Proton pump inhibitors and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients with COVID-19 infection
et al., Annals of Medicine, doi:10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581, Jun 2024
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
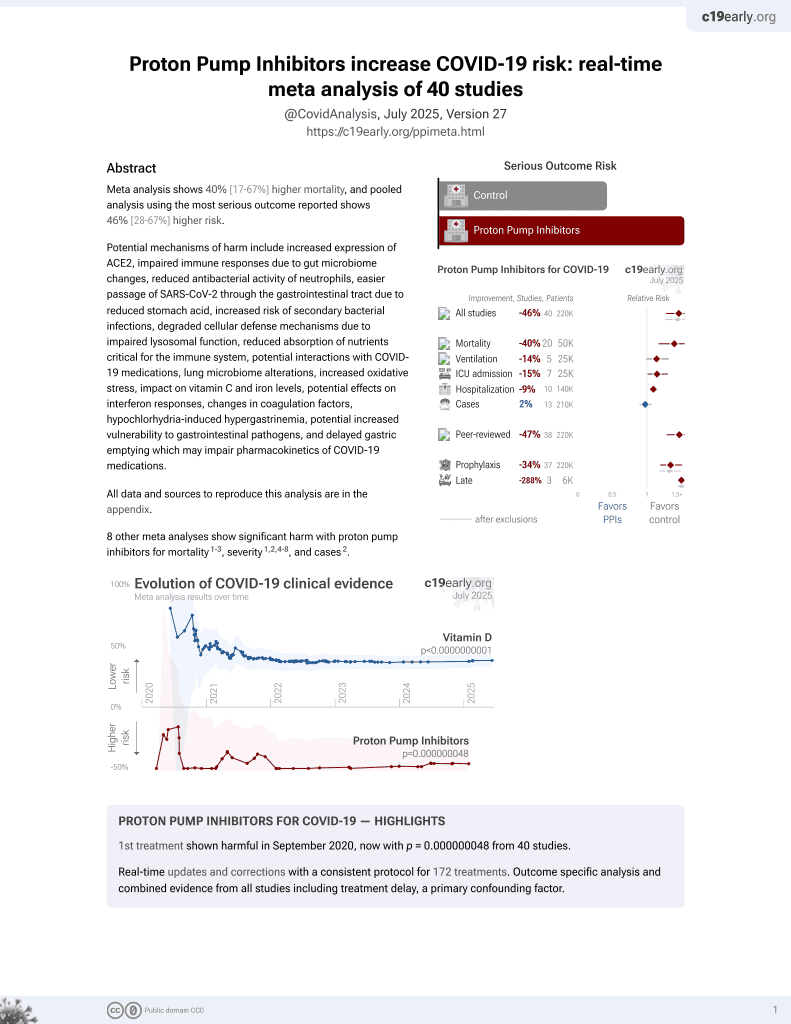
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
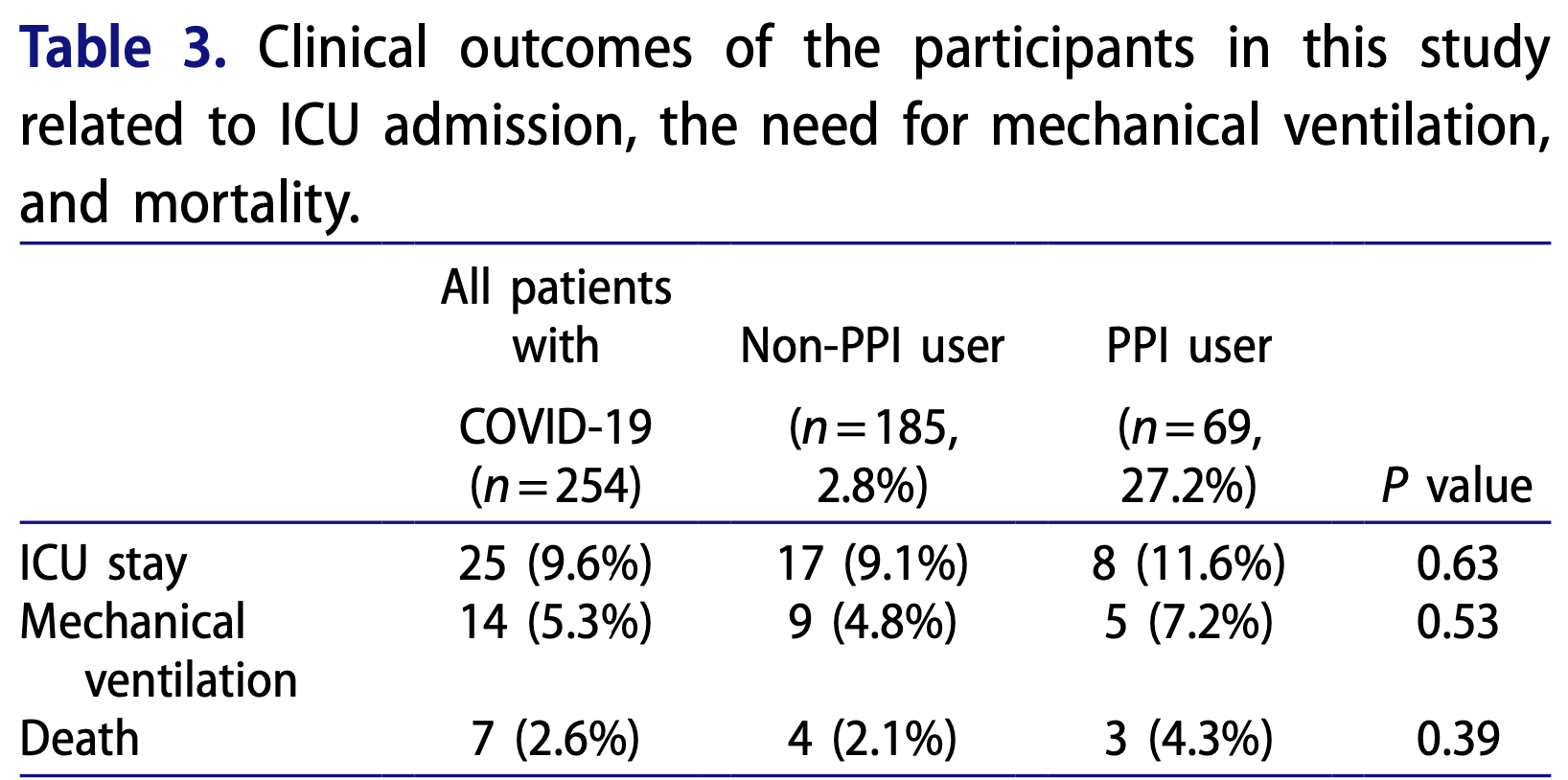
Retrospective 254 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Jordan showing higher rates of gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain and diarrhea with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use. There were no significant differences for mortality, ventilation, and ICU admission. Authors hypothesize that PPIs may facilitate SARS-CoV-2 survival and invasion in the gastrointestinal tract.
|
risk of death, 100% higher, RR 2.00, p = 0.39, treatment 3 of 69 (4.3%), control 4 of 184 (2.2%).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 48.1% higher, RR 1.48, p = 0.54, treatment 5 of 69 (7.2%), control 9 of 184 (4.9%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 25.5% higher, RR 1.25, p = 0.64, treatment 8 of 69 (11.6%), control 17 of 184 (9.2%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Al-Momani et al., 30 Jun 2024, retrospective, Jordan, peer-reviewed, mean age 59.7, 2 authors, study period 6 May, 2022 - 6 August, 2022.
Contact: hafez@hu.edu.jo.
Proton pump inhibitors and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients with COVID-19 infection
Annals of Medicine, doi:10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581
Introduction: the administration of proton pump inhibitors (PPis) is anticipated to elevate an individual's susceptibility to enteric infections as a result of altering the gut flora. the influence of PPis on the clinical manifestation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (saRs-coV-2) is still uncertain. this study aims to investigate the impact of PPi usage on the clinical manifestation of cOViD-19, namely its gastrointestinal symptoms. Methods: this is a cross-sectional cohort study involving cOViD-19 patients. Patients were interviewed using a predesigned questionnaire that asked about their demographics, clinical manifestations of cOViD-19 infection, and the extent and type of PPis in use. PPi usage was confirmed by reviewing patients' electronic medical records. the primary outcome was to establish any association between the use of PPi and the symptoms and clinical presentation of cOViD-19. Results: Out of a total of 254 participants, 69 (27.2%) were considered PPi users. Patients who were on PPi medications reported a significantly lower rate of myalgia (27.5% vs 51.9%; p = 0.0006) and heartburn (5.7% vs 15.6%; p = 0.03) but had a significantly higher rate of abdominal pain (27.5% vs 13.5%; p = 0.001) and diarrhoea (28.9% vs 14.5%, p = 0.02) when compared to those who were not using PPis. Patients on PPis were also shown to have significantly higher odds of developing diarrhoea (OR 2.0, 95% ci: 1.08 to 3.93, p = 0.02) and abdominal pain (OR 2.0, 95% ci: 1.22 to 3.93, p = 0.03), but a lower risk of developing myalgia (OR 0.5, 95% ci: 0.3 to 0.9, p = 0.02) when compared to non-PPi users. Conclusion: this study shows that the use of PPis could impact cOViD-19 clinical presentation toward more gastrointestinal manifestations. Further studies investigating the link between other acid suppression medications and cOViD-19 manifestations and severity should be carried out.
Ethical approval and consent to participate this study was granted ethical approval by the hashemite University and the Prince hamza hospital's ethics service committee with reference number 5/3/2020/2021. all experimental protocols were approved by hashemite University and the Prince hamza hospital's ethics service committee. all of the study participants have provided written informed consent prior to their induction into the study. all the methods were carried out in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Author contributions h. M was responsible for the study design, he analyzed data, prepared figures and co-wrote the manuscript. i. a: responsible for data analysis and co-wrote the manuscript.
Consent to publication
Not applicable
Disclosure statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Funding hashemite University (Jordan) provides the funding source for this research, h al-Momani received financial support from the Department of scientific research at the Jordanian hashemite University.
References
Arora, Gupta A, Golzy, Proton pump inhibitors are associated with increased risk of development of chronic kidney disease, BMc Nephrol, doi:10.1186/s12882-016-0325-4
Barabás, Pharmacological approach to gastric acid suppression: past, present, and future, Dig Dis, doi:10.1159/000505204
Biever, treatment with proton pump inhibitors increases the risk of secondary infections and aRDs in hospitalized patients with cOViD-19: coincidence or underestimated risk factor?, J intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13121
Bulthuis, tissue distribution of ace2 protein, the functional receptor for saRs coronavirus. a first step in understanding saRs pathogenesis, J Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.1570
Chan K-H, Zhang, Factors affecting stability and infectivity of saRs-coV-2, J hosp infect, doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.07.009
Chen, Deng, the presence of saRs-coV-2 RNa in the feces of cOViD-19 patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25825
Chen, Liu, Glass, Use of proton pump inhibitors and the risk of hospitalization for infectious gastroenteritis, Plos One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0168618
Dadras, Pashaei, the relationship between cOViD-19 viral load and disease severity: a systematic review, immun inflamm Dis, doi:10.1002/iid3.580
Debes, Proton pump inhibitors and mortality in individuals with cOViD-19, am J Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000992
Fatima, the use of proton pump inhibitors and cOViD-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, trop Med infect Dis, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed7030037
Ferrer Cb, Velasquez, association of Gastrointestinal Manifestations and laboratory abnormalities on clinical Outcomes of cOViD-19 Patients in a tertiary hospital, Biomed sci, doi:10.11648/j.bs.20220801.15
Furnari, side effects of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: practical considerations, Pol arch intern Med
Girleanu, Proton pump inhibitors therapy and risk of clostridium difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis, World J Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v23.i35.6500
Gu, Han, Wang, cOViD-19: gastrointestinal manifestations and potential fecal-oral transmission, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054
Hassing, Verbon, De Visser H, Proton pump inhibitors and gastroenteritis, eur J epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-016-0136-8
Kawaguchi, Proton pump inhibitors enhance intestinal permeability via dysbiosis of gut microbiota under stressed conditions in mice, Neurogastroenterol Motil, doi:10.1111/nmo.13841
Khraisat, Proton pump inhibitors: current use and the risk of coronavirus infectious disease 2019 development and its related mortality. Meta-analysis, arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.004
Ko Wc, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (saRs-coV-2) and coronavirus disease-2019 (cOViD-19): the epidemic and the challenges, int J antimicrob agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924
Macke, Koletzko, systematic review: the effects of proton pump inhibitors on the microbiome of the digestive tract-evidence from next-generation sequencing studies, aliment Pharmacol ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15604
Maes Ml, Fixen, adverse effects of proton-pump inhibitor use in older adults: a review of the evidence, ther adv Drug saf, doi:10.1177/2042098617715381
Matera, Will children reveal their secret? the coronavirus dilemma, eur Respiratory J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00749-2020
Me, Feinstone Sm, inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, saRs-coV, J Virol Methods, doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.006
Nobel, Mr, Relationship between body composition and death in patients with cOViD-19 differs based on the presence of gastrointestinal symptoms, Dig Dis sci, doi:10.1007/s10620-021-07324-4
Pan L, Mu, Yang, clinical characteristics of cOViD-19 patients with digestive symptoms in hubei, china: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, am J Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620
Restini C, Belavek T, Bernal, the significance of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ace2) in saRscov-2 infection and cOViD-19, cOViD, doi:10.2174/2666796701999201218141035
Savarino, Marabotto E, Zentilin, Proton pump inhibitors: use and misuse in the clinical setting, expert Rev clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1080/17512433.2018.1531703
Shin, Pharmacology of proton pump inhibitors, curr Gastroenterol Rep, doi:10.1007/s11894-008-0098-4
Strand Ds, Kim, Da, 25 Years of proton pump inhibitors: a comprehensive review, Gut liver, doi:10.5009/gnl15502
Tai, Me, Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the gastrointestinal tract, clin Med (lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2021-0039
Tariq, Gupta, association of gastric acid suppression with recurrent clostridium difficile infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JaMa intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0212
Ts, the use and misuse of proton pump inhibitors: an opportunity for deprescribing, J am Med Dir assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2020.09.046
Tseng C-Tk, Newman, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection of mice transgenic for the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 virus receptor, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01702-06
Villapol S, Gastrointestinal symptoms associated with cOViD-19: impact on the gut microbiome, transl Res, doi:10.1016/j.trsl.2020.08.004
Wang, Li, clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in wuhan, china, lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Wong, covid-19 and the digestive system, J Gastroenterol hepatol, doi:10.1111/jgh.15047
Xia, Shao, Guo, clinical and ct features in pediatric patients with cOViD-19 infection: different points from adults, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.24718
Xiao, the saRs-coV s glycoprotein: expression and functional characterization, Biochem Biophys Res commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.054
Yibirin, Oliveira, Valera, adverse effects associated with proton pump inhibitor use, cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.12759
Zhou L, Niu, Jiang, systemic analysis of tissue cells potentially vulnerable to saRs-coV-2 infection by the protein-proofed single-cell RNa profiling of ace2, tMPRss2 and furin proteases, BioRxiv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581",
"ISSN": [
"0785-3890",
"1365-2060"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=iann20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=iann20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-01-10"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-03-25"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-06-01"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2119-0811",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Pathology and Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Al-Momani",
"given": "Hafez",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anatomy, Physiology and Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, The Hashemite University, Zarqa, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Aolaymat",
"given": "Iman",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Annals of Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T23:01:17Z",
"timestamp": 1717282877000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-15T15:09:48Z",
"timestamp": 1721056188000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009697",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Hashemite University"
},
{
"name": "The Jordanian Hashemite University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T00:15:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721088900346
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717200000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25825",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01702-06",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5009/gnl15502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000505204",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17512433.2018.1531703",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-99067-1_22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2021-0039",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jamda.2020.09.046",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000992",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000993",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/tropicalmed7030037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.24718",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.13023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_22_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Side effects of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: practical considerations",
"author": "Castellana C",
"first-page": "541",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pol Arch Intern Med",
"key": "e_1_3_8_23_1",
"unstructured": "Castellana C, Pecere S, Furnari M, et al. Side effects of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: practical considerations. Pol Arch Intern Med. 2021;131(6):541–549.",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v23.i35.6500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nmo.13841",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12882-016-0325-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.12759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11894-008-0098-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/2666796701999201218141035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2020.07.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.06.028522",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.4745",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-016-0136-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.0212",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0168618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-021-07324-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.11648/j.bs.20220801.15",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13121",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2042098617715381",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00749-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MOG.0b013e328333d781",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15604",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2020.08.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.580",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_8_46_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/07853890.2024.2355581"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Proton pump inhibitors and gastrointestinal symptoms among patients with COVID-19 infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01",
"volume": "56"
}