Twice daily oral zinc in the treatment of patients with Coronavirus Disease-19: A randomized double-blind controlled trial
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac807, VIZIR, NCT05212480, Nov 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 470 patients with symptoms ≤7 days, showing significantly lower ICU admission and combined mortality/ICU admission with zinc treatment. Greater benefit was seen for patients treated within 3 days. 25mg elemental zinc bid for 15 days.
The inpatient/outpatient subgroups in Figure 2 are incorrect and were corrected by the authors in an update2.
The paper states 'Conflicts of interest: none declared.' However, the funding statement notes the study was funded by Opalia Recordati, the manufacturer of the evaluated treatment. Furthermore one author has the affiliation 'Medical affairs manager, Opalia Recordati'.
|
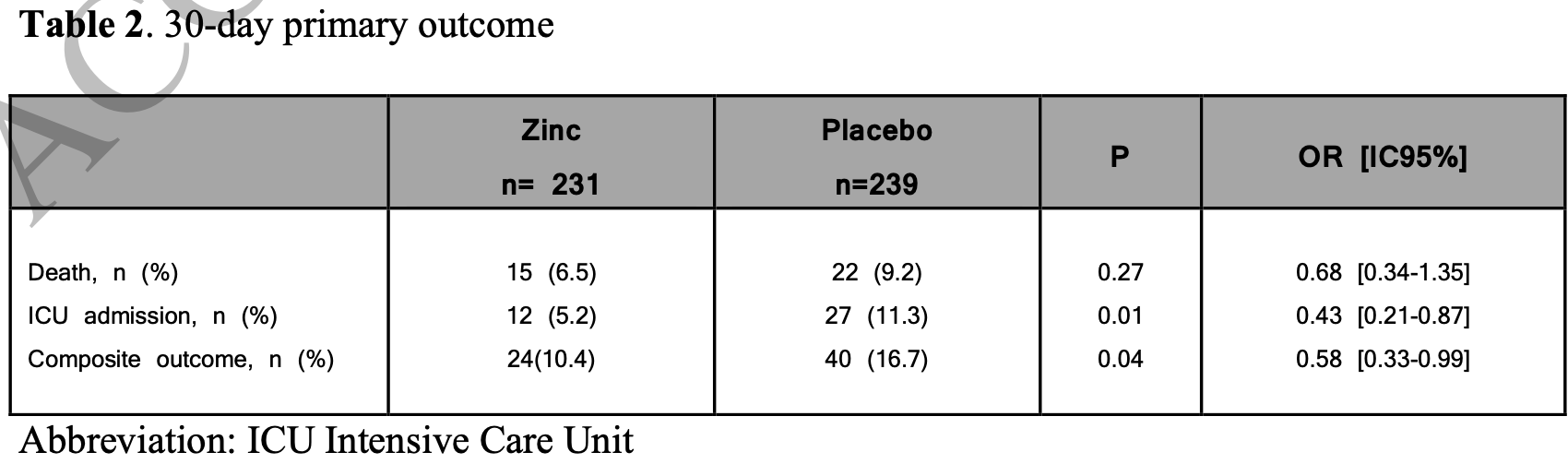
risk of death, 29.9% lower, RR 0.70, p = 0.27, treatment 15 of 231 (6.5%), control 22 of 239 (9.2%), NNT 37, odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 30.
|
|
risk of death/ICU, 37.6% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.04, treatment 24 of 231 (10.4%), control 40 of 239 (16.7%), NNT 16, odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 30.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 54.0% lower, RR 0.46, p = 0.01, treatment 12 of 231 (5.2%), control 27 of 239 (11.3%), NNT 16, odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 30.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 41.7% lower, RR 0.58, p = 0.009, treatment 31 of 231 (13.4%), control 55 of 239 (23.0%), NNT 10, grade III, day 30, Figure 3.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 22.9% lower, RR 0.77, p = 0.003, treatment 108 of 231 (46.8%), control 145 of 239 (60.7%), NNT 7.2, grade III, day 15, Figure 3.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 29.3% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.002, treatment 82 of 231 (35.5%), control 120 of 239 (50.2%), NNT 6.8, grade II/III, day 30.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 13.8% lower, RR 0.86, p < 0.001, treatment 180 of 231 (77.9%), control 216 of 239 (90.4%), NNT 8.0, grade II/III, day 15.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 69.1% lower, RR 0.31, p = 0.30, treatment 1 of 85 (1.2%), control 4 of 100 (4.0%), NNT 35, odds ratio converted to relative risk, outpatients.
|
|
hospitalization time, 33.0% lower, relative time 0.67, p < 0.001, treatment mean 7.1 (±3.4) n=146, control mean 10.6 (±2.8) n=134, inpatients.
|
|
recovery time, 25.0% lower, relative time 0.75, p < 0.001, treatment mean 9.6 (±4.1) n=85, control mean 12.8 (±6.7) n=100, outpatients.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Abdallah et al., 4 Nov 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Tunisia, peer-reviewed, mean age 54.2, 24 authors, study period 15 February, 2022 - 4 May, 2022, average treatment delay 4.6 days, trial NCT05212480 (history) (VIZIR).
Contact: semir.nouira@rns.tn, belhajalikhaoula@yahoo.fr.
Abstract: Clinical Infectious Diseases
RESEARCH ARTICLE
SC
RI
PT
Twice daily oral zinc in the treatment of patients with
Coronavirus Disease-19
A randomized double-blind controlled trial
A
N
U
Saoussen Ben Abdallah1, MD Yosra Mhalla13, MD Imen Trabelsi3, PhD Adel Sekma2,3, MD
Rim Youssef3,4, MD Khaoula Bel Haj Ali2,3, MD Houda Ben Soltane3,5, MD HajerYacoubi3,4,
MD Mohamed Amine Msolli2,3, MD Nejla Stambouli6, PhD Kaouthar Beltaief2,3, MD
Mohamed Habib Grissa2,3, MD Meriem Khrouf3,5, MD Zied Mezgar3,5, MD Chawki
Loussaief7, MD Wahid Bouida2,3, MD Rabie Razgallah8, MD Karima Hezbri9, PhD Asma
Belguith10, MD Naouel Belkacem11, MD Zohra Dridi12, MD Hamdi Boubaker2,3, MD Riadh
Boukef3,4, MD Semir Nouira2,3, MD
1
Medical intensive care unit, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000 Monastir, Tunisia;
Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000 Monastir, Tunisia;
3
Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir, 5019 Tunisia; 4Emergency Department,
Sahloul University Hospital, 4011 Sousse, Tunisia; 5Emergency Department, Farhat Hached
University Hospital, 4011 Sousse, Tunisia; 6UR17DN03 - Research Unit, Military Defense,
Military Hospital of Tunis, Tunisia; 7Department of Infectious Disease Fattouma Bourguiba
University Hospital, 5000 Monastir, Tunisia; 8DACIMA Consulting 1053 Tunis, Tunisia;
9
Medical affairs manager, Opalia Recordati, Tunis, Tunisia; 10Department of Preventive Medicine,
TE
D
M
2
EP
——————————————————————————————————————————
CC
Corresponding author: Pr. Semir Nouira, Emergency Department and Laboratory Research (LR12SP18),
Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000, Monastir, Tunisia; +216 73 106 046. E-mail :
semir.nouira@rns.tn.
A
Alternate corresponding author: Dr. Khaoula Bel Haj Ali, Emergency Department and Laboratory
Research (LR12SP18), Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000, Monastir, Tunisia. +216 29777277.
E-mail : belhajalikhaoula@yahoo.fr.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of
America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com This article
is published and distributed under the terms of the Oxford University Press, Standard Journals Publication
Model (https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_
publication_model)
DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac807
1
Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000 Monastir, Tunisia; 11District hospital Teboulba,
Tunisia; 12Department of cardiology, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000 Monastir,
Tunisia; 13Laboratory of microbiology, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital, 5000 Monastir,
Tunisia;
SC
RI
PT
Background: Zinc supplementation has been considered one of the potential therapies for
coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). We aimed to examine zinc efficacy in adult patients with
COVID-19 infection.
U
Methods: We conducted a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter
trial. Patients tested positive for COVID-19 without end organ failure were randomized to oral
zinc (n=231) or matching placebo (n=239) for 15 days. The primary combined outcome was death
due to COVID-19 or ICU admission within 30 days after randomization. Secondary outcomes
included length of hospital stay for inpatients and duration of COVID-19 symptoms with COVID19 related hospitalization for outpatients.
TE
D
M
A
N
Findings: One hundred ninety patients (40.4%) were ambulatory and 280..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac807",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac807",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>BACKGROUND</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Zinc supplementation has been considered one of the potential therapies for coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19). We aimed to examine zinc efficacy in adult patients with COVID-19 infection.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>METHODS</jats:title>\n <jats:p>We conducted a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Patients tested positive for COVID-19 without end organ failure were randomized to oral zinc (n = 231) or matching placebo (n = 239) for 15 days. The primary combined outcome was death due to COVID-19 or ICU admission within 30 days after randomization. Secondary outcomes included length of hospital stay for inpatients and duration of COVID-19 symptoms with COVID-19 related hospitalization for outpatients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>FINDINGS</jats:title>\n <jats:p>One hundred ninety patients (40.4%) were ambulatory and 280 patients (59.6%) were hospitalized. Mortality at 30-day was 6.5% in Zinc group and 9.2% in Placebo group [odds ratio (OR) 0.70 (0.37-1.32)]; ICU admission rate was respectively 5.2% and 11.3% [OR 0.46 (0.23-0.88)]. Combined outcome was lower in zinc group compared to placebo group [OR 0.62 (0.38-0.99)]. Consistent results were observed in prespecified subgroups of patients with age &lt; 65 years, those with comorbidity, and those who needed oxygen therapy at baseline. Length of hospital stay was shorter in zinc group compared to placebo group [difference 3.5 days, 95% CI (2.76-4.23)] in inpatients group; duration of COVID-19 symptoms decreased with zinc treatment compared to placebo in outpatients [difference 1.9 days, 95% CI (0.62-2.6)]. No severe adverse events were observed during the study.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>INTERPRETATION</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Our results showed that in COVID-19 patients, oral zinc can decrease 30-day death and ICU admission rate and can shorten symptoms duration.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical intensive care unit, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Abdallah",
"given": "Saoussen Ben",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of microbiology, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Mhalla",
"given": "Yosra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Trabelsi",
"given": "Imen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Sekma",
"given": "Adel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Sahloul University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Youssef",
"given": "Rim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Khaoula Bel Haj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Farhat Hached University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Soltane",
"given": "Houda Ben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Sahloul University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Yacoubi",
"given": "Hajer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Msolli",
"given": "Mohamed Amine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UR17DN03 - Research Unit, Military Defense, Military Hospital of Tunis , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Stambouli",
"given": "Nejla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Beltaief",
"given": "Kaouthar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Grissa",
"given": "Mohamed Habib",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Farhat Hached University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Khrouf",
"given": "Meriem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Farhat Hached University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Mezgar",
"given": "Zied",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Loussaief",
"given": "Chawki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Bouida",
"given": "Wahid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "DACIMA Consulting 1053 Tunis , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Razgallah",
"given": "Rabie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical affairs manager, Opalia Recordati , Tunis , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Hezbri",
"given": "Karima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Preventive Medicine, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Belguith",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "District hospital Teboulba , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Belkacem",
"given": "Naouel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of cardiology, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Dridi",
"given": "Zohra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Boubaker",
"given": "Hamdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Sahloul University Hospital , 4011 Sousse , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Boukef",
"given": "Riadh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, Fattouma Bourguiba University Hospital , 5000 Monastir , Tunisia"
},
{
"name": "Research Laboratory LR12SP18 University of Monastir , 5019 Monastir , Tunisia"
}
],
"family": "Nouira",
"given": "Semir",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-03T20:06:47Z",
"timestamp": 1664827607000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T20:27:59Z",
"timestamp": 1667507279000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-03T20:40:28Z",
"timestamp": 1667508028429
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667520000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac807/46782455/ciac807.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac807/46782455/ciac807.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/cid/ciac807/6795268"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Twice daily oral zinc in the treatment of patients with Coronavirus Disease-19 <i>A randomized double-blind controlled trial</i>",
"type": "journal-article"
}
