Strain-Specific Variability in Viral Kinetics, Cytokine Response, and Cellular Damage in Air–Liquid Cultures of Human Nasal Organoids After Infection with SARS-CoV-2
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17101343, Oct 2025
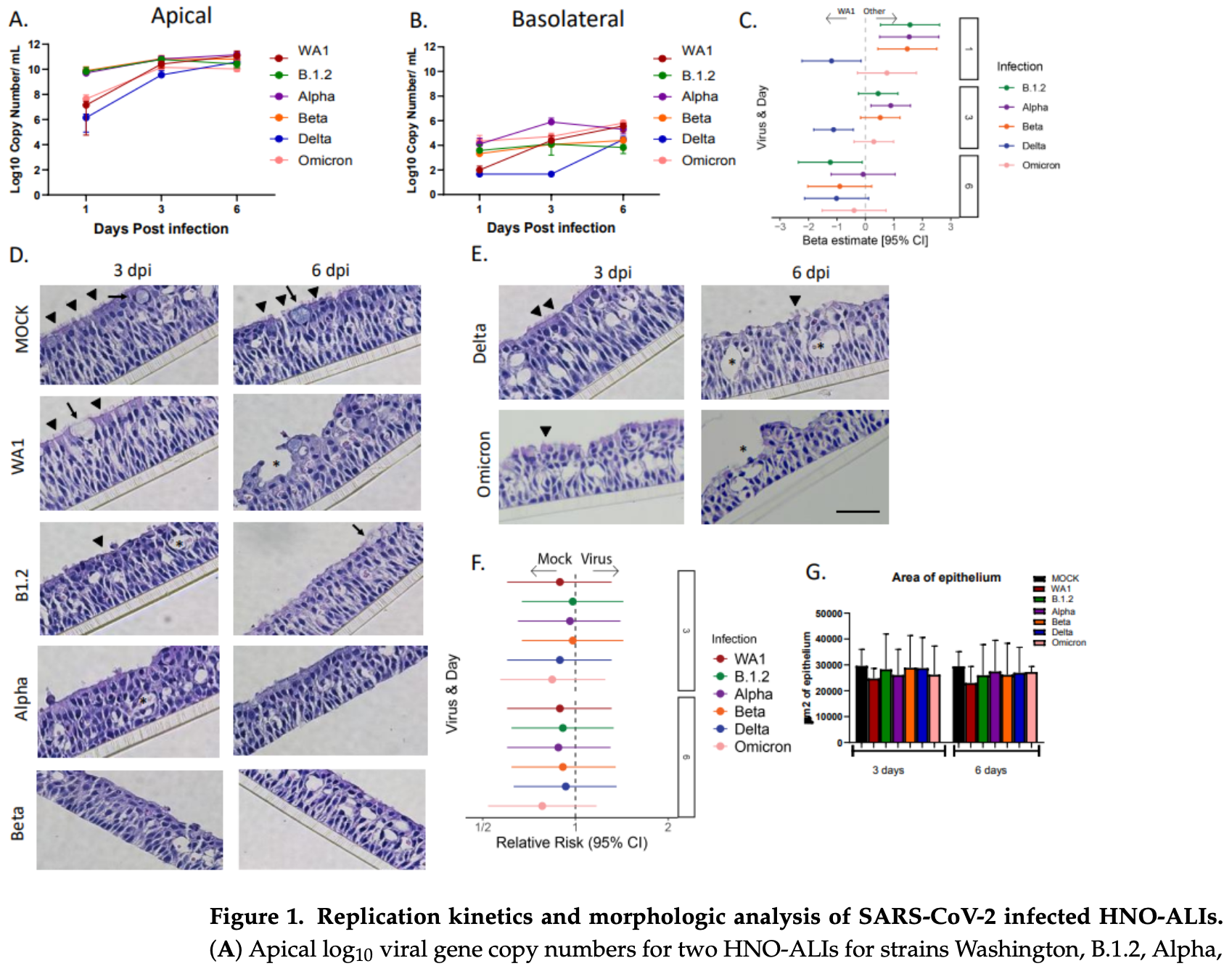
Ex vivo study comparing the viral kinetics, immune response, and cellular damage of six different SARS-CoV-2 strains (B.1.2, WA1, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Omicron) in human nasal organoid air-liquid interface (HNO-ALI) cultures. Authors found that the Delta variant employs a unique "stealth" strategy, showing delayed replication kinetics and a dampened innate immune response compared to the other variants. While most variants reached peak viral load by 3 days post-infection, Delta took 6 days to reach a similar level. The WA1, Alpha, Beta, and Omicron variants induced robust pro-inflammatory and chemoattractant cytokine responses, but the Delta variant did not significantly induce key cytokines such as IL-6, IP-10, CXCL9, or CXCL11. All variants caused significant damage to ciliated cells, though the Delta and WA1 strains appeared less destructive at early time points.
Aloisio et al., 6 Oct 2025, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
Contact: ppiedra@bcm.edu (corresponding author), gina.aloisio@bcm.edu, avadhanu@bcm.edu.
Ex vivo studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Strain-Specific Variability in Viral Kinetics, Cytokine Response, and Cellular Damage in Air–Liquid Cultures of Human Nasal Organoids After Infection with SARS-CoV-2
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17101343
SARS-CoV-2 variants have demonstrated distinct epidemiological patterns and clinical presentations throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding variant-specific differences at the respiratory epithelium is crucial for understanding their pathogenesis. Here, we utilized human nasal organoid air-liquid interface (HNO-ALI) cell cultures to compare the viral replication kinetics, innate immune response, and epithelial damage of six different strains of SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.2, WA, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Omicron). All variants replicated efficiently in HNO-ALIs, but with distinct replication kinetic patterns. The Delta variant exhibited delayed replication kinetics, achieving a steady state at 6 days post-infection compared to 3 days for other variants. Cytokine analysis revealed robust pro-inflammatory and chemoattractant responses (IL-6, IL-8, IP-10, CXCL9, and CXCL11) in WA1, Alpha, Beta, and Omicron infections, while Delta significantly dampened the innate immune response, with no significant induction of IL-6, IP-10, CXCL9, or CXCL11. Immunofluorescence and H&E analysis showed that all variants caused significant ciliary damage, though WA1 and Delta demonstrated less destruction at early time points (3 days post-infection). Together, these data show that, in our HNO-ALI model, the Delta variant employs a distinct "stealth" strategy characterized by delayed replication kinetics and epithelial cell innate immune evasion when compared to other variants of SARS-CoV-2, potentially explaining a mechanism that the Delta variant can use for its enhanced transmissibility and virulence observed clinically. Our findings demonstrate that variant-specific differences at the respiratory epithelium could explain some of the distinct clinical presentations and highlight the utility of the HNO-ALI system for the rapid assessment of emerging variants.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v17101343/s1 . File S1: Supplementary Figures; File S2: Supplementary Data. Author Contributions: G.M.A. designed the project, performed experiments, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript draft. T.J.M., L.A., E.M.S., A.M.M. and A.R. performed infections, viral kinetics and cytokine measurements, and imaging, and edited the manuscript. E.G.N. consented subjects, obtained nasal washes from subjects, and edited the manuscript. D.H. and L.F.-S. performed the statistical analysis and edited the manuscript. A.K. provided organoid cultures and edited the manuscript. H.L.J., E.A.M. and F.S. performed microscopy and edited the manuscript. S.E.B. supervised established organoid cultures and edited the manuscript. P.A.P. and V.A. designed the project, analyzed data, obtained funding, and wrote and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Ahn, Kim, Hong, Choi, Yang et al., Nasal ciliated cells are primary targets for SARS-CoV-2 replication in the early stage of COVID-19, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI148517
Aloisio, Nagaraj, Murray, Schultz, Mcbride et al., Infant-derived human nasal organoids exhibit relatively increased susceptibility, epithelial responses, and cytotoxicity during RSV infection, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106305
Anderberg, Luther, Berglund, Larsson, Rubertsson et al., Increased levels of plasma cytokines and correlations to organ failure and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155389
Atherstone, Guagliardo, Hawksworth, O'laughlin, Wong et al., COVID-19 Epidemiology during Delta Variant Dominance Period in 45 High-Income Countries, 2020-2021, Emerg. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2909.230142
Avadhanula, Nicholson, Ferlic-Stark, Piedra, Blunck et al., Viral Load of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Adults During the First and Second Wave of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in Houston, Texas: The Potential of the Superspreader, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab097
Bast, Tang, Dahn, Palacio, Increased risk of hospitalisation and death with the delta variant in the USA, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00685-X
Bloom, Drake, Docherty, Lipworth, Johnston et al., Risk of adverse outcomes in patients with underlying respiratory conditions admitted to hospital with COVID-19: A national, multicentre prospective cohort study using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00013-8
Cao, Wang, Jian, Xiao, Song et al., Omicron Escapes the Majority of Existing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3
Chen, Liu, Wang, Liu, Zhao et al., SARS-CoV-2 activates lung epithelial cell proinflammatory signaling and leads to immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103500
Chiu, Li, Liu, Song, Wan et al., Human Nasal Organoids Model SARS-CoV-2 Upper Respiratory Infection and Recapitulate the Differential Infectivity of Emerging Variants, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01944-22
Choi, Smith, SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern, Yonsei Med. J, doi:10.3349/ymj.2021.62.11.961
Davies, Abbott, Barnard, Jarvis, Kucharski et al., Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abg3055
Furnon, Cowton, De Lorenzo, Orton, Herder et al., Phenotypic evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-024-01878-5
Hasegawa, Hato, Okayama, Ikeo, Miyamoto et al., Th1 cytokine endotype discriminates and predicts severe complications in COVID-19, Eur. Cytokine Netw, doi:10.1684/ecn.2022.0477
Huang, Liu, Sun, Li, IL-10 Served as an Indicator in Severe COVID-19 Patients, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26580
Hui, Ho, Cheung, Ng, Ching et al., SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6
Hysenaj, Little, Kulhanek, Magnen, Bahl et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of airway organoids reveals conserved use of Tetraspanin-8 by Ancestral, Delta, and Omicron variants, Stem Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.01.011
Ju, Zheng, Guo, Fan, Li et al., Immune escape by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and structural basis of its effective neutralization by a broad neutralizing human antibody VacW-209, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-022-00638-6
Korobova, Arsentieva, Liubimova, Dedkov, Gladkikh et al., A Comparative Study of the Plasma Chemokine Profile in COVID-19 Patients Infected with Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23169058
Li, Huang, Yu, Wan, Chiu et al., Human airway and nasal organoids reveal escalating replicative fitness of SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2300376120
Liao, Liu, Yuan, Wen, Xu et al., Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0901-9
Lowery, Sariol, Perlman, Innate immune and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2: Implications for COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2021.05.004
Masui, Hashimoto, Matsumura, Yamamoto, Nagao et al., Micro-patterned culture of iPSC-derived alveolar and airway cells distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 variants, Stem Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.02.011
Mathieu, Ritchie, Rodés-Guirao, Appel, Giattino et al., Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19
Maxwell, Ding, You, Dong, Chehade et al., Identification of key signaling pathways induced by SARS-CoV2 that underlie thrombosis and vascular injury in COVID-19 patients, J. Leukoc. Biol, doi:10.1002/JLB.4COVR0920-552RR
Meganck, Edwards, Mallory, Lee, Dang et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern fitness and adaptation in primary human airway epithelia, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114076
Mlcochova, Kemp, Dhar, Papa, Meng et al., SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03944-y
Neufeldt, Cerikan, Cortese, Frankish, Lee et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a pro-inflammatory cytokine response through cGAS-STING and NF-κB, Commun. Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-021-02983-5
Nilsson-Payant, Uhl, Grimont, Doane, Cohen et al., The NF-κB Transcriptional Footprint Is Essential for SARS-CoV-2 Replication, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01257-21
Osan, Talukdar, Feldmann, Demontigny, Jerome et al., Goblet Cell Hyperplasia Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Microbiol. Spectr, doi:10.1128/spectrum.00459-22
Pum, Ennemoser, Adage, Kungl, Cytokines and Chemokines in SARS-CoV-2 Infections-Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Cytokine Storm, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11010091
Qin, Xiang, Su, Sun, Liu, Activation of the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.595342
Rajan, Piedra, Aideyan, Mcbride, Robertson et al., Multiple Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Strains Infecting HEp-2 and A549 Cells Reveal Cell Line-Dependent Differences in Resistance to RSV Infection, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.01904-21
Rajan, Weaver, Aloisio, Jelinski, Johnson et al., The Human Nose Organoid Respiratory Virus Model: An Ex Vivo Human Challenge Model To Study Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Pathogenesis and Evaluate Therapeutics, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.03511-21
Raychaudhuri, Bandopadhyay, Sarif, Mehta, Liu et al., Circulating Interleukin-8 Dynamics Parallels Disease Course and Is Linked to Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15020549
Robinot, Hubert, De Melo, Lazarini, Bruel et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the dedifferentiation of multiciliated cells and impairs mucociliary clearance, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24521-x
Saito, Horie, Nagase, TGF-β Signaling in Lung Health and Disease, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19082460
Saito, Irie, Suzuki, Maemura, Nasser et al., Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04266-9
Schindelin, Arganda-Carreras, Frise, Kaynig, Longair et al., Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis, Nat. Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.2019
Shi, Chaiwun, Young, Cote, Taylor, Antigen retrieval technique utilizing citrate buffer or urea solution for immunohistochemical demonstration of androgen receptor in formalin-fixed paraffin sections, J. Histochem. Cytochem, doi:10.1177/41.11.7691930
Shuai, Chan, Hu, Chai, Yuen et al., Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5
Steiner, Kratzel, Barut, Lang, Moreira et al., SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z
Suzuki, Yamasoba, Kimura, Wang, Kishimoto et al., Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1
Tanneti, Patel, Tan, Marques, Perera et al., Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in primary human nasal cultures demonstrates Delta as most cytopathic and Omicron as fastest replicating, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.03129-23
Tran, Grimley, Mcauley, Hachani, Earnest et al., Air-Liquid-Interface Differentiated Human Nose Epithelium: A Robust Primary Tissue Culture Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23020835
Twohig, Nyberg, Zaidi, Thelwall, Sinnathamby et al., Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: A cohort study, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8
Valle, Kim-Schulze, Huang, Beckmann, Nirenberg et al., An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival, Nat. Med
Wang, Liu, Miao, Kong, Zhao et al., Therapeutic targeting of interleukin-6 for the treatment of COVID-19, Eur. Cytokine Netw
Wang, Long, Wang, Li, Liu, Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 recombinants and emerging Omicron sublineages, Int. J. Med Sci, doi:10.7150/ijms.79116
Wu, Lidsky, Xiao, Cheng, Lee et al., SARS-CoV-2 replication in airway epithelia requires motile cilia and microvillar reprogramming, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.030
Xiong, Liu, Cao, Wang, Guo et al., Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1747363
Yang, Han, Nilsson-Payant, Gupta, Wang et al., A Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-based Platform to Study SARS-CoV-2 Tropism and Model Virus Infection in Human Cells and Organoids, Cell Stem Cell, doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.06.015
Yang, Shen, Li, Yuan, Wei et al., Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.027
Yang, Yang, Wang, Zhou, Xin et al., Clinical characteristics of 310 SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant patients and comparison with Delta and Beta variant patients in China, Virol. Sin, doi:10.1016/j.virs.2022.07.014
Zhou, Ren, Zhang, Zhong, Xiao et al., Heightened Innate Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of COVID-19 Patients, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v17101343",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v17101343",
"abstract": "<jats:p>SARS-CoV-2 variants have demonstrated distinct epidemiological patterns and clinical presentations throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Understanding variant-specific differences at the respiratory epithelium is crucial for understanding their pathogenesis. Here, we utilized human nasal organoid air–liquid interface (HNO-ALI) cell cultures to compare the viral replication kinetics, innate immune response, and epithelial damage of six different strains of SARS-CoV-2 (B.1.2, WA, Alpha, Beta, Delta, and Omicron). All variants replicated efficiently in HNO-ALIs, but with distinct replication kinetic patterns. The Delta variant exhibited delayed replication kinetics, achieving a steady state at 6 days post-infection compared to 3 days for other variants. Cytokine analysis revealed robust pro-inflammatory and chemoattractant responses (IL-6, IL-8, IP-10, CXCL9, and CXCL11) in WA1, Alpha, Beta, and Omicron infections, while Delta significantly dampened the innate immune response, with no significant induction of IL-6, IP-10, CXCL9, or CXCL11. Immunofluorescence and H&E analysis showed that all variants caused significant ciliary damage, though WA1 and Delta demonstrated less destruction at early time points (3 days post-infection). Together, these data show that, in our HNO-ALI model, the Delta variant employs a distinct “stealth” strategy characterized by delayed replication kinetics and epithelial cell innate immune evasion when compared to other variants of SARS-CoV-2, potentially explaining a mechanism that the Delta variant can use for its enhanced transmissibility and virulence observed clinically. Our findings demonstrate that variant-specific differences at the respiratory epithelium could explain some of the distinct clinical presentations and highlight the utility of the HNO-ALI system for the rapid assessment of emerging variants.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v17101343"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0710-5094",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aloisio",
"given": "Gina M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "McBride",
"given": "Trevor J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Aideyan",
"given": "Letisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1202-198X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schultz",
"given": "Emily M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9256-8071",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Murray",
"given": "Ashley M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Rajan",
"given": "Anubama",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Nicholson",
"given": "Erin G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Henke",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ferlic-Stark",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kambal",
"given": "Amal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Technology Cores, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Hannah L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Technology Cores, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Mosa",
"given": "Elina A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6029-5478",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Advanced Technology Cores, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Stossi",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Blutt",
"given": "Sarah E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Piedra",
"given": "Pedro A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Virology and Microbiology, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX 77030, USA"
}
],
"family": "Avadhanula",
"given": "Vasanthi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.mdpi.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-06T13:33:41Z",
"timestamp": 1759757621000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-06T13:49:14Z",
"timestamp": 1759758554000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"U19AI116497",
"U19AI144297"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"award": [
"DK056338"
],
"name": "Texas Medical Center Digestive Diseases Center (DDC) under the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases"
},
{
"name": "Integrated Microscopy Core at Baylor College of Medicine and the Center for Advanced Microscopy and Image Informatics"
},
{
"award": [
"DK56338",
"CA125123",
"ES030285",
"S10OD030414"
],
"name": "NIH"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004917",
"award": [
"RP150578",
"RP170719"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/100004917",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "CPRIT"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-07T00:41:40Z",
"timestamp": 1759797700134,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1759708800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/10/1343/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1343",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Mathieu, E., Ritchie, H., Rodés-Guirao, L., Appel, C., Giattino, C., Hasell, J., Macdonald, B., Dattani, S., Beltekian, D., and Ortiz-Ospina, E. (2025, October 01). Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19). Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions",
"author": "Steiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-024-01878-5",
"article-title": "Phenotypic evolution of SARS-CoV-2 spike during the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Furnon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "(2025, October 01). World Health Organization 2023 data.who.int WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19."
},
{
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "CDC (2025, October 01). CDC Museum COVID-19 Timeline, Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abg3055",
"article-title": "Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England",
"author": "Davies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabg3055",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3349/ymj.2021.62.11.961",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "961",
"journal-title": "Yonsei Med. J.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2909.230142",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Epidemiology during Delta Variant Dominance Period in 45 High-Income Countries, 2020–2021",
"author": "Atherstone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1757",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00685-X",
"article-title": "Increased risk of hospitalisation and death with the delta variant in the USA",
"author": "Bast",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1629",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"article-title": "Omicron Escapes the Majority of Existing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.79116",
"article-title": "Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 recombinants and emerging Omicron sublineages",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Med Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virs.2022.07.014",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 310 SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant patients and comparison with Delta and Beta variant patients in China",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "704",
"journal-title": "Virol. Sin.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-022-00638-6",
"article-title": "Immune escape by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant and structural basis of its effective neutralization by a broad neutralizing human antibody VacW-209",
"author": "Ju",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.06.015",
"article-title": "A Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-based Platform to Study SARS-CoV-2 Tropism and Model Virus Infection in Human Cells and Organoids",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03944-y",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 B.1.617.2 Delta variant replication and immune evasion",
"author": "Mlcochova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "599",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.03511-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Rajan, A., Weaver, A.M., Aloisio, G.M., Jelinski, J., Johnson, H.L., Venable, S.F., McBride, T., Aideyan, L., Piedra, F.-A., and Ye, X. (2022). The Human Nose Organoid Respiratory Virus Model: An Ex Vivo Human Challenge Model To Study Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Pathogenesis and Evaluate Therapeutics. mBio, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01944-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Chiu, M.C., Li, C., Liu, X., Song, W., Wan, Z., Yu, Y., Huang, J., Xiao, D., Chu, H., and Cai, J.-P. (2022). Human Nasal Organoids Model SARS-CoV-2 Upper Respiratory Infection and Recapitulate the Differential Infectivity of Emerging Variants. mBio, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23020835",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Tran, B.M., Grimley, S.L., McAuley, J.L., Hachani, A., Earnest, L., Wong, S.L., Caly, L., Druce, J., Purcell, D.F.J., and Jackson, D.C. (2022). Air-Liquid-Interface Differentiated Human Nose Epithelium: A Robust Primary Tissue Culture Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04442-5",
"article-title": "Attenuated replication and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron",
"author": "Shuai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04462-1",
"article-title": "Attenuated fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant",
"author": "Suzuki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "700",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.02.011",
"article-title": "Micro-patterned culture of iPSC-derived alveolar and airway cells distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Masui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2300376120",
"article-title": "Human airway and nasal organoids reveal escalating replicative fitness of SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2300376120",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01904-21",
"article-title": "Multiple Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Strains Infecting HEp-2 and A549 Cells Reveal Cell Line-Dependent Differences in Resistance to RSV Infection",
"author": "Rajan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0190421",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2024.106305",
"article-title": "Infant-derived human nasal organoids exhibit relatively increased susceptibility, epithelial responses, and cytotoxicity during RSV infection",
"author": "Aloisio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106305",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab097",
"article-title": "Viral Load of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Adults During the First and Second Wave of Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in Houston, Texas: The Potential of the Superspreader",
"author": "Avadhanula",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1528",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/41.11.7691930",
"article-title": "Antigen retrieval technique utilizing citrate buffer or urea solution for immunohistochemical demonstration of androgen receptor in formalin-fixed paraffin sections",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1599",
"journal-title": "J. Histochem. Cytochem.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "41",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.2019",
"article-title": "Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis",
"author": "Schindelin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1684/ecn.2022.0477",
"article-title": "Th1 cytokine endotype discriminates and predicts severe complications in COVID-19",
"author": "Hasegawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. Cytokine Netw.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0901-9",
"article-title": "Single-cell landscape of bronchoalveolar immune cells in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Liao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "842",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103500",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Chen, H., Liu, W., Wang, Y., Liu, D., Zhao, L., and Yu, J. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 activates lung epithelial cell proinflammatory signaling and leads to immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients. EBioMedicine, 70."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.05.004",
"article-title": "Innate immune and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2: Implications for COVID-19",
"author": "Lowery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1052",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1747363",
"article-title": "Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "761",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11010091",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Pum, A., Ennemoser, M., Adage, T., and Kungl, A.J. (2021). Cytokines and Chemokines in SARS-CoV-2 Infections—Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Cytokine Storm. Biomolecules, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JLB.4COVR0920-552RR",
"article-title": "Identification of key signaling pathways induced by SARS-CoV2 that underlie thrombosis and vascular injury in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Maxwell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "J. Leukoc. Biol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00013-8",
"article-title": "Risk of adverse outcomes in patients with underlying respiratory conditions admitted to hospital with COVID-19: A national, multicentre prospective cohort study using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK",
"author": "Drake",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "699",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.01.011",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of airway organoids reveals conserved use of Tetraspanin-8 by Ancestral, Delta, and Omicron variants",
"author": "Hysenaj",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "636",
"journal-title": "Stem Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.03129-23",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_38",
"unstructured": "Tanneti, N.S., Patel, A.K., Tan, L.H., Marques, A.D., Perera, R.A.P.M., Sherrill-Mix, S., Kelly, B.J., Renner, D.M., Collman, R.G., and Rodino, K. (2024). Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in primary human nasal cultures demonstrates Delta as most cytopathic and Omicron as fastest replicating. mBio, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114076",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern fitness and adaptation in primary human airway epithelia",
"author": "Meganck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "114076",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26580",
"article-title": "IL-10 Served as an Indicator in Severe COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.027",
"article-title": "Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Wang, Y., Liu, C., Miao, X., Kong, D., Zhao, Y., Gong, W., and Ding, X. (2020). Therapeutic targeting of interleukin-6 for the treatment of COVID-19. Eur. Cytokine Netw., 1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.595342",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "Qin, Z., Xiang, K., Su, D.-F., Sun, Y., and Liu, X. (2021). Activation of the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for COVID-19. Front. Immunol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.04.017",
"article-title": "Heightened Innate Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "883",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155389",
"article-title": "Increased levels of plasma cytokines and correlations to organ failure and 30-day mortality in critically ill Covid-19 patients",
"author": "Anderberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155389",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15020549",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "D’rozario, R., Raychaudhuri, D., Bandopadhyay, P., Sarif, J., Mehta, P., Liu, C.S.C., Sinha, B.P., Roy, J., Bhaduri, R., and Das, M. (2023). Circulating Interleukin-8 Dynamics Parallels Disease Course and Is Linked to Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19. Viruses, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23169058",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Korobova, Z.R., Arsentieva, N.A., Liubimova, N.E., Dedkov, V.G., Gladkikh, A.S., Sharova, A.A., Chernykh, E.I., Kashchenko, V.A., Ratnikov, V.A., and Gorelov, V.P. (2022). A Comparative Study of the Plasma Chemokine Profile in COVID-19 Patients Infected with Different SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00475-8",
"article-title": "Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: A cohort study",
"author": "Nyberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04266-9",
"article-title": "Enhanced fusogenicity and pathogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Delta P681R mutation",
"author": "Saito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01257-21",
"article-title": "The NF-κB Transcriptional Footprint Is Essential for SARS-CoV-2 Replication",
"author": "Uhl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0125721",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-021-02983-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection induces a pro-inflammatory cytokine response through cGAS-STING and NF-κB",
"author": "Neufeldt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19082460",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_52",
"unstructured": "Saito, A., Horie, M., and Nagase, T. (2018). TGF-β Signaling in Lung Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24521-x",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the dedifferentiation of multiciliated cells and impairs mucociliary clearance",
"author": "Robinot",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI148517",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Ahn, J.H., Kim, J.M., Hong, S.P., Choi, S.Y., Yang, M.J., Ju, Y.S., Kim, Y.T., Kim, H.M., Rahman, T., and Chung, M.K. (2021). Nasal ciliated cells are primary targets for SARS-CoV-2 replication in the early stage of COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig., 131."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.11.030",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 replication in airway epithelia requires motile cilia and microvillar reprogramming",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.00459-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_56",
"unstructured": "Osan, J., Talukdar, S.N., Feldmann, F., DeMontigny, B.A., Jerome, K., Bailey, K.L., Feldmann, H., and Mehedi, M. (2022). Goblet Cell Hyperplasia Increases SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Microbiol. Spectr., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-1051-9",
"article-title": "An inflammatory cytokine signature predicts COVID-19 severity and survival",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1636",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/17/10/1343"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Strain-Specific Variability in Viral Kinetics, Cytokine Response, and Cellular Damage in Air–Liquid Cultures of Human Nasal Organoids After Infection with SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3390/mdpi_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "17"
}