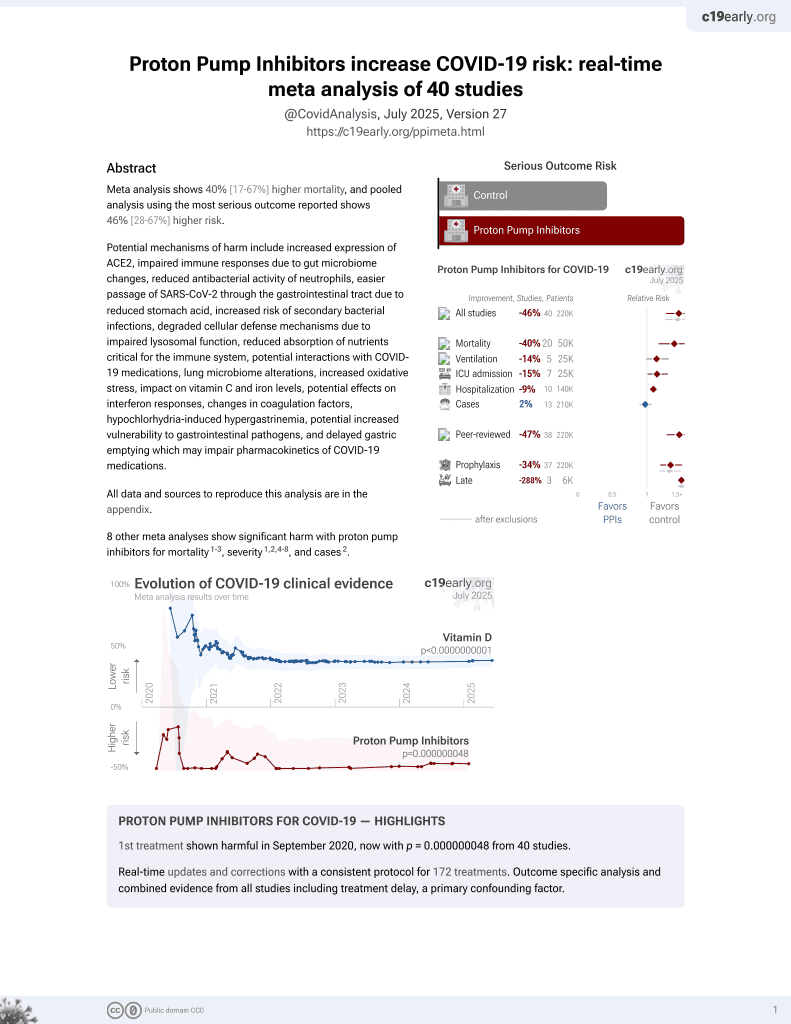
Associations of proton pump inhibitors with susceptibility to influenza, pneumonia, and COVID-19: Evidence from a large population-based cohort study
et al., eLife, doi:10.7554/elife.94973, Jul 2024
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
UK Biobank retrospective with 160,923 patients showing increased risks of influenza, pneumonia, COVID-19 severity, and COVID-19 mortality with proton pump inhibitor (PPI) use.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the United Kingdom, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
The United Kingdom focused on expensive high-profit treatments, approving only one low-cost early treatment, which required a prescription and had limited adoption. The high-cost prescription treatment strategy reduces the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminates complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 46.0% higher, HR 1.46, p = 0.02, treatment 9,997, control 150,926, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of severe case, 33.0% higher, HR 1.33, p = 0.004, treatment 9,997, control 150,926, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of case, 8.0% higher, HR 1.08, p = 0.10, treatment 9,997, control 150,926, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zeng et al., 16 Jul 2024, retrospective, United Kingdom, peer-reviewed, mean age 56.5, 13 authors, study period January 2020 - September 2021.
Contact: donyduang@126.com, shaweihong@gdph.org.cn, chenhao@gdph.org.cn.
Associations of proton pump inhibitors with susceptibility to influenza, pneumonia, and COVID-19: Evidence from a large population-based cohort study
eLife, doi:10.7554/elife.94973
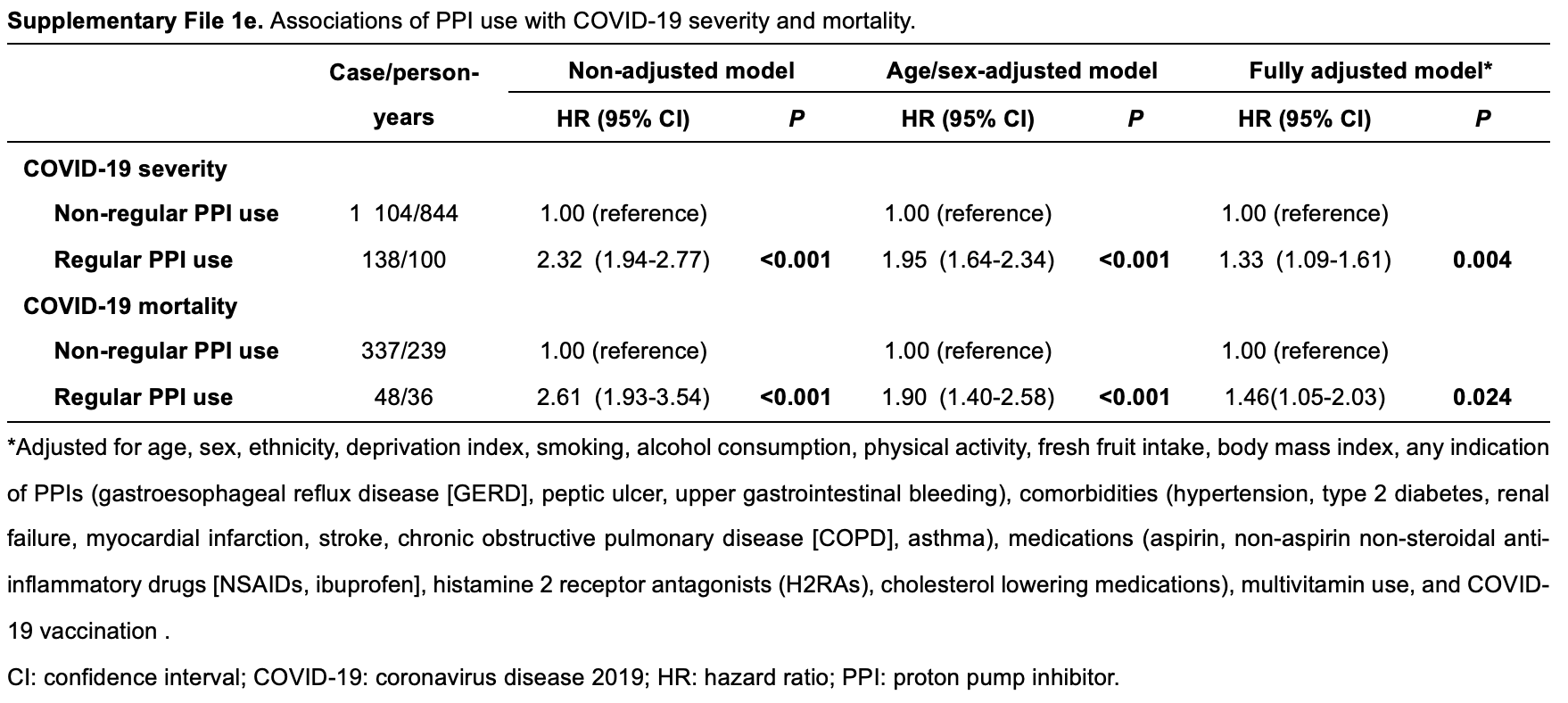
Background: Adverse effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have raised wide concerns. The association of PPIs with influenza is unexplored, while that with pneumonia or COVID-19 remains controversial. Our study aims to evaluate whether PPI use increases the risks of these respiratory infections. Methods: The current study included 160,923 eligible participants at baseline who completed questionnaires on medication use, which included PPI or histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2RA), from the UK Biobank. Cox proportional hazards regression and propensity score-matching analyses were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Results: Comparisons with H2RA users were tested. PPI use was associated with increased risks of developing influenza (HR 1.32, 95% CI 1.12-1.56) and pneumonia (hazard ratio [HR] 1.42, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.26-1.59). In contrast, the risk of COVID-19 infection was not significant with regular PPI use (HR 1.08, 95% CI 0.99-1.17), while the risks of severe COVID-19 ) and mortality (HR 1.37. 95% CI 1.29-1.46) were increased. However, when compared with H2RA users, PPI users were associated with a higher risk of influenza (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1.19-2.54), but the risks with pneumonia or COVID-19-related outcomes were not evident. Conclusions: PPI users are associated with increased risks of influenza, pneumonia, as well as COVID-19 severity and mortality compared to non-users, while the effects on pneumonia or COVID-19-related outcomes under PPI use were attenuated when compared to the use of H2RAs. Appropriate use of PPIs based on comprehensive evaluation is required.
Additional information
Additional files Supplementary files • Supplementary file 1. Supplementary information for the analyses. • MDAR checklist
References
Abrahami, Mcdonald, Schnitzer, Barkun, Suissa et al., Proton pump inhibitors and risk of gastric cancer: population-based cohort study, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325097
Abrahami, Mcdonald, Schnitzer, Barkun, Suissa et al., a. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of colorectal cancer, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325096
Abtahi, Driessen, Burden, Souverein, Van Den Bergh et al., Concomitant use of oral glucocorticoids and proton pump inhibitors and risk of osteoporotic fractures among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study, Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218758
Almario, Chey, Spiegel, Increased risk of covid-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors, The American Journal of Gastroenterology, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798
Armstrong, Rudkin, Allen, Crook, Wilson et al., Dynamic linkage of covid-19 test results between public health england's second generation surveillance system and uk biobank, Microbial Genomics, doi:10.1099/mgen.0.000397
Bycroft, Freeman, Petkova, Band, Elliott et al., The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z
Conroy, Lacey, Bešević, Omiyale, Feng et al., UK Biobank: a globally important resource for cancer research, British Journal of Cancer, doi:10.1038/s41416-022-02053-5
Etminan, Nazemipour, Candidate, Mansournia, Potential biases in studies of acidsuppressing drugs and covid-19 infection, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.053
Fan, Liu, Miyata, Dasarathy, Rotroff et al., Effect of acid suppressants on the risk of covid-19: a propensity score-matched study using uk biobank, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.028
Forgacs, Loganayagam, Overprescribing proton pump inhibitors, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.39406.449456.BE
Fu, Van Diepen, Xu, Trevisan, Dekker et al., Pharmacoepidemiology for nephrologists (part 2): potential biases and how to overcome them, Clinical Kidney Journal, doi:10.1093/ckj/sfaa242
Ghebrehewet, Macpherson, Ho, Influenza, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6258
Griffith, Morris, Tudball, Herbert, Mancano et al., Collider bias undermines our understanding of COVID-19 disease risk and severity, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19478-2
Herzig, Howell, Ngo, Marcantonio, Acid-suppressive medication use and the risk for hospital-acquired pneumonia, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2009.722
Horwitz, Feinstein, The problem of "protopathic bias" in case-control studies, The American Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1016/0002-9343(80)90363-0
Irwin, French, Chang, Altman, Adams et al., Classification of cough as a symptom in adults and management algorithms, CHEST, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.016
Israelsen, Ernst, Lundh, Lundbo, Sandholdt et al., Proton pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with sars-cov-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis, Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.011
Jeon, Kim, Risk of post-myocardial infarction pneumonia with proton pump inhibitors, h2 receptor antagonists and mucoprotective agents: a retrospective nationwide cohort study, Journal of Personalized Medicine, doi:10.3390/jpm12010078
Kahrilas, Altman, Chang, Field, Harding et al., Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux in adults, CHEST, doi:10.1016/j.chest.2016.08.1458
Kantor, Rehm, Haas, Chan, Giovannucci, Trends in prescription drug use among adults in the united states from 1999-2012, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2015.13766
Laine, Shah, Bemanian, Intragastric pH with oral vs intravenous bolus plus infusion proton-pump inhibitor therapy in patients with bleeding ulcers, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.006
Lee, Ha, Yeniova, Moon, Kim et al., Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248
Li, An, Yu, Jiao, Canarutto et al., Do proton pump inhibitors influence SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes? a meta-analysis, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323366
Lima, Thomas, Barbarino, Desta, Van Driest et al., Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (cpic) guideline for cyp2c19 and proton pump inhibitor dosing, Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, doi:10.1002/cpt.2015
Malfertheiner, Kandulski, Venerito, Proton-pump inhibitors: understanding the complications and risks, Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology, doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.117
Meijvis, Cornips, Voorn, Souverein, Endeman et al., Microbial evaluation of proton-pump inhibitors and the risk of pneumonia, The European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/09031936.00020811
Normand, Landrum, Guadagnoli, Ayanian, Ryan et al., Validating recommendations for coronary angiography following acute myocardial infarction in the elderly: a matched analysis using propensity scores, Journal of Clinical Epidemiology, doi:10.1016/s0895-4356(00)00321-8
Othman, Crooks, Card, Community acquired pneumonia incidence before and after proton pump inhibitor prescription: population based study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i5813
Redelmeier, Mcalister, Kandel, Lu, Daneman, Postoperative pneumonia in elderly patients receiving acid suppressants: a retrospective cohort analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.c2608
Sarkar, Hennessy, Yang, Proton-pump inhibitor use and the risk for community-acquired pneumonia, Annals of Internal Medicine, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-149-6-200809160-00005
Scholtissek, Stability of infectious influenza a viruses at low pH and at elevated temperature, Vaccine, doi:10.1016/0264-410x(85)90109-4
Shafrir, Benson, Katz, Hershcovici, Bitan et al., The association between proton pump inhibitors and covid-19 is confounded by hyperglycemia in a population-based study, Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.791074
Shah, Halvorson, Mcbay, Dorn, Wilson et al., Proton-pump inhibitor use is not associated with severe COVID-19-related outcomes: a propensity score-weighted analysis of a national veteran cohort, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325701
Shupp, Mehta, Chirayath, Patel, Aiad et al., Proton pump inhibitor therapy usage and associated hospitalization rates and critical care outcomes of COVID-19 patients, Scientific Reports, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-11680-0
Stuart, King, Imai, MatchIt: nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference, Journal of Statistical Software, doi:10.18637/jss.v042.i08
Sudlow, Gallacher, Allen, Beral, Burton et al., UK biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age, PLOS Medicine, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001779
Targownik, Fisher, Saini, Aga clinical practice update on de-prescribing of proton pump inhibitors: expert review, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247
Vaezi, Yang, Howden, Complications of proton pump inhibitor therapy, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.047
Van Buuren, Groothuis-Oudshoorn, Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R, Journal of Statistical Software, doi:10.18637/jss.v045.i03
Van Der Sande, Jöbsis, Bannier, Van De Garde, Coremans et al., The risk of community-acquired pneumonia in children using gastric acid suppressants, The European Respiratory Journal, doi:10.1183/13993003.03229-2020
Vanderweele, Ding, Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the e-value, Annals of Internal Medicine, doi:10.7326/M16-2607
Wu, Peng, Li, Cheng, Zhu et al., Use of proton pump inhibitors are associated with higher mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Journal of Global Health, doi:10.7189/jogh.12.05005
Xie, Bowe, Yan, Xian, Li et al., Estimates of all cause mortality and cause specific mortality associated with proton pump inhibitors among US veterans: cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l1580
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7554/elife.94973",
"ISSN": [
"2050-084X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/elife.94973",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"abs1\"><jats:title>Background:</jats:title><jats:p>Adverse effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have raised wide concerns. The association of PPIs with influenza is unexplored, while that with pneumonia or COVID-19 remains controversial. Our study aims to evaluate whether PPI use increases the risks of these respiratory infections.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"abs2\"><jats:title>Methods:</jats:title><jats:p>The current study included 160,923 eligible participants at baseline who completed questionnaires on medication use, which included PPI or histamine-2 receptor antagonist (H2RA), from the UK Biobank. Cox proportional hazards regression and propensity score-matching analyses were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"abs3\"><jats:title>Results:</jats:title><jats:p>Comparisons with H2RA users were tested. PPI use was associated with increased risks of developing influenza (HR 1.32, 95% CI 1.12–1.56) and pneumonia (hazard ratio [HR] 1.42, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.26–1.59). In contrast, the risk of COVID-19 infection was not significant with regular PPI use (HR 1.08, 95% CI 0.99–1.17), while the risks of severe COVID-19 (HR 1.19. 95% CI 1.11–1.27) and mortality (HR 1.37. 95% CI 1.29–1.46) were increased. However, when compared with H2RA users, PPI users were associated with a higher risk of influenza (HR 1.74, 95% CI 1.19–2.54), but the risks with pneumonia or COVID-19-related outcomes were not evident.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"abs4\"><jats:title>Conclusions:</jats:title><jats:p>PPI users are associated with increased risks of influenza, pneumonia, as well as COVID-19 severity and mortality compared to non-users, while the effects on pneumonia or COVID-19-related outcomes under PPI use were attenuated when compared to the use of H2RAs. Appropriate use of PPIs based on comprehensive evaluation is required.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec id=\"abs5\"><jats:title>Funding:</jats:title><jats:p>This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82171698, 82170561, 81300279, 81741067, 82100238), the Program for High-level Foreign Expert Introduction of China (G2022030047L), the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Guangdong Province (2021B1515020003), the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2022A1515012081), the Foreign Distinguished Teacher Program of Guangdong Science and Technology Department (KD0120220129), the Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People’s Hospital (DFJH201923, DFJH201803, KJ012019099, KJ012021143, KY012021183), and in part by VA Clinical Merit and ASGE clinical research funds (FWL).</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.7554/eLife.94973"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review transparency",
"name": "peer_review_transparency",
"value": "single anonymised"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review interaction",
"name": "peer_review_interaction",
"value": "other reviewer(s), editor"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review published",
"name": "peer_review_published",
"value": "review summaries, review reports, author/editor communication, reviewer identities reviewer opt in, editor identities"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "post_publication_commenting"
},
"label": "Post publication commenting",
"name": "post_publication_commenting",
"value": "open (sign in with ORCID iD required)"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/02gxych78",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Shantou University Medical College",
"place": [
"Guangdong, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Ruijie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Yuying",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Lijun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0432p8t34",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Guangdong Cardiovascular Institute, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital, Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Dongling",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Rui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Huihuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Zhuo",
"given": "Zewei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Qi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jingwei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/046rm7j60",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles",
"place": [
"Los Angeles, United States"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/05xcarb80",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Sepulveda Ambulatory Care Center, Veterans Affairs Greater Los Angeles Healthcare System",
"place": [
"North Hills, United States"
]
}
],
"family": "Leung",
"given": "Felix W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, School of Public Health, Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Duan",
"given": "Chongyang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/02gxych78",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Shantou University Medical College",
"place": [
"Guangdong, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Sha",
"given": "Weihong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4339-3441",
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Gastroenterology, Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital (Guangdong Academy of Medical Sciences), Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/01vjw4z39",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Southern Medical University",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/02gxych78",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Shantou University Medical College",
"place": [
"Guangdong, China"
]
},
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/0530pts50",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "School of Medicine, South China University of Technology",
"place": [
"Guangzhou, China"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Hao",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "eLife",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"elifesciences.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T09:25:13Z",
"timestamp": 1712222713000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-18T09:15:49Z",
"timestamp": 1721294149000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"U23A20408"
],
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China Regional Innovation and Development Joint Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82171698"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82170561"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81300279"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81741067"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"82100238"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"G2022030047L"
],
"name": "Program for High-level Foreign Expert Introduction of China"
},
{
"award": [
"2021B1515020003"
],
"name": "Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholar of Guangdong Province"
},
{
"award": [
"Project for Pilot Voyage 2024A04J6573"
],
"name": "Guangzhou Basic and Applied Basic Research Scheme"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100021171",
"award": [
"2022A1515012081"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation"
},
{
"award": [
"KD0120220129"
],
"name": "Foreign Distinguished Teacher Program of Guangdong Science and Technology Department"
},
{
"award": [
"DFJH201923"
],
"name": "Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"award": [
"DFJH201803"
],
"name": "Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"award": [
"KJ012019099"
],
"name": "Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"award": [
"KJ012021143"
],
"name": "Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"award": [
"KY012021183"
],
"name": "Climbing Program of Introduced Talents and High-level Hospital Construction Project of Guangdong Provincial People's Hospital"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100001947",
"award": [
"VA Clinical Merit and ASGE clinical research funds"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-19T00:15:46Z",
"timestamp": 1721348146688
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721088000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721088000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721088000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94973/elife-94973-v2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/94973/elife-94973-v2.xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://elifesciences.org/articles/94973",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4374",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7554",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "eLife Sciences Publications, Ltd",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325096",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors and risk of colorectal cancer",
"author": "Abrahami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bib1",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325097",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors and risk of gastric cancer: population-based cohort study",
"author": "Abrahami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bib2",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218758",
"article-title": "Concomitant use of oral glucocorticoids and proton pump inhibitors and risk of osteoporotic fractures among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "Abtahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases",
"key": "bib3",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of covid-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1707",
"journal-title": "The American Journal of Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib4",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/mgen.0.000397",
"article-title": "Dynamic linkage of covid-19 test results between public health england’s second generation surveillance system and uk biobank",
"author": "Armstrong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Microbial Genomics",
"key": "bib5",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z",
"article-title": "The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data",
"author": "Bycroft",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "bib6",
"volume": "562",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41416-022-02053-5",
"article-title": "UK Biobank: a globally important resource for cancer research",
"author": "Conroy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "519",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Cancer",
"key": "bib7",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.11.053",
"article-title": "Potential biases in studies of acid-suppressing drugs and covid-19 infection",
"author": "Etminan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1443",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib8",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.028",
"article-title": "Effect of acid suppressants on the risk of covid-19: a propensity score-matched study using uk biobank",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "455",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib9",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39406.449456.BE",
"article-title": "Overprescribing proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Forgacs",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "bib10",
"volume": "336",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ckj/sfaa242",
"article-title": "Pharmacoepidemiology for nephrologists (part 2): potential biases and how to overcome them",
"author": "Fu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1317",
"journal-title": "Clinical Kidney Journal",
"key": "bib11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6258",
"article-title": "Influenza",
"author": "Ghebrehewet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "bib12",
"volume": "355",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19478-2",
"article-title": "Collider bias undermines our understanding of COVID-19 disease risk and severity",
"author": "Griffith",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature Communications",
"key": "bib13",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2009.722",
"article-title": "Acid-suppressive medication use and the risk for hospital-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Herzig",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2120",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "bib14",
"volume": "301",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9343(80)90363-0",
"article-title": "The problem of “protopathic bias” in case-control studies",
"author": "Horwitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "The American Journal of Medicine",
"key": "bib15",
"volume": "68",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2017.10.016",
"article-title": "Classification of cough as a symptom in adults and management algorithms",
"author": "Irwin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "196",
"journal-title": "CHEST",
"key": "bib16",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.011",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with sars-cov-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis",
"author": "Israelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1845",
"journal-title": "Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology",
"key": "bib17",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm12010078",
"article-title": "Risk of post-myocardial infarction pneumonia with proton pump inhibitors, h2 receptor antagonists and mucoprotective agents: a retrospective nationwide cohort study",
"author": "Jeon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Journal of Personalized Medicine",
"key": "bib18",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2016.08.1458",
"article-title": "Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux in adults",
"author": "Kahrilas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1341",
"journal-title": "CHEST",
"key": "bib19",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2015.13766",
"article-title": "Trends in prescription drug use among adults in the united states from 1999-2012",
"author": "Kantor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1818",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "bib20",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.006",
"article-title": "Intragastric pH with oral vs intravenous bolus plus infusion proton-pump inhibitor therapy in patients with bleeding ulcers",
"author": "Laine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1836",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib21",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bib22",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323366",
"article-title": "Do proton pump inhibitors influence SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes? a meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1806",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bib23",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2015",
"article-title": "Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (cpic) guideline for cyp2c19 and proton pump inhibitor dosing",
"author": "Lima",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1417",
"journal-title": "Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics",
"key": "bib24",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrgastro.2017.117",
"article-title": "Proton-pump inhibitors: understanding the complications and risks",
"author": "Malfertheiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology",
"key": "bib25",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00020811",
"article-title": "Microbial evaluation of proton-pump inhibitors and the risk of pneumonia",
"author": "Meijvis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1165",
"journal-title": "The European Respiratory Journal",
"key": "bib26",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0895-4356(00)00321-8",
"article-title": "Validating recommendations for coronary angiography following acute myocardial infarction in the elderly: a matched analysis using propensity scores",
"author": "Normand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Epidemiology",
"key": "bib27",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i5813",
"article-title": "Community acquired pneumonia incidence before and after proton pump inhibitor prescription: population based study",
"author": "Othman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "bib28",
"volume": "355",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "R: A language and environment for statistical computing",
"author": "R Development Core Team",
"key": "bib29",
"unstructured": "R Development Core Team. 2022. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 4.2.0. http://www.R-project.org.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.c2608",
"article-title": "Postoperative pneumonia in elderly patients receiving acid suppressants: a retrospective cohort analysis",
"author": "Redelmeier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "bib30",
"volume": "340",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-149-6-200809160-00005",
"article-title": "Proton-pump inhibitor use and the risk for community-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Sarkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Annals of Internal Medicine",
"key": "bib31",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0264-410x(85)90109-4",
"article-title": "Stability of infectious influenza a viruses at low pH and at elevated temperature",
"author": "Scholtissek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Vaccine",
"key": "bib32",
"volume": "3",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.791074",
"article-title": "The association between proton pump inhibitors and covid-19 is confounded by hyperglycemia in a population-based study",
"author": "Shafrir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"key": "bib33",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325701",
"article-title": "Proton-pump inhibitor use is not associated with severe COVID-19-related outcomes: a propensity score-weighted analysis of a national veteran cohort",
"author": "Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1447",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "bib34",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-11680-0",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor therapy usage and associated hospitalization rates and critical care outcomes of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Shupp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Scientific Reports",
"key": "bib35",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v042.i08",
"article-title": "MatchIt: nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference",
"author": "Stuart",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Journal of Statistical Software",
"key": "bib36",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1001779",
"article-title": "UK biobank: an open access resource for identifying the causes of a wide range of complex diseases of middle and old age",
"author": "Sudlow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLOS Medicine",
"key": "bib37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.12.247",
"article-title": "Aga clinical practice update on de-prescribing of proton pump inhibitors: expert review",
"author": "Targownik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1334",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib38",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2017.04.047",
"article-title": "Complications of proton pump inhibitor therapy",
"author": "Vaezi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "bib39",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v045.i03",
"article-title": "Multivariate imputation by chained equations in R",
"author": "van Buuren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Statistical Software",
"key": "bib40",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.03229-2020",
"article-title": "The risk of community-acquired pneumonia in children using gastric acid suppressants",
"author": "van der Sande",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "The European Respiratory Journal",
"key": "bib41",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M16-2607",
"article-title": "Sensitivity analysis in observational research: introducing the e-value",
"author": "VanderWeele",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Annals of Internal Medicine",
"key": "bib42",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7189/jogh.12.05005",
"article-title": "Use of proton pump inhibitors are associated with higher mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Journal of Global Health",
"key": "bib43",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l1580",
"article-title": "Estimates of all cause mortality and cause specific mortality associated with proton pump inhibitors among US veterans: cohort study",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "bib44",
"volume": "365",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://elifesciences.org/articles/94973"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Associations of proton pump inhibitors with susceptibility to influenza, pneumonia, and COVID-19: Evidence from a large population-based cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/elife.94973",
"volume": "13"
}