A Pilot Study on Controlling Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Inflammation Using Melatonin Supplement
et al., Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, May 2021
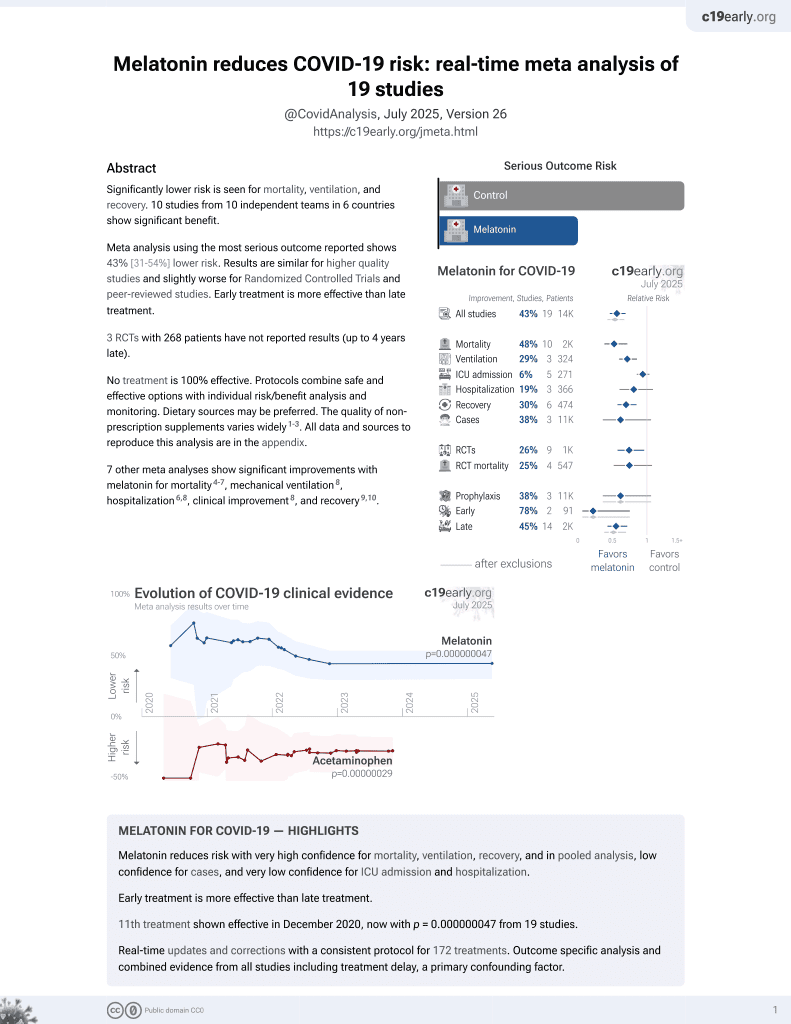
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.0000000099 from 19 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Small RCT 31 mild/moderate COVID-19 outpatients in Iran, 14 treated with melatonin, showing improved recovery with treatment.
|
risk of no recovery, 73.0% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.06, treatment 2 of 14 (14.3%), control 9 of 17 (52.9%), NNT 2.6, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Alizadeh et al., 29 May 2021, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 30 June, 2020 - 5 August, 2020.
A Pilot Study on Controlling Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Inflammation Using Melatonin Supplement
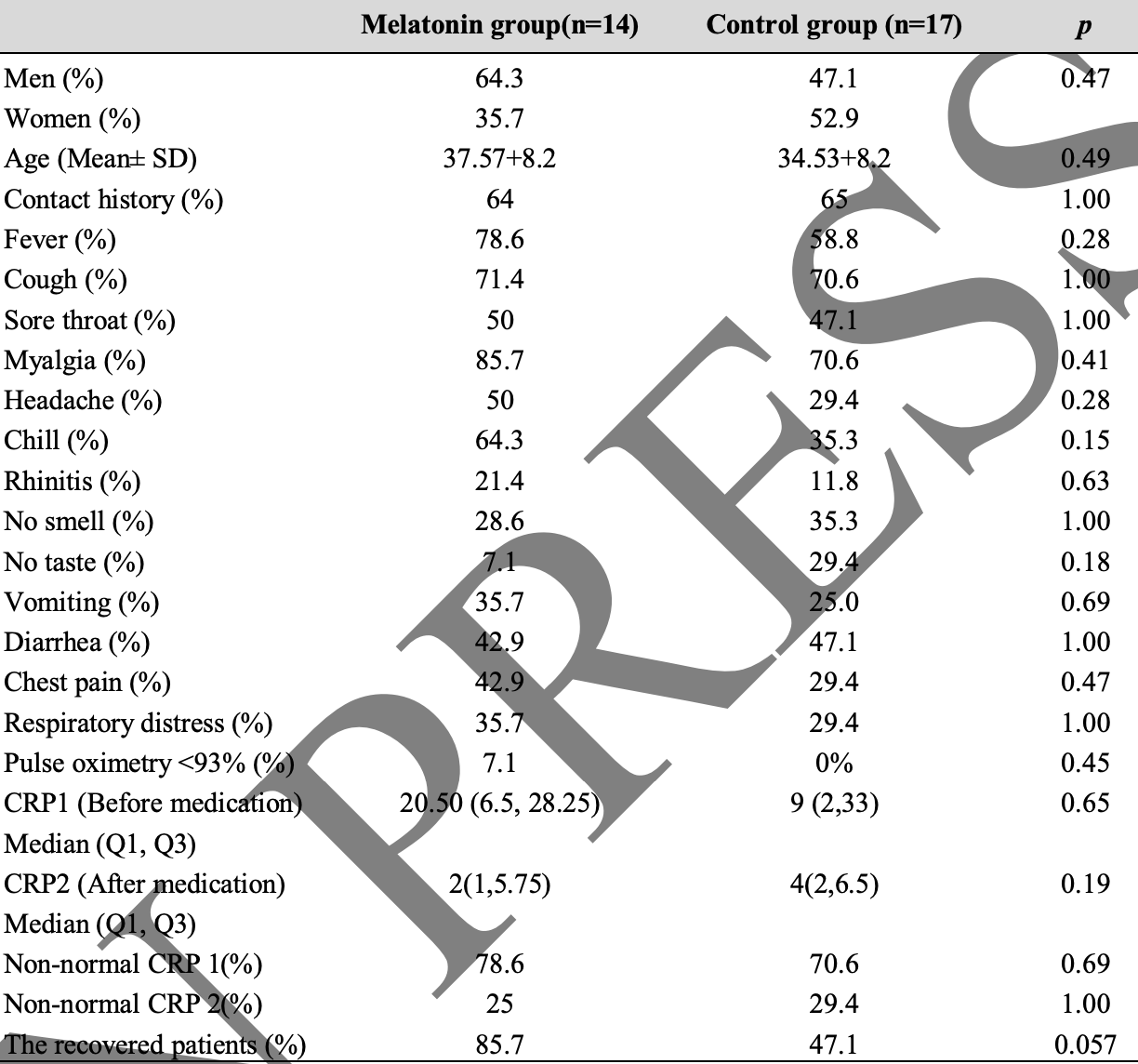
No effective antiviral drugs and vaccines are available for the treatment of patients with severe coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19). Therefore, available, safe, and inexpensive drugs and supplements such as melatonin are among the proposed options for controlling inflammation. We did a randomized, single-blind study in Imam Khomeini Hospital between June 30, 2020, and August 5, 2020. Mild to moderate COVID-19 patients aged 25-65 years were eligible to enter the study based on chest CT scan, clinical symptoms, and physician diagnosis. The intervention group was prescribed 6 mg of oral melatonin for 2 weeks, which consumed half an hour before bedtime every night in low light conditions. Clinical symptoms and Creactive protein (CRP) were measured before and after treatment in the melatonin received and control (regular medications) groups. among screened patients with COVID-19, 14 patients were assigned to receive melatonin, and 17 patients were considered as controls. A significant difference (p=0.005) between CRP 1 and CRP 2 levels (before and after using melatonin) was found in the melatonin group while this difference (p=0.069) was not significant in the control group. Also, the percentage of recovery (based on symptoms) in patients who took melatonin was higher than that of patients in the control group (85.7% VS 47.1%). The result of this study confirmed the effectiveness of melatonin in mild to moderate outpatients with COVID-19. More clinical trials on elderly, diabetic, obese patients and severe cases are suggested in future studies.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Ahn, Anderson, Zhang, Tan, Lim et al., Dampened NLRP3-mediated inflammation in bats and implications for a special viral reservoir host, Nat Microbiol
Danielski, Giustina, Bonfante, Barichello, Petronilho, The NLRP3 Inflammasome and Its Role in Sepsis Development, Inflammation
El-Missiry, El-Missiry, Othman, Melatonin is a potential adjuvant to improve clinical outcomes in individuals with obesity and diabetes with coexistence of Covid-19, Eur J Pharmacol
Essa, Hamdan, Chidambaram, Al-Balushi, Guillemin et al., Possible role of tryptophan and melatonin in COVID-19, Int J Tryptophan Res
Feitosa, Júnior, Neto, Matos, Moura et al., COVID-19: Rational discovery of the therapeutic potential of Melatonin as a SARS-CoV-2 main Protease Inhibitor, Int J Med. Sci
Har-Deland, Aging, Melatonin, and the Pro-and Anti-Inflammatory Networks, Int J Mol Sci
Hu, Deng, Ma, Wang, Fan et al., Utilizing melatonin to combat bacterial infections and septic injury, Br J Pharmacol
Im, Ammit, The NLRP3 inflammasome: role in airway inflammation, Clin Exp Allergy
Juybari, Pourhanifeh, Hosseinzadeh, Hemati, Mehrzadi, Melatonin potentials against viral infections including COVID-19: Current evidence and new findings, Virus Res
Kow, Hasan, Could melatonin be used in COVID-19 patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux disease?, J Med Virol
Lin, Xu, Lv, Han, Xiang et al., An NLRP3 inflammasome-triggered cytokine storm contributes to Streptococcal toxic shock-like syndrome (STSLS), PLoS Pathog
Merad, Martin, Author Correction: Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat Rev Immunol
Naveenkumar, Hemshekhar, Jagadish, Manikanta, Vishalakshi et al., Melatonin restores neutrophil functions and prevents apoptosis amid dysfunctional glutathione redox system, J Pineal Res
Peng, Zhang, Qiao, He, Melatonin attenuates airway inflammation via SIRT1 dependent inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-1beta in rats with COPD, Int Immunopharmacol
Prado, Ferder, Manucha, Diez, Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Melatonin in Obesity and Hypertension, Curr Hypertens
Rahim, Djerdjouri, Sayed, Fernandez-Ortiz, Fernandez-Gil et al., Melatonin administration to wild-type mice and nontreated NLRP3 mutant mice share similar inhibition of the inflammatory response during sepsis, JPineal Res
Reiter, Mayo, Tan, Sainz, Jimenez et al., Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers, J Pineal Res
Reiter, Sharma, Ma, Dominquez-Rodriguez, Marik et al., Melatonin Inhibits COVID-19-induced Cytokine Storm by Reversing Aerobic Glycolysis in Immune Cells: A Mechanistic Analysis, Med Drug Discov
Rodríguez-Rubio, Figueira, Acuña-Castroviejo, Borobia, Escames et al., A phase II, single-center, double-blind, randomized placebocontrolled trial to explore the efficacy and safety of intravenous melatonin in patients with COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit (MelCOVID study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Salles, Correspondence COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci
Szewczyk-Golec, Rajewski, Gackowski, Kierzenkowska, Wesołowski et al., Melatonin Supplementation Lowers Oxidative Stress and Regulates Adipokines in Obese Patients on a Calorie-Restricted Diet, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Volt, Garcia, Doerrier, Diaz-Casado, Guerra-Librero et al., Same molecule but different expression: aging and sepsis trigger NLRP3 inflammasome activation, a target of melatonin, J Pineal Res
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA
Wirtz, Spillmann, Bärtschi, Ehlert, Känel, Oral melatonin reduces blood coagulation activity: a placebo-controlled study in healthy young men, J Pineal Res
Zhang, Lu, Liu, Fan, Zheng et al., Melatonin inhibits inflammasome-associated activation of endothelium and macrophages attenuating pulmonary arterial hypertension, Cardiovasc Res
Zhang, Wang, Ni, Di, Ma et al., COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci
Ziaei, Davoodian, Dadvand, Safa, Hassanipour et al., Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of Melatonin in moderately ill patients with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, Trials
Öztürk, Akbulut, Güney, Melatonin, Aging and COVID-19: Could melatonin be beneficial for COVID-19 treatment in elderly?, Turk J Med Sci