050205",
"author": "HJ Schnittler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "30",
"issue": "Suppl 3",
"journal-title": "Basic. Res. Cardiol.",
"key": "31755_CR38",
"unstructured": "Schnittler, H. J. Structural and functional aspects of intercellular junctions in vascular endothelium. Basic. Res. Cardiol. 93 (Suppl 3), 30–39 (1998).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.00155.2015",
"author": "CH Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "C600",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol.",
"key": "31755_CR39",
"unstructured": "Chen, C. H. et al. The connexin 43/ZO-1 complex regulates cerebral endothelial F-actin architecture and migration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 309, C600–607 (2015).",
"volume": "309",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "P Weber",
"first-page": "4451",
"journal-title": "Mol. Basel Switz.",
"key": "31755_CR40",
"unstructured": "Weber, P. et al. High-Throughput crystallization pipeline at the crystallography core facility of the Institut Pasteur. Mol. Basel Switz. 24, 4451 (2019).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444909047337",
"author": "WXDS Kabsch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "31755_CR41",
"unstructured": "Kabsch, W. X. D. S. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 125–132 (2010).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444906045975",
"author": "AJ McCoy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "31755_CR42",
"unstructured": "McCoy, A. J. Solving structures of protein complexes by molecular replacement with phaser. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 63, 32–41 (2007).",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444910007493",
"author": "P Emsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "486",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "31755_CR43",
"unstructured": "Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., Scott, W. G. & Cowtan, K. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 486–501 (2010).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444909052925",
"author": "PD Adams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "213",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "31755_CR44",
"unstructured": "Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: a comprehensive python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 (2010).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/minf.201700023",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "31755_CR45",
"unstructured": "Gally, J. M., Bourg, S., Do, Q. T., Aci-Sèche, S. & Bonnet, P. VSPrep: A general KNIME workflow for the Preparation of molecules for virtual screening. Mol. Inform. 36, (2017)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/0929867326666190614160451",
"author": "JM Gally",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6480",
"journal-title": "Curr. Med. Chem.",
"key": "31755_CR46",
"unstructured": "Gally, J. M. et al. VSPrep: A KNIME workflow for the preparation of molecular databases for virtual screening. Curr. Med. Chem. 27, 6480–6494 (2020).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1098/rsif.2013.0860",
"author": "V Hamon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20130860",
"journal-title": "J. R. Soc. Interface",
"key": "31755_CR47",
"unstructured": "Hamon, V. et al. 2P2IHUNTER: a tool for filtering orthosteric protein–protein interaction modulators via a dedicated support vector machine. J. R Soc. Interface. 11, 20130860 (2014).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jm901137j",
"author": "JB Baell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2719",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "31755_CR48",
"unstructured": "Baell, J. B. & Holloway, G. A. New substructure filters for removal of Pan assay interference compounds (PAINS) from screening libraries and for their exclusion in bioassays. J. Med. Chem. 53, 2719–2740 (2010).",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "RC Glem",
"first-page": "199",
"journal-title": "IDrugs Investig. Drugs J.",
"key": "31755_CR49",
"unstructured": "Glem, R. C. et al. Circular fingerprints: flexible molecular descriptors with applications from physical chemistry to ADME. IDrugs Investig. Drugs J. 9, 199–204 (2006).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/ci9803381",
"author": "D Butina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci.",
"key": "31755_CR50",
"unstructured": "Butina, D. Unsupervised data base clustering based on daylight’s fingerprint and Tanimoto similarity: A fast and automated way to cluster small and large data sets. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 39, 747–750 (1999).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20084",
"author": "EF Pettersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "31755_CR51",
"unstructured": "Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612 (2004).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1758-2946-3-33",
"author": "NM O’Boyle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "J. Cheminform.",
"key": "31755_CR52",
"unstructured": "O’Boyle, N. M. et al. Open babel: an open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 3, 33 (2011).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-40228-7",
"author": "GD de Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4485",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "31755_CR53",
"unstructured": "de Melo, G. D. et al. Neuroinvasion and anosmia are independent phenomena upon infection with SARS-CoV-2 and its variants. Nat. Commun. 14, 4485 (2023).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-31755-y"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "HTRF-based identification of small molecules targeting SARS-CoV-2 E protein interaction with ZO-1 PDZ2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "16"
}