Ibuprofen and NSAID Use in COVID-19 Infected Patients Is Not Associated with Worse Outcomes: A Prospective Cohort Study
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w, Nov 2020
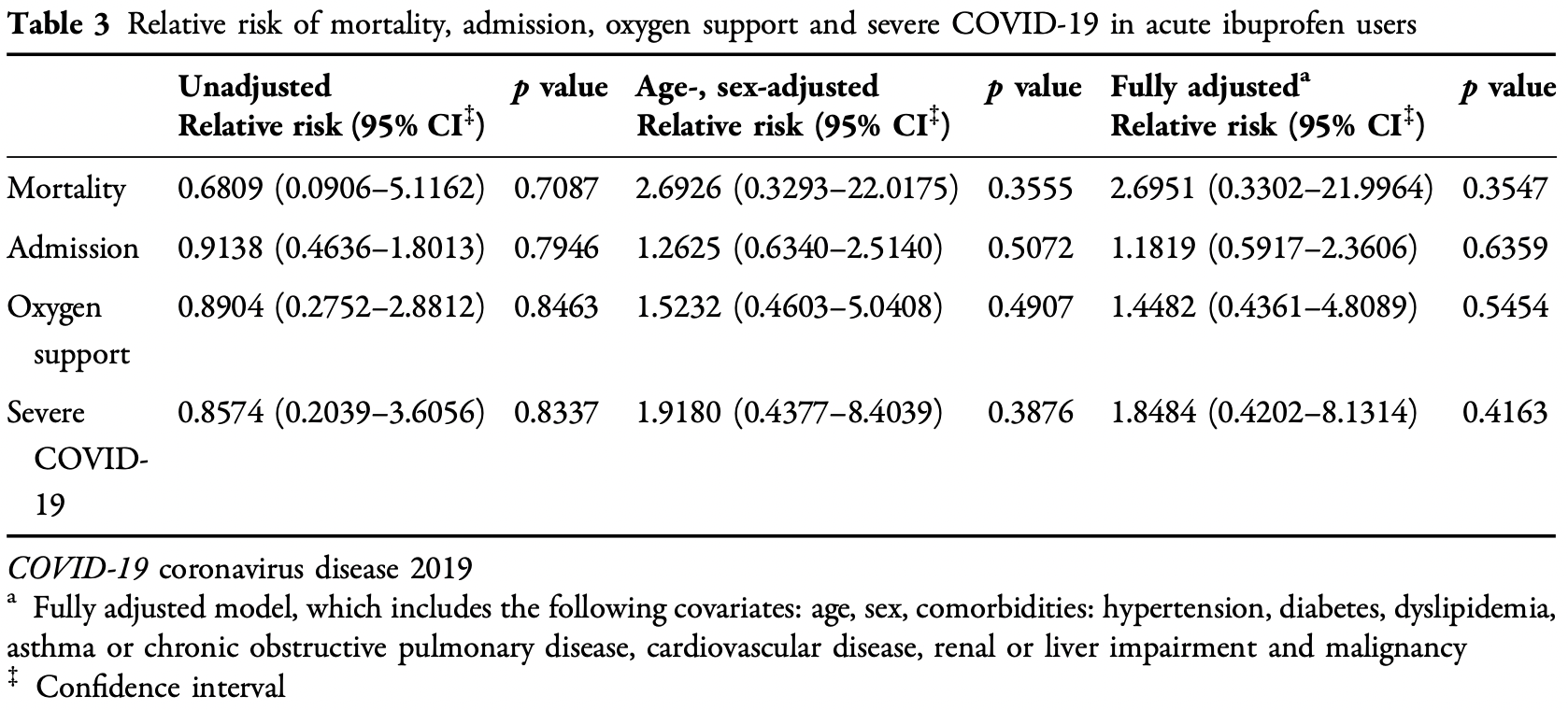
Prospective study of 503 COVID-19 cases in Saudi Arabia, 40 using ibuprofen during infection, and 357 not using NSAIDs, showing no significant differences in outcomes. Results are subject to confounding by indication.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
substantial unadjusted confounding by indication likely.
|
risk of death, 169.5% higher, RR 2.70, p = 0.35, treatment 1 of 40 (2.5%), control 11 of 357 (3.1%), adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
|
risk of death, 36.8% lower, HR 0.63, p = 0.68, treatment 40, control 357, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 44.8% higher, RR 1.45, p = 0.64, treatment 40, control 357, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 18.2% higher, RR 1.18, p = 0.64, treatment 40, control 357, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
|
risk of severe case, 84.8% higher, RR 1.85, p = 0.42, treatment 40, control 357, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Abu Esba et al., 2 Nov 2020, prospective, Saudi Arabia, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period 12 April, 2020 - 1 June, 2020.
Contact: abuesbala@ngha.med.sa.
Ibuprofen and NSAID Use in COVID-19 Infected Patients Is Not Associated with Worse Outcomes: A Prospective Cohort Study
Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w
Introduction: Ibuprofen disappeared from the pharmacy shelves during the 2019 coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. However, a while later, information circulated that ibuprofen should be avoided as it could worsen COVID-19 symptoms. The aim of our study was to assess the association of acute and chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with worse COVID-19 outcomes. Methods: We did a prospective cohort study between April 12 and June 1, 2020. Adults consecutively diagnosed with COVID-19 were included. Information on NSAID use was collected through a telephone questionnaire, and patients were followed up for COVID-19 infection outcomes, including death, admission, severity, time to clinical improvement, oxygen requirement and length of stay. Results: Acute use of ibuprofen was not associated with a greater risk of mortality relative to non-use (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 0.632 [95% CI 0.073-5.441; P = 0.6758]). Chronic NSAID use was also not associated with a greater risk of mortality (adjusted HR 0.492 [95% CI 0.178-1.362; P = 0.1721]). Acute ibuprofen use was not associated with a higher risk of admission compared to non-NSAID users (adjusted odds ratio OR 1.271; 95% CI 0.548-2.953). NSAID users did not have a significantly longer time to clinical improvement or length of stay. Conclusion: Acute or chronic use of ibuprofen and other NSAIDs was not associated with worse COVID-19 disease outcomes.
References
Agency, EMA gives advice on the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories for COVID-19
Amici, Coro, Ciucci, Chiappa, Castilletti et al., Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus, Antiviral Therapy
Castro, Ross, Mcbride, Perlis, Identifying common pharmacotherapies associated with reduced COVID-19 morbidity using electronic health records, doi:10.1101/2020.04.11.20061994
Chandler, Global ibuprofen shortage hits UK supermarkets-with shelves left empty
Clinicaltrials, Gov, Efficacy of addition of naproxen in the treatment of critically ill patients hospitalized for COVID-19 infection
Curhan, Bullock, Hankinson, Willett, Speizer et al., Frequency of use of acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and aspirin in US women, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf
Drug, Usf, FDA advises patients on use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for COVID-19
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med
Gov, Uk, COVID-19
Khan, Benthin, Zeno, Albertson, Boyd et al., A pilot clinical trial of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat Med
Lejal, Tarus, Bouguyon, Chenavas, Bertho et al., Structure-based discovery of the novel antiviral properties of naproxen against the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Liu, Yang, Zhang, Huang, Wang et al., Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury, Sci China Life Sci
Micallef, Soeiro, Ap, French Society of Pharmacology, Therapeutics (SFPT). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pharmacology and COVID-19 infection, Therapies, doi:10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.003
News, Concerned about taking ibuprofen for coronavirus symptoms? Here's What Experts Say
News, Coronavirus and ibuprofen: separating fact from fiction
Paulose-Ram, Hirsch, Dillon, Gu, Frequent monthly use of selected non-prescription and prescription non-narcotic analgesics among US adults, Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf
Qiao, Wang, Chen, Zhang, Liu et al., Ibuprofen attenuates cardiac fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Cardiology
Safidahaj, Re, Response to the emerging novel coronavirus outbreak
Smart, Fawkes, Goggin, A narrative review of the potential pharmacological influence and safety of ibuprofen on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), ACE2, and the immune system: a dichotomy of expectation and reality, Inflammopharmacol, doi:10.1007/s10787-020-00745-z
Times, Managing and Treating Fever: A Guide to Nonprescription Antipyretics
Today, Fact check: does using ibuprofen when you have coronavirus make symptoms worse?
Wan, Shang, Graham, Baric, Li, Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00127-20
Wh, R&D Blueprint and COVID-19
Willsher, Anti-inflammatories may aggravate Covid-19
Yang, Gu, Zhao, Wang, Cao et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) mediates influenza H7N9 virus-induced acute lung injury, Sci Rep
Zheng, Zhang, Jiao, Shang, Cui, Naproxen exhibits broad anti-influenza virus activity in mice impeding viral nucleoprotein nuclear export, Cell Rep
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w",
"ISSN": [
"2193-8229",
"2193-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w",
"alternative-id": [
"363"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "17 September 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "19 October 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "2 November 2020"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2459-1485",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abu Esba",
"given": "Laila Carolina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alqahtani",
"given": "Rahaf Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Abin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shamas",
"given": "Nour",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alswaidan",
"given": "Lolowa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mardawi",
"given": "Gahdah",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-02T04:18:16Z",
"timestamp": 1604290696000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-12T06:39:11Z",
"timestamp": 1615531151000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-06T13:52:16Z",
"timestamp": 1659793936156
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 31,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604275200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1604275200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "253-268",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "363_CR1",
"unstructured": "Times P. Managing and Treating Fever: A Guide to Nonprescription Antipyretics 2018. https://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/issue/2018/February2018/managing-and-treating-fever-a-guide-to-nonprescription-antipyretics. Accessed 19 March 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR2",
"unstructured": "Chandler M. Global ibuprofen shortage hits UK supermarkets—with shelves left empty. 2019. https://www.mirror.co.uk/news/uk-news/global-ibuprofen-shortage-hits-uk-20465178. Accessed 1 April 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR3",
"unstructured": "News B. Coronavirus and ibuprofen: separating fact from fiction. 2020. https://www.bbc.com/news/51929628. Accessed 1 April 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR4",
"unstructured": "Today U. Fact check: does using ibuprofen when you have coronavirus make symptoms worse? 2020. https://www.usatoday.com/story/news/factcheck/2020/03/18/fact-check-coronavirus-and-ibuprofen-do-nsaids-make-coronavirus-worse/2865866001/. Accessed 1 April 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR5",
"unstructured": "News N. Concerned about taking ibuprofen for coronavirus symptoms? Here's What Experts Say. 2020. https://www.npr.org/sections/health-shots/2020/03/18/818026613/advice-from-france-to-avoid-ibuprofen-for-covid-19-leaves-experts-baffled. Accessed 1 April 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR6",
"unstructured": "Willsher K. Anti-inflammatories may aggravate Covid-19, France advises. 2020. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/14/anti-inflammatory-drugs-may-aggravate-coronavirus-infection. Accessed 1 April 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"author": "L Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e21",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "363_CR7",
"unstructured": "Fang L, Karakiulakis G, Roth M. Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection? Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(4):e21.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "363_CR8",
"unstructured": "Agency EM. EMA gives advice on the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatories for COVID-19. 2020. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-gives-advice-use-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatories-covid-19. Accessed 3 May 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.11.20061994",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "363_CR9",
"unstructured": "Castro VM, Ross RA, McBride SM, Perlis RH. Identifying common pharmacotherapies associated with reduced COVID-19 morbidity using electronic health records. medRxiv. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.11.20061994"
},
{
"key": "363_CR10",
"unstructured": "DRUG USF. FDA advises patients on use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for COVID-19. 2020. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-advises-patients-use-non-steroidal-anti-inflammatory-drugs-nsaids-covid-19. Accessed 3 May 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR11",
"unstructured": "GOV.UK. Commission on Human Medicines advice on ibuprofen and coronavirus (COVID-19). 2020. https://www.gov.uk/government/news/commission-on-human-medicines-advice-on-ibuprofen-and-coronavirus-covid-19. Accessed 3 May 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00127-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "363_CR12",
"unstructured": "Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS, Li F. Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus. J Virol. 2020;94(7):e00127–20. PMID: 31996437; PMCID: PMC7081895. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00127-20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000375362",
"author": "W Qiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "97",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cardiology",
"key": "363_CR13",
"unstructured": "Qiao W, Wang C, Chen B, Zhang F, Liu Y, Lu Q, et al. Ibuprofen attenuates cardiac fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Cardiology. 2015;131(2):97–106.",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.983",
"author": "R Paulose-Ram",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf.",
"key": "363_CR14",
"unstructured": "Paulose-Ram R, Hirsch R, Dillon C, Gu Q. Frequent monthly use of selected non-prescription and prescription non-narcotic analgesics among US adults. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2005;14(4):257–66.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pds.732",
"author": "GC Curhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "687",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf",
"key": "363_CR15",
"unstructured": "Curhan GC, Bullock AJ, Hankinson SE, Willett WC, Speizer FE, Stampfer MJ. Frequency of use of acetaminophen, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and aspirin in US women. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2002;11(8):687–93.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep07027",
"author": "P Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7027",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "363_CR16",
"unstructured": "Yang P, Gu H, Zhao Z, Wang W, Cao B, Lai C, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) mediates influenza H7N9 virus-induced acute lung injury. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7027.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"author": "K Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "875",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "363_CR17",
"unstructured": "Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F, Guan B, et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus–induced lung injury. Nat Med. 2005;11(8):875–9.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-017-1823-x",
"author": "A Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "363_CR18",
"unstructured": "Khan A, Benthin C, Zeno B, Albertson TE, Boyd J, Christie JD, et al. A pilot clinical trial of recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care. 2017;21(1):1–9.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "363_CR19",
"unstructured": "Worl Health Organization WH. R&D Blueprint and COVID-19. 2020. https://www.who.int/teams/blueprint/covid-19. Accessed 12 June 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "363_CR20",
"unstructured": "Micallef J, Soeiro T, Jonville-Béra AP. French Society of Pharmacology, Therapeutics (SFPT). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, pharmacology and COVID-19 infection. Therapies. 2020;75(4):355-362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.therap.2020.05.003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8",
"author": "Y Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "364",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Sci China Life Sci",
"key": "363_CR21",
"unstructured": "Liu Y, Yang Y, Zhang C, Huang F, Wang F, Yuan J, et al. Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury. Sci China Life Sci. 2020;63(3):364–74.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "363_CR22",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. LIBERATE Trial in COVID-19 (LIBERATE). 2020. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04334629. Accessed 12 June 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-020-00745-z",
"author": "L Smart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacol",
"key": "363_CR23",
"unstructured": "Smart L, Fawkes N, Goggin P, et al. A narrative review of the potential pharmacological influence and safety of ibuprofen on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), ACE2, and the immune system: a dichotomy of expectation and reality. Inflammopharmacol. 2020;28:1141–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-020-00745-z.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "C Amici",
"first-page": "1021",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Therapy",
"key": "363_CR24",
"unstructured": "Amici C, Di Coro A, Ciucci A, Chiappa L, Castilletti C, Martella V, et al. Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus. Antiviral Therapy. 2006;11(8):1021.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02335-12",
"author": "N Lejal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2231",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "363_CR25",
"unstructured": "Lejal N, Tarus B, Bouguyon E, Chenavas S, Bertho N, Delmas B, et al. Structure-based discovery of the novel antiviral properties of naproxen against the nucleoprotein of influenza A virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(5):2231–42.",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.053",
"author": "W Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1875",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "363_CR26",
"unstructured": "Zheng W, Fan W, Zhang S, Jiao P, Shang Y, Cui L, et al. Naproxen exhibits broad anti-influenza virus activity in mice by impeding viral nucleoprotein nuclear export. Cell Rep. 2019;27(6):1875-855.e5.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m406",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "363_CR27",
"unstructured": "SafiDahaj F. RE: Response to the emerging novel coronavirus outbreak: British Medical Journal Publishing Group. 2020. https://www.bmj.com/content/368/bmj.m406/rapid-responses. Accessed 12 June 2020."
},
{
"key": "363_CR28",
"unstructured": "ClinicalTrials.gov. Efficacy of addition of naproxen in the treatment of critically ill patients hospitalized for COVID-19 infection (ENACOVID). 2020. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04325633. Accessed 12 June 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ibuprofen and NSAID Use in COVID-19 Infected Patients Is Not Associated with Worse Outcomes: A Prospective Cohort Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "10"
}