The Effects of Vitamin D3 and N-Acetylcysteine Administration in Patients with COVID-19 Hospitalization in the Iranian Population
et al., International Journal of Medical Laboratory, doi:10.18502/ijml.v10i3.13746, IRCT20200324046850N1, Oct 2023
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
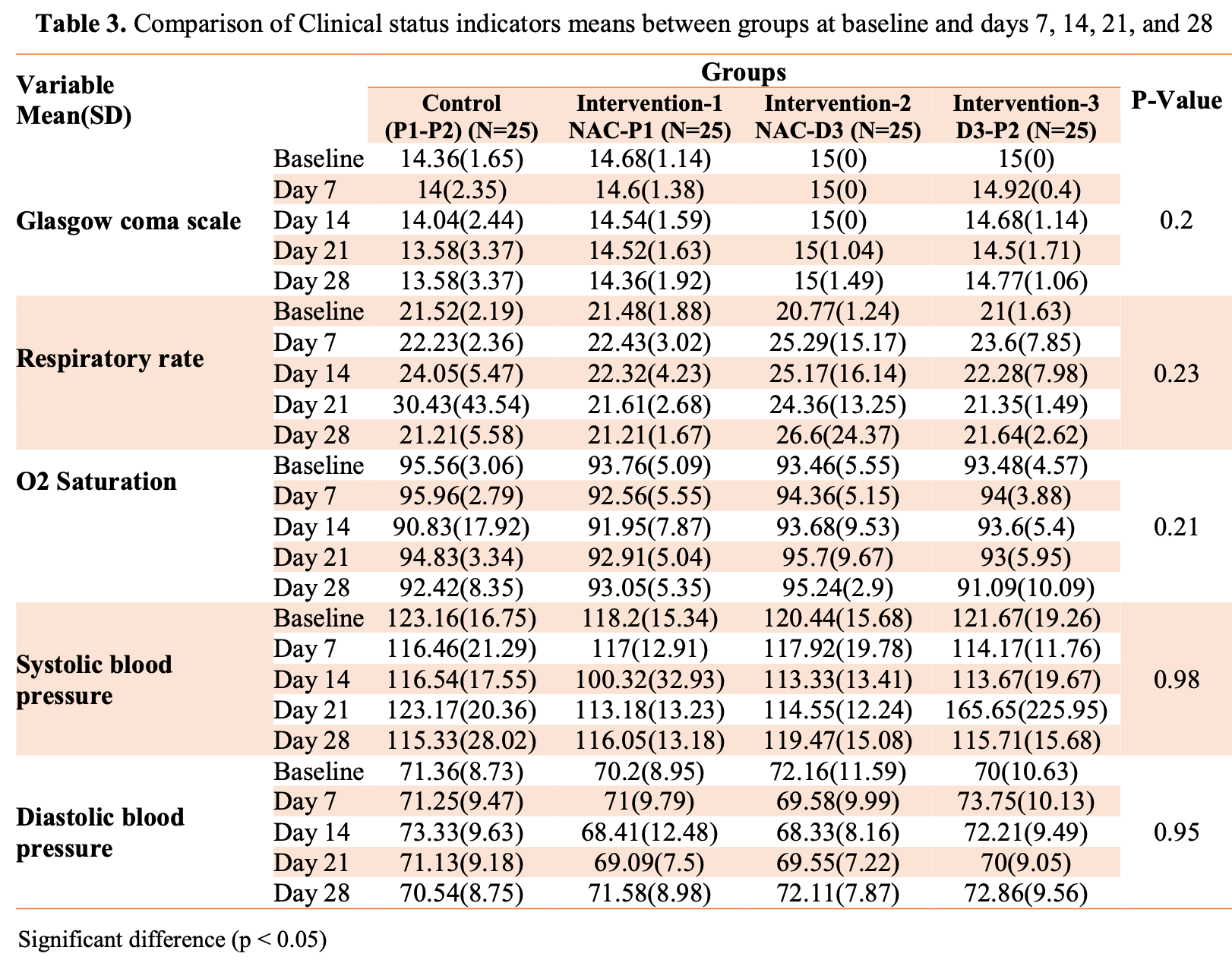
RCT 100 hospitalized patients reporting shorter hospitalization with vitamin D + N-acetylcysteine. However, day 28 SaO2 is not consistent with the reported recovery values. For three arms the day 28 values are worse than the baseline values. The control group day 21 RR value has a standard deviation which is larger than the mean 30.4 ± 43.5.
Study covers vitamin D and N-acetylcysteine.
Abbasi et al., 4 Oct 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period June 2020 - July 2020, trial IRCT20200324046850N1.
Contact: saramobarak95@yahoo.com.
The Effects of Vitamin D3 and N-Acetylcysteine Administration in Patients with COVID-19 Hospitalization in the Iranian Population
International Journal of Medical Laboratory, doi:10.18502/ijml.v10i3.13746
N-Acetylcysteine Vitamin
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
Abrishami, Dalili, Torbati, Asgari, Ahmadi et al., Possible association of vitamin D status with lung involvement and outcome in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study, European Journal of Nutrition
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Atefi, Behrangi, Mozafarpoor, Seirafianpour, Peighambari et al.,
Benskin, A basic review of the preliminary evidence that COVID-19 risk and severity is increased in vitamin D deficiency, Front Public Health
Calzetta, Matera, Rogliani, Cazzola, Multifaceted activity of N-acetyl-l-cysteine in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine
Fani, Zandi, Ebrahimi, Soltani, Abbasi, The role of miRNAs in COVID-19 disease, Future Virol
Feketea, Vlacha, Bocsan, Vassilopoulou, Stanciu et al., Vitamin D in corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) related multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C), Front Immunol
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Hamad, Vitamin D supplements improve efficacy of minocycline, nacetylcysteine and aspirin triple therapy to COVID-19 infection, Saudi J Biomed Res
Horowitz, Freeman, Bruzzese, Efficacy of glutathione therapy in relieving dyspnea associated with COVID-19 pneumonia: A report of 2 cases, Respiratory Medicine Case Reports
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res
Jeronimo, Farias, Val, Sampaio, Alexandre et al., Methylprednisolone as adjunctive therapy for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19; Metcovid): A randomized, double-blind, phase iib, placebo-controlled trial, Clin Infect Dis
Khoshbaten, Aliasgarzadeh, Masnadi, Tarzamani, Farhang et al., N Acetylcysteine improves liver function in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, Hepatitis Monthly
Liu, Wang, Luo, Qian, Wu et al., Experience of n-acetylcysteine airway management in the successful treatment of one case of critical condition with COVID-19: A case report, Medicine
Liu, Zhang, Yang, Zhang, Li et al., Respiratory rehabilitation in elderly patients with COVID-19: A randomized controlled study, Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Jf et al., vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: Systematic review and metaanalysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Pinto, Goessler et al., Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stayin patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: A randomized clinical Trial, JAMA
Schaefer, Bloom, Chung, Nterrelationship between coronavirus infection and liver disease, Clinical Liver Disease
Sharafkhah, Abdolrazaghnejad, Zarinfar, Mohammadbeigi, Massoudifar et al., Safety andefficacy of n-acetylcysteine for prophylaxis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: A randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Med Gas Res
Yang, Han, Wang, COVID-19: Gastrointestinal manifestations and potential fecal-oral transmission, Gastroenterology
Zemb, Bergmanb, Camargojr, Cavalier, Cormier et al., Vitamin D deficiency and the COVID-19 pandemic, Journal Of Global Antimicrobial Resistance
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18502/ijml.v10i3.13746",
"ISSN": [
"2423-3714",
"2423-3706"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18502/ijml.v10i3.13746",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and Aims: In the absence of treatment for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, there is an urgent need to find alternative methods to control the spread of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study was conducted to compare the effects of vitamin D3 and N-acetylcysteine (NAC) on clinical status indicators in patients with COVID-19 hospitalization in Abadan, Iran.
\nMaterials and Methods: 100 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 infection participated in this study. Patients were randomly allocated to four groups: 3 intervention groups and 1 control group. All patients received standard treatment. In addition, the intervention-1 group received NAC tablets and vitamin D3 placebo ampoules. The intervention-2 group received NAC tablets and vitamin D3 ampoules. The intervention-3 group received vitamin D3 ampoules and NAC placebo tablets. The control group received vitamin D3 placebo ampoules and NAC placebo tablets. Symptoms of the disease and clinical status indicators were compared in groups in the baseline and on days 7, 14, 21, and 28, respectively.
\nResults: The trial comparison showed that the incidence of cough, dyspnea, and serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase in laboratory tests in the NAC-P1 group was lower than in the other three groups (p <0.005). Also, the results showed a significant difference in the length of hospitalization between the four groups. The length of hospitalization was decreased in the NAC-D3 group (p < 0.024).
\nConclusion: Based on the results, vitamin D3 supplements and NAC can improve some outcomes in COVID-19 treatment; however, more randomized controlled trial studies are required in this field.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abbasi",
"given": "Samaneh",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fani",
"given": "Mona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sayar",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radmanesh",
"given": "Esmat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jelvay",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pahlavanzadeh",
"given": "Bagher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arizavi",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esmaeelian",
"given": "Hani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Asadi",
"given": "Masoomeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Babaeian",
"given": "Najmeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yoosefi",
"given": "Raheleh Pour",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bitaraf",
"given": "Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elhami",
"given": "Saeedeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mobarak",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Medical Laboratory",
"container-title-short": "IJML",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-04T08:29:53Z",
"timestamp": 1696408193000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-09T12:19:51Z",
"timestamp": 1696853991000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-10T04:50:52Z",
"timestamp": 1696913452715
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
]
},
"member": "7770",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.18502",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Knowledge E DMCC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://publish.kne-publishing.com/index.php/IJML/article/view/13746"
},
"secondary": [
{
"URL": "https://ijml.ssu.ac.ir/article-1-472-en.html"
}
]
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Engineering",
"General Environmental Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Effects of Vitamin D3 and N-Acetylcysteine Administration in Patients with COVID-19 Hospitalization in the Iranian Population",
"type": "journal-article"
}
