N-acetylcysteine as adjuvant therapy for hospitalized Covid-19 patients: A single-center prospective cohort study
et al., Caspian J Intern Med, doi:10.22088/cjim.14.3.553, Jun 2023
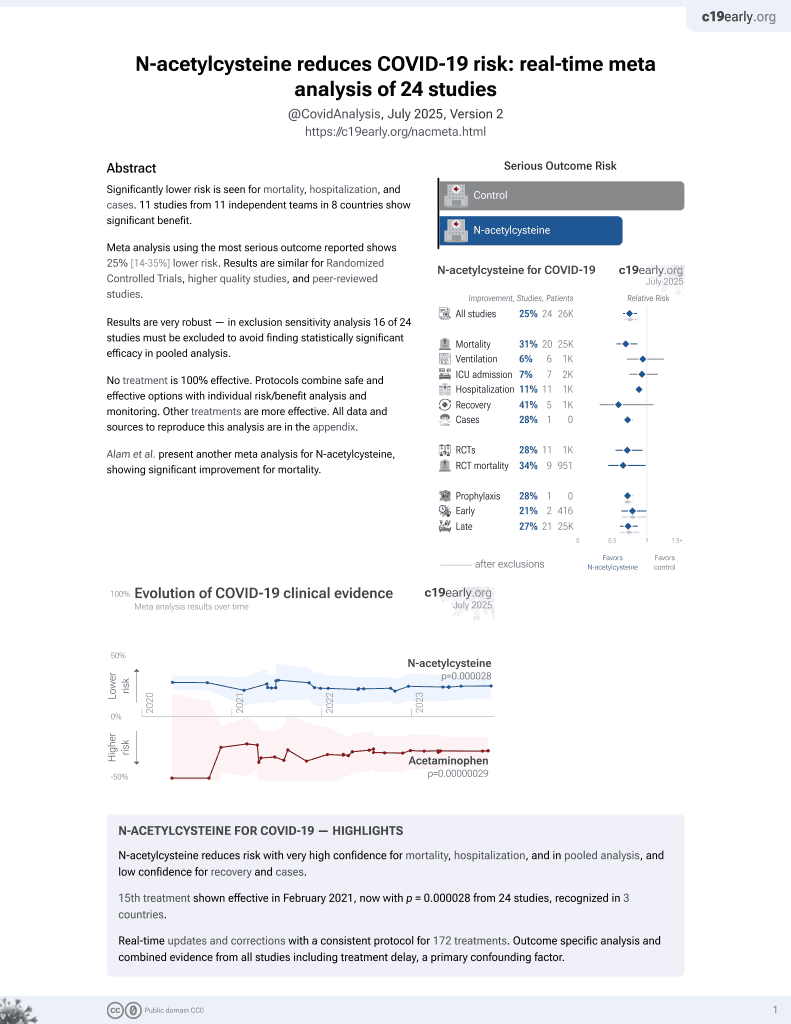
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 217 patients treated with NAC and 245 matched controls, showing improved recovery with treatment. 1500mg intravenous NAC daily.
|
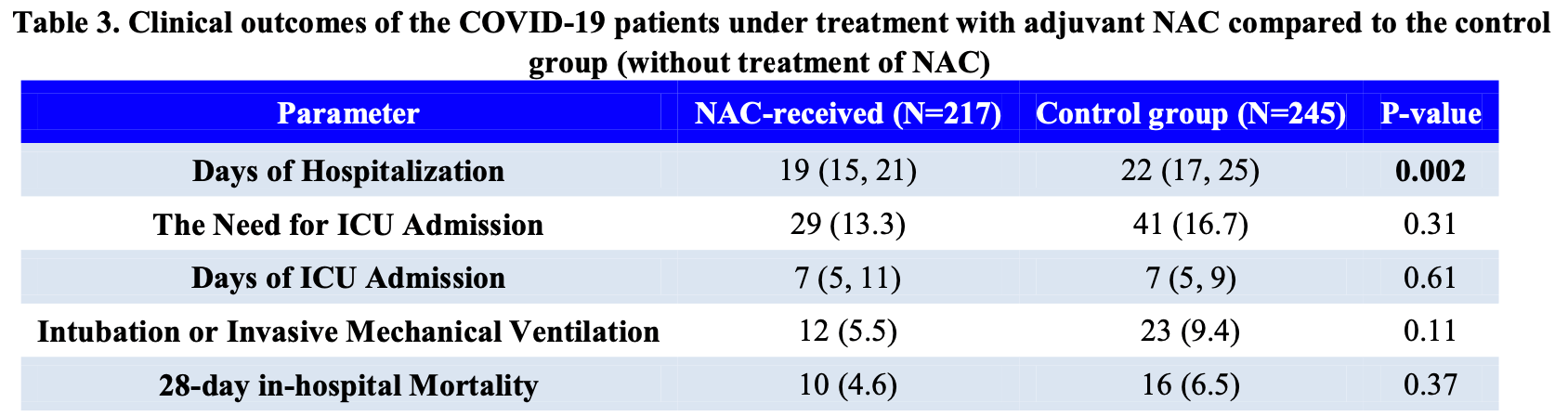
risk of death, 29.4% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.42, treatment 10 of 217 (4.6%), control 16 of 245 (6.5%), NNT 52.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 41.1% lower, RR 0.59, p = 0.16, treatment 12 of 217 (5.5%), control 23 of 245 (9.4%), NNT 26.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 20.1% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.36, treatment 29 of 217 (13.4%), control 41 of 245 (16.7%), NNT 30.
|
|
hospitalization time, 13.6% lower, relative time 0.86, p = 0.002, treatment 217, control 245.
|
|
relative ΔSpO2, 57.1% better, RR 0.43, treatment 217, control 245, relative improvement in SpO2, day 10.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Afaghi et al., 1 Jun 2023, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 1 June, 2020 - 13 March, 2021, average treatment delay 6.0 days.
N-acetylcysteine as adjuvant therapy for hospitalized Covid-19 patients: A single-center prospective cohort study
doi:10.22088/cjim.14.3.553
Background: Whilst over two years have passed since the COVID-19 pandemic's emergence, the proper management of the disease remains challenging. Nacetylcysteine (NAC) as a potentially effective therapeutic option has been suggested by studies, while the exact clinical role of this agent is yet to be evaluated. Methods: This prospective case-control study was conducted in a major referral respiratory center in Tehran, Iran. We enrolled 217 patients treated with an intravenous daily dose of 1500 mg NAC as a case group; and 245 control patients who did not receive NAC. Two groups were matched based on other treatments, sociodemographics, medical history, and comorbidities. Results: After ten days of adjuvant therapy with NAC, patients in the NAC group and control group had median room-air SpO2 of 91% and 88%, respectively (P=0.02). Also, the SpO2 to FiO2 ratio had a median of 463 and 421 in the case and control groups, respectively (P=0.01). Furthermore, the case group's hospitalization period was three days shorter (P=0.002). Further, cough, dyspnea, and decreased appetite were reported to have a significantly lower incidence in the case group (P=0.03, 0.001, 0.008).
Conclusion: We showed that a daily intravenous dose of NAC in hospitalized COVID-19 patients could shorten the hospital stay and improve some clinical symptoms; however, it does not remarkably improve the risk of ICU admission and the 28 days inhospital mortality rate.
Conflict of Interests
References
Afaghi, Tarki, Rahimi, Prevalence and clinical outcomes of vitamin d deficiency in covid-19 hospitalized patients: a retrospective single-center analysis, Tohoku J Exp Med
Al-Rawahi, Prakash, Al-Wahaibi, Epidemiological characteristics of pandemic coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in Oman, Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J
Andreou, Trantza, Filippou, Sipsas, Tsiodras, COVID-19: The Potential Role of Copper and Nacetylcysteine (NAC) in a Combination of Candidate Antiviral Treatments Against SARS-CoV-2
Atluri, Aimlin, Arora, Current effective therapeutics in management of COVID-19, J Clin Med
Avdeev, Gaynitdinova, Merzhoeva, Berikkhanov, N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of COVID-19 among hospitalized patients, J Infect
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Besharat, Rahimi, Afaghi, Chest CT imaging characteristics of COVID-19 pneumonia in surviving and non-surviving hospitalized patients: a retrospective study in a referral center in Tehran, Iran. Iran J Radiol
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Bourgonje, Offringa, Van Eijk, N-Acetylcysteine and Hydrogen Sulfide in Coronavirus Disease, Antioxid Redox Signal
Cazzola, Calzetta, Page, Rogliani, Matera, Thiol-Based drugs in pulmonary medicine: much more than mucolytics, Trends Pharmacol Sci
D_Bwe, None
De Alencar, Moreira, Müller, Doubleblind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with nacetylcysteine for treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis
Dominari, Hathaway Iii, Kapasi, Bottomup analysis of emergent properties of N-acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19, World J Virol
Du Preez, Aldous, Kruger, Johnson, Nacetylcysteine and other sulfur-donors as a preventative and adjunct therapy for COVID-19, Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci
Fisher, Curry, Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity, Adv Pharmacol
Gaynitdinova, Avdeev, Merzhoeva, Nuralieva, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) in the complex treatment of COVID-associated pneumonia, Eur Res J
Gurwitz, Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics, Drug Dev Res
Gül, Ayan, Seydanoğlu, The effect of Nacetyl cysteine on serum glutathione, TNF-alpha and tissue malondialdehyde levels in the treatment of sepsis, Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg
Haghpanah, Lin, Levin, Klein, Analysis of the potential impact of durability, timing, and transmission blocking of COVID-19 vaccine on morbidity and mortality, EClinicalMedicine
Imanpour, Rezaee, Vaskeh, Angiotensin 1-7: A Novel Strategy in COVID-19 Treatment, Adv Pharm Bull
Lee, Hynan, Rossaro, Intravenous Nacetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure, Gastroenterology
Lv, Yuan, Xiong, Li, Mortality rate and characteristics of deaths following COVID-19 vaccination, Front Med (Lausanne)
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat Rev Immunol
Ni, Yang, Yang, Role of angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19, Crit Care
Oliveira, Laurindo, Implications of plasma thiol redox in disease, Clin Sci (Lond)
Olliaro, What does 95% COVID-19 vaccine efficacy really mean?, Lancet Infect Dis
Patoulias, Katsimardou, Stavropoulos, Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and covid-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. evidence for significant geographical disparities, Curr Hypertens Rep
Poe, Corn, N-Acetylcysteine, A potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Med Hypotheses
Qomara, Primanissa, Amalia, Purwadi, Zakiyah, Effectiveness of Remdesivir, Lopinavir/Ritonavir, and Favipiravir for COVID-19 treatment: A Systematic Review, Int J Gen Med
Rabaan, Sh, Muhammad, Role of inflammatory cytokines in covid-19 patients: a review on molecular mechanisms, immune functions, immunopathology and immunomodulatory drugs to counter cytokine storm, Vaccines (Basel)
Recovery Collaborative Group; Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Reina, Iglesias, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir (Paxlovid) a potent SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro protease inhibitor combination, Rev Esp Quimioter
Renieris, Katrini, Damoulari, Association in pneumonia by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, Shock
Shi, Puyo, N-acetylcysteine to combat COVID-19: an evidence review, Ther Clin Risk Manag
Simpson, Kay, Abbara, Radiological society of north America expert consensus document on reporting chest CT findings related to COVID-19: endorsed by the society of thoracic Radiology, the American college of Radiology, and RSNA, Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging
Soto, Guarner-Lans, Soria-Castro, Pech, Torres, Is antioxidant therapy a useful complementary measure for covid-19 treatment? an algorithm for its application
Suter, Domenighetti, Schaller, Nacetylcysteine enhances recovery from acute lung injury in man. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Chest
Wang, Wu, Zuo, Evaluation of current medical approaches for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Support Palliat Care
Who, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Vaccines
Wong, Lee, Kua, N-acetylcysteine as adjuvant therapy for COVID-19-a perspective on the current state of the evidence, J Inflam Res
Zemlin, Wiese, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the renin-angiotensin system: A closer look at angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), Ann Clin Biochem
Zhang, Ding, Li, Effects of Nacetylcysteine treatment in acute respiratory distress syndrome: A meta-analysis, Exp Ther Med