High dose melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in intubated patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial
et al., Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, doi:10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012, May 2022
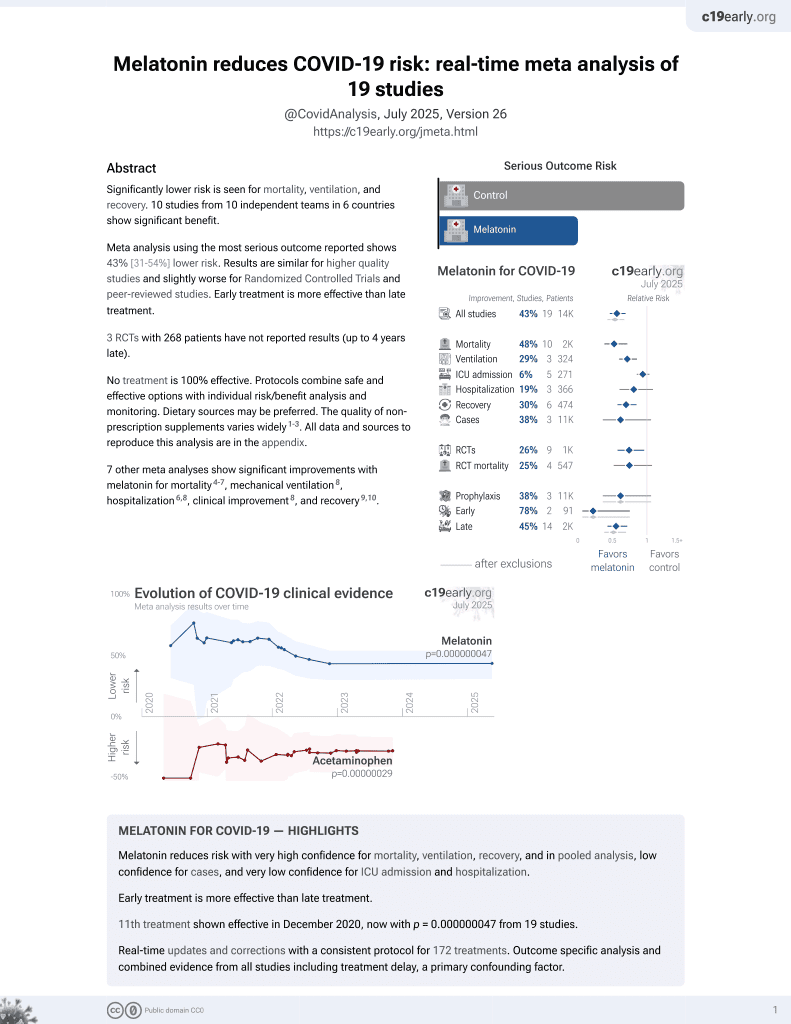
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000015 from 18 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
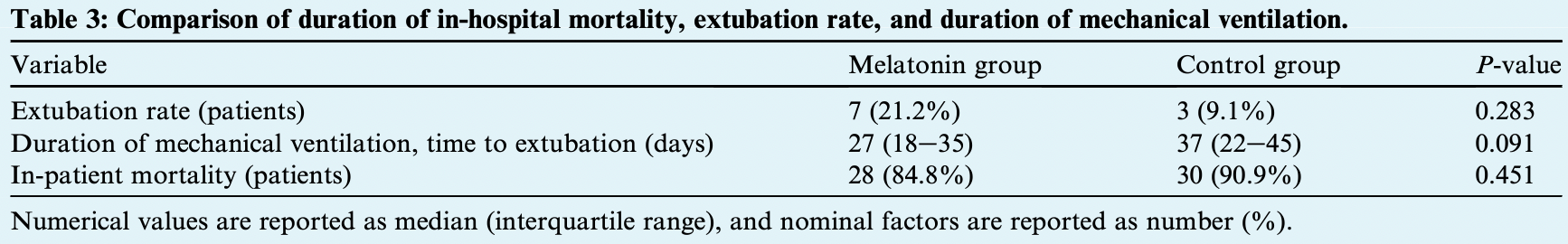
RCT 67 extremely late stage intubated patients in Iran, showing lower CRP with melatonin treatment, but no significant difference in outcomes.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
extremely late treatment, over 75% control mortality.
|
risk of death, 3.8% lower, RR 0.96, p = 0.73, treatment 28 of 33 (84.8%), control 30 of 34 (88.2%), NNT 30.
|
|
risk of no extubation, 13.6% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.19, treatment 26 of 33 (78.8%), control 31 of 34 (91.2%), NNT 8.1.
|
|
ventilation time, 27.0% lower, relative time 0.73, p = 0.09, treatment 33, control 34.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Alizadeh et al., 13 May 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period June 2020 - September 2020.
Contact: h-hosami@sina.tums.ac.ir.
Abstract: JTUMED916_proof ■ 13 May 2022 ■ 1/7
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences (xxxx) xxx(xxx), xxx
Taibah University
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences
www.sciencedirect.com
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Original Article
High dose melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in intubated patients with
Q2 COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial
Nafiseh Alizadeh a, Mehrnoush Dianatkhah b, Yousef Alimohamadi c, Hazhir Moradi d,
Samaneh Akbarpour e, Majid Akrami f, Fariba Mansouri g, Neda Faraji g, Zahra Rezaie h,
i
i,
Q3 Mahboubeh Alizadeh and Hadiseh Hosamirudsari *
Q18
a
Department of Pharmaceutical Care, Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
c
Health Research Center, Life Style Institute, Baqiyatallah University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Q4
d
Medical School, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran
Q5
e
Occupational Sleep Research Center, Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
f
Department of Anesthesiology, Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
g
Department of Internal Medicine, Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
h
Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
i
Department of Infectious Diseases, Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
b
Received 13 February 2022; revised 11 April 2022; accepted 28 April 2022; Available online - - -
ﺍﻟﻤﻠﺨﺺ
ﺍﻟﻤﻼﻳﻴﻦ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻨﺎﺱ ﻓﻲ ﺟﻤﻴﻊ ﺃﻧﺤﺎﺀ19- ﺃﺻﺎﺑﺖ ﺟﺎﺋﺤﺔ ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ:ﺃﻫﺪﺍﻑ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻌﺮﻭﻑ ﺃﻥ ﺟﺮﻋﺔ. ﺗﺮﺟﻊ ﺍﻟﻮﻓﻴﺎﺕ ﺃﺳﺎﺳﺎ ﻟﺤﺎﻟﺔ ﺍﻻﻟﺘﻬﺎﺏ ﻭﻣﻀﺎﻋﻔﺎﺗﻪ.ﺍﻟﻌﺎﻟﻢ
ﻗﻴﻤﺖ ﻫﺬﻩ ﺍﻟﺪﺭﺍﺳﺔ ﺟﺮﻋﺔ.ﻋﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ ﺗﻌﺘﺒﺮ ﻋﺎﻣﻼ ﻣﻀﺎﺩﺍ ﻟﻼﻟﺘﻬﺎﺑﺎﺕ
ﻋﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ ﻛﻌﻼﺝ ﻣﺴﺎﻋﺪ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﺤﺎﻻﺕ ﺍﻟﺤﺮﺟﺔ ﻟﻠﻤﺮﺿﻰ ﺍﻟﻤﺼﺎﺑﻴﻦ
.19-ﺑﻌﺪﻭﻯ ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ
ﻣﻠﻎ21 ﺃﺟﺮﻳﻨﺎ ﺗﺠﺮﺑﺔ ﺳﺮﻳﺮﻳﺔ ﻋﺸﻮﺍﺋﻴﺔ ﻣﺰﺩﻭﺟﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﻌﻤﻴﺔ ﻟﺠﺮﻋﺔ:ﻃﺮﻕ ﺍﻟﺒﺤﺚ
ﺗﻢ.19- ﻣﺮﻳﻀﺎ ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ67 ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻴﻮﻡ ﻣﻘﺎﺭﻧﺔ ﻣﻊ ﺩﻭﺍﺀ ﻭﻫﻤﻲ ﺑﻴﻦ
ﺍﻟﻤﻮﺛﻘﺔ19- ﻋﺎﻣﺎ ﻭﺍﻟﻤﺼﺎﺑﻴﻦ ﺑﻌﺪﻭﻯ ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ18 ﺍﻟﺘﺴﺠﻴﻞ ﻟﻠﻤﺮﺿﻰ ﺍﻷﻛﺒﺮ ﻣﻦ
ﺍﺳﺘﻤﺮ.ﻭﺍﻟﺬﻳﻦ ﺗﻢ ﺇﺩﺧﺎﻟﻬﻢ ﺇﻟﻰ ﻭﺣﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﻌﻨﺎﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﺮﻛﺰﺓ ﻭﺧﻀﻌﻮﺍ ﻟﺘﻬﻮﻳﺔ ﻣﻴﻜﺎﻧﻴﻜﻴﺔ
.ﺇﻋﻄﺎﺀ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ ﻭﺍﻟﻌﻼﺝ ﺍﻟﻮﻫﻤﻲ ﻟﻤﺪﺓ ﺧﻤﺴﺔ ﺃﻳﺎﻡ ﻣﻦ ﺧﻼﻝ ﺃﻧﺒﻮﺏ ﺃﻧﻔﻲ ﻣﻌﺪﻱ
ﻭﺍﻟﺘﻐﻴﺮﺍﺕ ﻓﻲ، ﻭﻣﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻬﻮﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻜﺎﻧﻴﻜﻴﺔ،ﻛﺎﻧﺖ ﺍﻟﻨﺘﺎﺋﺞ ﺍﻟﺮﺋﻴﺴﻴﺔ ﻣﻌﺪﻝ ﺍﻟﻮﻓﻴﺎﺕ
. ﻭﻣﺴﺘﻮﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻭﺗﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺳﻲ،ﻣﺆﺷﺮﺍﺕ ﺍﻷﻭﻛﺴﺠﻴﻦ
ﻟﻢ ﻳﻜﻦ ﻫﻨﺎﻙ ﻓﺮﻕ ﺟﻮﻫﺮﻱ ﻓﻲ ﺍﻟﻮﻓﻴﺎﺕ ﻭﻣﺪﺓ ﺍﻟﺘﻬﻮﻳﺔ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻜﺎﻧﻴﻜﻴﺔ ﺑﻴﻦ:ﺍﻟﻨﺘﺎﺋﺞ
ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻮﺳﻂ ) ﺍﻻﻧﺤﺮﺍﻑ، ﺃﻳﺎﻡ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺧﻞ5 ﺑﻌﺪ.ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻢ ﻭﺍﻟﺘﺪﺧﻞ
* Corresponding address: Department of Infectious Disease,
Baharloo Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Behdari
Q6 Street, Railway Square, Tehran, Iran.
E-mail: h-hosami@sina.tums.ac.ir (H. Hosamirudsari)
Peer review under responsibility of Taibah University.
Production and hosting by Elsevier
) 47.28 ﺍﻟﻤﻌﻴﺎﺭﻱ( ﻟـﻠﺒﺮﻭﺗﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺳﻲ ﻭ ﻋﺪﺩ ﺍﻟﺼﻔﺎﺋﺢ ﺍﻟﺪﻣﻮﻳﺔ ﻛﺎﻥ
ﻣﻴﻜﺮﻭﻟﺘﺮ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ/ 1000 (87.13 ) 195.73 ﻟﺘﺮ ﻭ/ ( ﻣﻠﻐﻢ38.86
/ 1000 (68.03 ) 149.62 ﻟﺘﺮ ﻭ/ ( ﻣﻠﻐﻢ48.02 ) 75.52 ﺍﻟﺘﺪﺧﻞ ﻭ
.ﻣﻴﻜﺮﻭﻟﺘﺮ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺠﻤﻮﻋﺔ ﺍﻟﺘﺤﻜﻢ ﻋﻠﻰ ﺍﻟﺘﻮﺍﻟﻲ
19- ﺍﺭﺗﺒﻂ ﺗﻨﺎﻭﻝ ﺟﺮﻋﺎﺕ ﻋﺎﻟﻴﺔ ﻣﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ ﻓﻲ ﻣﺮﺿﻰ ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ:ﺍﻻﺳﺘﻨﺘﺎﺟﺎﺕ
ﻓﺈﻥ ﺗﺄﺛﻴﺮﻩ ﻋﻠﻰ ﻧﺘﺎﺋﺞ، ﻭﻣﻊ ﺫﻟﻚ.ﺑﺎﻟﺘﻨﺎﻗﺺ ﻓﻰ ﻣﺴﺘﻮﻳﺎﺕ ﺍﻟﺒﺮﻭﺗﻴﻦ ﺍﻟﻤﺘﻔﺎﻋﻞ ﺳﻲ
.ﺍﻟﻤﺮﺿﻰ ﻟﻢ ﻳﻜﻦ ﻣﻠﺤﻮﻇﺎ
؛ ﺍﻟﻤﻴﻼﺗﻮﻧﻴﻦ؛ ﺗﻨﺒﻴﺐ؛ ﻣﻌﺪﻝ ﺍﻟﻮﻓﻴﺎﺕ؛ ﺍﻟﻌﻼﺝ19- ﻛﻮﻓﻴﺪ:ﺍﻟﻜﻠﻤﺎﺕ..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012",
"ISSN": [
"1658-3612"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012",
"alternative-id": [
"S1658361222000877"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh",
"given": "Nafiseh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dianatkhah",
"given": "Mehrnoush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alimohamadi",
"given": "Yousef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moradi",
"given": "Hazhir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbarpour",
"given": "Samaneh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akrami",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansouri",
"given": "Fariba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faraji",
"given": "Neda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rezaie",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh",
"given": "Mahboubeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosamirudsari",
"given": "Hadiseh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T09:18:35Z",
"timestamp": 1652433515000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-13T09:19:09Z",
"timestamp": 1652433549000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004484",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Tehran University of Medical Sciences and Health Services"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-14T11:11:07Z",
"timestamp": 1652526667586
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1651363200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1651276800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1658361222000877?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1658361222000877?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic",
"author": "Cucinotta",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Acta Biomed",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib1",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19—navigating the uncharted",
"author": "Fauci",
"first-page": "1268",
"journal-title": "Mass Medical Soc",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Mahase",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib3",
"series-title": "Covid-19: doctors are told not to perform CPR on patients in cardiac arrest",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Overview of the pathogenesis of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Exp Ther Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib4",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11046-021-00528-2",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease (Covid-19) associated mucormycosis (CAM): case report and systematic review of literature",
"author": "Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Mycopathologia",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib5",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12663-021-01532-1",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, uncontrolled diabetes, and corticosteroids—an unholy trinity in invasive fungal infections of the maxillofacial region? A retrospective, multi-centric analysis",
"author": "Moorthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"journal-title": "J Maxillofac Oral Surg",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib6",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Longitudinal Changes of liver function and hepatitis B reactivation in COVID-19 patients with pre-existing chronic HBV infection",
"author": "Liu",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14740338.2021.1946513",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in COVID-19: a study of adverse drug events reported in the WHO database",
"author": "Charan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1125",
"journal-title": "Expet Opin Drug Saf",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib8",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.24130",
"article-title": "Ebola virus: melatonin as a readily available treatment option",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib9",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/NPM-15814072",
"article-title": "Use of Melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in neonatal sepsis",
"author": "El Frargy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "J Neonatal Perinat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00226",
"article-title": "Therapeutic algorithm for use of melatonin in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Reiter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib11",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08830185.2020.1756284",
"article-title": "Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Shneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Int Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib12",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15171/npj.2020.06",
"article-title": "Melatonin and alpha lipoic acid restore electrolytes and kidney morphology of lopinavir/ritonavir-treated rats",
"author": "Adikwu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e06",
"journal-title": "J Nephropharmacology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1203/00006450-200112000-00021",
"article-title": "Effects of melatonin treatment in septic newborns",
"author": "Gitto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "756",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib14",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12560",
"article-title": "Melatonin attenuates TNF-α and IL-1β expression in synovial fibroblasts and diminishes cartilage degradation: implications for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Pineal Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib15",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2109",
"article-title": "Melatonin: roles in influenza, Covid-19, and other viral infections",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib16",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2018.08.037",
"article-title": "MicroRNA-494 inhibition alleviates acute lung injury through Nrf2 signaling pathway via NQO1 in sepsis-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Ling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib17",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0902961",
"article-title": "Melatonin protects CD4+ T cells from activation-induced cell death by blocking NFAT-mediated CD95 ligand upregulation",
"author": "da Cunha Pedrosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3487",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib18",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jpi.12199",
"article-title": "Systemic combined melatonin–mitochondria treatment improves acute respiratory distress syndrome in the rat",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "J Pineal Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib19",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "The economic burden of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): evidence from Iran",
"author": "Darab",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Health Serv Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib20",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib21",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0308-3",
"article-title": "COVID-19: immunopathology and its implications for therapy",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib22",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"article-title": "Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages",
"author": "Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib23",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/hepr.13553",
"article-title": "Longitudinal changes of liver function and hepatitis B reactivation in COVID-19 patients with pre-existing chronic hepatitis B virus infection",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1211",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib24",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026616666160824120338",
"article-title": "Melatonin and respiratory diseases: a review",
"author": "Habtemariam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Curr Top Med Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib25",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2018.12.004",
"article-title": "Efficacy of melatonin on serum pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Sánchez-López",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib26",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/102490790100800305",
"article-title": "An upsurge in melatonin overdose",
"author": "Chung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Hong Kong J Emerg Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib27",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 ICU and mechanical ventilation patient characteristics and outcomes—a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chang",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib28",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/08850666211020281",
"article-title": "Extubation failure in critically ill COVID-19 patients: risk factors and impact on in-hospital mortality",
"author": "Ionescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1018",
"journal-title": "J Intensive Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib29",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "C-reactive protein as an early predictor of COVID-19 severity",
"author": "Ahnach",
"first-page": "500",
"journal-title": "J Med Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib30",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1753466620937175",
"article-title": "C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and ferritin in severe coronavirus disease-2019: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Ther Adv Respir Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib31",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26097",
"article-title": "Elevated level of C-reactive protein may be an early marker to predict risk for severity of COVID-19",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Serum Amyloid A is a biomarker of severe Coronavirus Disease and poor prognosis",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "646",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib33",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of mean platelet volume as a predictor of mortality in critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tajarernmuang",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Res Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib34",
"volume": "2016",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00277-020-04019-0",
"article-title": "Mechanism of thrombocytopenia in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1205",
"journal-title": "Ann Hematol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib35",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00521-8",
"article-title": "Immune thrombocytopenia secondary to COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Bhattacharjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2048",
"journal-title": "SN Compr Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib36",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Mei",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib37",
"series-title": "Thrombocytopenia and thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000512007",
"article-title": "The impact of COVID-19 disease on platelets and coagulation",
"author": "Wool",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Pathobiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib38",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0369",
"article-title": "Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Henry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem Lab Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib39",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hematological abnormalities in patients with COVID-19: an emerging approach to differentiate between severe COVID-19; compared with non-severe forms of the disease",
"author": "Mehrpouri",
"journal-title": "Acta Med Iran",
"key": "10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.04.012_bib40",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1658361222000877"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "High dose melatonin as an adjuvant therapy in intubated patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}