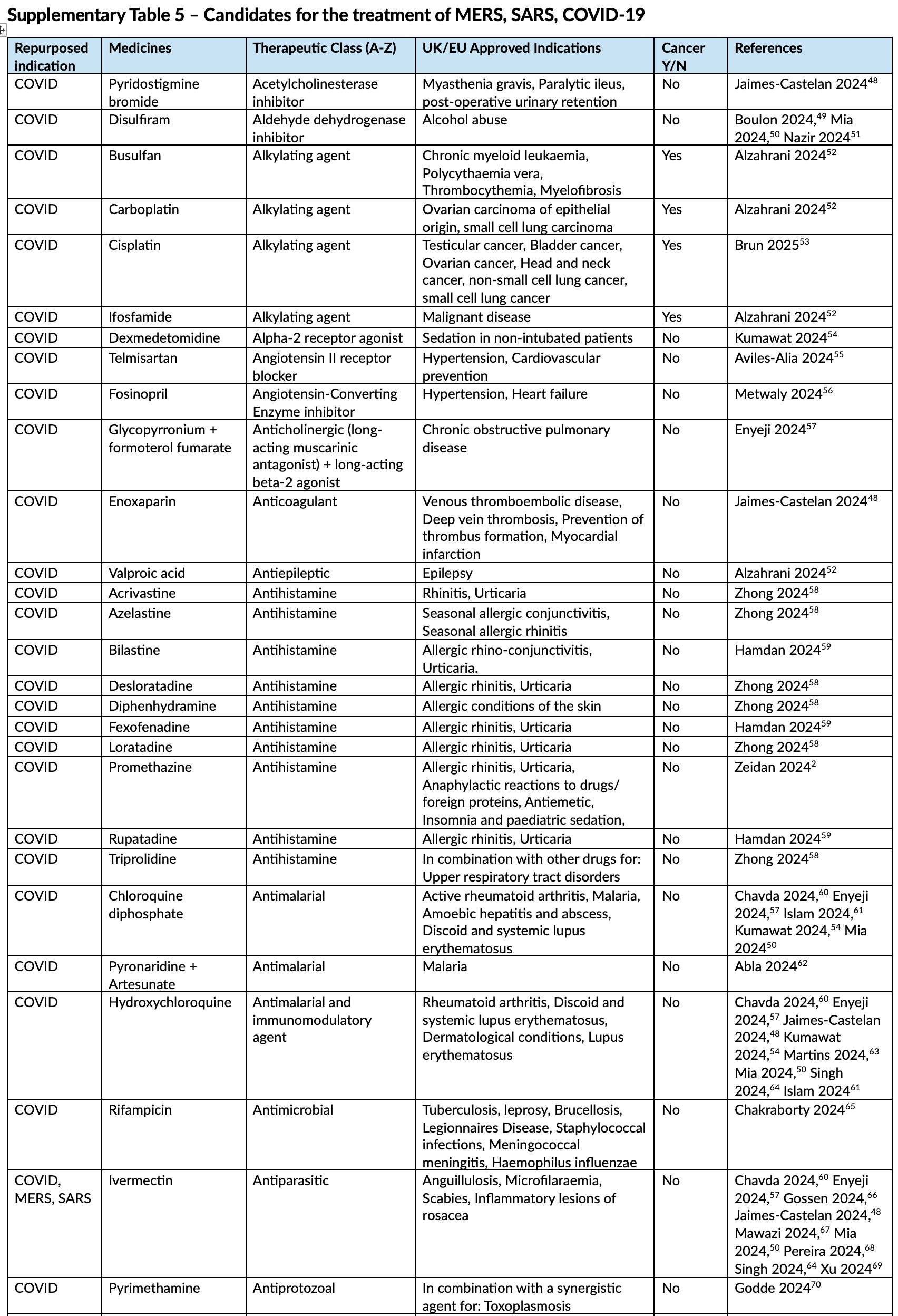
Repurposed antiviral medicines for potential pandemic viruses: A horizon scan
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403, Sep 2025
Review of repurposed antiviral medicines for potential pandemic viruses, identifying 196 repurposed technologies from literature and 58 in active clinical development, with interventional clinical trial activity primarily for COVID-19 and influenza. For COVID-19, 29 technologies advanced to phase III evaluation, from diverse pharmacological classes including direct-acting antivirals, interleukin-6 inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, and immunomodulators.
Akinbolade et al., 12 Sep 2025, United Kingdom, preprint, 6 authors.
Contact: sola.akinbolade@ncl.ac.uk, rhiannon.potter@ncl.ac.uk, alex.inskip@ncl.ac.uk, jane.nesworthy@ncl.ac.uk, kirsti.brock@ncl.ac.uk, gill.norman@ncl.ac.uk.
Repurposed antiviral medicines for potential pandemic viruses: A horizon scan
doi:10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403
Background Viruses such as Ebola, Marburg, influenza, mpox, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 pose a significant risk for future pandemics. Developing novel antiviral medicines can be time-consuming and resource intensive. Repurposing existing medicines with antiviral activity offers a faster, cost-effective strategy to expand treatment options during public health emergencies. This scan aimed to identify and synthesise recent evidence on repurposed antiviral medicines under investigation for these viruses.
Method A horizon scanning approach was employed, starting with a targeted search in Embase, followed by a systematic search of ClinicalTrials.gov to capture the developmental stages of the technologies. Eligible technologies included UK-or EU-licensed medicines repurposed as antiviral therapies for the viruses of interest. Vaccines, unlicensed medicines, and already approved treatments for the targeted viruses were excluded.
Results A total of 196 repurposed technologies targeting the viruses were identified from published literature, and the expanded search on the clinical trials registry yielded 58 technologies in active clinical development. Interventional clinical trial activity was limited to influenza and COVID-19, with 29 technologies for COVID-19 and two for influenza advancing to phase III evaluation. For other viruses, proposed antiviral candidates were identified in the literature but had not progressed into clinical development. Commonly investigated pharmacological classes included direct-acting antivirals, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunomodulators, and anti-inflammatory agents.
Conclusion Repurposing antiviral medicines represents a pragmatic strategy for rapid therapeutic deployment against emerging viral threats. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, research funders, and regulatory bodies will be essential to improve pandemic preparedness and support repurposing efforts in emergency situations.
Author contributions SA drafted the manuscript. AI conducted the literature and clinical trial searches. SA, RP, JN, and KB carried out data screening and extraction. SA and RP analysed the data. GN reviewed and provided feedback on the final draft of the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and helped refine the manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Akinbolade, Fairbairn, Inskip, Potter, Oliver et al., Repurposed Medicines: A Scan of the Non-commercial Clinical Research Landscape, Pharmacology Research & Perspectives, doi:10.1002/prp2.70049
Banerjee, Shokeen, Chakraborty, Agarwal, Kumar, Modulation of immune response in Ebola virus disease, Current Opinion in Pharmacology, doi:10.1016/j.coph.2021.07.004
Gao, Guyatt, Uyeki, Liu, Chen et al., Antivirals for treatment of severe influenza: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01307-2
Han, Song, Pierson, Shen-Gunther, Xia, Emerging infectious diseases are virulent viruses-Are we prepared? An overview, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11112618
Khan, Fairbairn, Potter, Hussain, Inskip et al., Horizon scanning methods for identification of new and repurposed medicines for stakeholders in the United Kingdom, Futures & Foresight Science, doi:10.1002/ffo2.210.13
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Peterson, Unlocking drug repurposing clinical trials: resources for investigators, Drug Repurposing, doi:10.58647/DRUGREPO.24.2.0016
Pushpakom, Iorio, Eyers, Escott, Hopper et al., Drug repurposing: progress, challenges and recommendations, Nature reviews Drug Discovery, doi:10.1038/nrd.2018.168
Pustake, Tambolkar, Giri, Gandhi, SARS, MERS and CoVID-19: An overview and comparison of clinical, laboratory and radiological features, Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care, doi:10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_839_21
Schreiber, Ludwig, Host-targeted antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 in clinical development-Prospect or disappointment?, Antiviral Research, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106101
Varghese, Patel, Kumar, Sharma, Monkeypox and drug repurposing: seven potential antivirals to combat the viral disease, Reviews on Environmental Health, doi:10.1515/reveh-2023-0001
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Viruses such as Ebola, Marburg, influenza, mpox, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 pose a significant risk for future pandemics. Developing novel antiviral medicines can be time-consuming and resource intensive. Repurposing existing medicines with antiviral activity offers a faster, cost-effective strategy to expand treatment options during public health emergencies. This scan aimed to identify and synthesise recent evidence on repurposed antiviral medicines under investigation for these viruses.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Method</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A horizon scanning approach was employed, starting with a targeted search in Embase, followed by a systematic search of ClinicalTrials.gov to capture the developmental stages of the technologies. Eligible technologies included UK- or EU-licensed medicines repurposed as antiviral therapies for the viruses of interest. Vaccines, unlicensed medicines, and already approved treatments for the targeted viruses were excluded.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A total of 196 repurposed technologies targeting the viruses were identified from published literature, and the expanded search on the clinical trials registry yielded 58 technologies in active clinical development. Interventional clinical trial activity was limited to influenza and COVID-19, with 29 technologies for COVID-19 and two for influenza advancing to phase III evaluation. For other viruses, proposed antiviral candidates were identified in the literature but had not progressed into clinical development. Commonly investigated pharmacological classes included direct-acting antivirals, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, immunomodulators, and anti-inflammatory agents.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Repurposing antiviral medicines represents a pragmatic strategy for rapid therapeutic deployment against emerging viral threats. Collaboration among researchers, policymakers, research funders, and regulatory bodies will be essential to improve pandemic preparedness and support repurposing efforts in emergency situations.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0464-6426",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Akinbolade",
"given": "Sola",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0000-4316-250X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Potter",
"given": "Rhiannon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0006-9946-667X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Inskip",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0008-8525-1357",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nesworthy",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0003-3272-6674",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brock",
"given": "Kirsti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3972-5733",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Norman",
"given": "Gill",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-12T23:25:13Z",
"timestamp": 1757719513000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-15T11:35:14Z",
"timestamp": 1757936114000
},
"group-title": "Pharmacology and Therapeutics",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-16T20:54:23Z",
"timestamp": 1758056063140,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1757635200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.1",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. Potential Pandemic Pathogens. 2023. Available from: https://www.nih.gov/news-events/research-involving-potential-pandemic-pathogens [Accessed 01/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.2",
"unstructured": "National Human Genome Research Institute. Virus. 2025. Available from: https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Virus [Accessed 01/04/2025]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms11112618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.3"
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.4",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation (WHO). Emergencies: Pandemic Influenza. 2025. Available from: https://www.who.int/europe/emergencies/emergency-cycle/prepare/pandemic-influenza [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.5",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation (WHO). Smallpox. 2025. Available from: https://www.who.int/health-topics/smallpox#tab=tab_1 [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.6",
"unstructured": "World Health Organisation (WHO). Mpox. 2024. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mpox [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.7",
"unstructured": "U.S. Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Smallpox. 2024. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/smallpox/about/index.html [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prp2.70049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd.2018.168",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.58647/DRUGREPO.24.2.0016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ffo2.210",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.12"
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.13",
"unstructured": "Embase (Ovid). 2025. Available from: https://ovidsp.dc1.ovid.com/ovid-new-b/ovidweb.cgi [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.14",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. 2025. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.15",
"unstructured": "Electronic medicines compendium (emc). 2025. Available from: https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.16",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency (EMA). Search for medicines. 2025. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines [Accessed 07/04/2025]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2021.07.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.18"
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.19",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). Marburg virus disease. 2025. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/marburg-virus-disease [Accessed 28/07/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.20",
"unstructured": "U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Treating Flu with Antiviral Drugs. 2024. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/treatment/antiviral-drugs.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/flu/treatment/whatyoushould.htm [Accessed 28/07/2025]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01307-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.21"
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.22",
"unstructured": "NHS England. Tecovirimat as treatment for patients hospitalised due to monkeypox virus infection. 2022. Available from: https://www.england.nhs.uk/commissioning/publication/tecovirimat-as-treatment-for-patients-hospitalised-due-to-monkeypox-virus-infection/ [Accessed 28/07/2025]."
},
{
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.23",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency (EMA). Tecovirimat SIGA. 2024. Available from: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/tecovirimat-siga [Accessed 28/07/2025]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/reveh-2023-0001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_839_21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2025091504350778000_2025.09.09.25335403v1.25"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2025.09.09.25335403"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Repurposed antiviral medicines for potential pandemic viruses: A horizon scan",
"type": "posted-content"
}