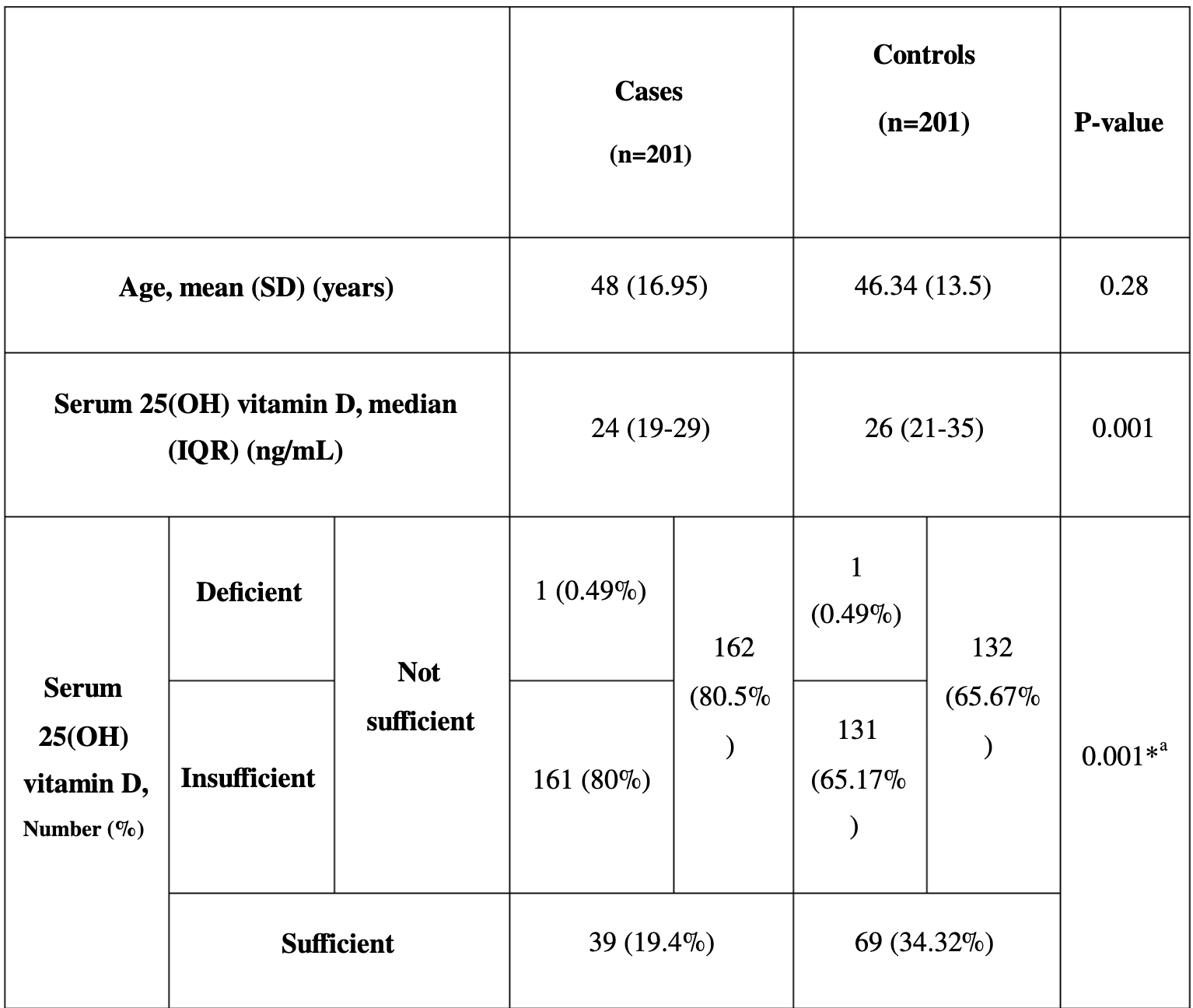
The Association Between the Level of Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D, Obesity, and underlying Diseases with the risk of Developing COVID-19 Infection: A case-control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26726, Dec 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Case control study with 201 patients and 201 matched controls in Iran showing vitamin D deficiency associated with COVID-19.
This is the 33rd of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of case, 53.9% lower, RR 0.46, p = 0.001, high D levels 108, low D levels 294, >30ng/ml.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Abdollahi et al., 12 Dec 2020, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
The association between the level of serum 25(OH) vitamin D, obesity, and underlying diseases with the risk of developing COVID‐19 infection: A case–control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.26726
Background and Objectives: The outbreak of COVID-19 has created a global public health crisis. Little is known about the predisposing factors of this infection. The aim of this study was to explore an association between the serum vitamin D level, obesity, and underlying health conditions, as well as the vulnerability to COVID-19 in the Iranian population. Methods: We conducted a case-control study of 201 patients with coronavirus infection and 201 controls. Cases and controls were matched for age and gender. The study was carried out for 2 months (February 2020-April 2020) at Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex, Tehran, Iran. Serum 25(OH) vitamin D was measured using the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method. Information containing age, gender, clinical symptoms, body mass index, computed tomography scan findings, and underlying health conditions related to each participant were elicited from health records. Results: A significant negative correlation (p = .02) was observed between the serum vitamin D level and developing coronavirus infection. Also, the results showed that the COVID-19 cases were more likely to be overweight than the controls (p = .023). Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and respiratory infections were found in 20.89%, 9.65%, and 6.96% of cases, respectively. These underlying health conditions were not significantly different between cases and controls (p = .81). Conclusions: Vitamin D deficiency and obesity are two main predisposing factors associated with the vulnerability to coronavirus infection in the Iranian population.
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Conceptualization, supervision, project administration: Alireza Abdollahi. Data analysis, writing original draft: Hasti Kamali Sarvestani. Investigation, data curation: Zahra Rafat. Methodology, validation: Sara Ghaderkhani. Resources: Maedeh Mahmoudi-Aliabadi. Writing-Review and Editing, conceptualization: Bita Jafarzadeh. Writing-Review and Editing, data analysis, methodology, data curation: Vahid Mehrtash.
ORCID
Vahid Mehrtash http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1187-7580
References
Adams, Hewison, Unexpected actions of vitamin D: new perspectives on the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity, Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab
Akoumianakis, Filippatos, The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system as a link between obesity and coronavirus disease 2019 severity, Obes Rev
Bhatraju, Ghassemieh, Nichols, Covid-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region-case series, N Engl J Med
Blackburn, Zhao, Pebody, Hayward, Gash, Laboratory-confirmed respiratory infections as predictors of hospital admission for myocardial infarction and stroke: time-series analysis of English data for 2004-2015, Clin Infect Dis
Boulos, Geraghty, Geographical tracking and mapping of coronavirus disease COVID-19/severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic and associated events around the world: how 21st century GIS technologies are supporting the global fight against outbreaks and epidemics, Int J Health Geogr
Braiman, Latitude dependence of the COVID-19 mortality rate-a possible relationship to vitamin D deficiency?
Cantorna, Mechanisms underlying the effect of vitamin D on the immune system, Proc Nutr Soc
Chang, Chou, Chang, Effect of obesity and body mass index on coronavirus disease 2019 severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Obes Rev
Dietz, Santos-Burgoa, Obesity and its implications for COVID-19 mortality, Obesity
Dixon, Peters, The effect of obesity on lung function, Expert Rev Respir Med
Fabbri, Infante, Ricordi, Editorial-Vitamin D status: a key modulator of innate immunity and natural defense from acute viral respiratory infections, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Gombart, The vitamin D-antimicrobial peptide pathway and its role in protection against infection, Future Microbiol
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA
Guan, Ni, -Y, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hansdottir, Monick, Lovan, Powers, Gerke et al., Vitamin D decreases respiratory syncytial virus induction of NF-κB-linked chemokines and cytokines in airway epithelium while maintaining the antiviral state, J Immunol
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Huttunen, Syrjänen, Obesity and the risk and outcome of infection, Int J Obes
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
Janghorbani, Amini, Willett, First nationwide survey of prevalence of overweight, underweight, and abdominal obesity in Iranian adults, Obesity
Kalligeros, Shehadeh, Mylona, Association of obesity with disease severity among patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Obesity
Kalupahana, Moustaid-Moussa, The renin-angiotensin system: a link between obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance, Obes Rev
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus' or two related pandemics: COVID-19 & vitamin D deficiency, Br J Nutr
Li, Guan, Wu, Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One
Marrie, Shariatzadeh, Community-acquired pneumonia requiring admission to an intensive care unit: a descriptive study, Medicine
Martineau, Forouhi, Vitamin D for COVID-19: a case to answer?, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mok, Ng, Ahidjo, Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID-19 prophylaxis
Molla, Badawi, Hammoud, Vitamin D status of mothers and their neonates in Kuwait, Pediatr Int
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ
Popkin, Du, Green, Individuals with obesity and COVID-19: a global perspective on the epidemiology and biological relationships, Obes Rev
Ramirez, Dal Nogare, Hsia, Relationship between diabetes control and pulmonary function in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, Am J Med
Rastad, Karim, Ejtahed, Risk and predictors of in-hospital mortality from COVID-19 in patients with diabetes and cardiovascular disease, Diabetol Metab Syndr
Relkin, Szabo, Adamiak, Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIg) Treatment Causes Dose-Dependent Alterations in Beta-Amyloid (A beta) Levels and Anti-Beta Antibody Titers in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Self-care for common colds: the pivotal role of vitamin D, vitamin C, zinc, and echinacea in three main immune interactive clusters (physical barriers, innate and adaptive immunity) involved during an episode of common colds-practical advice on dosages and on the time to take these nutrients/botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Sales-Peres, Azevedo-Silva, Bonato, Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) and the risk of obesity for critically illness and ICU admitted: meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence, Obes Res Clin Pract
Sharifi, Vahedi, Nedjat, Rafiei, Hosseinzadeh-Attar, Effect of single-dose injection of vitamin D on immune cytokines in ulcerative colitis patients: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, APMIS
Shi, Han, Jiang, The association between the level of serum 25(OH) vitamin D, obesity, and underlying diseases with the risk of developing COVID-19 infection: A case-control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran, Lancet Infect Dis
Simonnet, Chetboun, Poissy, High prevalence of obesity in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, Obesity
Udell, Zawi, Bhatt, Association between influenza vaccination and cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk patients: a meta-analysis, JAMA
Vf, Musher, Shachkina, Chirinos, Acute pneumonia and the cardiovascular system, Lancet
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature
Wimalawansa, Global epidemic of coronavirus-covid-19: what can we do to minimize risks, Eur J Biomed
Wu, Pan, Teng, Xu, Feng et al., Interpretation of CT signs of 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) pneumonia, Eur Radiol
Zhang, Zheng, Zhang, Systemic inflammation mediates the detrimental effects of obesity on asthma control, Allergy Asthma Proc
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26726",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.26726",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background and Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>The outbreak of COVID‐19 has created a global public health crisis. Little is known about the predisposing factors of this infection. The aim of this study was to explore an association between the serum vitamin D level, obesity, and underlying health conditions, as well as the vulnerability to COVID‐19 in the Iranian population.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a case–control study of 201 patients with coronavirus infection and 201 controls. Cases and controls were matched for age and gender. The study was carried out for 2 months (February 2020–April 2020) at Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex, Tehran, Iran. Serum 25(OH) vitamin D was measured using the enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay method. Information containing age, gender, clinical symptoms, body mass index, computed tomography scan findings, and underlying health conditions related to each participant were elicited from health records.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>A significant negative correlation (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .02) was observed between the serum vitamin D level and developing coronavirus infection. Also, the results showed that the COVID‐19 cases were more likely to be overweight than the controls (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .023). Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and respiratory infections were found in 20.89%, 9.65%, and 6.96% of cases, respectively. These underlying health conditions were not significantly different between cases and controls (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = .81).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin D deficiency and obesity are two main predisposing factors associated with the vulnerability to coronavirus infection in the Iranian population.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.26726"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-09-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-12-10"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-12-29"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Imam Hospital Complex, School of Medicine Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Abdollahi",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Mycology, School of Public Health Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Kamali Sarvestani",
"given": "Hasti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology, School of Medicine Guilan University of Medical Sciences Rasht Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rafat",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases and Tropical Medicine, School of Medicine Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghaderkhani",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory, Imam Khomeini Hospital Complex Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mahmoudi‐Aliabadi",
"given": "Maedeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Imam Hospital Complex, School of Medicine Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jafarzadeh",
"given": "Bita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1187-7580",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology, Imam Hospital Complex, School of Medicine Tehran University of Medical Sciences Tehran Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mehrtash",
"given": "Vahid",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Medical Virology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-12T09:06:32Z",
"timestamp": 1607763992000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-01T12:28:18Z",
"timestamp": 1693571298000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T15:05:55Z",
"timestamp": 1712070355228
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 33,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609200000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.26726",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/jmv.26726",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.26726",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2359-2364",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12942-020-00202-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114520001749",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.0902840",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta‐analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau AR",
"first-page": "356",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Self‐care for common colds: the pivotal role of vitamin D, vitamin C, zinc, and echinacea in three main immune interactive clusters (physical barriers, innate and adaptive immunity) involved during an episode of common colds—practical advice on dosages and on the time to take these nutrients/botanicals in order to prevent or treat common colds",
"author": "Rondanelli M",
"first-page": "5813095",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665110001722",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apm.12982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Global epidemic of coronavirus—covid‐19: what can we do to minimize risks",
"author": "Wimalawansa SJ",
"first-page": "432",
"journal-title": "Eur J Biomed",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3561958",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1",
"unstructured": "BraimanM. Latitude dependence of the COVID‐19 mortality rate—a possible relationship to vitamin D deficiency?2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1442-200x.2005.02141.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"author": "Relkin N",
"first-page": "A144",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1",
"volume-title": "Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIg) Treatment Causes Dose‐Dependent Alterations in Beta‐Amyloid (A beta) Levels and Anti‐Beta Antibody Titers in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22859",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.13128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/oby.2007.332",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1467-789X.2011.00942.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.13077",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.Information note on COVID‐19 and NCDs.https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-and-ncds. Accessed August 12 2020. "
},
{
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study",
"author": "Petrilli CM",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncpendmet0716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb.09.87",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Editorial–Vitamin D status: a key modulator of innate immunity and natural defense from acute viral respiratory infections",
"author": "Fabbri A",
"first-page": "4048",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Calcitriol, the active form of vitamin D, is a promising candidate for COVID‐19 prophylaxis",
"author": "Mok CK",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30268-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13098-020-00565-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.13089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.orcp.2020.07.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22831",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2018.1506331",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ijo.2012.62",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2500/aap.2018.39.4096",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0b013e3180421c16",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2004500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001316",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61266-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/cix1144",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.279206",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9343(91)90154-P",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_49_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Interpretation of CT signs of 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID‐19) pneumonia",
"author": "Wu J",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Radiol",
"key": "e_1_2_10_50_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30086-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_51_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jmv.26726"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The association between the level of serum 25(OH) vitamin D, obesity, and underlying diseases with the risk of developing COVID‐19 infection: A case–control study of hospitalized patients in Tehran, Iran",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "93"
}
